Chapter 11 Atkins
1/334
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
335 Terms
What are arrhenius acids and bases?
An acid is a substance that produces H+ (or H3O+) in water, and a base is a substance that produces OH− in water.
Who proposed the new definitions in 1923, and what are those definitions verbatim?
The Danish chemist Johannes Brønsted proposed:
1. An acid is a proton donor.
2. A base is a proton acceptor.
What does the term "proton" refer to in Brønsted-Lowry definitions?
It refers to the hydrogen ion, H+.
What is an "acidic hydrogen atom"?
A hydrogen atom that can be transferred as its nucleus, a proton, to another species acting as a base.
What is the formal name of the theory proposed by Brønsted and Lowry?
The Brønsted-Lowry theory of acids and bases.
Under what specific condition can a substance act as an acid?
Only if a base is present to accept its acidic protons.
How is a proton transferred from an acid to a base?
A proton is transferred to the base through direct contact, rather than being simply released.
What is a "proton transfer reaction"?
A reaction in which a proton is transferred from one species to another.
What term is used to describe an acid molecule, like HCl, after it loses its proton?
We say the molecule becomes deprotonated.
Why is HCl classified as a strong acid?
Because at equilibrium virtually all the HCl molecules have donated their protons to water; the proton transfer reaction essentially goes to completion.
What is the H3O+ ion called?
The hydronium ion.
What is a better representation of the hydronium ion in solution than H3O+?
There is evidence that a better representation is H9O4+ (or even larger clusters of water molecules attached to a proton).
Why is H3O+ a better representation than H+(aq)?
Because H+ does not exist by itself in water and H3O+ indicates that a Brønsted base (H2O) has accepted a proton.
Why is hydrogen cyanide (HCN) classified as a weak acid in water?
Because only a small fraction of the HCN molecules donate their protons.
How should we think of the dynamic equilibrium of HCN in water?
We should think of protons as ceaselessly exchanging between HCN and H2O molecules, with a constant but low concentration of CN− and H3O+ ions.
How do we represent the proton transfer of a strong acid like HCl compared to a weak acid?
A strong acid reaction is represented just by its forward reaction with a single arrow because the equilibrium lies so strongly in favor of products.
How is the Brønsted definition more general than the Arrhenius definition?
It includes the possibility that an ion is an acid (an option not allowed by the Arrhenius definition).
Give an example of an ion that can act as a Brønsted acid.
A hydrogen carbonate ion, HCO3−, which can donate a proton to an H2O molecule.
Under what condition does the deprotonation of HCO3− proceed to completion?
The reaction proceeds to completion if the CO32− ions are removed by precipitation with Ca2+ ions to form a precipitate of calcium carbonate.
In the absence of ions that remove products, which way does the HCO3− equilibrium lie?
The equilibrium remains strongly in favor of the reactants.
Why is it difficult to remove a proton from a hydrogen carbonate ion (HCO3−)?
Because a positively charged proton can be removed from the negatively charged HCO3− ion only with difficulty(due to electrostatic attraction).
How does the charge of an ion affect its strength as a Brønsted acid?
A negatively charged ion (like HCO3−) is generally a weaker acid than a neutral molecule (like H2CO3) because it is harder to pull a positive proton away from a negative species.
Why does the deprotonation of HCO3− normally favor the reactants?
Because a positively charged proton can be removed from a negatively charged ion (HCO3−) only with difficultydue to electrostatic attraction.
hat happens to the equilibrium when Ca2+ ions are added to a solution of HCO3−?
The Ca2+ ions react with the CO32− product to form a solid precipitate of calcium carbonate (CaCO3).
How does the formation of a precipitate affect the concentration of CO32− in the solution?
It effectively "removes" the CO32− ions from the solution by turning them into a solid.
According to Le Chatelier’s principle, how does the system respond to the removal of CO32−?
The reaction is forced to move forward toward completion to try and replace the missing product.
What is the "driving force" that overcomes the electrostatic difficulty of removing a proton from HCO3− in this scenario?
The precipitation of the product (CO32−) as CaCO3(s), which shifts the equilibrium entirely to the right.
How is a strong acid defined in Brønsted-Lowry theory?
A strong acid is fully deprotonated in solution.
How is a weak acid defined in Brønsted-Lowry theory?
A weak acid is only partly deprotonated in solution.
What physical feature must a Brønsted base possess?
A Brønsted base possesses a lone pair of electrons to which a proton can bond.
Why is the oxide ion (O2−) considered a strong base in water?
Because every oxide ion present accepts a proton from water; it is a species that is fully protonated.
What is the verbatim reaction for the oxide ion in water?
O2−(aq)+H2O(l)→2OH−(aq).
