Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 2
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
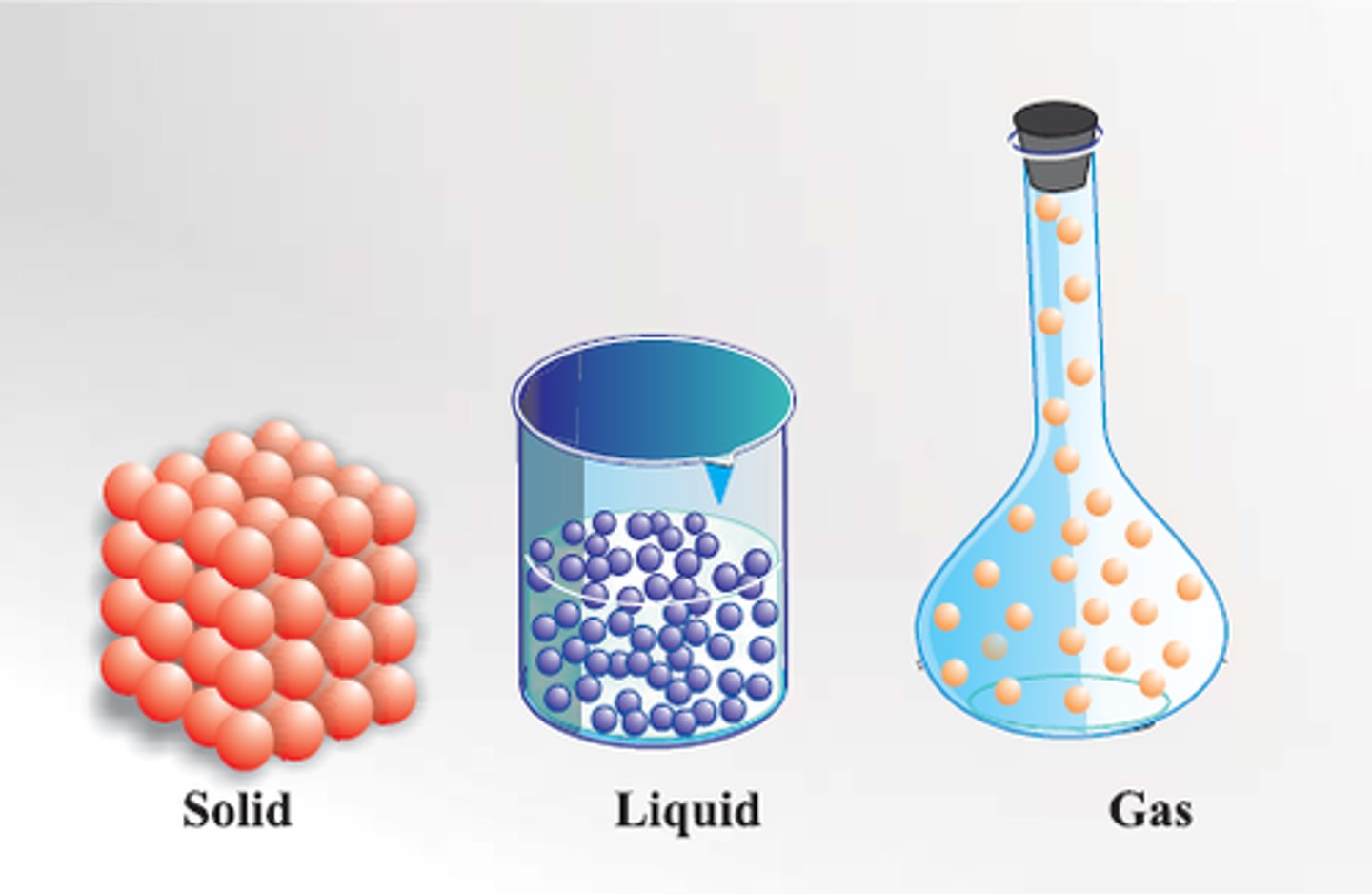
Matter
Anything that has mass and occupies space
Kinetic Energy
Energy in action

Potential Energy
Stored energy

Chemical Energy
Stored in bonds of chemical substances
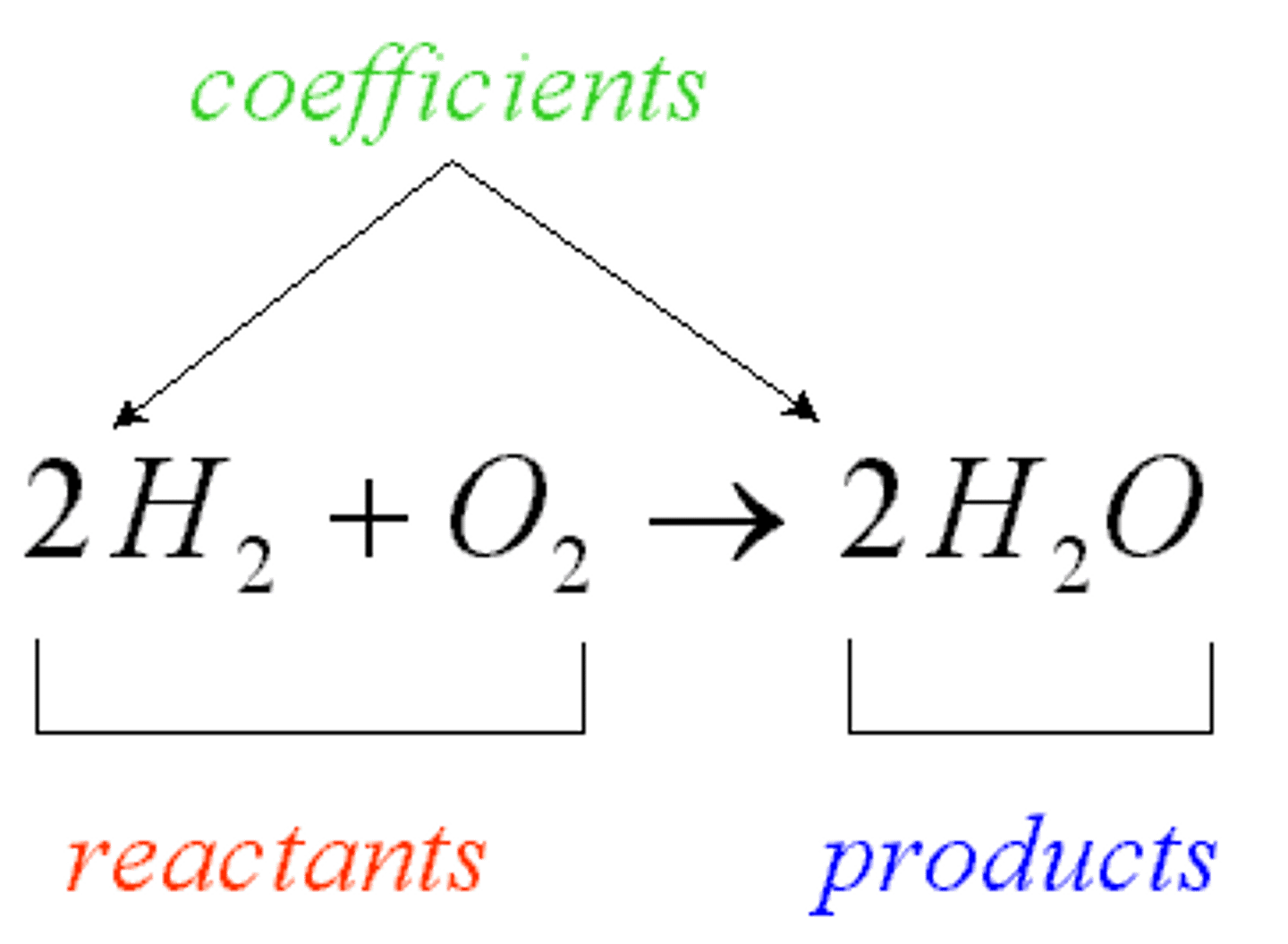
Element
Matter is composed of elements, cannot be broken into simpler substances by ordinary chemical methods
Atom
Unique building blocks for each element
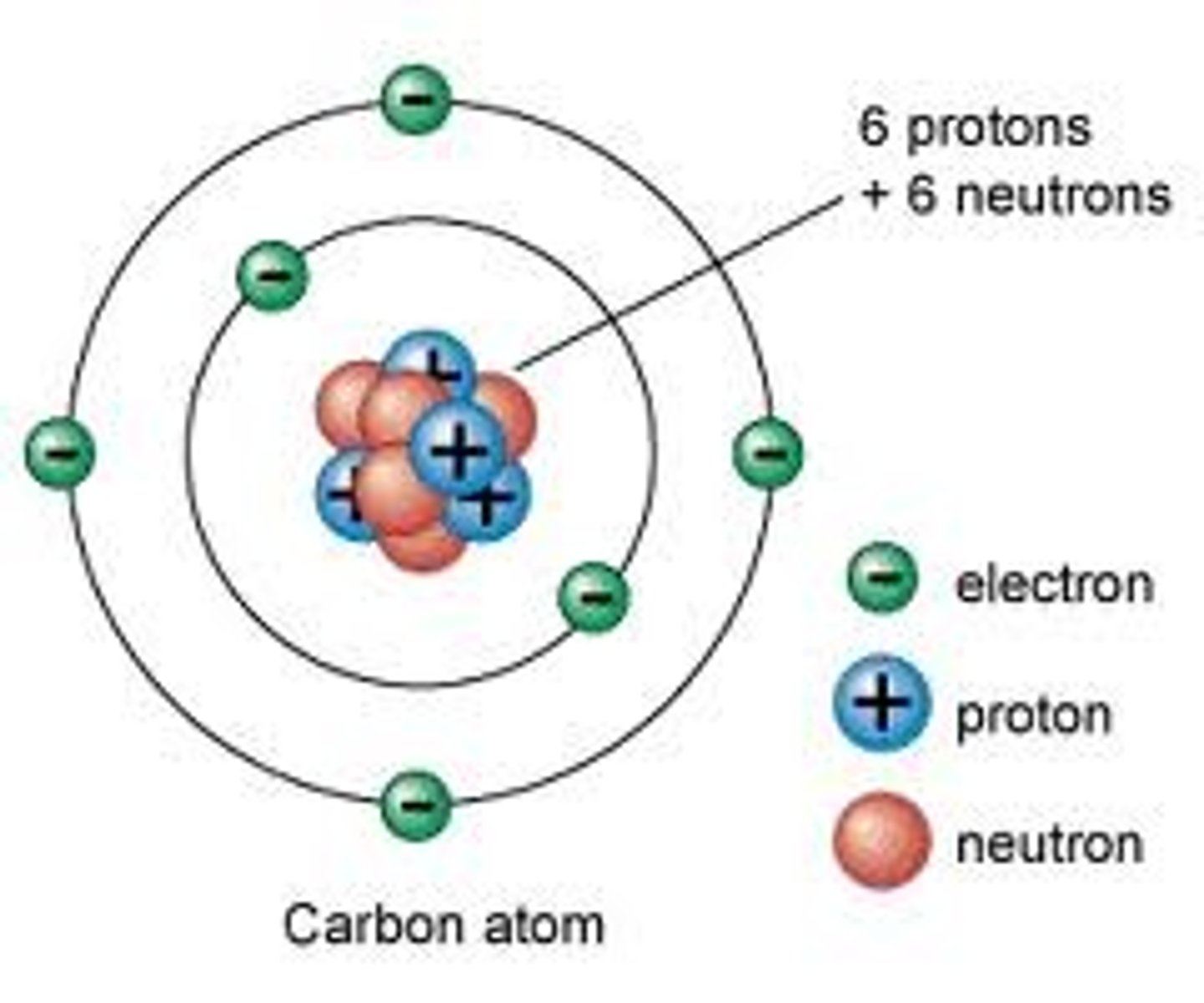
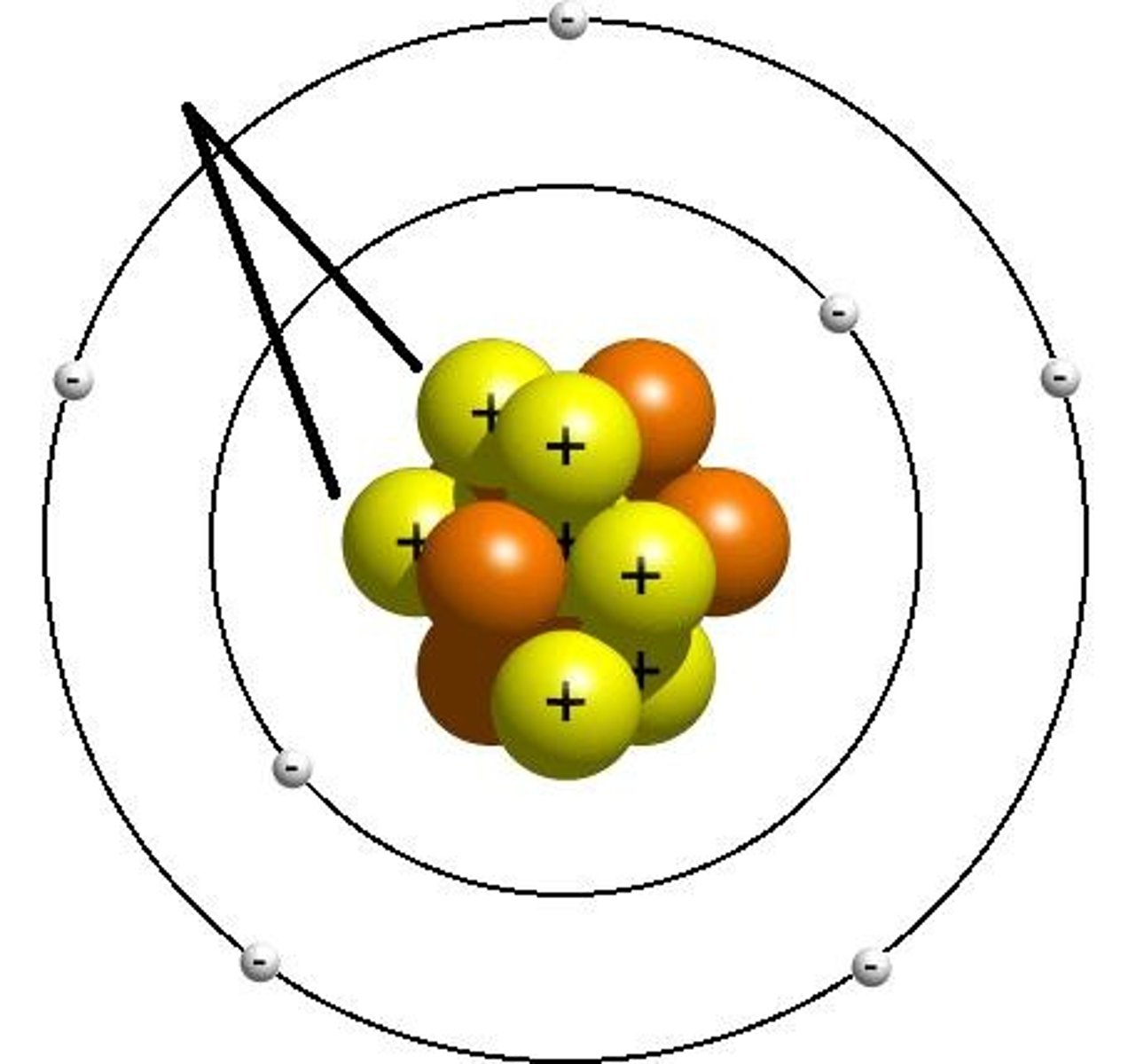
Proton
Positive charge, found in nucleus
Neutron
No charge, found in nucleus
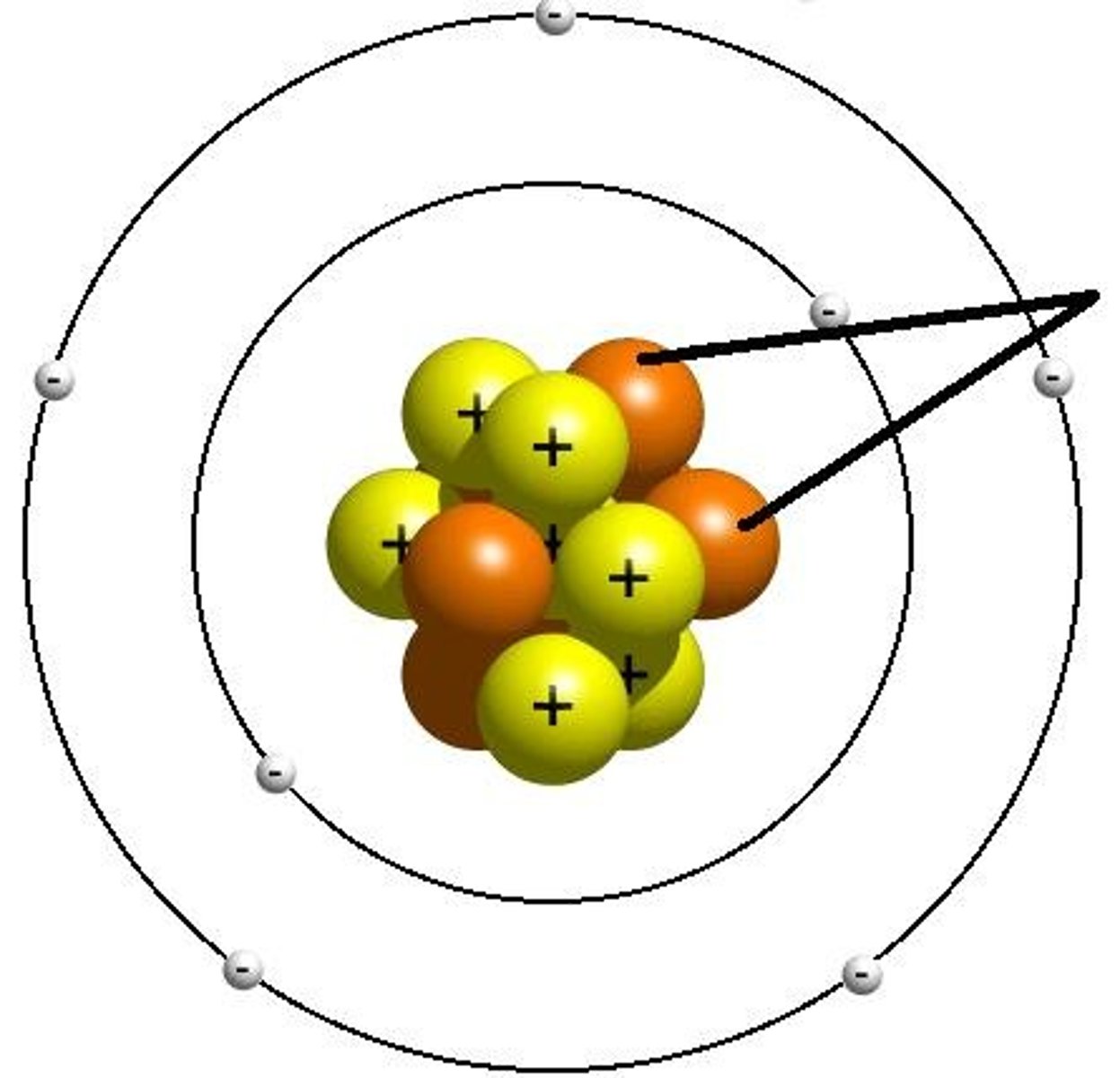
