Cell Structure and Transport: Nucleus, Membranes, and Organelles
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Nucleus
Contains DNA in the form of chromatin or chromosomes.
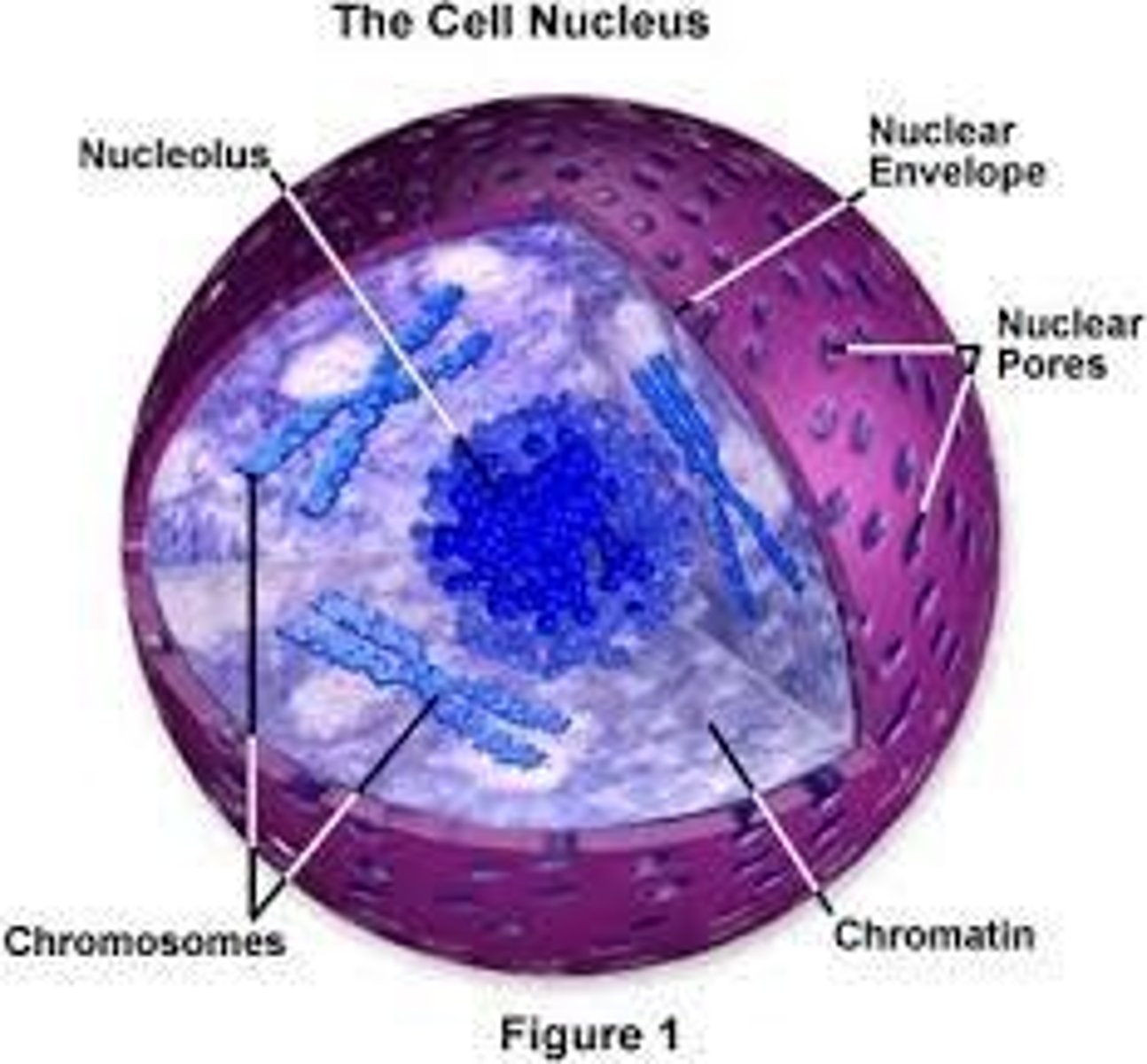
Nucleolus
Produces ribosomes.
Plasma Membrane
Boundary & Protection; consists of a phospholipid bilayer, cholesterol for fluidity, protein channels/gates for transport, glycoproteins for cell recognition.
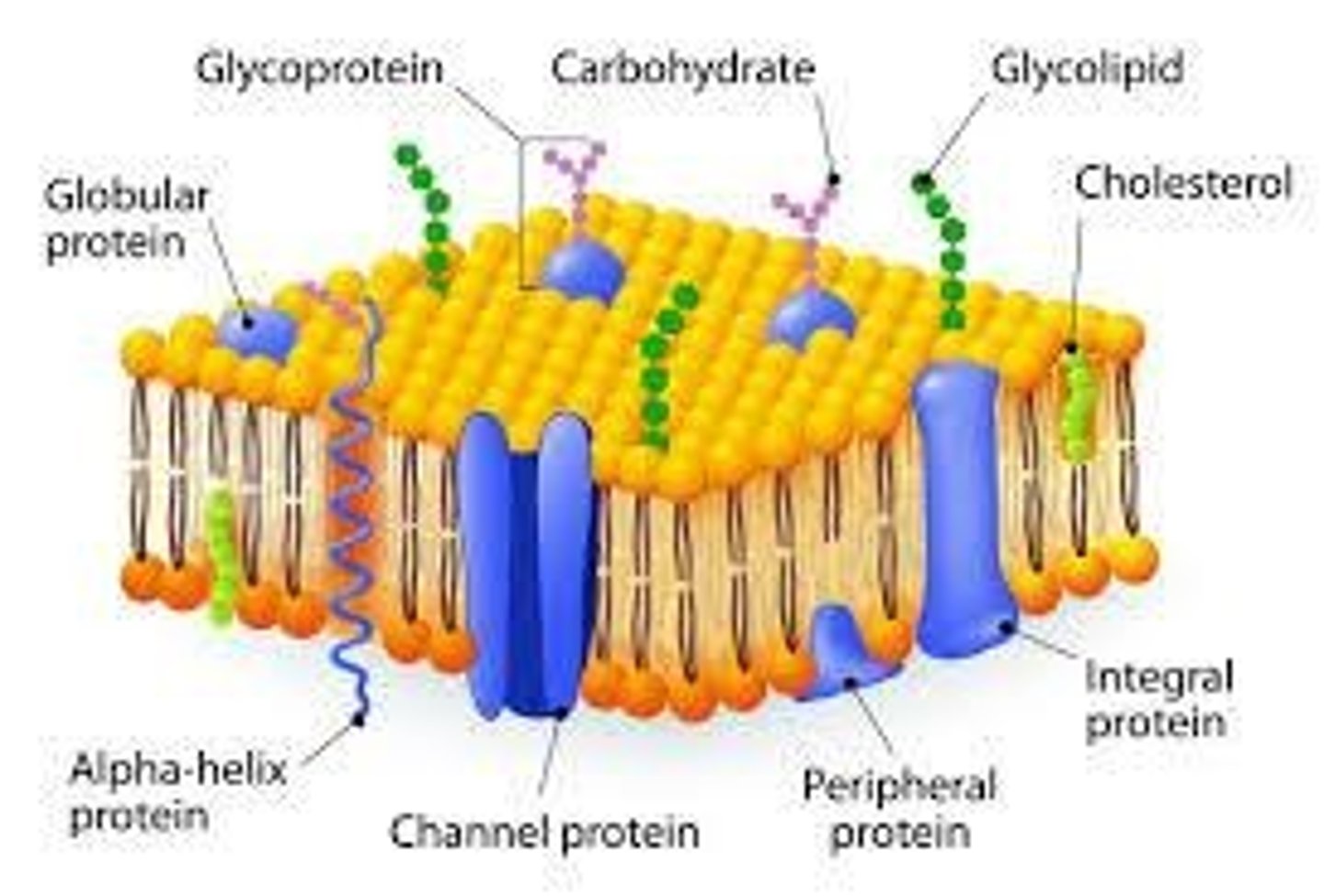
Fluid Mosaic Model
Describes the plasma membrane structure.
