Chapter 7: Renewable or Alternate Energy
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
Renewable energy means that the energy production and use generate very low _____ emissions and whose production can be sustained _____.
greenhouse, indefinitely
Renewable energy means
a) less sustainable
b) low-cost
c) produce less greenhouse gases
d) efficient
c
Which one is not the incentives behind the production and use of such biofuels rather than fossil fuels
a) carbon-neutral characteristic
b) they are renewable
c) low price and efficient
d) results in smaller amounts of air pollutants
c
E10 means
a) 90% ethanol
b) 10% efficient
c) 90% efficient
d) 10% ethanol
d
Ethanol is produced ___ in industries
a) sugarcane
b) catalytically
c) corn
d) fermentation
b
What are the sources of ethanol
a) sugarcane
b) sugar beets
c) corn
d) cassava
f) All of them
f
Which are the disadvantages of ethanol
a) produce less energy
b) require a large amount
c) lower cost
d) low vapor pressure
e) all of them
e
Bioethanol, second generation of biofuel, mainly produced
a) sugarcane
b) sugar beets
c) corn
d) woody plant
c
The cellulose contains woody plants
a) 35-50%
b) 15-50%
c) 20-30%
d) 50-70%
a
The hemicellulose contains in the woody plants
a) 35-50%
b) 15-50%
c) 20-30%
d) 50-70%
c
The lignin contains in the woody plants
a) 25-50%
b) 10-30%
c) 20-30%
d) 50-70%
6
What are not the advantages of the second generation to biofuel over first generation biofuels
a) much smaller need for fertilizers and irrigation
b) easy to be converted into an alcohol
c) the lower product cost
d) the lesser competition with food crops
b
what is the main depolymerized product lignin
a) D-glucose
b) phenol derivatives
c) ethanol
d) monosaccharides
b
what is the main depolymerized product of cellulose
a) D-glucose
b) phenol derivatives
c) ethanol
d) Monosaccharides
a
what is the main depolymerized product of hemicellulose
a) D-glucose
b) Phenol derivatives
c) ethanol
d) monosaccharides
d
T/F : biofuels are renewable
True
T/F: biofuels produce less air pollutants
true
biofuels produce only a small quantity of _____.
oxygen
biofuels can replace ____
petroleum
the use of ___, ___ residues and dung was the world’s first energy source
wood,crop
biomass was second to ____ power in the production of renewable energy even in the US in the late twentieth century
hydroelectric
ethanol can be used in ____ form or as a component in a solution that includes gasoline
pure
E100 is used mainly in ____
brazil
in cold climates, with pure ethanol there is very little _____ fuel available to start a ____ automobile engine
vaporized, cold
a blend of ___% gasoline and ___ % ethanol has a high enough vapor pressure to overcome the cold start problem of a car (where a car is too cold to start)>
85%, 15%
____ ethanol is currently the most important example of second-generation biofuel.
cellulosic
are second generation biofuels produced from edible food crops?
no
second-generation biofuels are produced from ____ materials from crops such as ____, ____, and ____, from crops not used for food purposes, and from industrial waste ___.
waste, stems, husks, leaves, biomass
in general, second-generation biofuels are more ____.
sustainable
what are some advantages of second-over first-generation biofuels?
Smaller need for ____ and ____ water
greater savings in _____ gas emissions required for their processing.
the lesser competition with ____, or land devoted to ____.
the lower ____ cost
fertilizer, irrigation
greenhouse
food crops, food crops
production
in order to be converted into an alcohol, the biomass must first?
first be ground up and pretreated to break the seal of lignin.