Electron
Negative charge, Orbit nucleus in an electron cloud
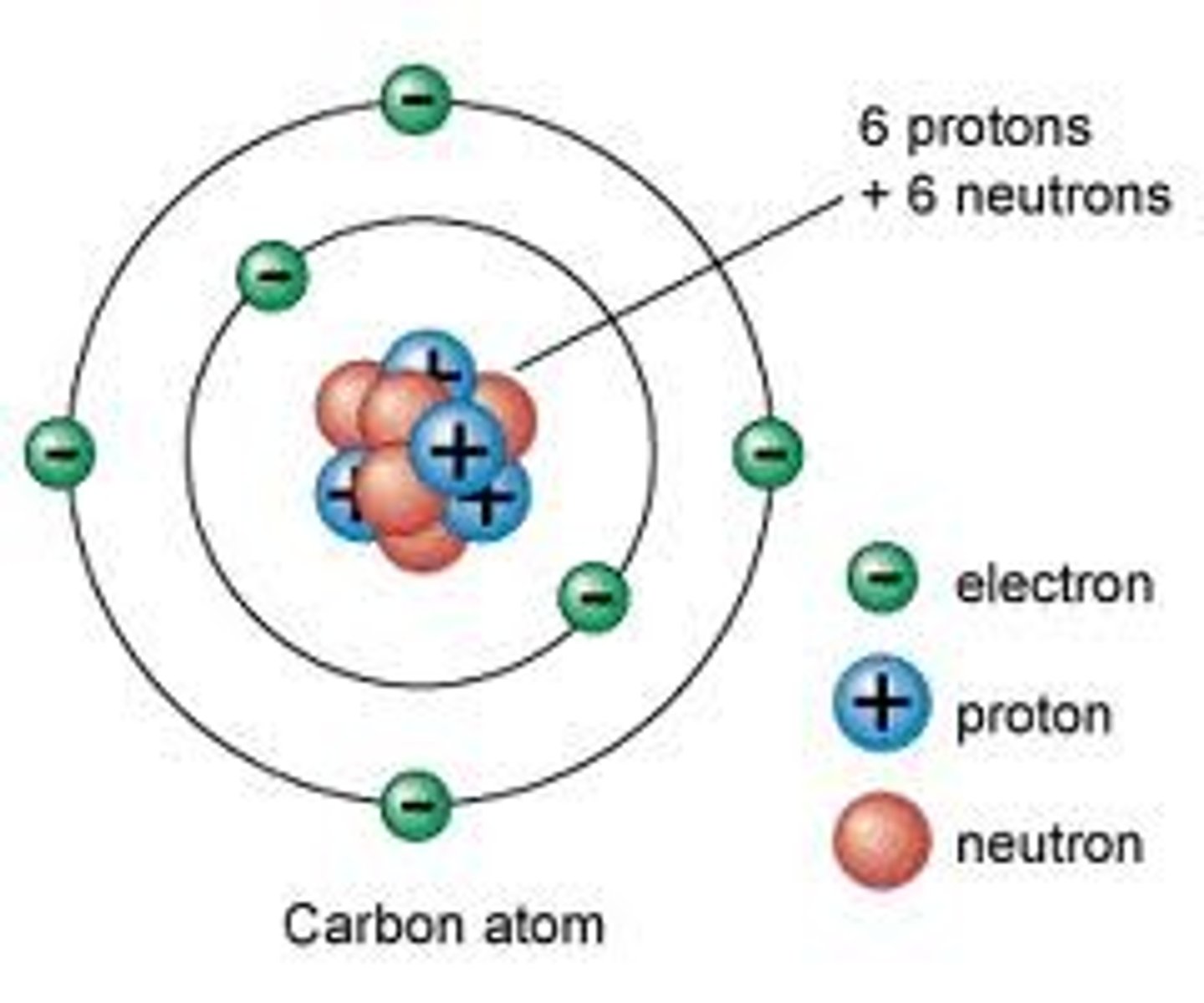
Nucleus
Almost entire mass of the atom composed of Neutrons and Protons
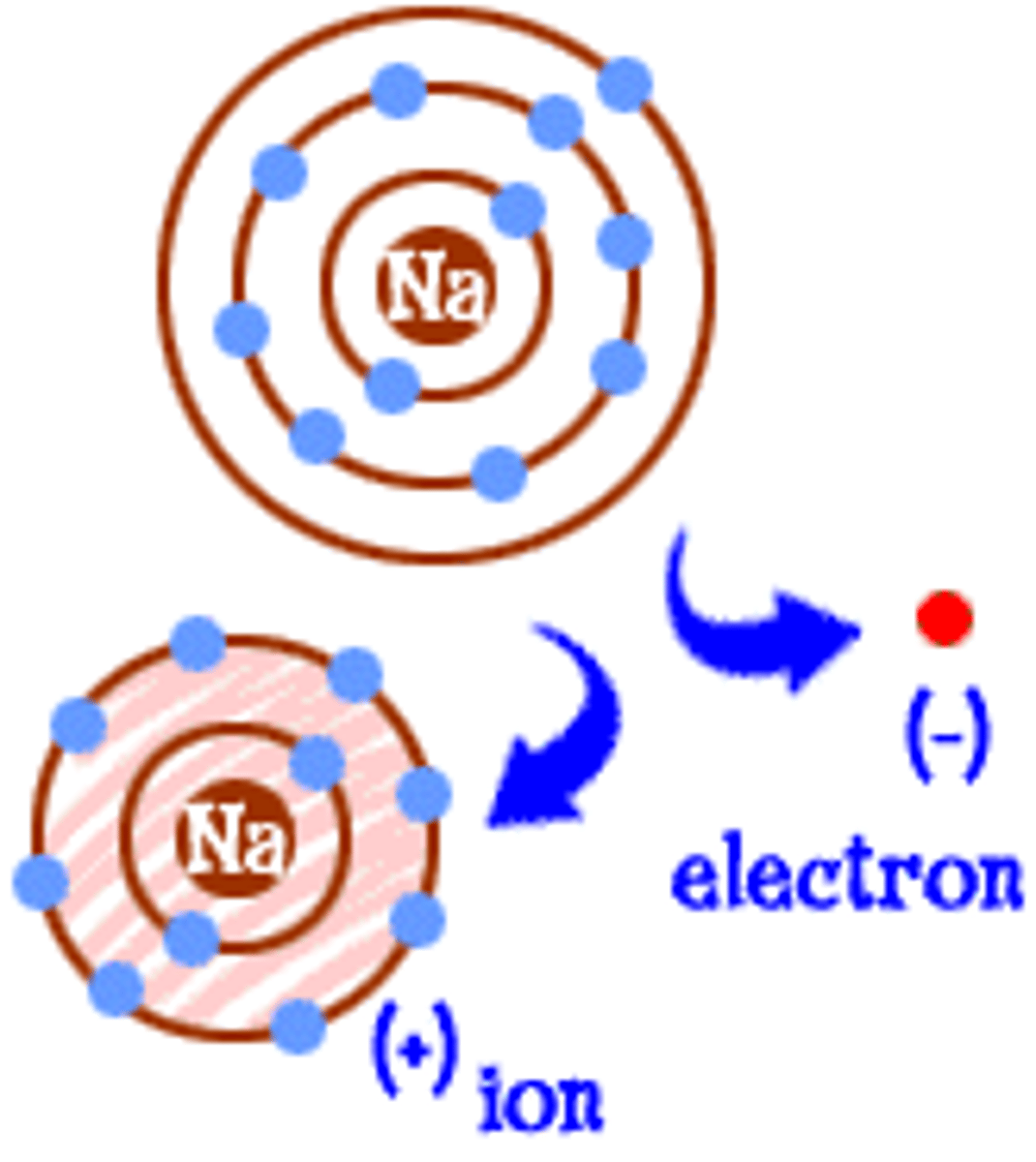
Ion
Atom with net electric charge due to loss or gain of one or more electron
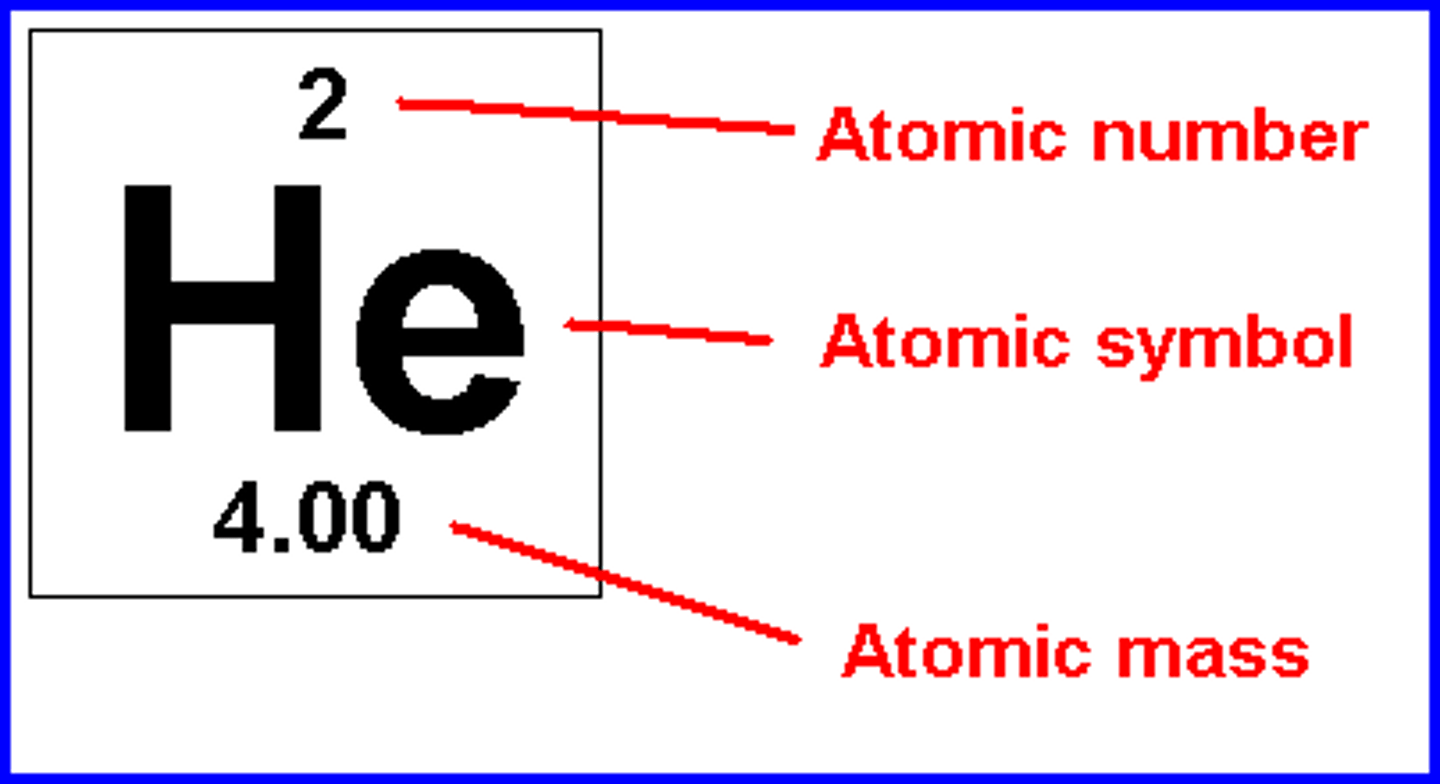
Atomic Symbol
One or two letter chemical shorthand for each element
Isotope
Structural variations of atoms, differ in number of neutrons they contain
Molecule
2 or more atoms bonded together; all compounds are molecules
Mixture
Two or more components physically intermixed

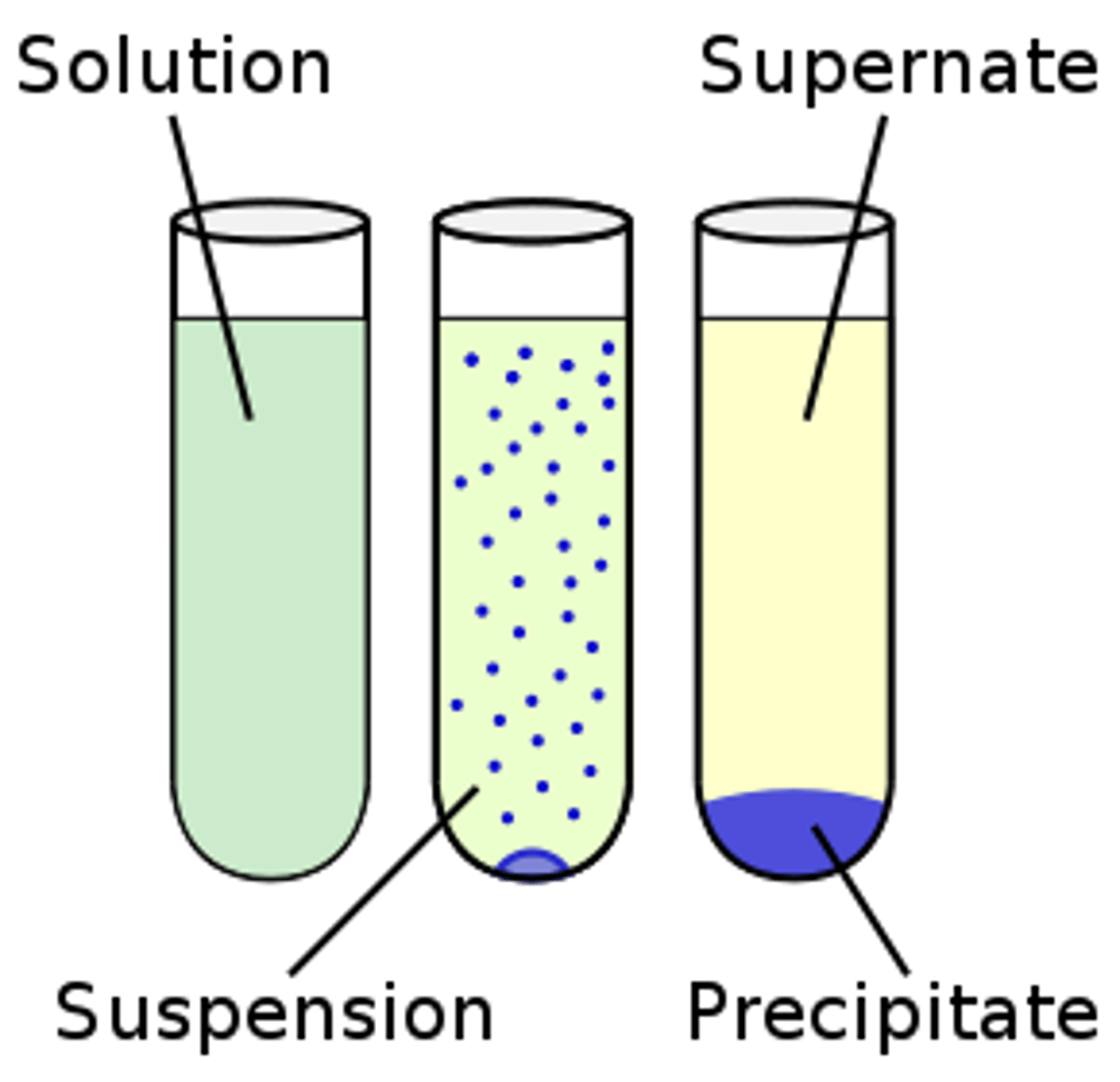
Solution
Homogeneous (same) Mixtures