Tight Junctions
Zipper-like, leak proof connections found in the intestines.
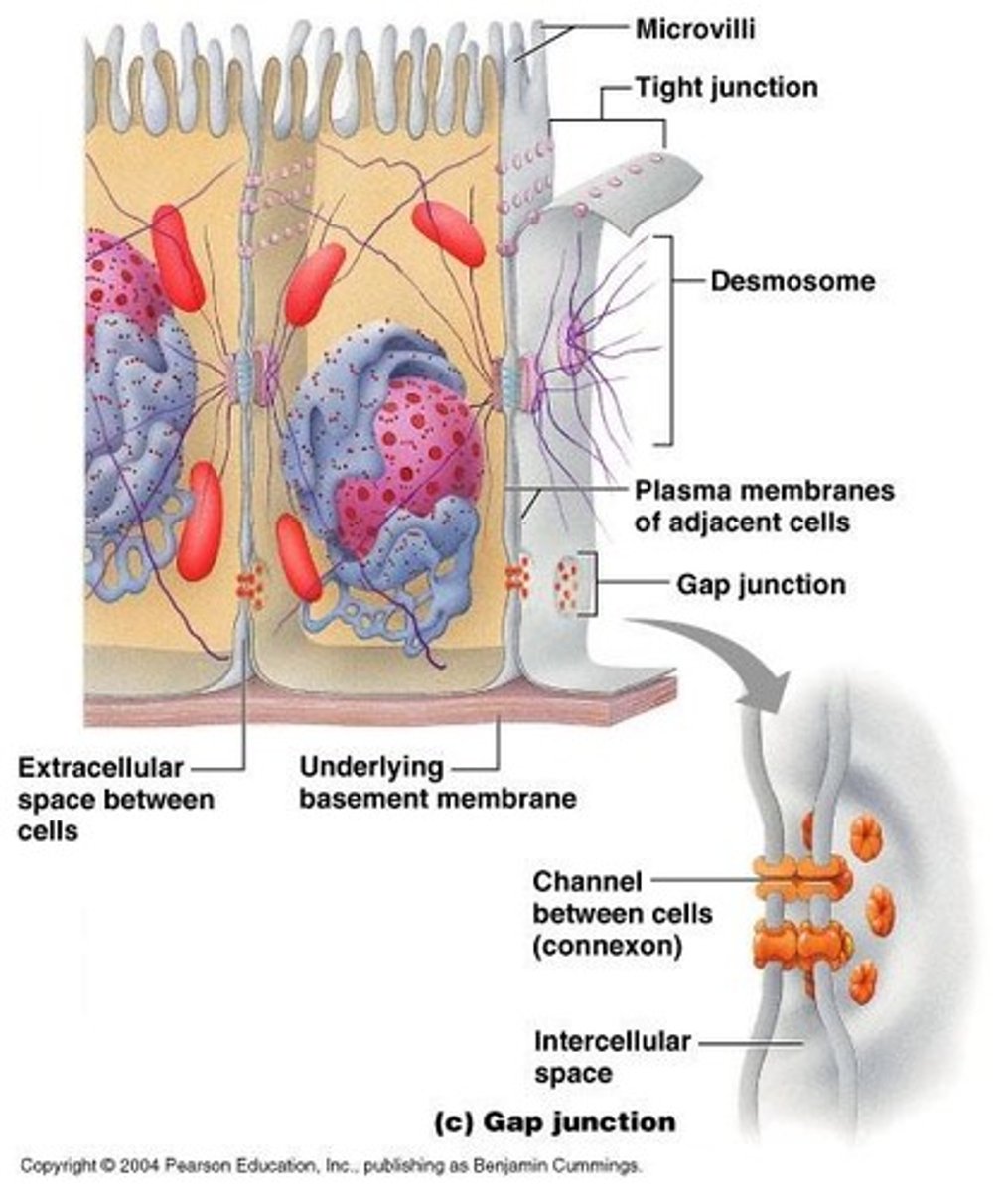
Desmosomes
Anchors that prevent cells from separating; button-like structures found in skin.
Gap Junctions
Connexons channel communication; found in heart & embryonic cells.
Cytoplasm
Location of chemical reactions; contains organelles and nutrients.
Mitochondria
Site of cellular respiration; converts glucose and oxygen into ATP.