___-based cooking oils (whether corn oil, olive oil, or sunflower oil) are candidates for fuels in ____ engines
plant, deisel
the first diesel could be powered using ____ oil.
peanut
Modern diesel engines are designed to use fuel that is not as ____. what does viscous mean?
viscous, not as resistant to flow
natural oils are highly ___ and their component molecules are very ___, each containing about __ to __ carbon atoms- about three times as many as those in petrodiesel.
viscous, large, 50 to 60
unrefined vegetable oils contain unwanted impurities such as ____ acids, ___ and ____ substances
free fatty, water, odorous
the polymerization of unsaturated ____ components produces gum, which results in ____ deposits and thickening of ____ oil in the engine.
hydrocarbons, carbon, lubricating
to overcome the difficulties in using SVOs, the virgin vegetable oils commonly are
transformed into a less viscous, less corrosive fuel called _____.
biodiesel
Because there are technical problems in using the acids themselves as fuel, the ___ acids are reacted with _____, which converts them into ____; thus, the hydrogen atom (green) of the acid group is replaced by a methyl group.
fatty, methanol, methyl esters,
fatty acid methyl esters are the ____ of biodiesel.
constituents
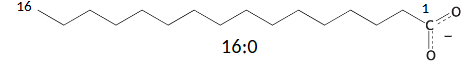
what us this fatty acid called
palmitate
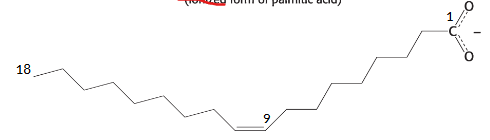
what is the name of this fatty acid
oleate
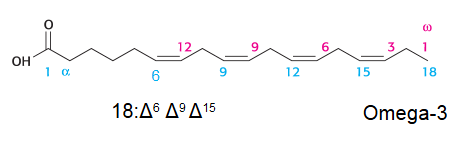
Fatty acid carbon atoms are usually numbered beginning with the ____ terminal carbon atom
carbon atoms 2 and 3 are also referred to as ___ and ___
fatty acids can also be numbered from the ___ carbon atom, which is called the omega carbon.
carboxyl
alpha, beta
methyl
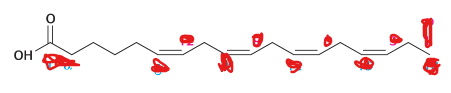
number this fatty acid
vegetable oils consist largely of _____.
triglycerides
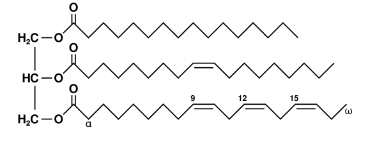
this is a ?
triglyceride
the total number of carbon atoms in a typical glyceride is about ___. This large size accounts for its high ____.
60, viscosity
Petrol fuel is
A liquid fuel that mainly consists of light hydrocarbons raging from C_ to C_
more ___ than diesel
more ____ than diesel because it contains light hydrocarbons.
C5, C12
flammable
volatile
Disel is
a liquid fuel that consists of heavy hydrocarbons, greater than C_
less ____ than petrol
less ____ than petrol because it contains heavy hydrocarbons
flammable, volatile
Diesel contains about ___% saturated hydrocarbons and __% aromatic hydrocarbons. Diesel contains hydrocarbons with ____ chains than petrol and is thus less volatile.
75, 25, longer
Advantages of biodiesel:
produces significantly fewer ____, other than NOx
significantly higher ___ point so it is safer to handle
____ faster in freshwater and soil and is much less ____
The growth of plants for biofuel absorbs much of the ____ emitted during its combustion and thus reduces about ___ the greenhouse gas emissions from diesel fuel combustion
air pollutants
flash
biodegrades, toxic
CO2, half
disadvantages of biodiesel
biodiesel has a slightly lower ___ content.
is more ____
undergoes _____
may attract __ from atmospheric moisture
the water causes ____ of the engines fuel system
the ____ reduction is more than offset for decades if the new land must be cleared to grow plants
energy
viscous
degradation
corrosion
CO2
Methanol can be blended with gasoline to produce a fuel that burns more ___than gasoline.
cleany
Blends of methanol are designated by an M rating; thus, M5 corresponds to?
5% methanol and 95% gasoline
disadvantage of methanol blends
the pure alcohol is only soluble to the extent of about __% gasoline.
