Aerobic Metabolism
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Where is energy generated in the cell?
mitochondria
Which step produces the most ATP
electron transport chain
______ respiration uses oxygen as the final electron acceptor
aerobic
______ respiration includes glycolosis, adn krebs/tca/citric acid cycle
aerobic
_______ is the sum collection of reactions responsible for the generation of energy for cells. The use of this energy in combination with organic precursor molecules, to make more complicated molecules for the cell
metabolism
What is the one energy source our bodys have?
mitochondria
energy is stored and released from chemical bonds of
ATP
ATP
adenosine triphosphate
components of ATP
phosphate groups, ribose, and adenine (nitrogenous base)
ATP hydrolysis ____ energy stored in bonds
releases
cells couple _______ chemical reactions to use energy
opposing
anabolic
SMALL molecules are assembled into LARGE ones. energy is required
catabolic
LARGE molecules are broken down into SMALL ones. energy is released
anabolic
non-spontaneous and endergonic
catabolic
spontaneous and exergonic
what is gibbs free energy (G)
the energy available to do work
what form of energy is utilized by the cell
ATP
spontaneous and exergonic describe _____ reactions
catabolic
there is less potential energy at the start of ______ reactions
anabolic
all reactions in biological systems are considered to be _______ reactions
reversible
△G=GB-GA
△G=-1
△G=GA-GB
△G=1
△G in metabolism: reactions are ______
coupled
if the reaction is spontaneous or exergonic, △G is
less than 0, negative
if the reaction is non-spontaneous or endergonic, △G is
greater than 0, positive
components of energy
ATP + heat
cellular respiration includes