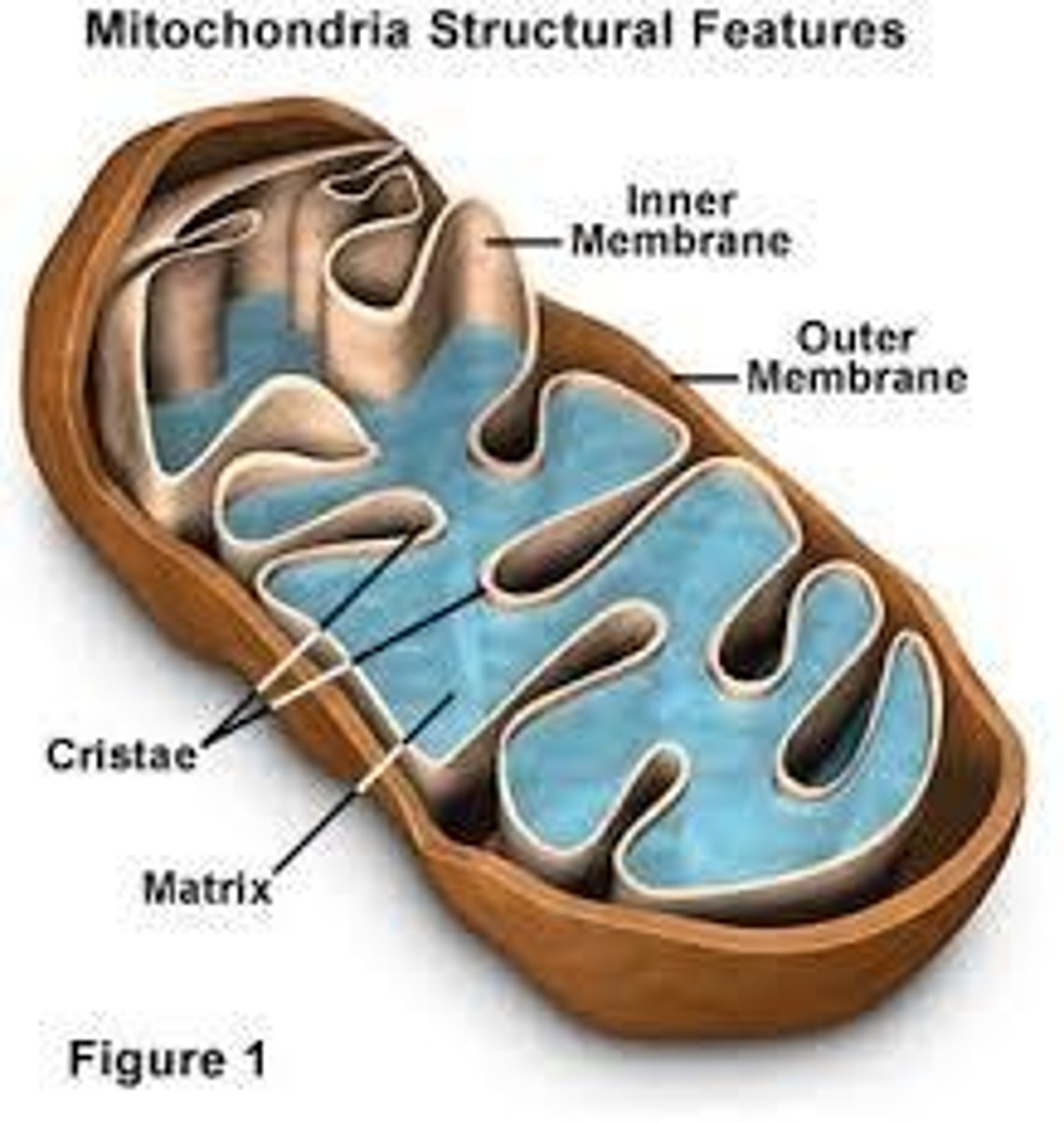
Cristae
Folds of the inner membrane of mitochondria; more folds increase surface area to volume ratio.
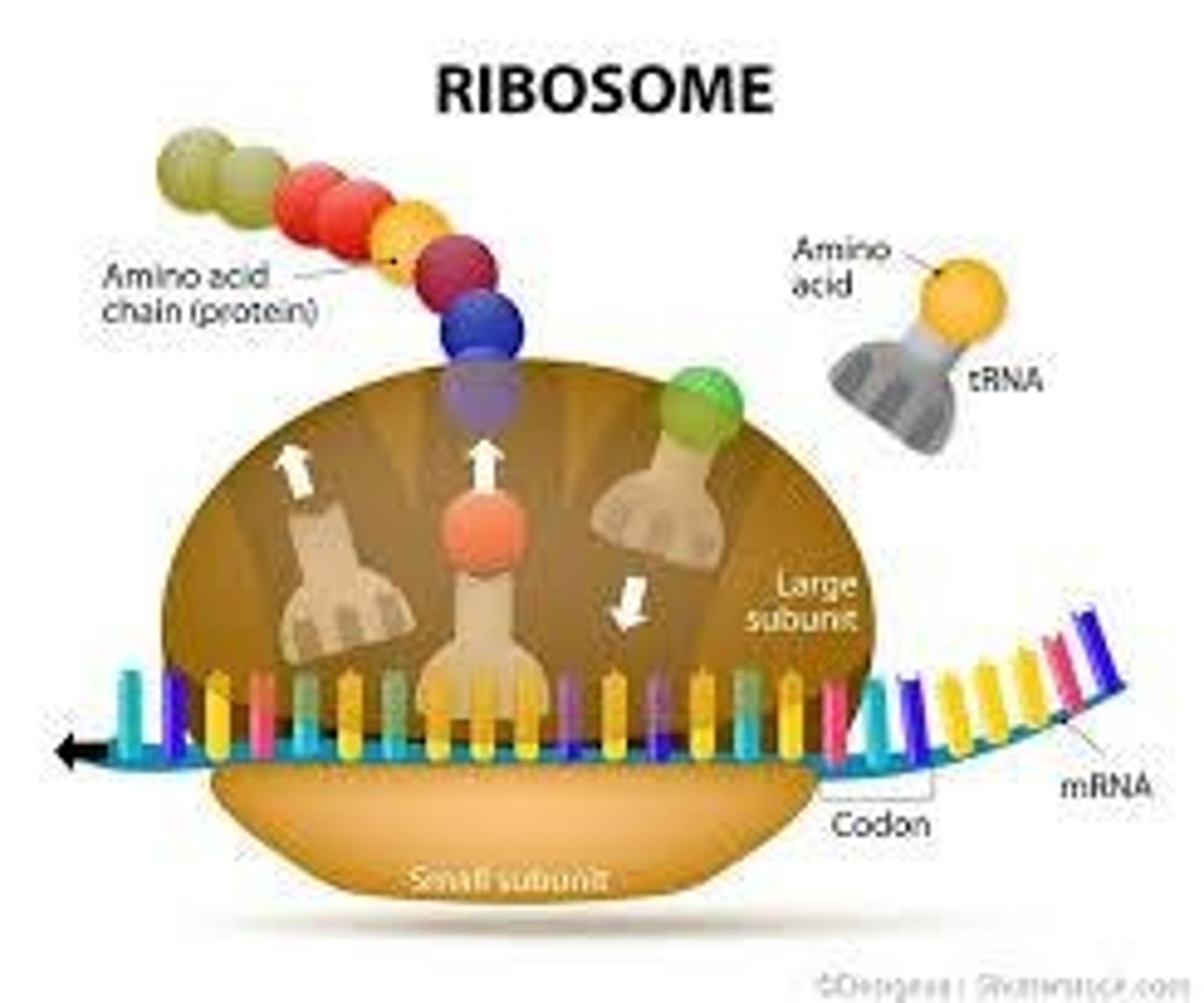
Ribosomes
Sites of protein synthesis made of 2 subunits of rRNA; can be free-floating or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
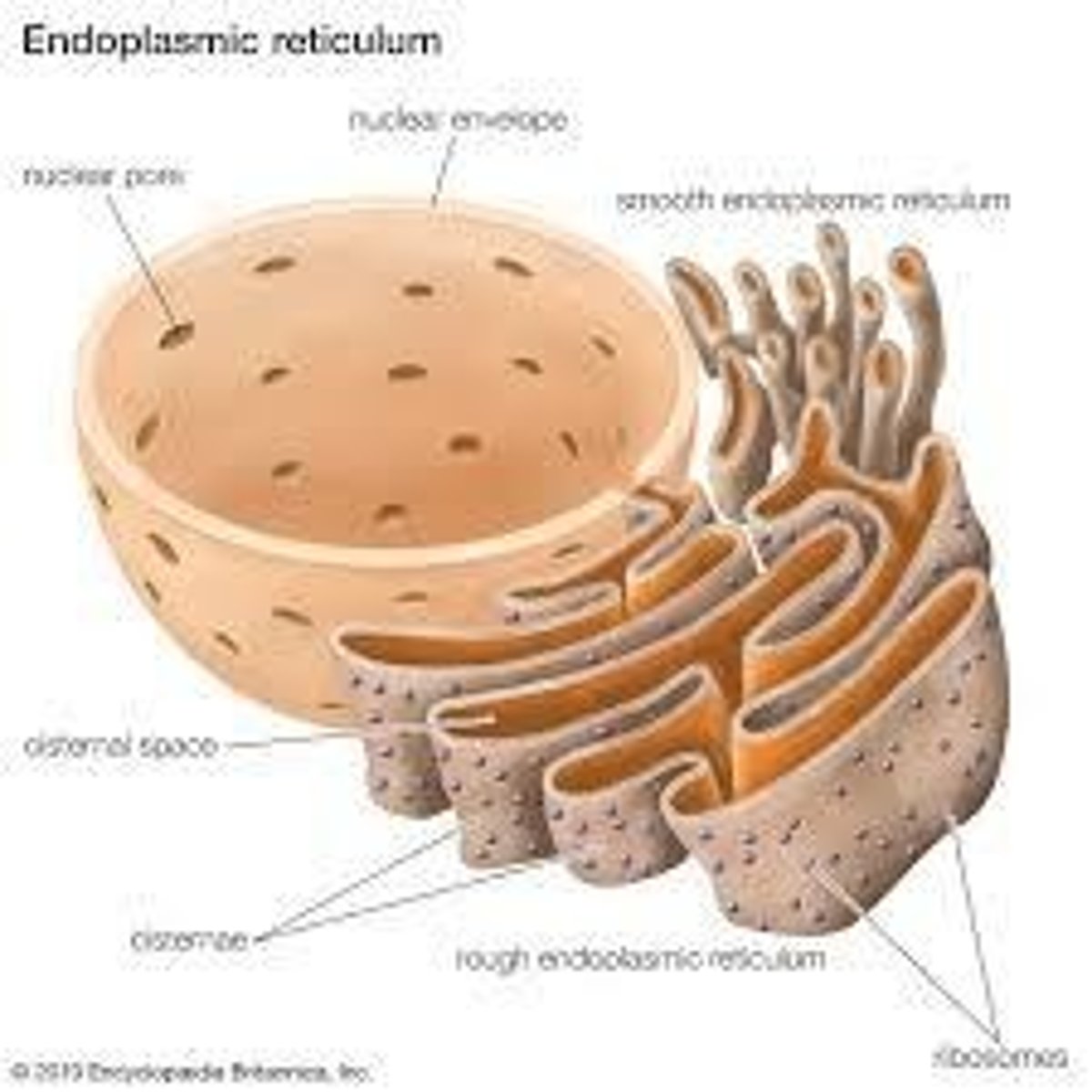
