electricity
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
1
New cards
AC current
changes direction and instantaneous value with time
2
New cards
EMF
the energy supplied to each coulomb of charge passing through the battery.
3
New cards
Lost volts
The potential difference across the internal resistor of a source of e.m.f.
4
New cards
Internal resistance
resistance inside the source of electrical energy.
5
New cards
terminal potential difference (t.p.d.)
Voltage that appears across the terminals of a source when the source is supplying a current to a circuit. It is the potential difference that appears in the circuit.
6
New cards
short circuit
A connection that allows current to take the path of least resistance
7
New cards
open circuit
an incomplete electrical circuit in which no current flows
8
New cards
Information from a Vtpd vs Current Graph.
Y Intercept - EMF
X Intercept - Short Circuit Current
Gradient = -r
X Intercept - Short Circuit Current
Gradient = -r
9
New cards
1 Farad
1 coulomb of charge stored per unit volt
10
New cards
Capacitance (C)
Measured in Farads (F)
11
New cards
Charge (Q)
Measured in Coulombs (C)
12
New cards
Area under a Q vs V graph.
Energy Stored in a capacitor.
13
New cards
Voltage vs Time for Charging Capacitor
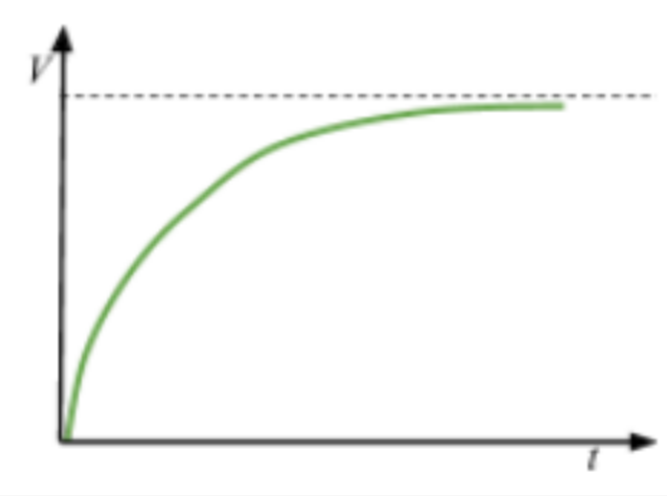
14
New cards
Current vs Time for Charging Capacitor
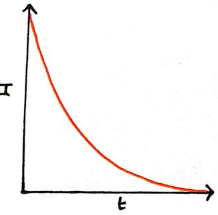
15
New cards
Voltage vs Time for Discharging Capacitor
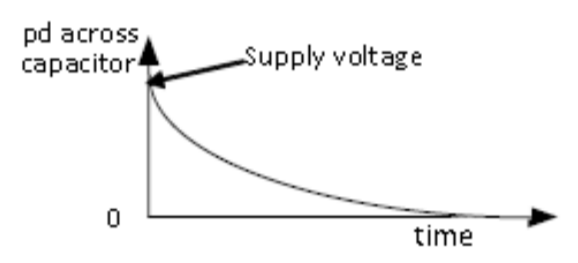
16
New cards
Current vs Time for discharging Capacitor
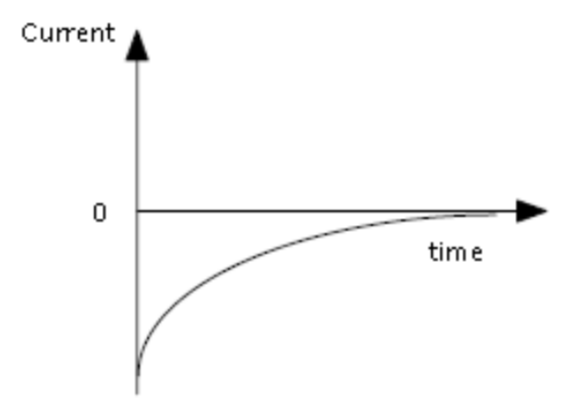
17
New cards
Adding a resistor in series to an internal resistance circuit.
Resistance increases.
Current decreases.
Lost volts decrease.
VTPD increases
Current decreases.
Lost volts decrease.
VTPD increases
18
New cards
Removing a resistor from a internal resistance circuit. Or adding in parallel.
Resistance decreases
Current increases
Lost volts increase
VTPD decreases
Current increases
Lost volts increase
VTPD decreases
19
New cards
Capacitor/Resistance Circuit - What happens when you increase resistance?
Initial Current reduces.
Longer time to charge.
Longer time to charge.
20
New cards
Capacitor/Resistance Circuit - What happens when you increase capacitance?
Longer time to charge.
Same final voltage.
Same final voltage.
21
New cards
conduction band
A band higher in energy than the fully occupied valence band. Will have electrons free to move in this energy band.
22
New cards
valence band
The highest energy band that is fully occupied.
23
New cards
For conduction to occur you need
Free electrons, accessible empty states
24
New cards
Conductivity increases with temperature increasing
Semiconductor
25
New cards
Conductivity decreases with temperature increasing.
Conductor
26
New cards
Has partially filled valence and conduction bands.
Metals (Conductors).
27
New cards
Has a filled valence band.
Insulators.
28
New cards
At room temperature there is enough energy to move electrons from valence to conduction band.
Semiconductor.
29
New cards
Term to describe adding impurities to semiconductor.
Doping
30
New cards
Why are semiconductors doped?
To increase conductivity.
31
New cards
Negative terminal connected to N-Type
Positive terminal connected to P-Type
Positive terminal connected to P-Type
Forward bias
32
New cards
Positive terminal connected to N-Type
Negative terminal connected to P-Type
Negative terminal connected to P-Type
Reverse bias
33
New cards
Forward bias does what to the depletion layer?
Makes it smaller, reduces electric field
34
New cards
Reverse bias does what to the depletion layer?
Makes it larger, increases electric field
35
New cards
For an LED to light it needs to be in ...
Forward Bias
36
New cards
For a solar cell to produce electricity it needs to be ...
Unbias
37
New cards
When the LED is forward bias it works because ....
Voltage applied causes electron from the conduction band of the n type to move towards the conduction band of p type. Electrons fall from the conduction band to valence band, photon emitted.
38
New cards
A solar cell works because...
Electrons gain/absorb energy from photons/light, electrons move form valence band to conduction band. Electrons move towards n-type semiconductor (producing a P.D.)