Large intestine, constipation diarrhoea and lactose intolerance
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
what happens when longitudinal muscle contraction occurs?
lumen becomes shorter and fatter
what happens when circular muscle contraction occurs?
lumen becomes narrower and longer
what happens when the muscularis mucosae contraction occurs?
hange in absorptive and secretory area of mucosa
why does gastrointesintal motility take place?
It is mostly due to the activity of smooth muscle (circular, longitudinal layers and the muscularis mucosa)
where is the enteric nerbous system located?
in the gut - in the G.I tissue
the cells are located in the ganglia, within the myenteric and submucuous plexus
how are the 2 plexus connected?
they are connected by interganglionic fibres
what does the enteric nervous system compromsise of?
sensory neurones
interneurons
effector neurons
name examples of sensory neurones
mechanoreceptors
chemoreceptors
thermoreceptors
name examples of effector neurones
excitatory and inhibitory motor neurones
what is the function of interneurons
co-ordinating reflexes and motor programs
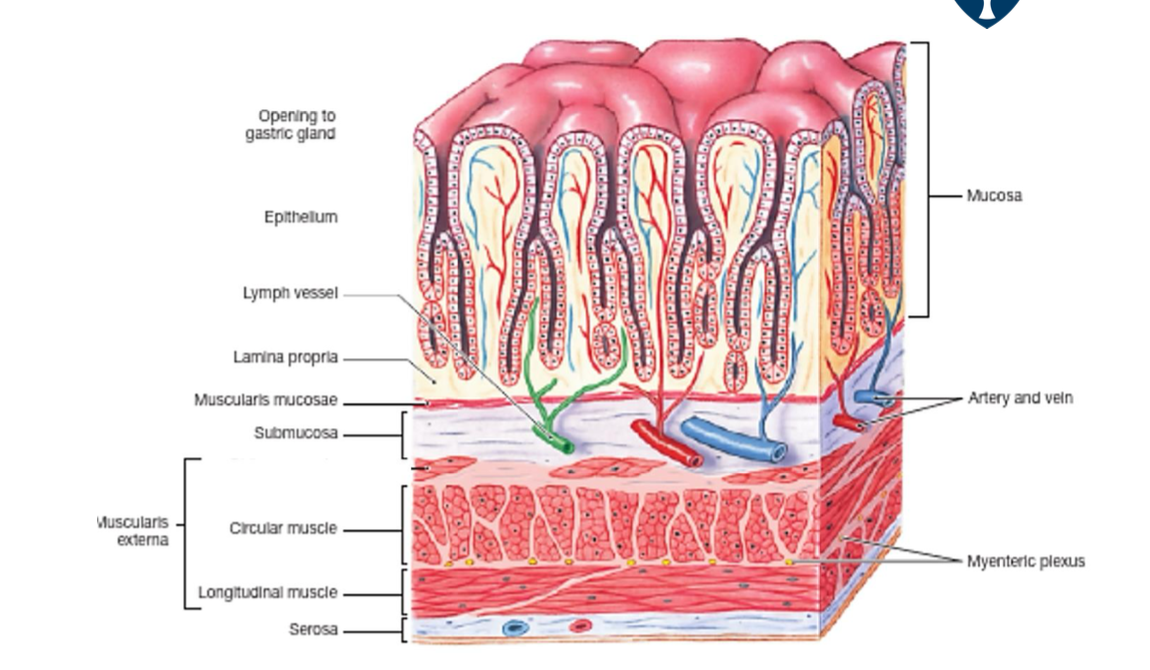
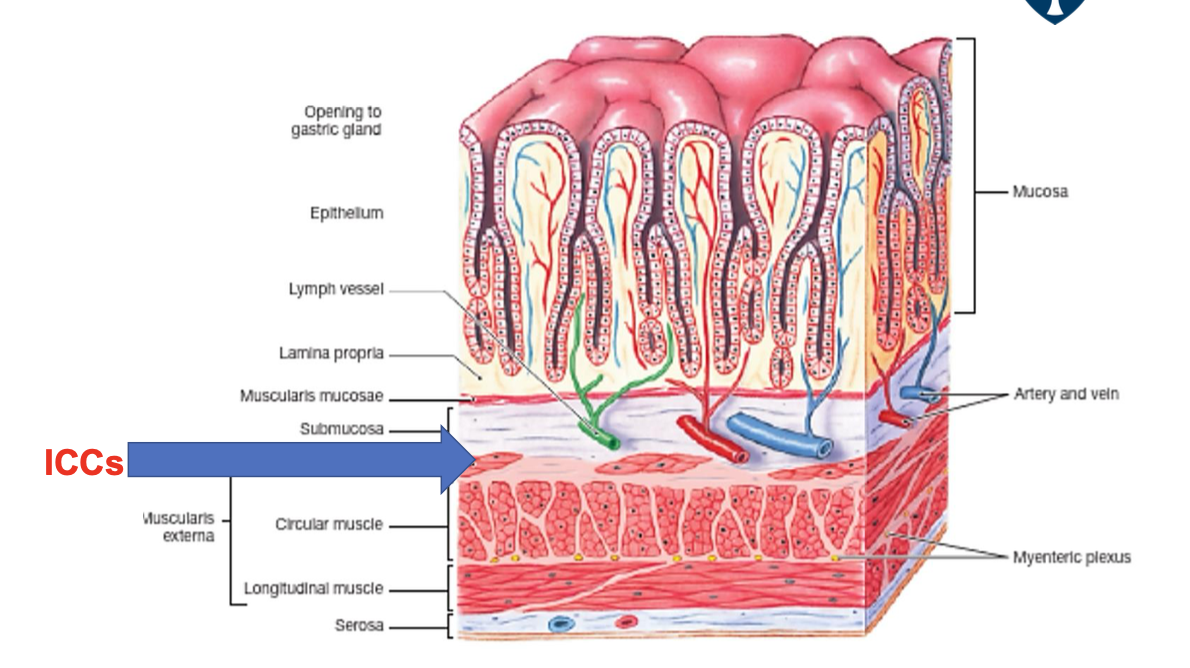
where is the ICCs?
what does slow waves determine?
the basic electric rhythym - not all slow waves trigger contraction
what does the ampitude of the slow wave depend on?
neuronal stimuli
hormonal stimuli
mechanical stimuli