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Rough ER is involved in protein synthesis; Smooth ER is involved in lipid metabolism and detoxification of drugs.
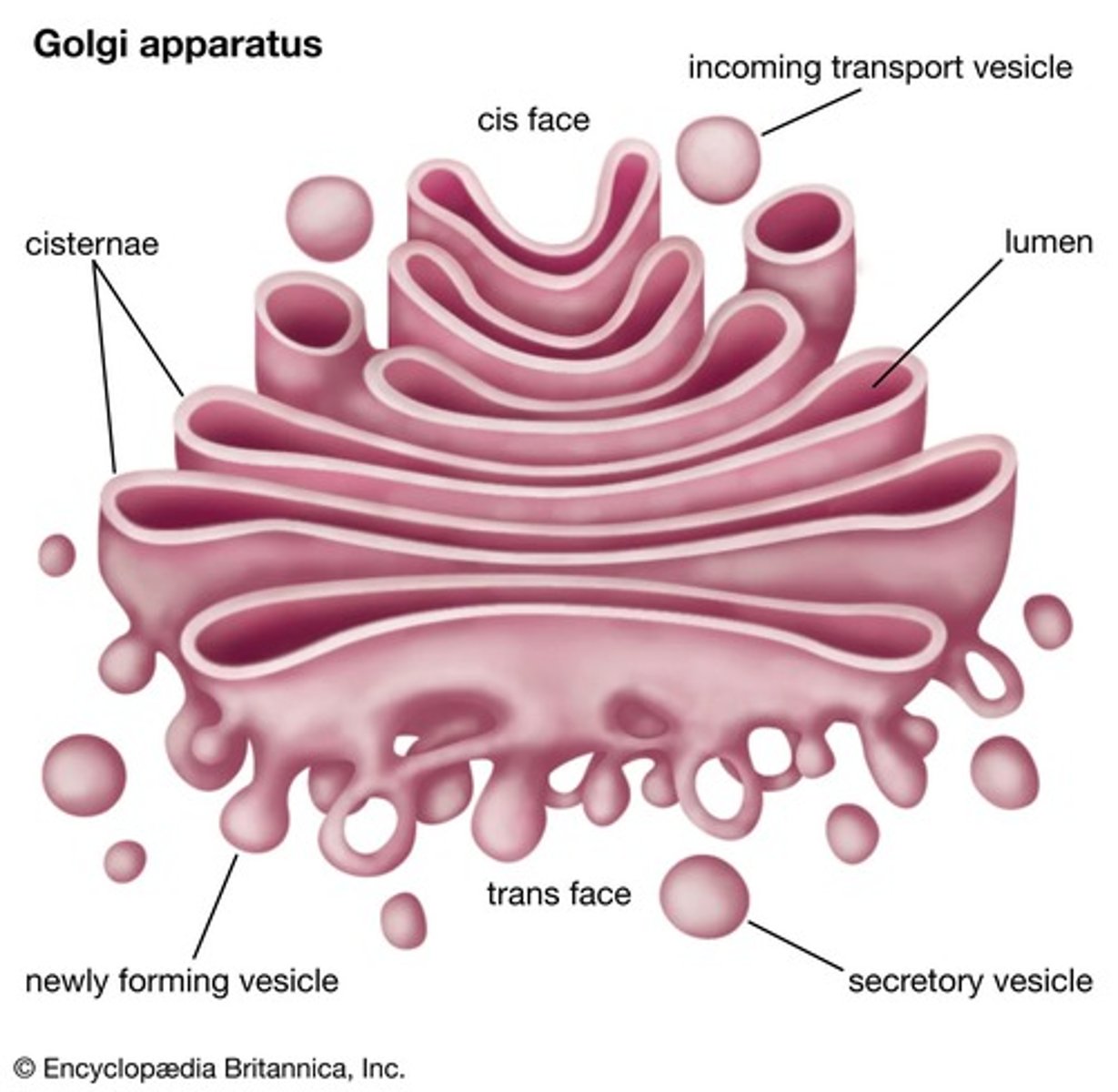
Golgi Body
Modifies, packages, and sorts molecules made by the rough and smooth ER with the help of transport vesicles.