aerobic and anaerobic respiration
_______ respiration produces the most ATP
aerobic
oxidation is _____ of electrons
loss
reduction is ______ of electrons
gain
the most metabolic energy is produces by ________ reactions in the mitochondria
redox (oxidation/reduction)
main metabolic fuel
fats, carbs, proteins
direct results of cellular respiration
produces CO2 and uses O2
generation of ATP
controlled breakdown and release of energy
how is energy stored/distributed as it is released through the step wise process of cellular respiration
ATP
electron carriers
the potential energy at the end of cellular respiration is ______ compared to the begining of cellular respiration
lower
what would happen if hydrogen ions were not compartmentalized during the electron transport chain
little to no ATP would be generated
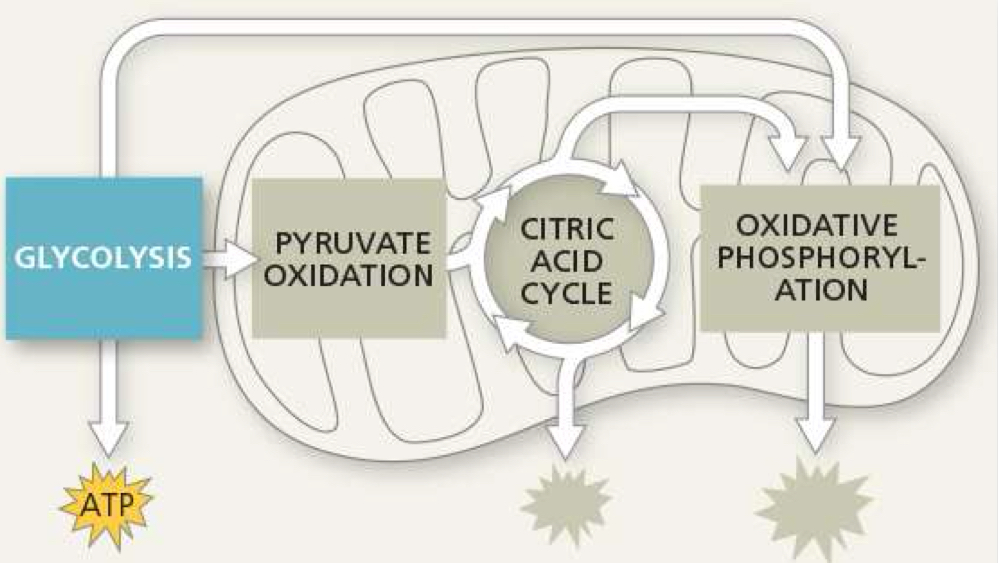