Why is ammonia (NH3) a weak base compared to the oxide ion?
Because the NH3 molecule is electrically neutral, it has much less proton-pulling power than the oxide ion
How is a strong base summarized in Brønsted-Lowry theory?
A strong base is completely protonated in solution.
How is a weak base summarized in Brønsted-Lowry theory?
A weak base is only partially protonated in solution.
What is the "good practice" note regarding alkali metal oxides and hydroxides?
These compounds are not Brønsted bases themselves; the oxide and hydroxide ions they contain are the bases (the cations are spectator ions).
What is a conjugate base?
The species left when the acid donates a proton.
What is a conjugate acid?
The species formed when the base accepts a proton.
In the HCN system, what is the conjugate base of the acid HCN?
The CN− ion is the conjugate base of the acid HCN.
In the CN− system, what is the conjugate acid of the base CN−?
HCN is the conjugate acid of the base CN−.
What is the general symbolic relationship for forming a conjugate base?
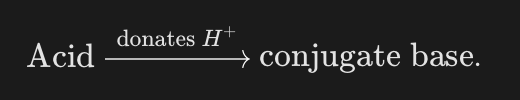
What is the general symbolic relationship for forming a conjugate acid?
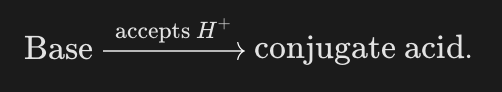
Do the Brønsted definitions of acids and bases apply to nonaqueous solvents and gas-phase reactions?
Yes, the Brønsted definitions also apply to species in nonaqueous solvents and even to gas-phase reactions where there is no solvent.
What are the verbatim definitions of acids and bases according to G. N. Lewis?
A Lewis acid is an electron pair acceptor.
A Lewis base is an electron pair donor.
What happens when a Lewis base donates an electron pair to a Lewis acid?
The two species share the pair and become joined by a coordinate covalent bond.
Why is a proton (H+) considered a Lewis acid?
Because it is an electron pair acceptor that can attach to ("accept") a lone pair of electrons on a Lewis base.
How does the Brønsted acid definition relate to the Lewis theory?
A Brønsted acid is a supplier of one particular Lewis acid, a proton.
Why is the Lewis theory considered more general than the Brønsted-Lowry theory?
Because species like metal atoms and ions can act as Lewis acids (e.g., Ni in Ni(CO)4), but they are not Brønsted acids.
What is a Brønsted base in the context of Lewis theory?
A Brønsted base is a special kind of Lewis base, one that can use a lone pair of electrons to form a coordinate covalent bond to a proton.
How does CO2 act as a Lewis acid when reacting with water?
The C atom of CO2 accepts an electron pair from the O atom of a water molecule (the Lewis base).
What is the product when the Lewis acid CO2 reacts with the Lewis base H2O?
The product is an H2CO3 molecule, which is a Brønsted acid.
Arrhenius aid/base
Acid - Compound that supplies H3O+
Base - Compound that supplies OH−
Bronsted lowry acid/base
Acid - The species that supplies the proton
Base - The species that accepts a proton
Lewis Acid/Base
Acid - The proton itself (or any electron pair acceptor)
Base - The electron pair donor
What is the definition of an acidic oxide?
An acidic oxide is an oxide that reacts with water to form a solution of a Brønsted acid.
What type of compounds are acidic oxides, and what is their role in Lewis theory?
Acidic oxides are molecular compounds, such as CO2, which are Lewis acids that react with bases.
What is the "white crust" often seen on pellets of sodium hydroxide?
A mixture of sodium carbonate formed by reaction with CO2 and of sodium hydrogen carbonate formed in a similar reaction.
What is the definition of a basic oxide?
A basic oxide is an oxide that reacts with water to form a solution of hydroxide ions.
What type of compounds are basic oxides and what do they react with to give a salt and water?
Basic oxides are ionic compounds that can react with acids to give a salt and water.
In the reaction of MgO and HCl, what specific interaction occurs between the base O2− and the acid?
The base O2− accepts two protons from the hydronium ions present in the hydrochloric acid solution.
Which types of elements typically form basic oxides vs. acidic oxides?
Metals typically form basic oxides and nonmetals typically form acidic oxides.
What does the term amphoteric mean, and where do these elements lie on the periodic table?
Amphoteric means substances that react with both acids and bases; these elements lie on the diagonal frontier between the metals and nonmetals.
On what does the character (acidic, amphoteric, or basic) of d-block metal oxides depend?
It depends on their oxidation state.
What does it mean for water to be amphiprotic?
It means that a water molecule can act both as a proton donor (acid) and as a proton acceptor (base).