Lysosomes
Vesicles full of digestive enzymes to break down food molecules.
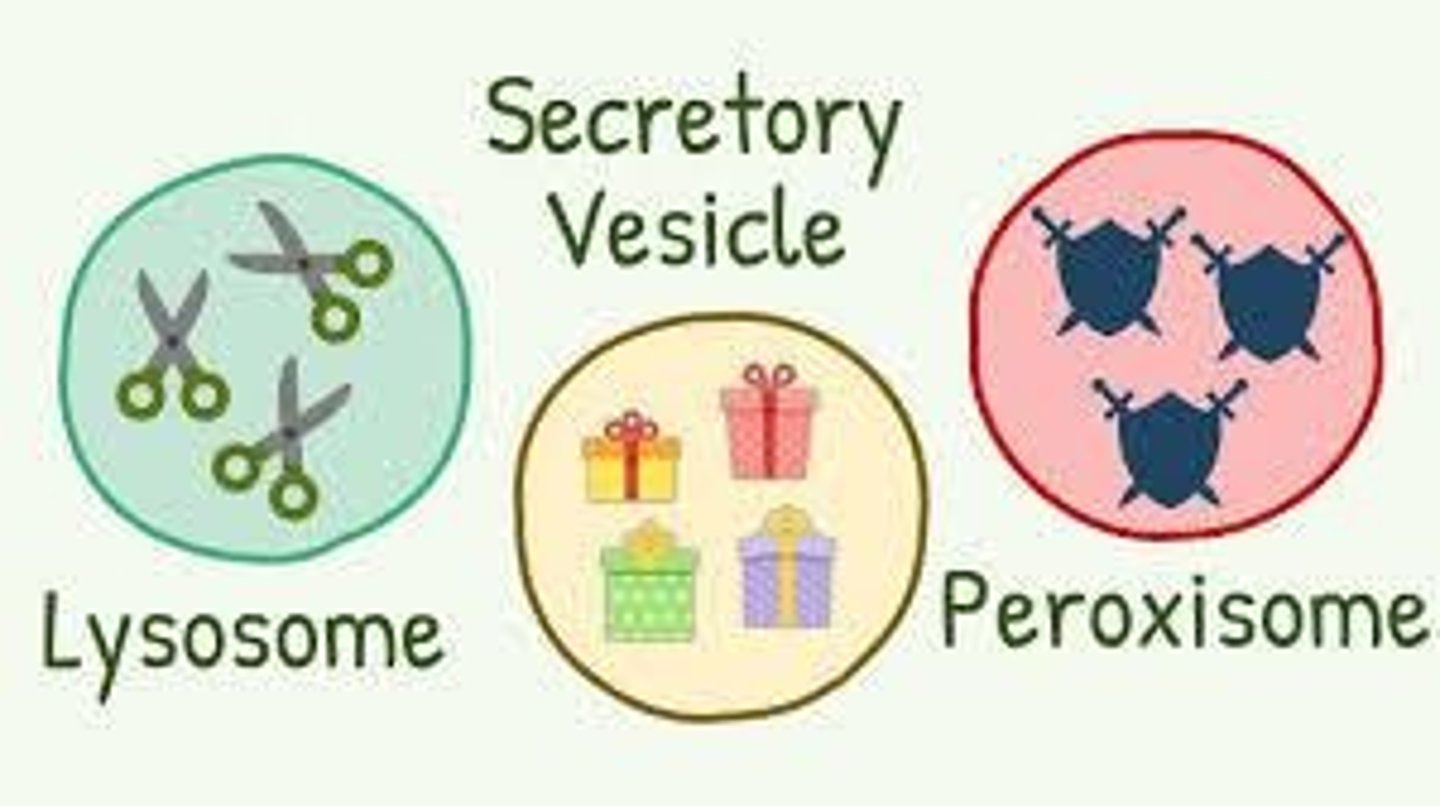
Peroxisomes
Vesicles full of oxidase enzymes to detox harmful molecules; convert DNA damaging free radicals to peroxide (H2O2).
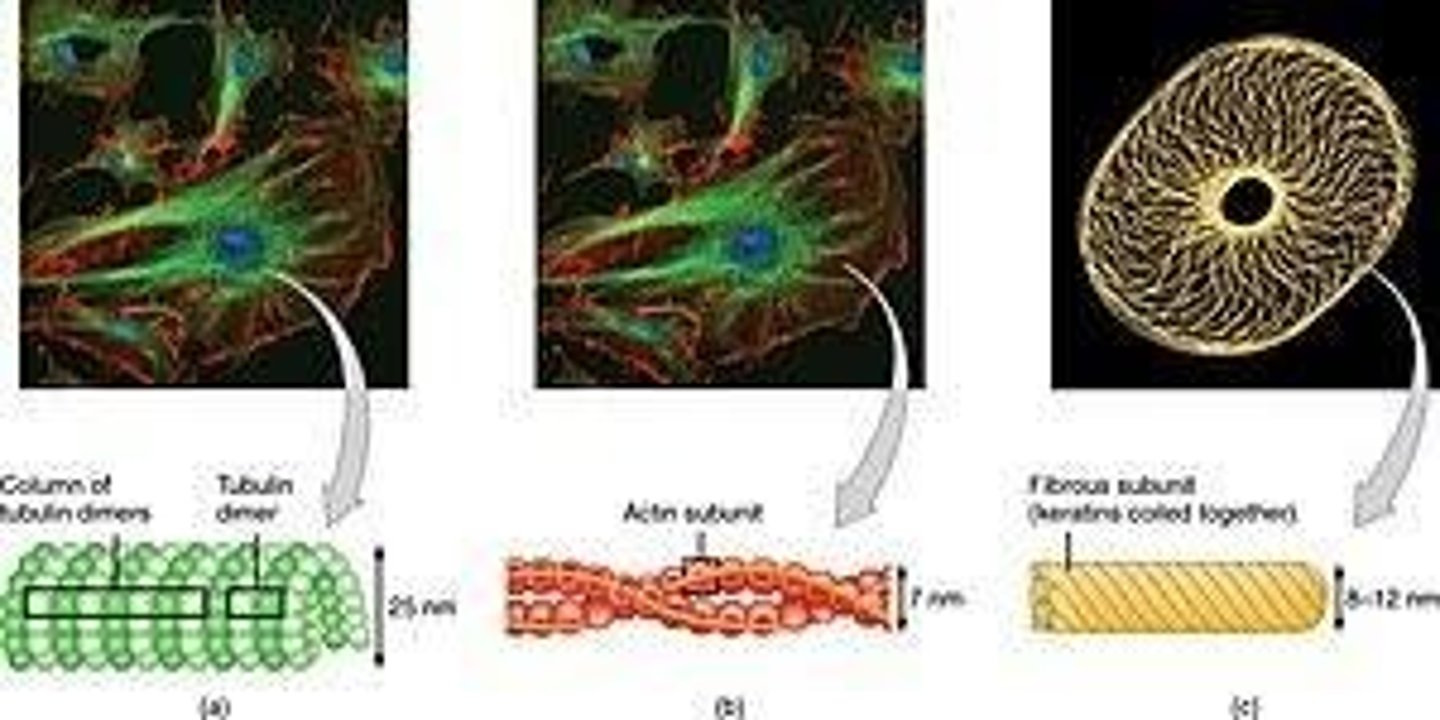
Cytoskeleton
Provides internal support; consists of microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules.