where does glycolosis take place
cytoplasm
what is produced from glycolysis
2 pyruvate, 4 ATP (net 2), 2NADH (electron carrier)
what is required for glycolysis
glucose, 2ATP, 2NAD+ (electron acceptor)
3 phases of glycolysis
phosphorylation, cleavage, and oxidation
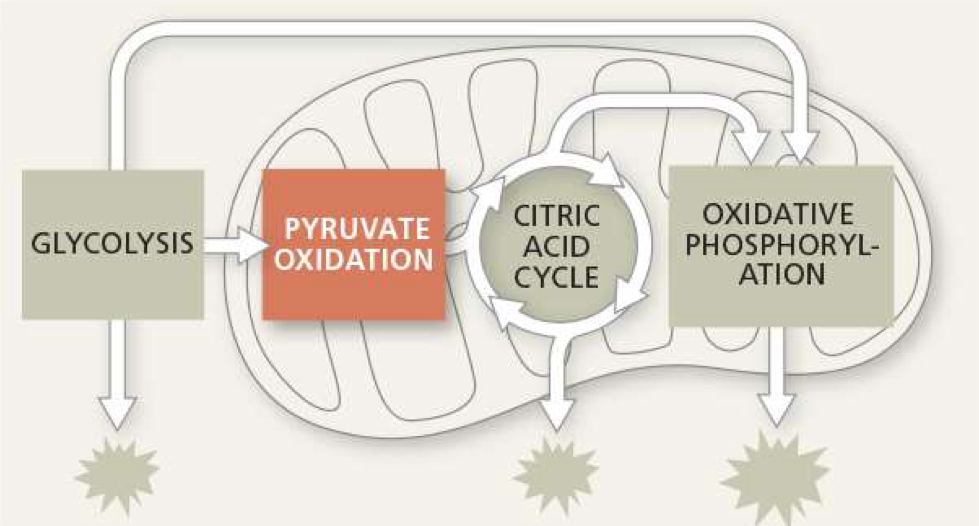
where is pyruvate oxidation located
mitochondrial matrix (inside inner membrane)
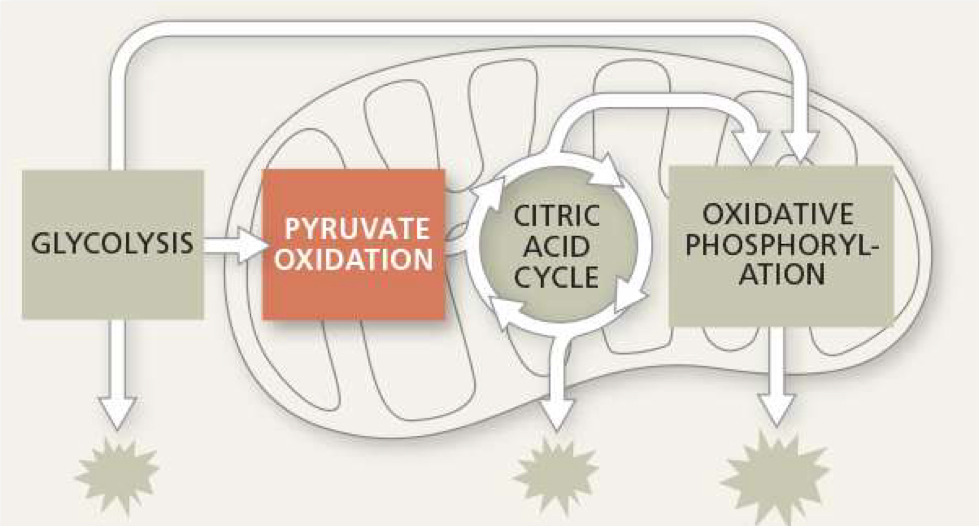
what is needed for pyruvate oxidation
2 pyruvate, 2 NAD+, 2 coenzyme A
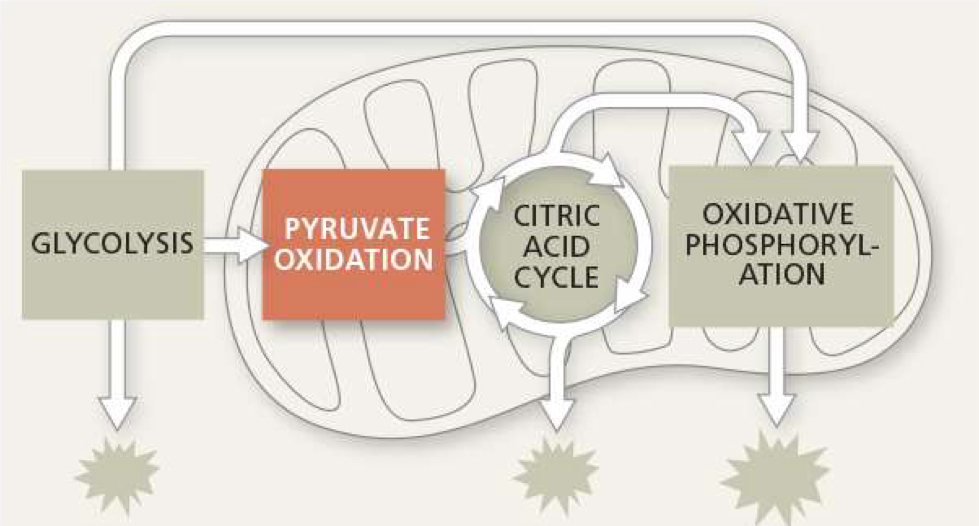
what is produced from pyruvate oxidation
2 acetyl-CoA, 2 NADH, 2 CO2
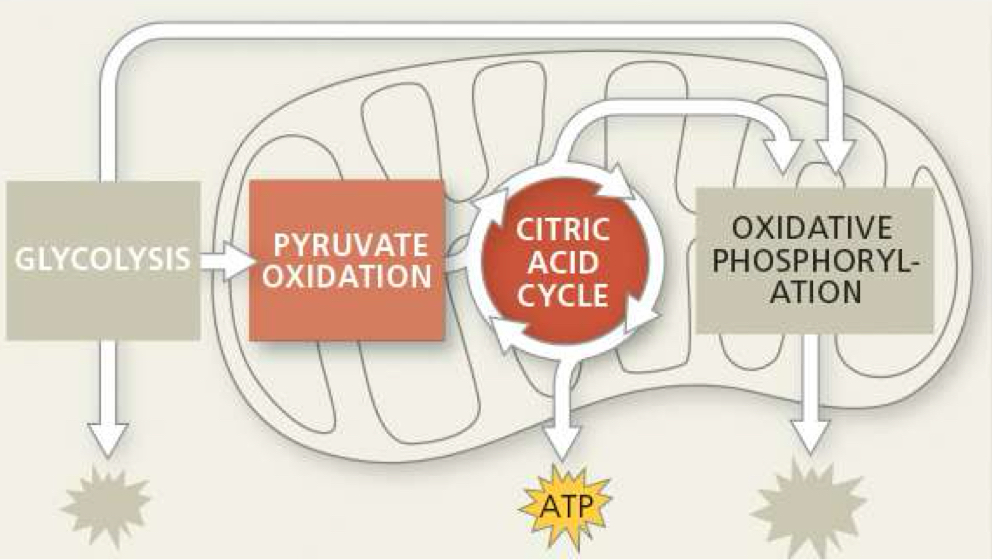
where does krebs cycle take place
mitochondrial matrix
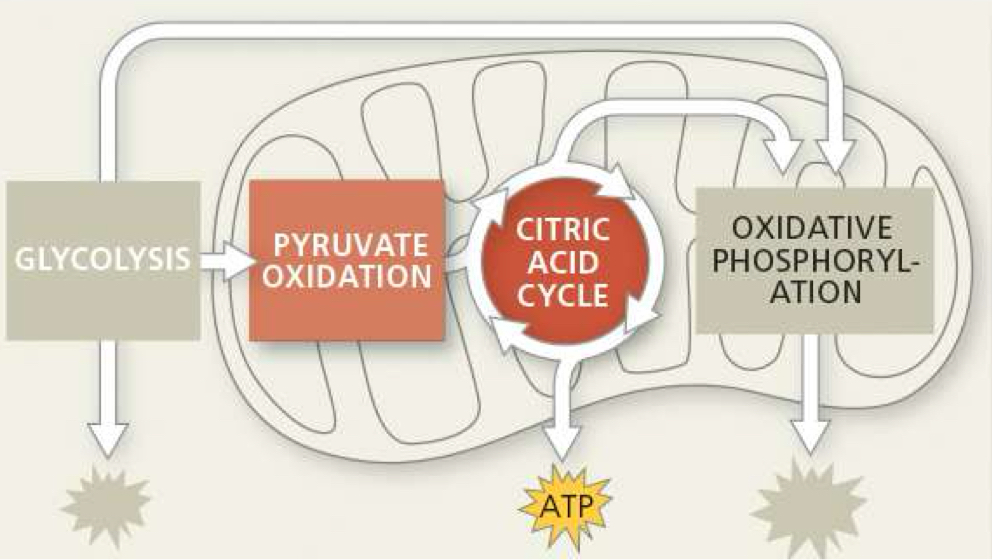
what is needed for krebs cycle
2 acetyl-CoA, 2 ADP, 2 FADH, 6 NAD+
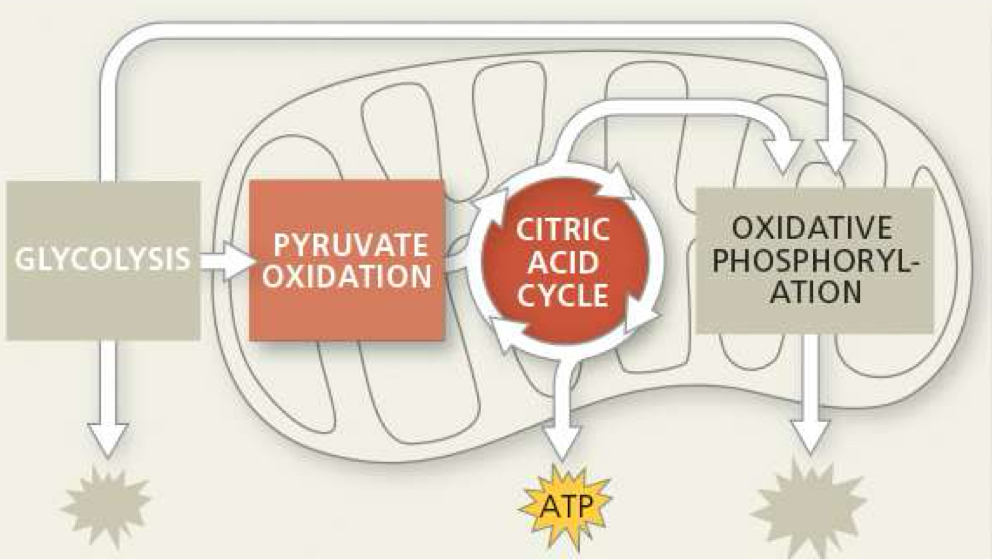
what is produced from krebs cycle
