12 Rates of Reaction
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Slow reaction examples
Rusting of iron
Weathering of rocks
Fermentation
Fast reaction examples
Fireworks
Explosions
Precipitation reaction
Rate of reaction formulae

Rate of reaction
The change in concentration (mole) of reactants or products in unit time (seconds).
Unit: mol s^-1
Ways to measure rate of reaction
Measuring a change in volume of gas produced over time using a gas syringe - if reaction produces a gas
Decrease in mass of the reactants can be measured over time - if reaction produces a gas that escapes
A change in colour intensity, pressure, temperature or pH - if any of these properties change during a reaction
The appearance of a precipitate - if one is formed in reaction
Conditions needed for a reaction to occur
Reactant particles must collide with eachother to break their bonds
They must collide with enough energy to break their bonds and enable new bonds to form (the minimum energy needed is the activation energy)
Reactant particles must collide with the correct orientation so bonds can break and reform in the required way
Draw a rate curve
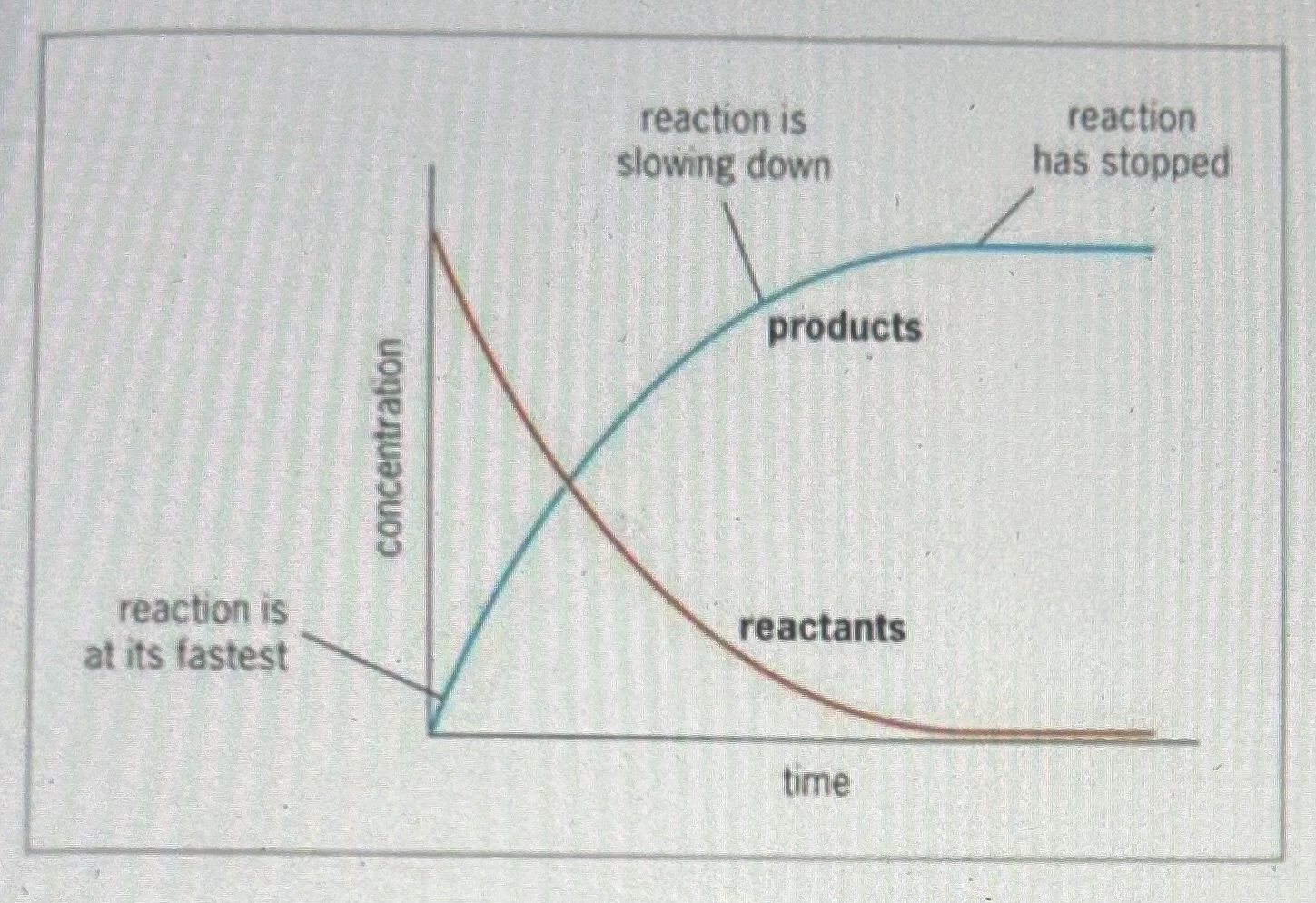
Describe what’s happening in a rate curve
At the beginning of the reaction the gradient is steepest showing the rate of reaction is at its highest (there are a lot of particles meaning a lot of collisions can happen)
As the reaction progresses, the curve becomes shallower showing the rate is decreasing (there are less and less reactant particles)
The curve becomes horizontal (the gradient = 0) showing the reaction is complete
Factors that affect rate of reaction
concentration of reactants
temperature
Surface area (particle size)
Presence of a catalyst
Pressure and light (for some reactions: pressure - if reactions are gases, light - reactions like photosynthesis)
Draw a rate curve after adding a factor that increases rate of reaction