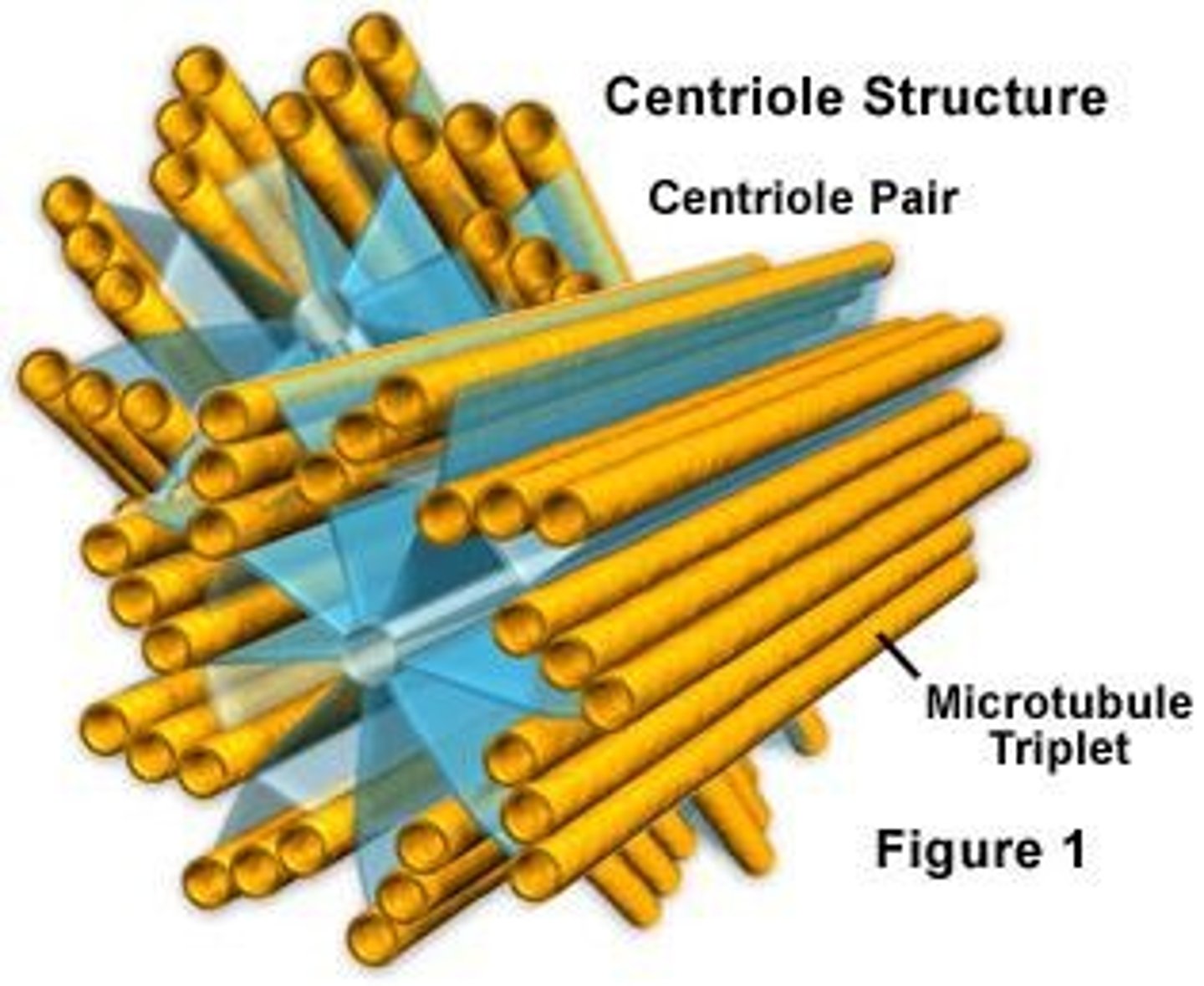
Centrioles
Arrangement of microtubules used in moving chromosomes around during cell division; found in pairs.
Cilia
Little hairs made of microtubules; involved in movement, found in the respiratory tract, brain ventricles, and fallopian tubes.