What is the distinction between amphoteric and amphiprotic
Amphoteric substances react with both acids and bases; amphiprotic substances specifically can both donate and accept protons.
Why is aluminum metal amphoteric but not amphiprotic?
It reacts with both acids and bases, but it has no hydrogen atoms to donate as protons.
What is the verbatim chemical equation for the proton transfer between water molecules?
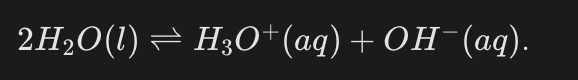
What is autoprotolysis?
A reaction in which one molecule transfers a proton to another molecule of the same kind.
What is the expression for the autoprotolysis constant of water (Kw) using activities?
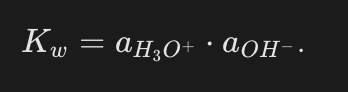
Why can the activity of water be taken as 1 in the Kw expression?
Because in dilute aqueous solutions, the solvent, water, is very nearly pure.
What is the practical molar concentration form of the Kw expression (Eq. 1b)?
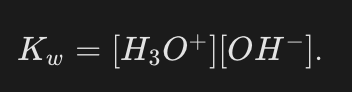
What are the experimental molar concentrations of H3O+ and OH− in pure water at 25°C?
They are equal and are known to be 1.0×10−7 mol⋅L−1.
What is the value of Kw at 25°C?
1.0×10−14.
Why is pure water such a poor conductor of electricity?
Because the concentrations of H3O+ and OH− are very low in pure water.
Based on the "Thinking point," how should Kw change with temperature?
Since the autoprotolysis reaction is endothermic, we expect Kw to increase with increasing temperature.
Is the product of [H3O+] and [OH−] always equal to Kw in any aqueous solution?
Yes; because Kw is an equilibrium constant, the product of the concentrations is always equal to Kw.
What happens to [OH−] if we increase the concentration of [H3O+] by adding acid?
The concentration of OH− ions will immediately respond by decreasing to preserve the value of Kw
What analogy is used to describe the link between [H3O+] and [OH−]?
The autoprotolysis equilibrium links the concentrations rather like a seesaw: when one goes up, the other must go down.
Why do chemists report hydronium ion concentrations in terms of pH?
To avoid the awkwardness of working with a wide range of values (from higher than 1 mol⋅L−1 to lower than 10−14 mol⋅L−1).
What is the verbatim definition of pH in terms of activity?

What is the simplified, practical formula for pH in dilute solutions?
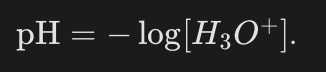
How is [H3O+] interpreted in the pH formula?
As the molar concentration of H3O+ in moles per liter with the units struck out.
What is the pH of pure water at 25°C?
pH=−log(1.0×10−7)=7.00.
Based on the "Thinking point," how does the pH of pure water change with temperature?
Since Kw increases with temperature (meaning [H3O+] increases), the pH of pure water decreases as temperature increases.
What does the negative sign in the definition of pH mean for hydronium concentration?
It means that the higher the concentration of H3O+ ions, the lower the pH.
What is the pH of a basic solution?
Greater than 7.
What is the pH of pure water?
7.
What is the pH of an acidic solution?
Less than 7.
What happens to the pH as the concentration of hydronium ions increases?
The pH decreases.
Because pH is a common logarithm, what does a change of one pH unit represent?
It means that the concentration of H3O+ ions has changed by a factor of 10.
If concentration increases by a factor of 10 from 10−5 mol⋅L−1 to 10−4 mol⋅L−1, what is the pH change?
The pH decreases from 5 to 4.
What is the typical pH range for most solutions used in chemistry?
A pH ranging from 0 to 14, but values outside this range are possible.
According to the "Thinking point," what would a negative pH signify?
It signifies that the hydronium ion concentration is higher than 1 mol⋅L−1 (since log(1)=0, any number >1 has a positive log, which becomes negative with the − sign).
How can the approximate value of the pH of an aqueous solution be determined very quickly?
By using a strip of universal indicator paper, which turns different colors at different pH values
What instrument is used to make more precise pH measurements?
A pH meter.
What are the basic components of a pH meter?
It consists of a voltmeter connected to two electrodes that dip into the solution.
The difference in electrical potential between pH meter electrodes is proportional to what?
The hydronium ion activity.
How is a concentration of H3O+ ions calculated from a pH value?
By reversing the sign of the pH and then taking its antilogarithm.
What is the verbatim formula to convert pH into H3O+ concentration?
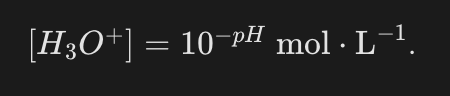
What is the general definition of the quantity pX?
pX = –log X.