15
some concern has been expressed about the safety of methanol for use as a ____ fuel, given the toxicity of the compound.
vehicular
methanol can be used to produce ____, which has been tested as a replacement for diesel fuel trucks and buses
dimethyl ether
dimethyl ether is nontoxic and degrades easily in the ____
atmosphere
since dimethyl ether contains no C-C bonds, ___ particulate matter is produced in its combustion but only in very small quantities compared to diesel fuel.
soot-based
the ___ emissions from dimethyl ether combustion are also lower than usually found for diesel engines.
NOx
methanol is also used to produce methyltertiary-____
methyltertiary-butylether
MTBE is used in north American and European unleaded gasoline blends up to __%.
15
hydrogen is not an ____ source, since it does not occur as the free element on earth’s crust
energy
hydrogen gas is an energy ____ only.
vector
Natural gas or petroleum or coal is reacted with steam to form ____ and ____.
H, CO2

this is a ___ gas reaction
Natural
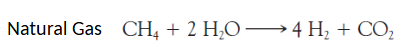

this is a ____ reaction.
petroleum
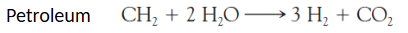
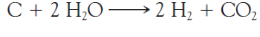
this is a ____ reaction
coal
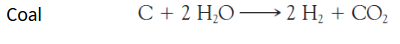
hydrogen is superior to ____ in some ways since its transmission by pipelines over long distances consumes less energy.
electricity
the _______ problems in the production, storage, transportation and usage of hydrogen plus the need to _______ for it means that a hydrogen economy is probably still many decades away.
substantial technical, create a new infrastructure for it.
hydrogen is not an _____ since it doesn’t occur as the free element on the Earth’s crust.
energy
hydrogen fuel must be produced from water and/or _____, by the consumption of large amounts of energy and/ or other ____.
methanol, fuels
virtually all (__%) the hydrogen gas that is currently produced in the world is obtained by reactions of ____, i.e., non-sustainably.
95%, fossil fuels
the most commercial way to produce hydrogen is by _____ of water, using DC electricity generated by an energy source. The water is made by alkaline and conducting by the addition of ____ hydroxide
electrolysis, potassium
one catalyst that has been found to convert sunlight into hydrogen by electrolyzing water is ____ dioxide. Unfortunately, a quarter to one half of the electrical energy is unavoidably converted to ___ and therefore wasted in the process.
titanium, heat
in principle, thermal conversions of sunlight into heat can produce temperature hot enough to decompose water into ___ and ____.
hydrogen,oxygen
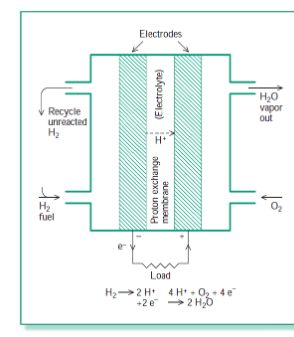
hydrogen and oxygen can be combined in ____cells in order to produce electricity.
fuel
fuel cells are similar in operation to ____ except that the reactants are supplied continuously.
batteries
fuel cells have the advantage over combustion in that a more useful form of energy is produced, and the process creates no ______ as by-products.
polluting gases
real fuel cells overall are now about ___-___% efficient, ____% efficiency may be obtained eventually. By contrast, internal combustion engines using gasoline are ___-___% efficient, while diesels are ___-___% efficient.
55-55%, 70%, 15-25%
generating electricity by powering fuel cells with hydrogen:
in the hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell, the two gases are each passed by an _____ electrical connect through which electrons travel, by an _____ through which ions travel.
at the catalytic surface of the first electrode, the H2 gas produces H ____ and ____, which travel around the external circuit to the second electrode, across which O2 gas is bubbled.
Meanwhile, the H ions travel through the electrolyte and ____ with the electrons and O2 to produce ___ at the second electrode.
external, electrolyte
ions, electrons
recombine, water