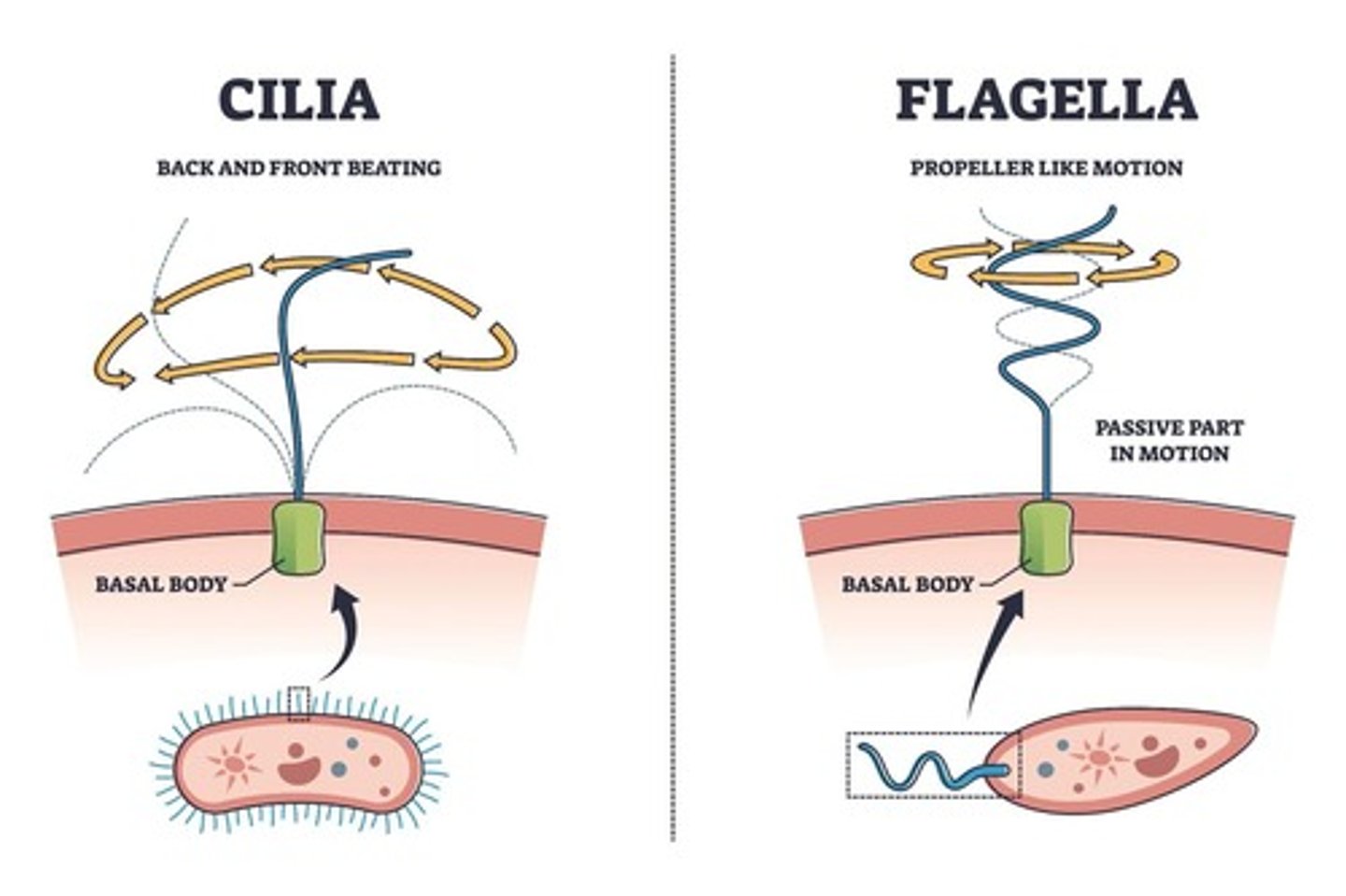
Flagella
Long tail made of microtubules; involved in movement, found in sperm cells.
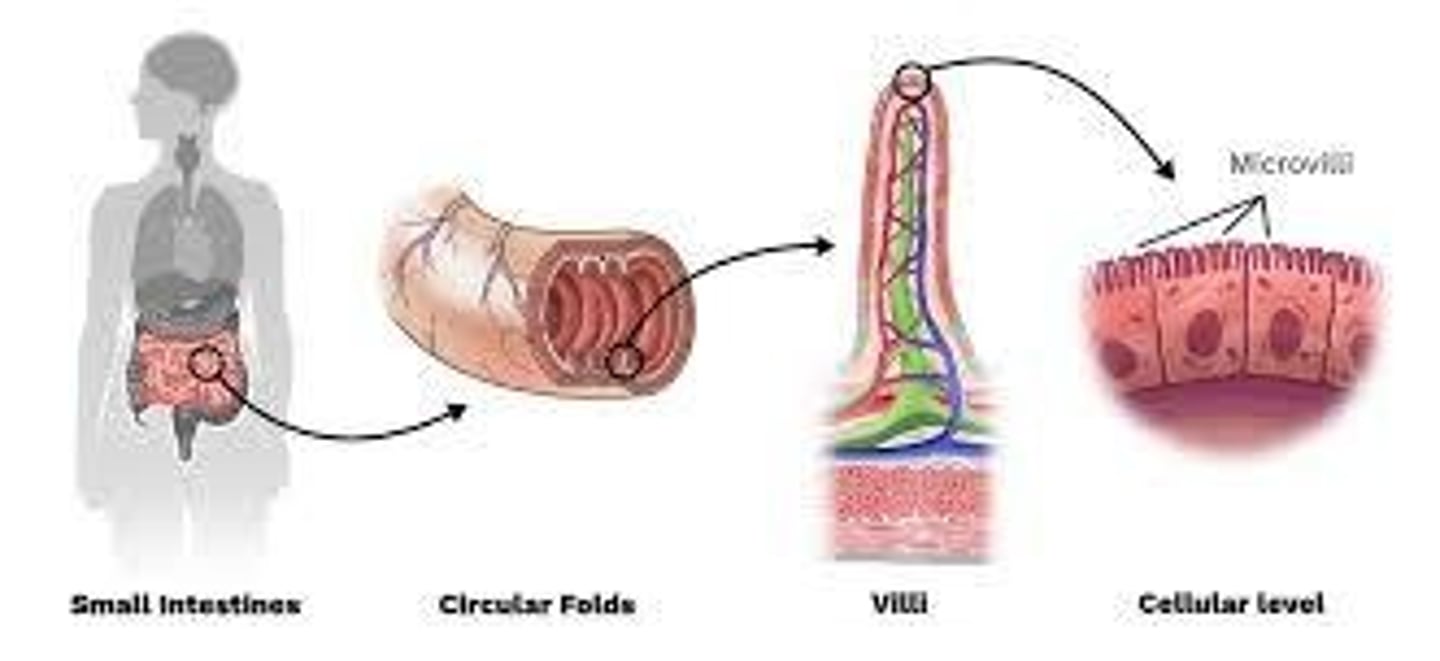
Microvilli
Tiny hairs, similar to cilia; increase surface area of the membrane for greater absorption, found in intestines.
Active Transport
Movement of molecules against their concentration gradient, requiring ATP.
Passive Transport
Movement of uncharged atoms/molecules (H2O, O2, CO2) through phospholipids from high to low concentration to achieve equilibrium.