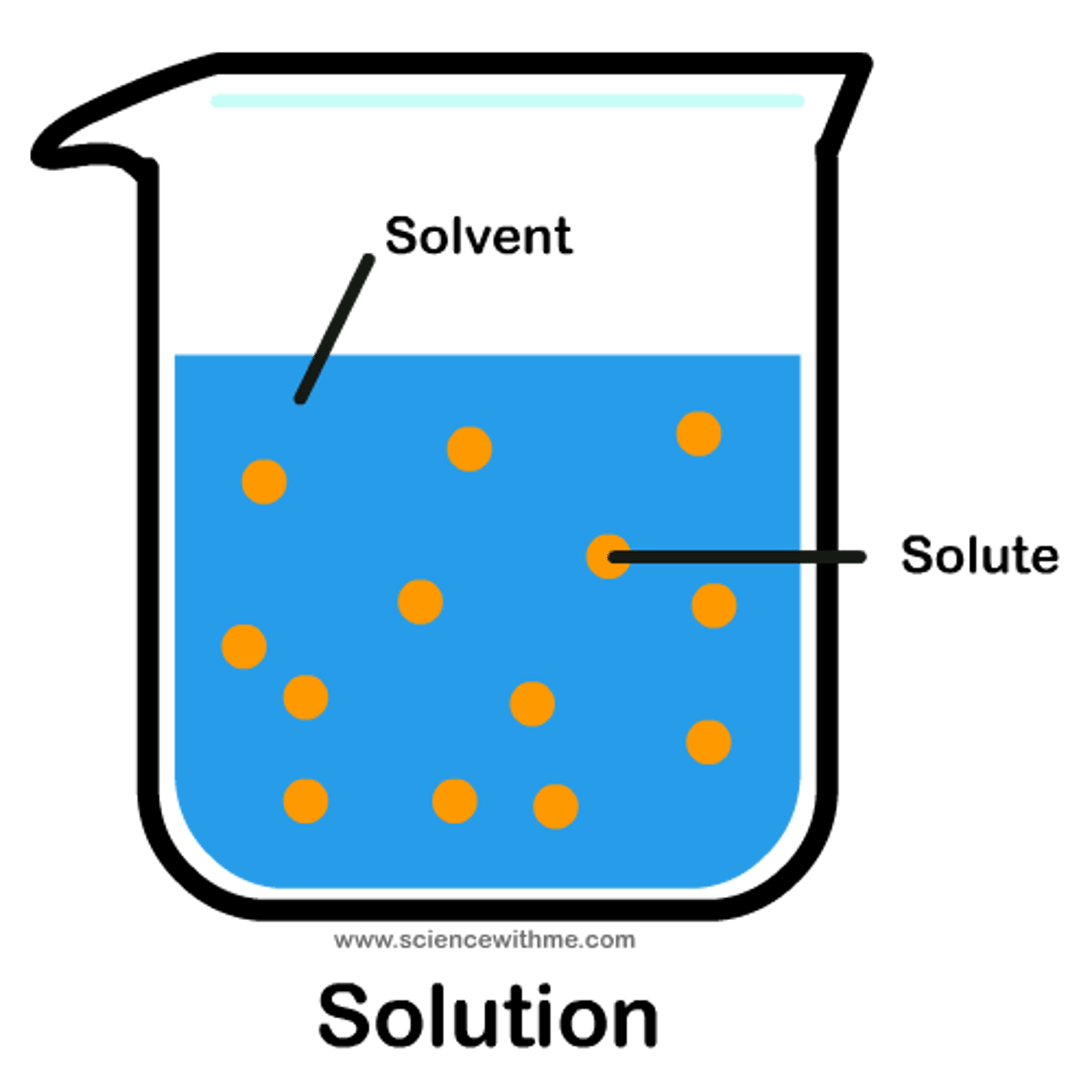
Solvent
The dissolver
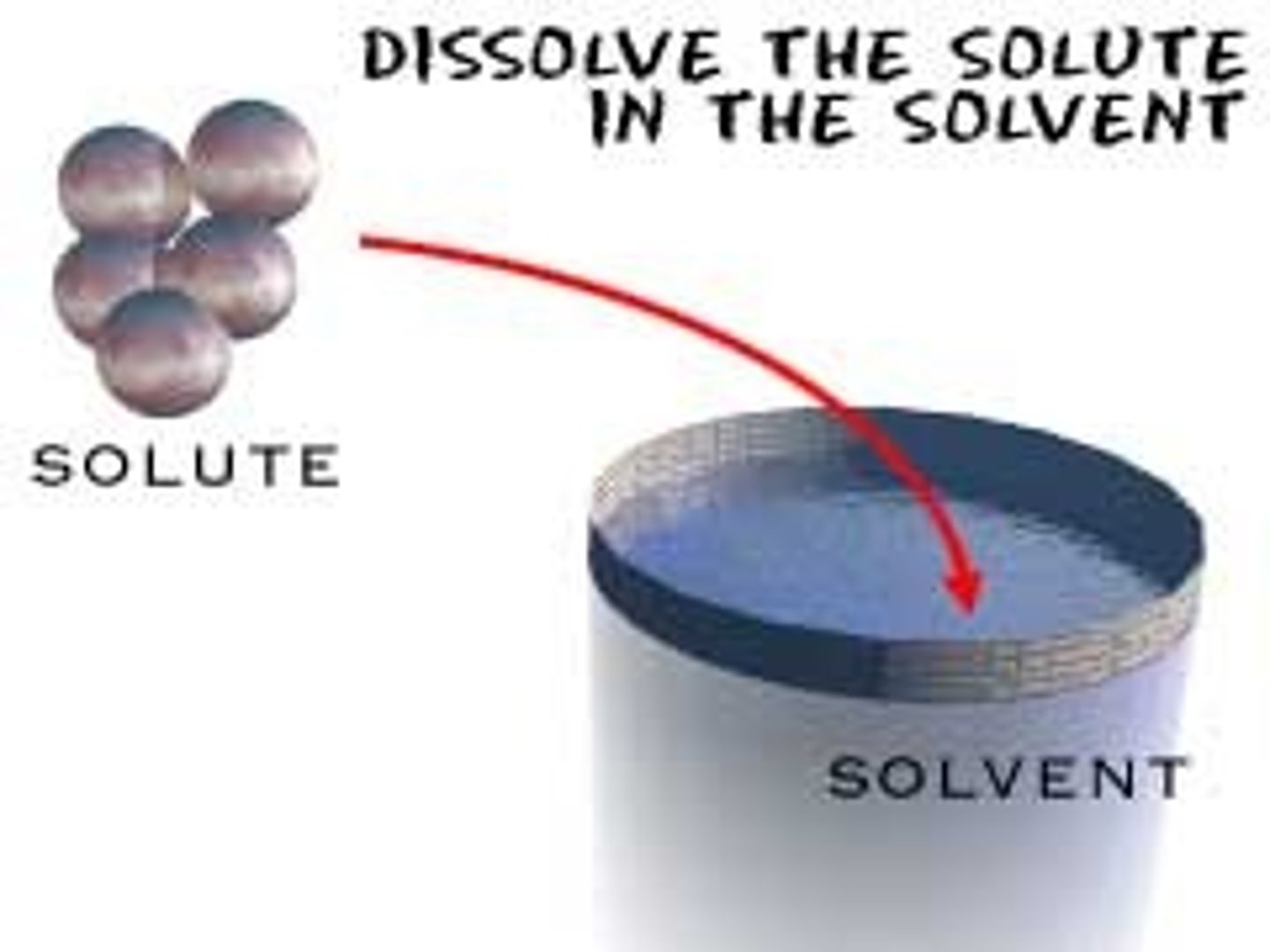
Solute
What's dissolved

Suspension
Heterogenous mixtures; large, visible solutes settle out
e.g. blood
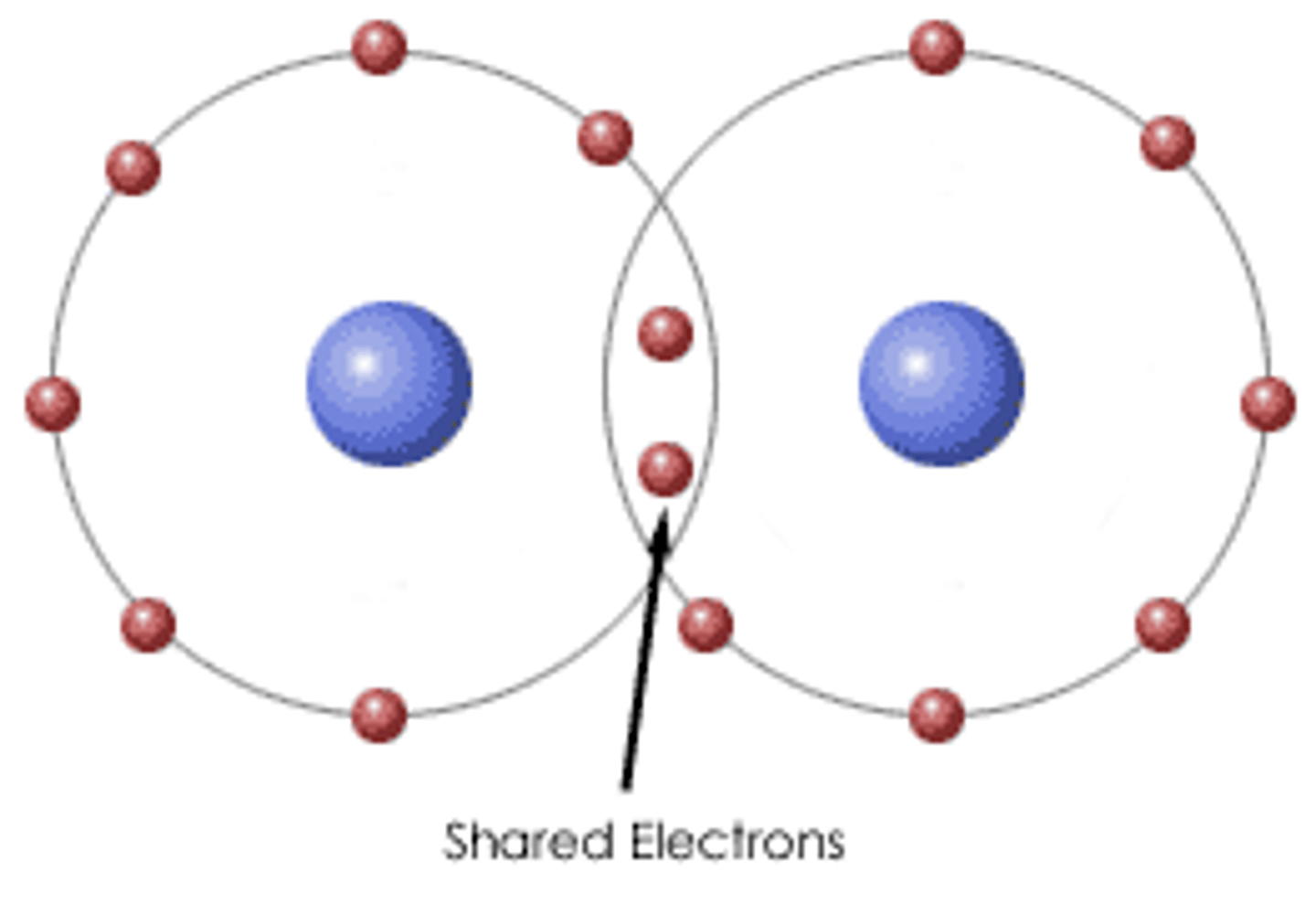
Chemical Bond
Energy relationships between electrons of atoms; electrons in valence shells
-has most potential energy
-chemically reactive electrons
Octet rule
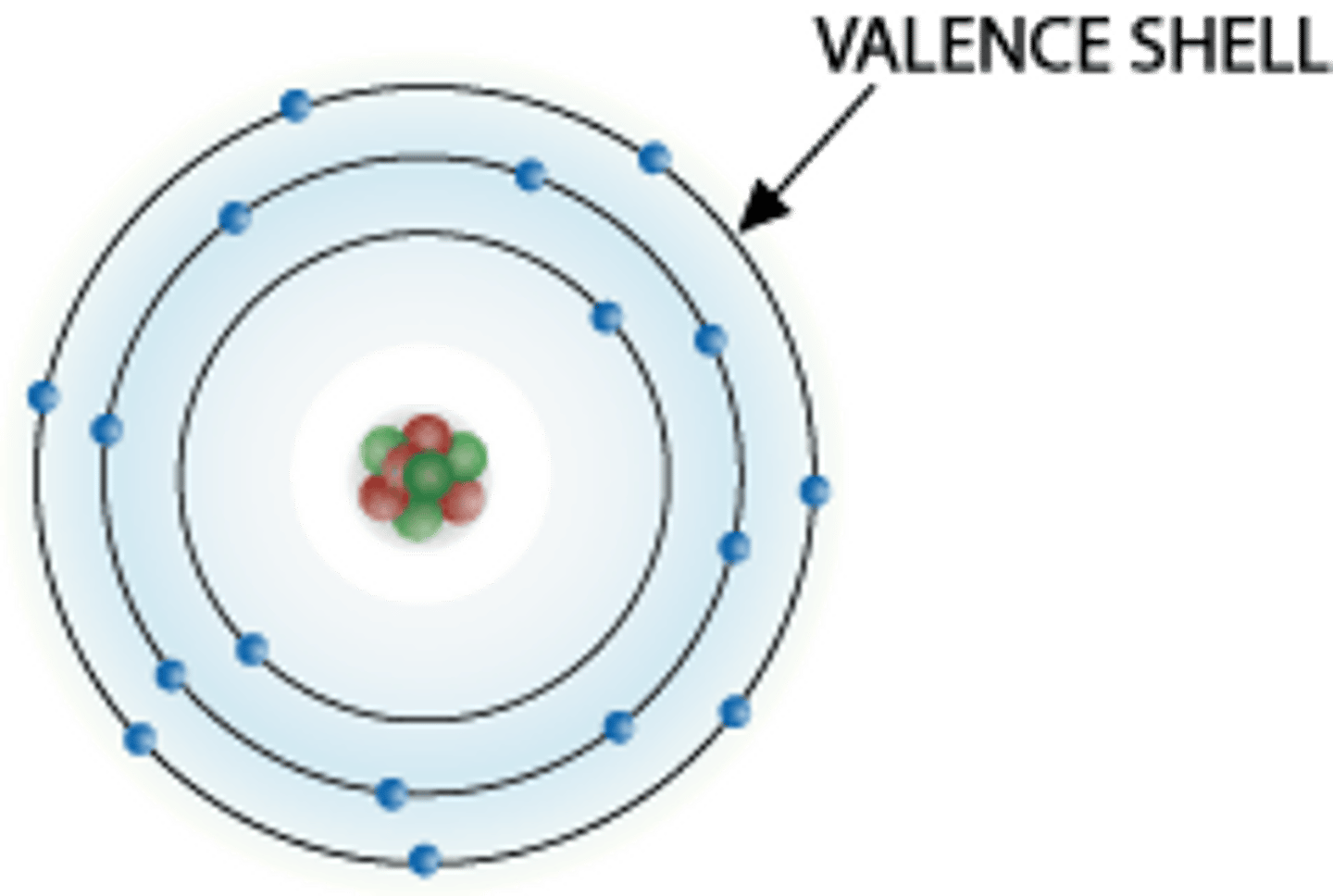
Valence Shell
Outermost electron shell
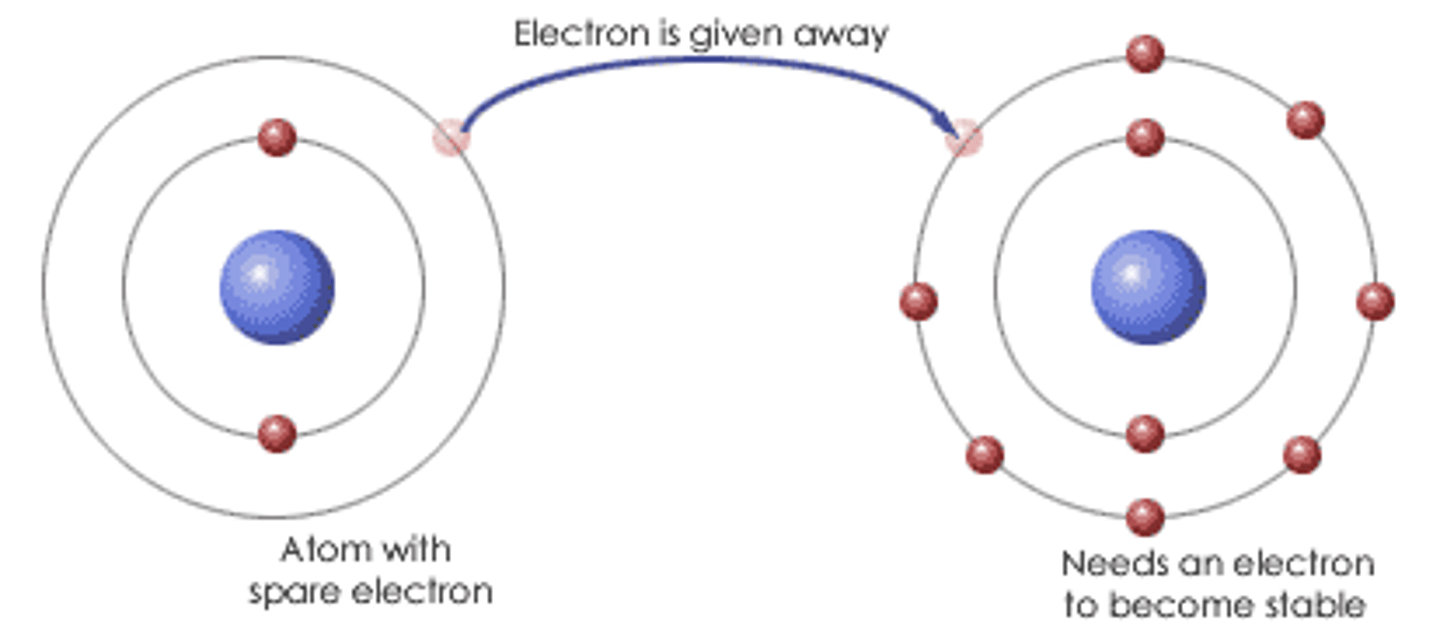
Ionic Bond
Transfer of valence shell electrons from one atom to another forms ions
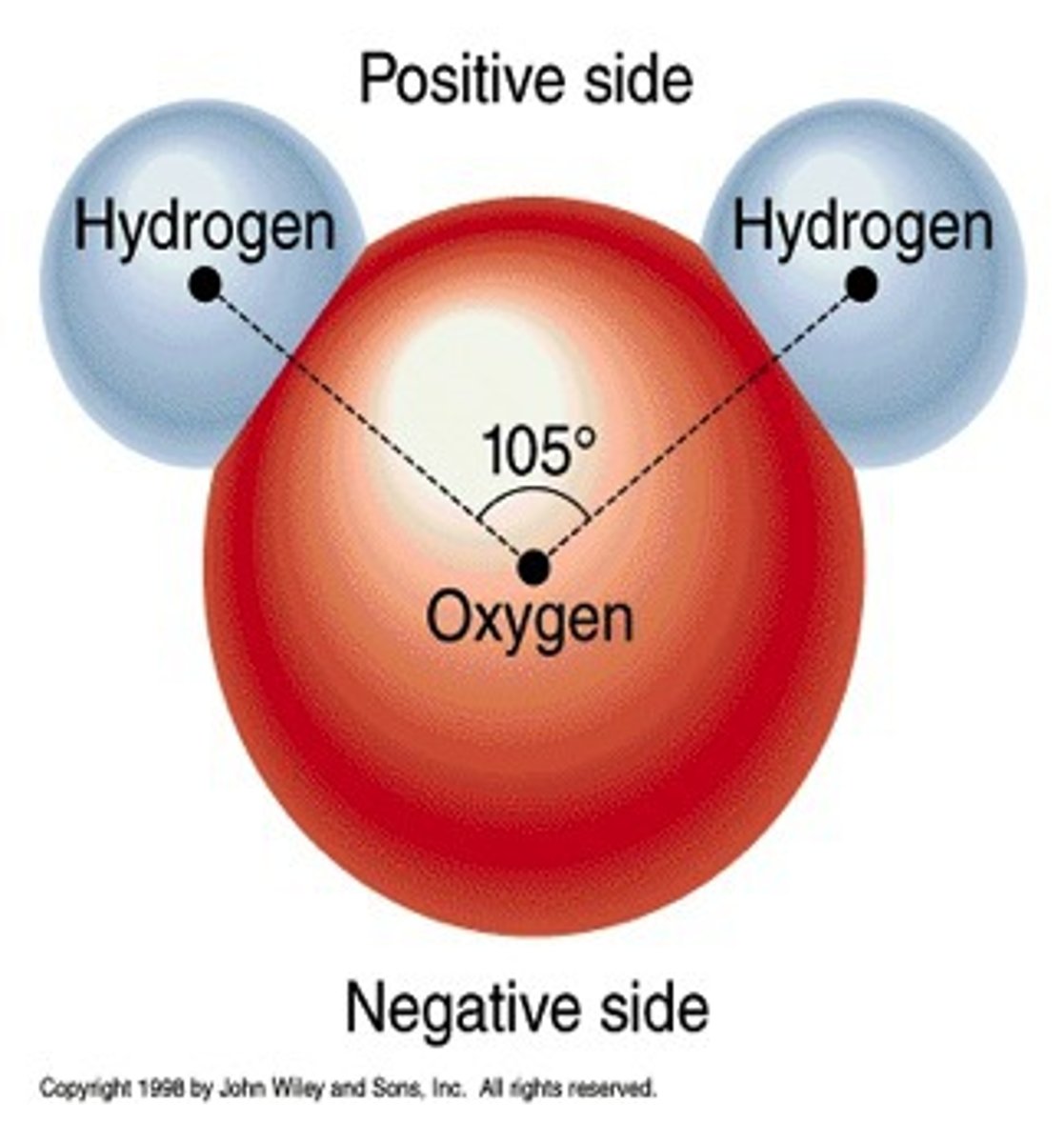
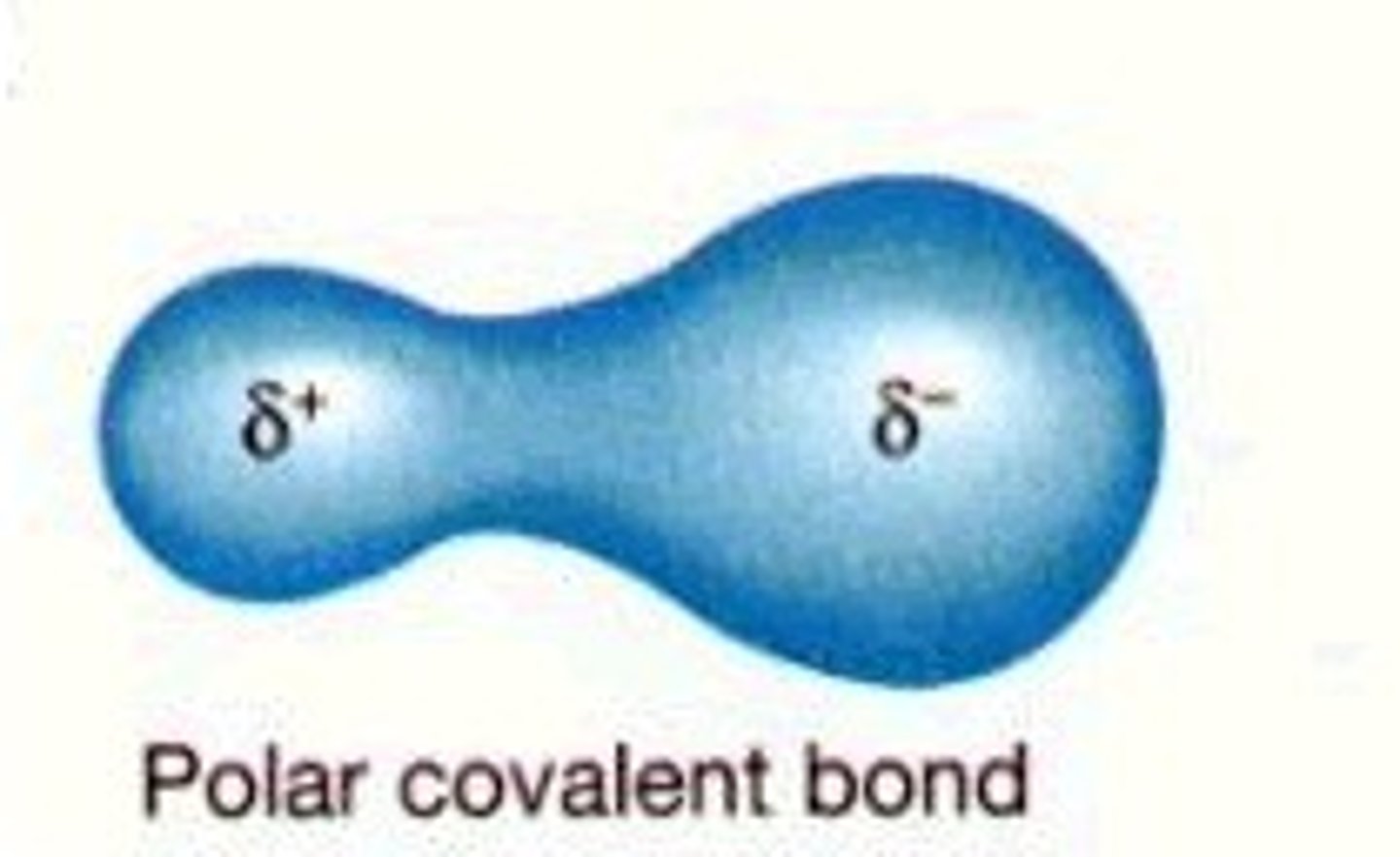
Polar Covalent Bond