how many slow waves are there in the stomach per minute?
3 slow waves per minute
how many slow waves are there in the small intestine per minute?
1-12 waves per minute in the duodenum
8 waves per minute in the terminal ileum
what do the slow waves do in the large intestine per minute?
favours retention of luminal contents, facilitating absorption of water and electrolytes
what type of process is the absorption of water?
its a passive process
what drives the process of absoprtion of water in the G.I tract?
driven by the transport of solutes (particularly Na+) from the lumen of the intestines to the bloodstream
what is diarrhoea?
the loss of fluid and solutes from the GI tract in excess of 500ml per day
what are the types of mechanisms of sodium/water absorption?
Na+/glucose co-transport
Na+/amino acid co-transport
Na+/H+ exchange
Parallel Na+/H+ and Cl-/HCO3- exchange
epithelial Na+ channels (ENaC)
what is the feature of Na+/glucose co-transport?
its electrogenic
what is th feature of Na+/amino acid co-transport?
its electrogenic
what is the feature of Na+/H+ exchange?
its electroneutral
its powered by the presence of bicarbonate
what is the feature of Parallel Na+/H+ and Cl-/HCO3- exchange?
its electroneutral
its powered by the presence of cAMP/cGMP and calcium dependent
what is the feature of epithelial Na+ channels (ENaC)?
its electrogenic
regulated by aldosterone
what are the causes of diarrhoea?