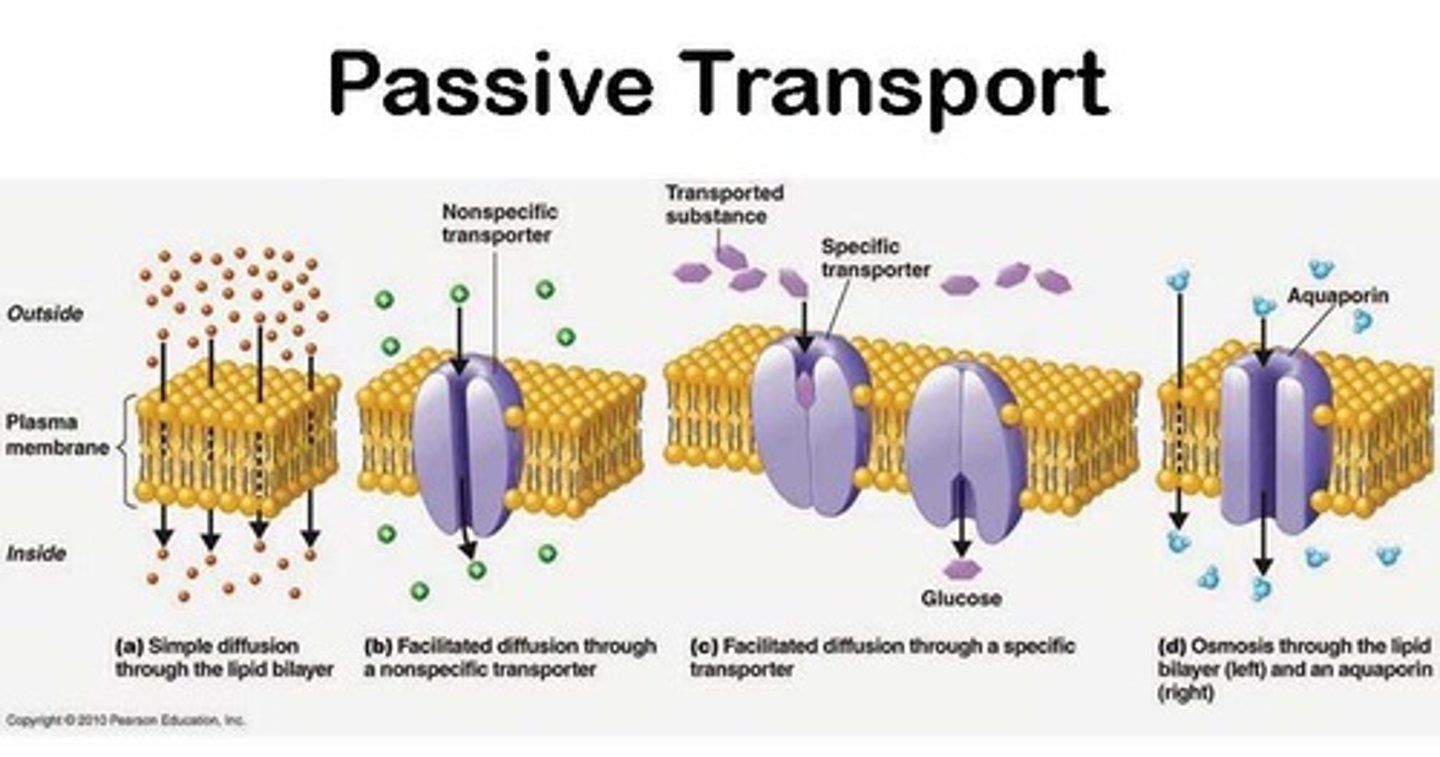
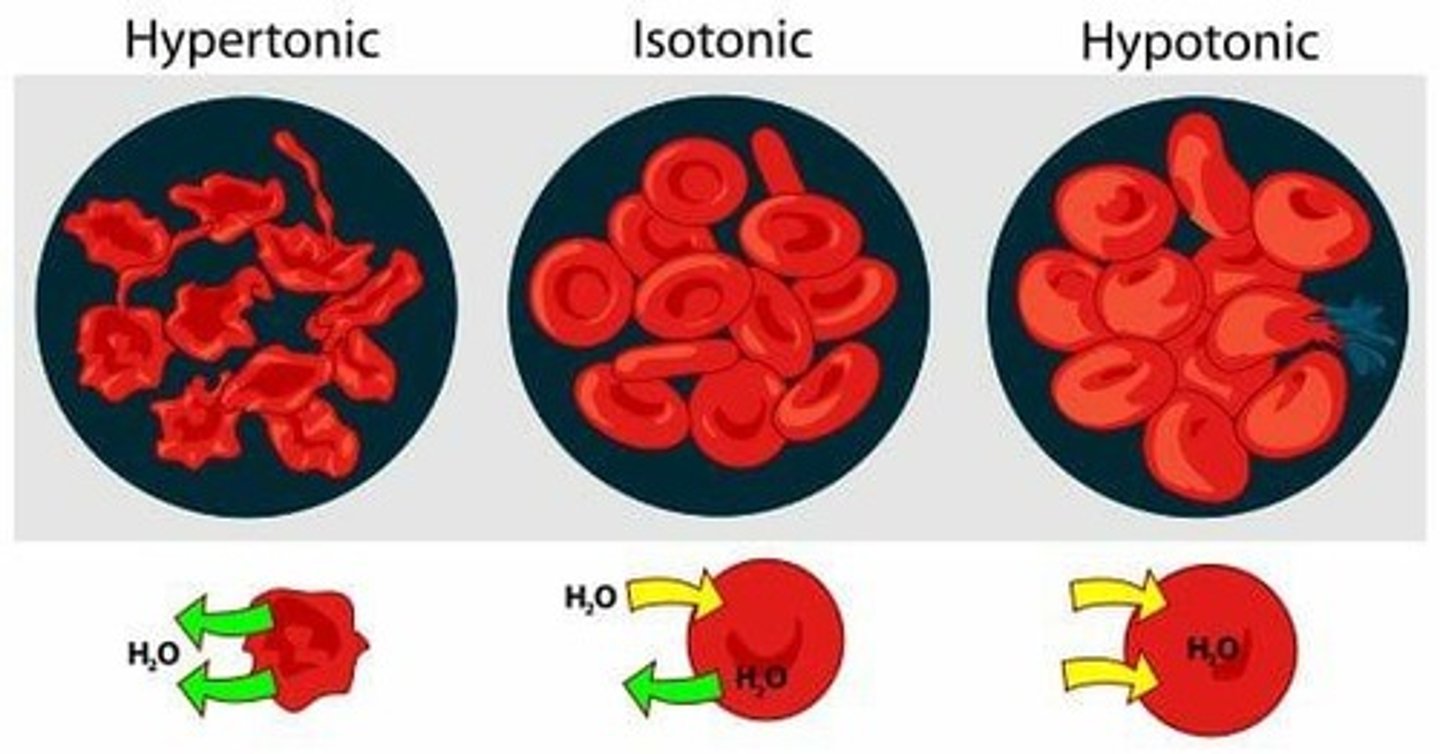
Osmosis
In a solution, if there's less water, then there's more solutes and vice versa; cells in a hypotonic solution will expand, while cells in a hypertonic solution will shrink.