6 NADH, 1 FADH2, 2 ATP, 4 CO2
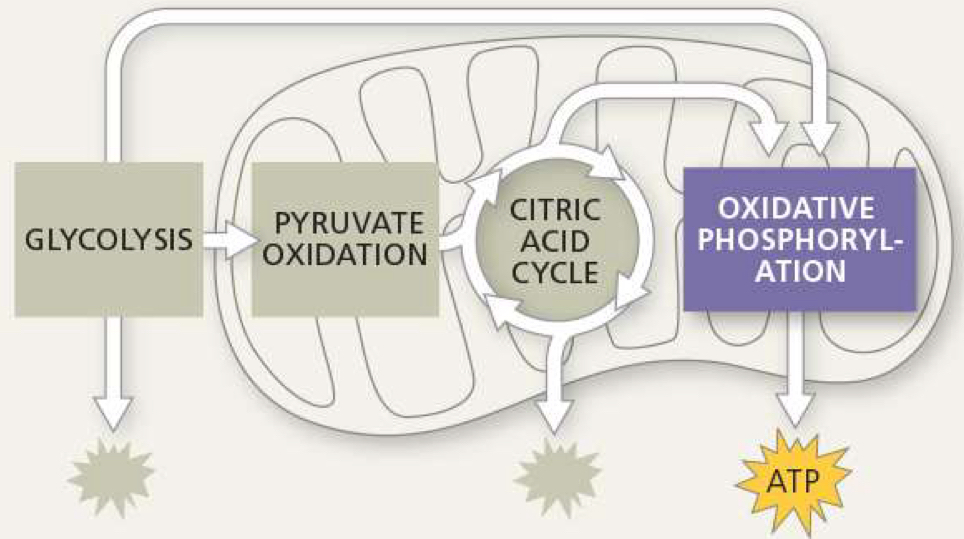
another name for oxidative phosphorylation
electron transport chain
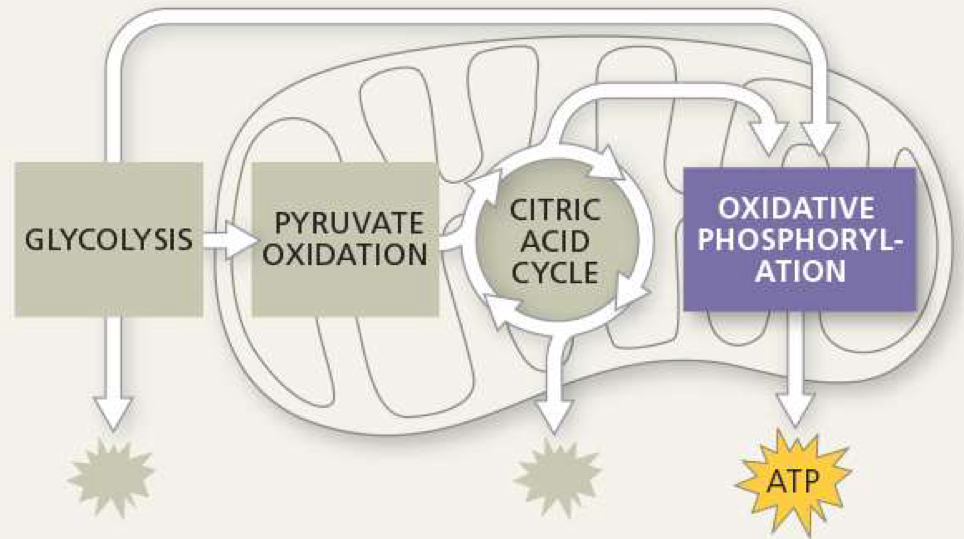
where is the electron transport chain located
inner mitochondrial membrane
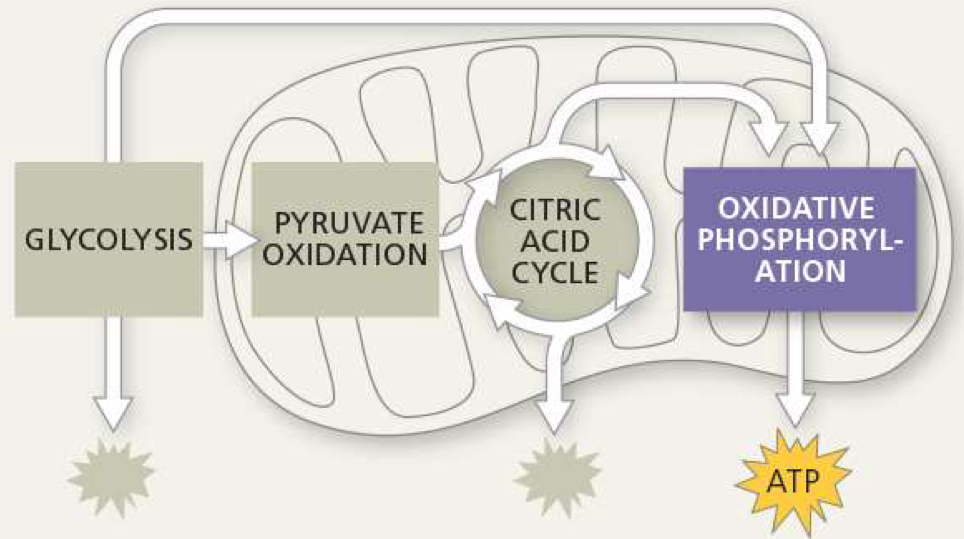
what is needed for electron transport chain
reduced electron carriers (NADH, FADH2), O2
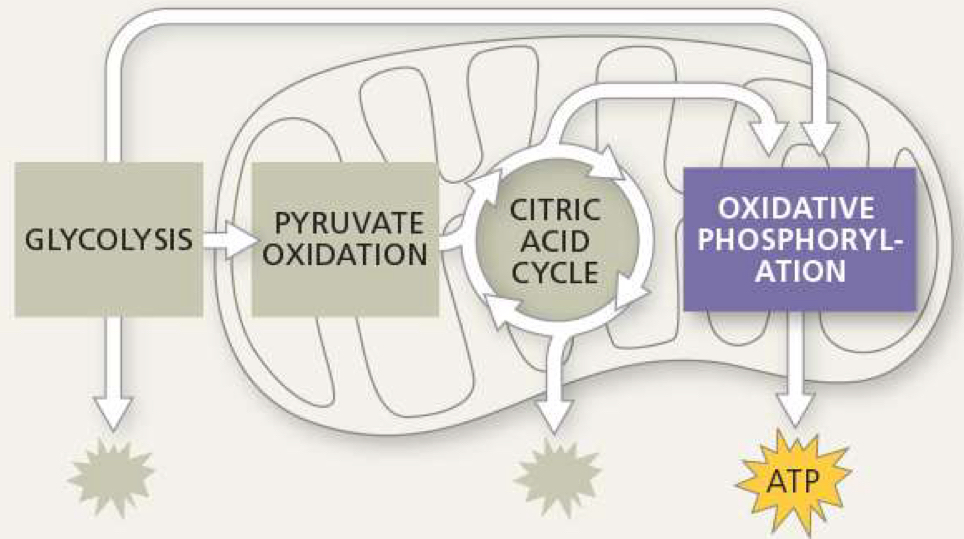
what is produced from electron transport chain
ATP, NAD+, FADH, H2O
gibbs free energy
the maximum amount of energy that can be obtained from a reaction at a constant temperature and pressure (kcal/mol)
structural difference between ATP and nucleotides
ATP has 2 OH groups
DNA nucleotide has 1 OH group
deoxyadenosine triphosphate (dATP)
used in replication to form DNA strands
the phosphate group in nucleotides and ATP are broken by ________
hydrolysis
DNA backbone is formed when ______ is lost on the nucleotide
phosphate group
metabolism
generation of energy for cells
________ has a lot of free energy
glucose
if glucose breaks down immediately, it will be released as _____ and we can’t harness any of the energy
heat
glucose → ?
CO2 + H2O
glucose bonds are _______ released so we can harness the energy
slowly
where is ATP generated
mitochondria
compartmentalization
different or opposing pathways are placed in different cellular compartments
what pathway is in the nucleus
DNA replication, synthesis of mRNA
what pathway is in the mitochondria
krebs cycle, fatty acid oxidation
what pathway is in the cytosol
glycolysis, fatty acid synthesis
the mitochondria has a ______ membrane
double
when a molecule is oxidized it ______ electrons
loses
FADH2 is an example of a ________
fully reduced electron carrier