Unequal sharing of electrons produces polar molecules such as H2O
H-:O, C-:O, H-:N
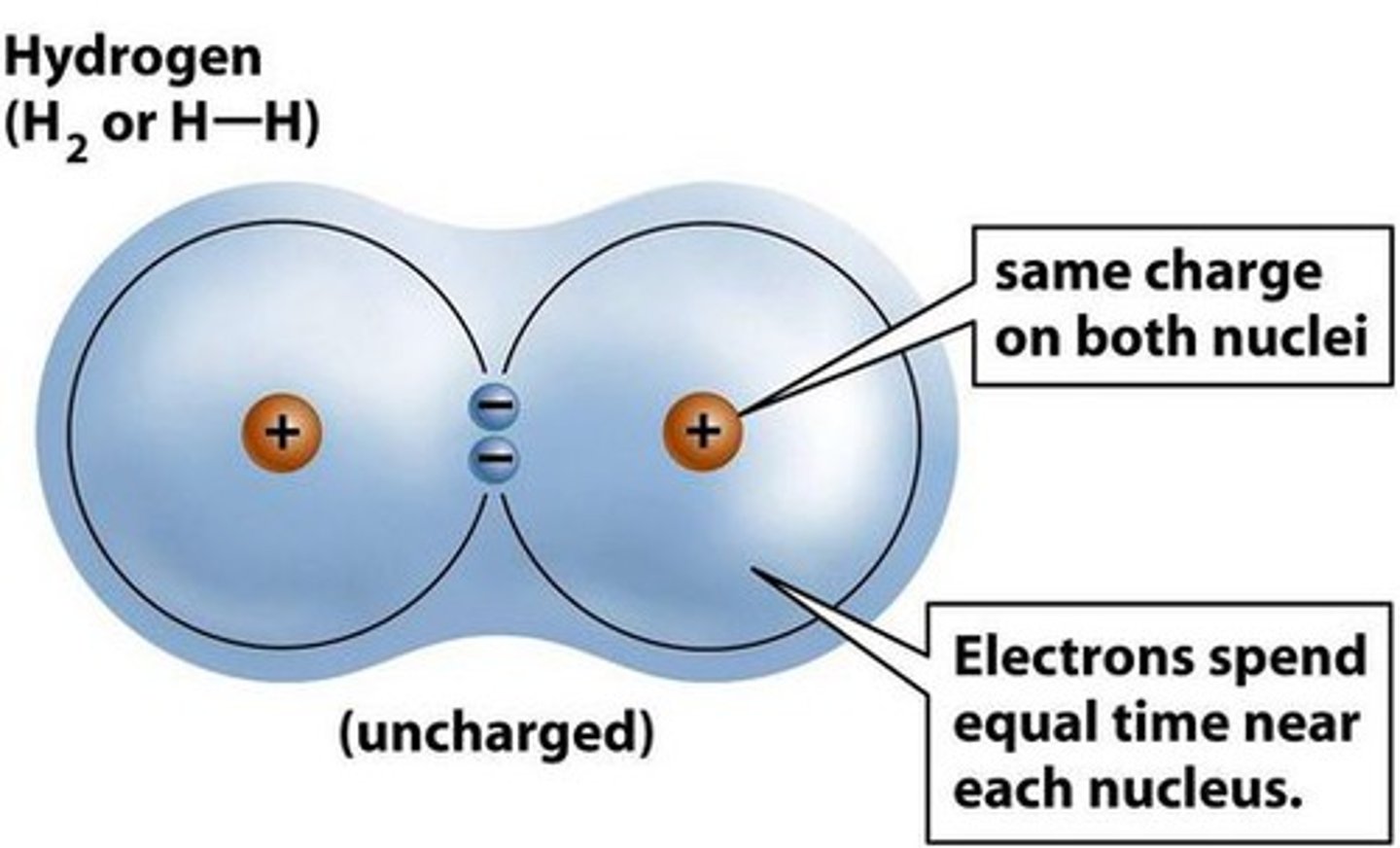
Nonpolar Covalent Bond
Electrons shared equally such as CO2
H-H, C-H, O-N
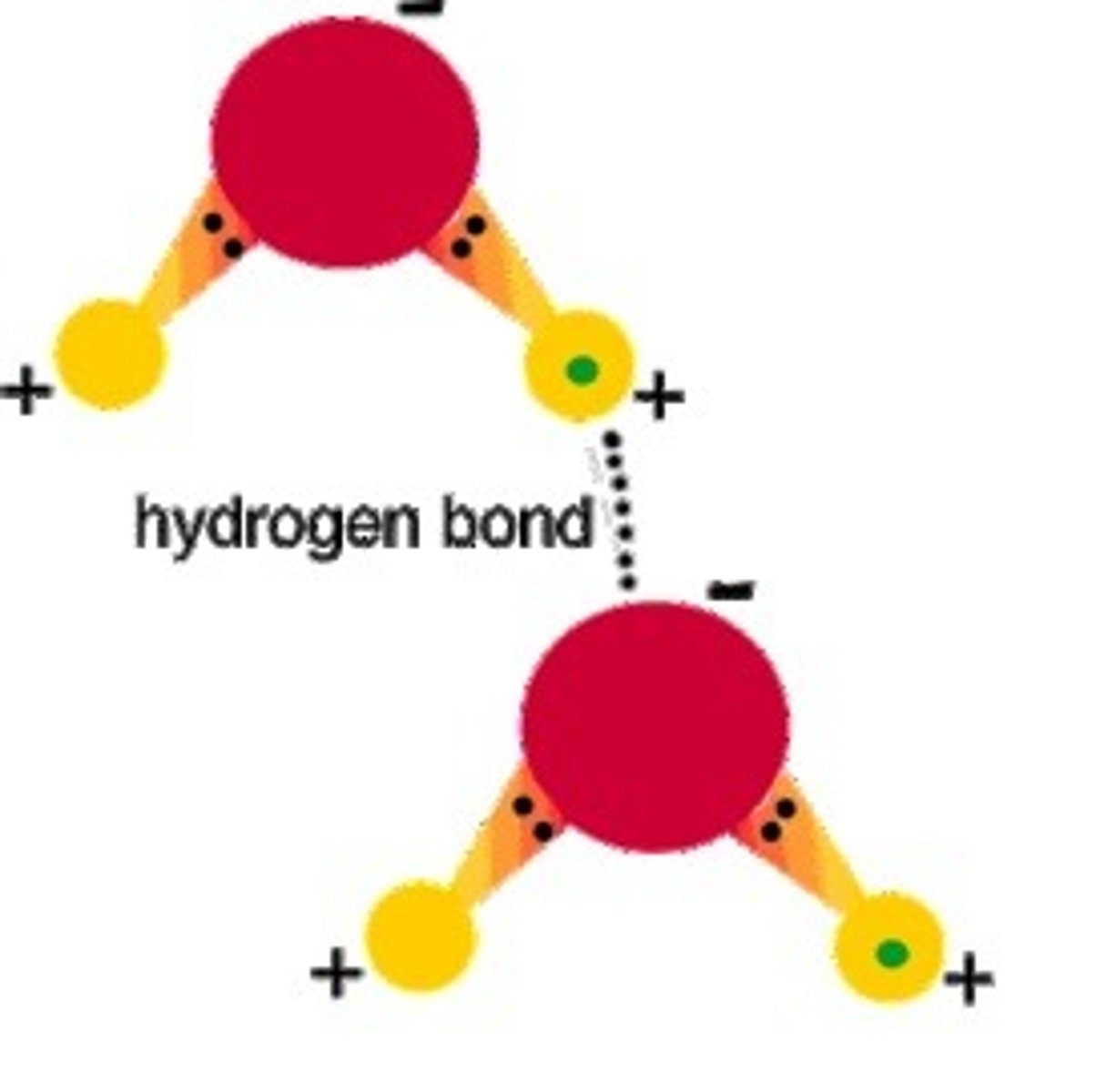
Hydrogen Bond
Attractive force between electropositive hydrogen of one molecule and an electronegative atom of another molecule
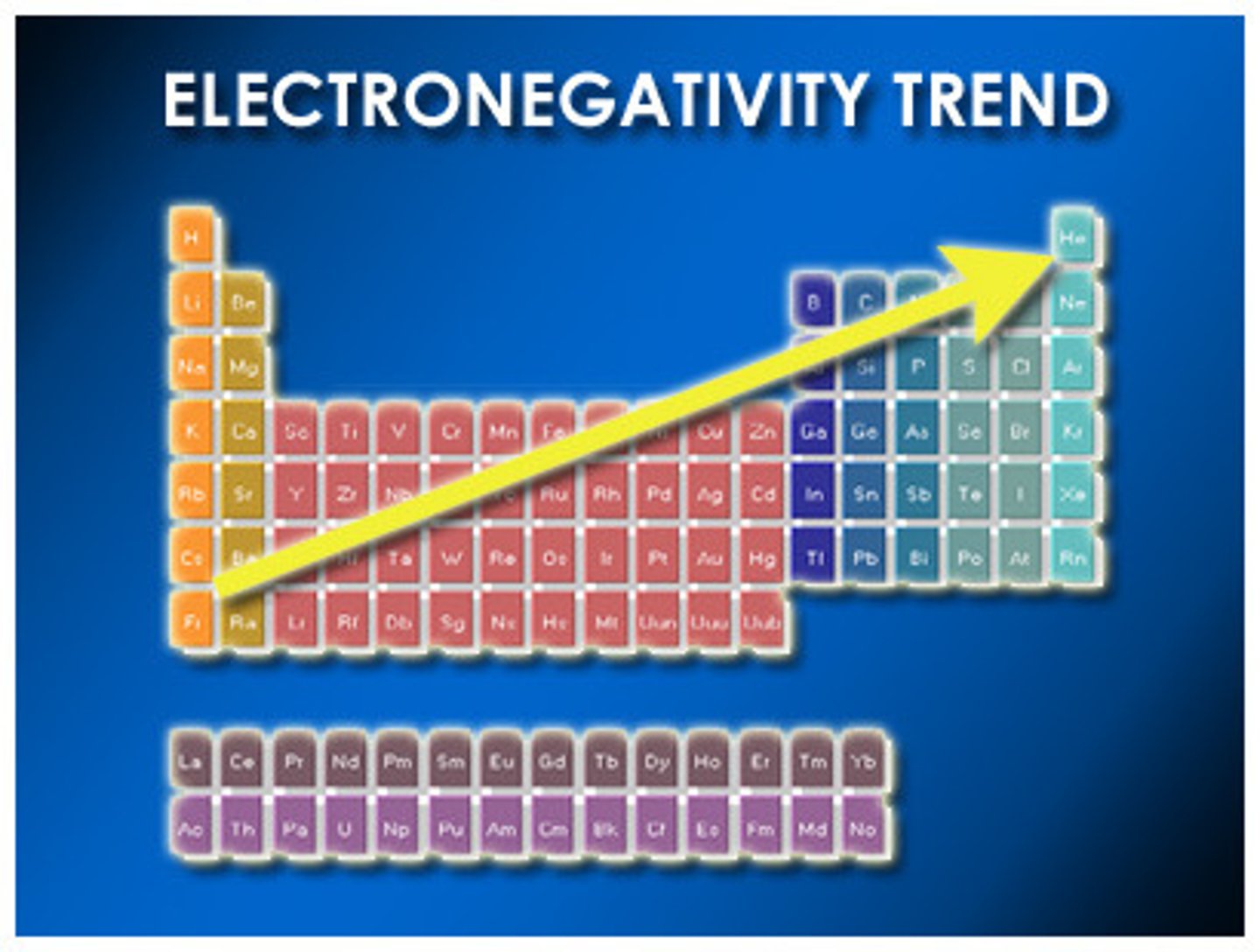
Electronegativity
Tendenancy for atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons
Molecular Formula
Subscript indicates atoms joined by bonds, prefix denotes number of unjoined atoms or molecules
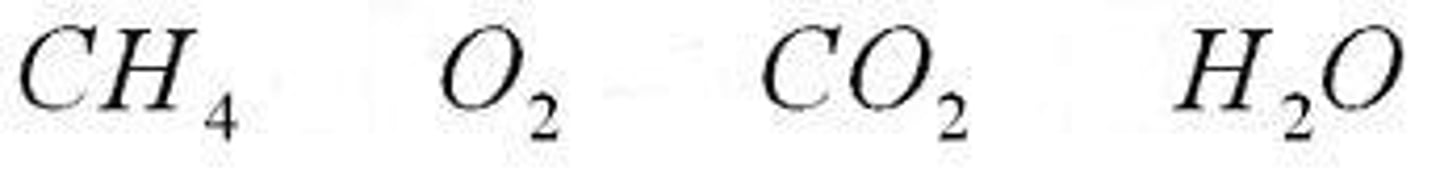
Synthesis Reaction
Combine to form larger, more complex anabolic
A+B -> AB