Excessive secretion - Secretory diarrhoea
most common cause: E. Coli (Traveller’s diarrhoea)
impaired absorption of NaCl
non-absorbable/poorly absorbable solutes of intestinal lumen
hyper motility
what does electrogenic mean?
changes the charge of the blood
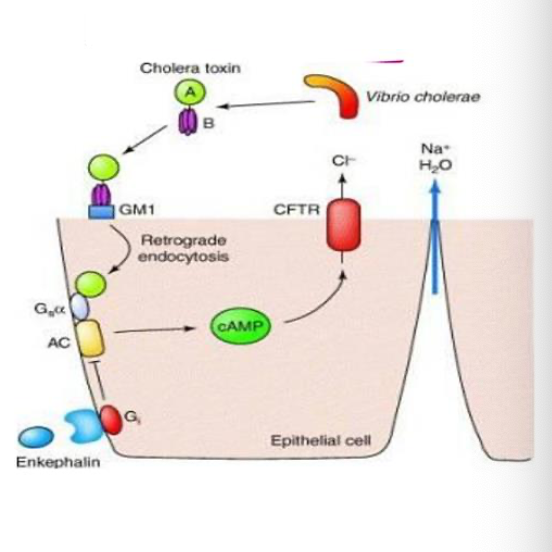
describe the mechanism of excessive diarrhoea:
Cholera toxin enters the enterocyte and enzymatically inhibits the GTPase activity of the Gsa subunit
increased activity of adenylate cyclase
increased concentration of cAMP
cAMP stimulates CFTR
Hypersecretion of Cl-, with Na+ and water following
what is the consequences of diarrhoea?
can result in dehydration (Na+ and H2O loss)
metabolic acidosis (HCO3- loss)
hypokalaemia (K+ loss)
may be fatal if severe (e.g cholera)
what are the types of treatments used to treat diarrhoea?
Maintenance of fluid and electrolyte balance (first priority)
use of antiinfective agents (if appropriate)
Use of anti-motility agents
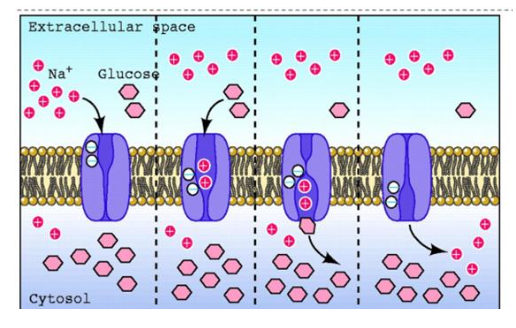
what happens in rehydration therapy?
it exploits Na+/glucose
describe the process of rehydration therapy:
Two Na+ bind
2. Affinity for glucose increases, and glucose binds
3. Na+ and glucose translocate from the extracellular to the intracellular
4. 2 Na+ dissociate, affinity for glucose falls
glucose dissociates
6. The cycle is repeated
how can lactose intolerance be caused?
Primary lactase deficiency– due to lack of the lactase persistence
(LP) allele – most common cause world wide
Secondary lactase deficiency – caused by damage to/ infection of/
the proximal small intestine
Congenital lactase deficiency – rare autosomal recessive disease –
no ability to digest lactose from birth
how is lactose intolerance diagnosed?
diet observation:
Association of symptoms with lactose consumption
hydrogen breath test
Lactose/milk tolerance test
what are the symptoms of lactose-intolerance?
bloating
abdominal pains
dirrhoea
how is lactose intolerance treated?
Reduction or elimination of consumption of milk products
use of milk prodicts treated with lactase
Use of milk lactose-free
What are the causes of constipation?
neurological disorders of the large intestine
Abdominal muscle weakness
Diet poor of fibres
Sedentary life style
Constant suppression of the urge to empty
Antidepressant drugs -anticholinergics
Opiates
Aging
treatment for constipation:
More water and less alcohol should be consumed
Some wheat bran can be added to the diet
Increase your activity- exercise
Improve your toilet routine - Keep to a regular time and give yourself plenty of time to use the toilet
don’t delay
feet can be rested on a low stool while going to the toilet
what are the types of laxatives to treat constipation?
purgatives:
bulk laxatives
osmotic laxatives
faecal softeners
stimulant laxatives
drugs which increase GI motility without purgation:
antimetics