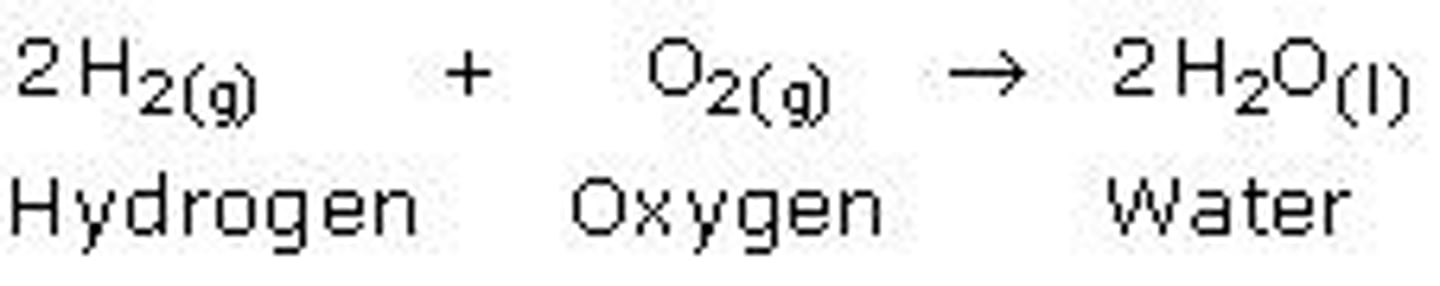
Anabolic
Synthesis
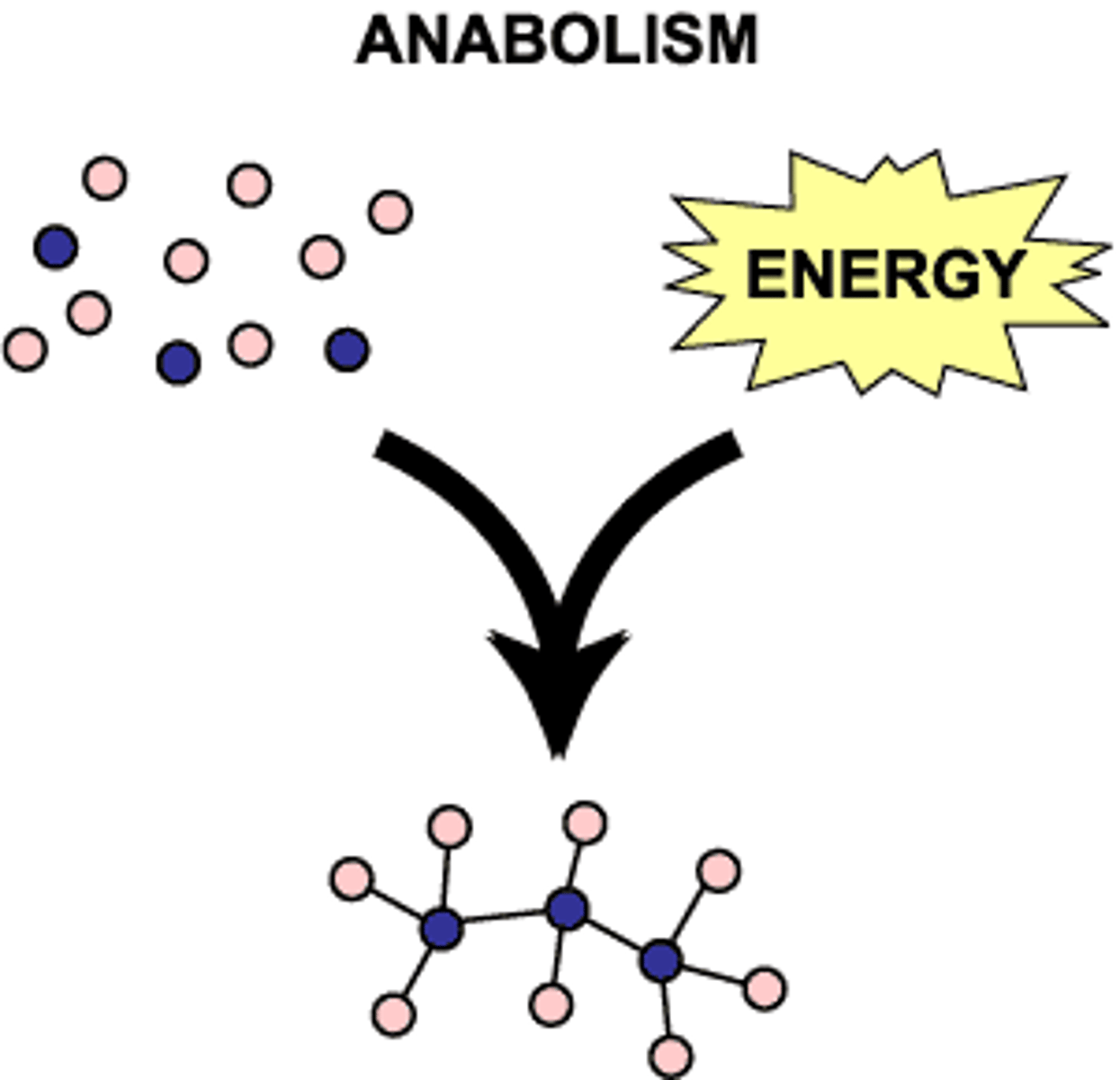
Catabolic
Decomposition
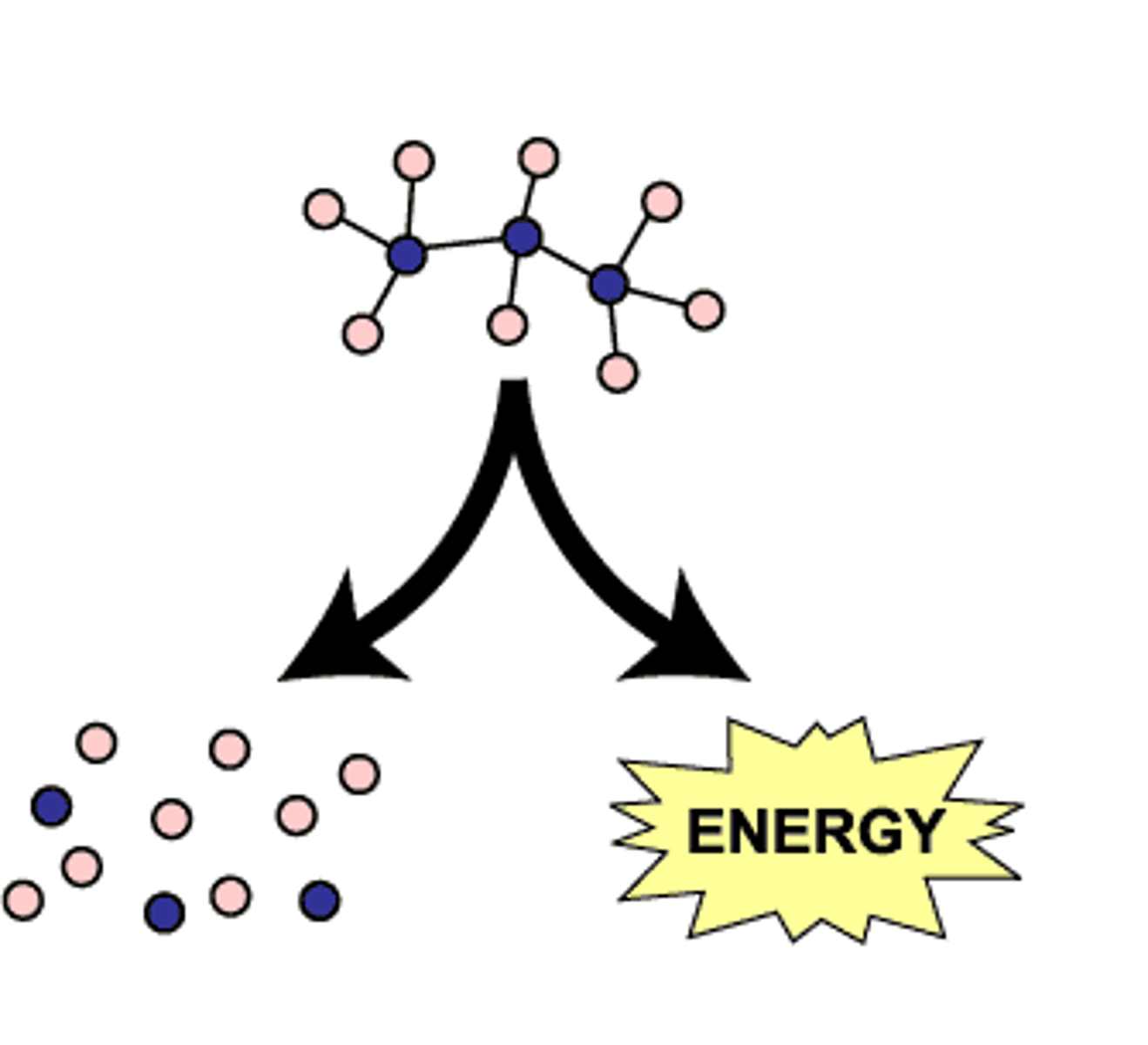
Decomposition Reaction
Molecule is broken down into smaller molecules or its constituent atoms
AB -> A+B

Exchange Reaction
Displacement reactions; synthesis and decomposition; bonds made and broke
AB+C -> AC+B
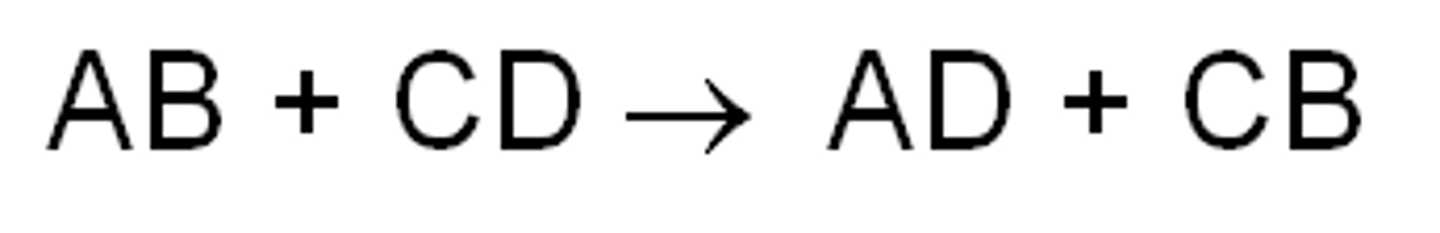
Rate of Chemical Reaction
Affected by temperature, concentration of reactant, particle size
Water Properties
High heat capacity, high heat of vaporization, polar solvent properties, reactivity, cushioning
Electrolytes
Ions
Acids
Proton donors, release H+
0-6 on pH scale
Base
Remove protons, take up H+
8-14 on pH scale
Buffer
Acidity reflects only free H+
Help maintain pH stability
pH
Rates the acidity and basicity of things
Inorganic
Do not contain carbon
Organic
Contain carbon
Monomer
Building blocks
Polymer
Chains of similar units called monomers
Carbohydrate
Sugars and Starches; Polymers; Major source of cellular fule
Monosaccharide
One sugar
Disaccharide
Two sugars
Polysaccharide
Many sugars
Lipid
Insoluble in water
Triglycerides
Neutral fats; energy storage; composed of three fatty acids bonded to glycerol molecule
Phospholipids
Modified triglycerides
Glycerol + two fatty acids and A phosphorus (P)- containing group
Steroids
Interlocking four ring structure
e.g. cholesterol, vitamin D, steroid hormones, and bile salts
Saturated Fatty Acid
Single covalent bonds between C atoms; solid animal fats e.g. butter
Unsaturated Fatty Acid
One or more double bonds between C atoms; Plant oils e.g. olive oil
Cholesterol
Important steroid
Protein
Polymers; amino acids are the monomers in the proteins
Amino Acid
Joined by peptide bonds, contain amine group and acid group, can act as either acid or base
Peptide Bond
Covalent bonds
Protein Structure
Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, Quaternary
Primary
Order of amino acids
Secondary
Repetitivie shape; a-helix and b-sheet
Tertiary
Secondary structures combined into 3D; protein
Quaternary
Two or more tertiary polypeptide chains
Denaturation
Globular proteins unfold and lose functional, 3-D shape
Enzyme
Globular proteins that act as biological catalysts
Substrate
Substance or layer that underlies something
Nucleic Acids
DNA and RNA; Polymers; composed of nitrogen base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group
Nucleotides
Monomer
DNA
Deoxyribose Acid, Double Helix, contain Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, and Thymine
RNA
Ribonucleic Acid, single stranded molecule, contains Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Uracil
Parts of Nucleotides
1. Five carbon ribose sugar
2. Phosphate molecule
3. One of four nitrogenous bases
Formula for Chemical Bonds
N=O>C=H
= Polar, > Non Polar