lesson 5 abdomen
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
the abdomen is ….. to the thorax
inferior
the abdominal cavity is bounded ….1…. by the diaphragm and …..2….. by the pelvic inlet
superiorly
inferiorly
how high can the abdominal cavity extend superiorly
4th intercostal space
the abdominal cavity continuously inferiorly to the
pelvis inlet
what is the Abdominopelvic Quadrants : Topographical divisions
used to describe the location of abdominal organs and the pain associated with abdominal problems
the abdominopelvic surface is divided into how many segments
4
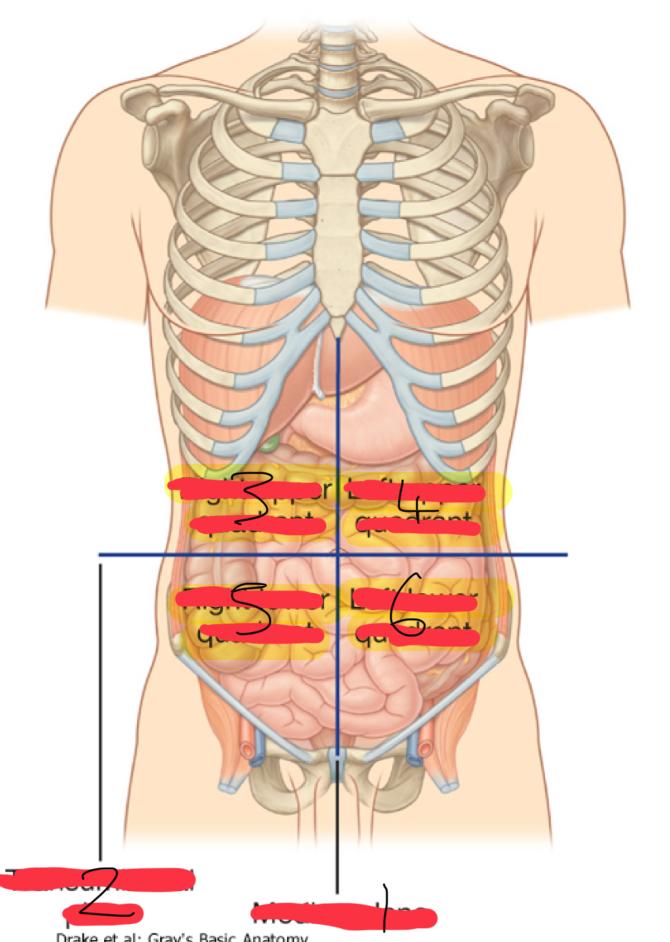
1
median plane (vertical)
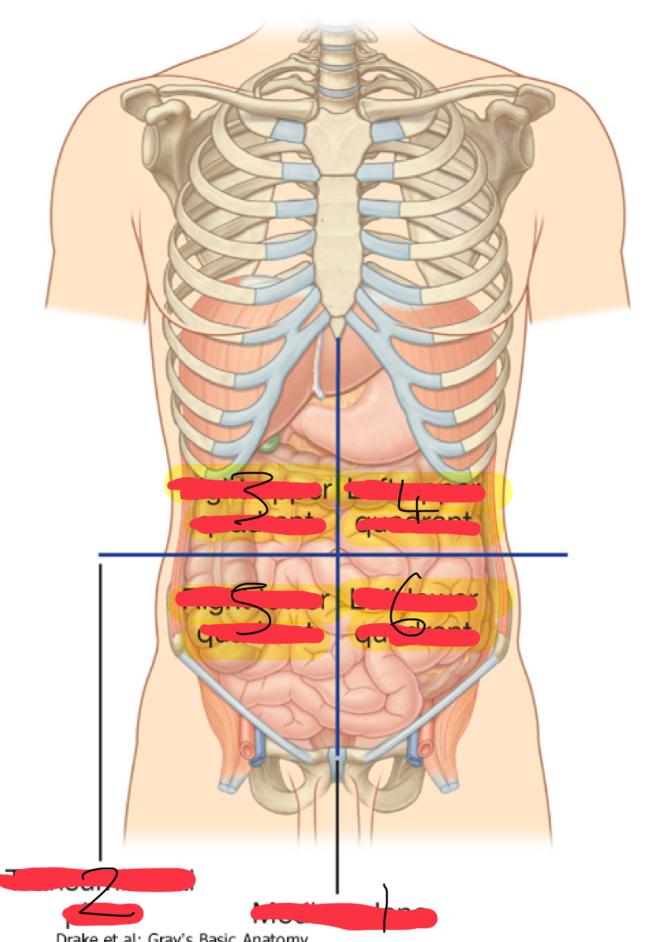
2
Transumbilical plane (horizontal)
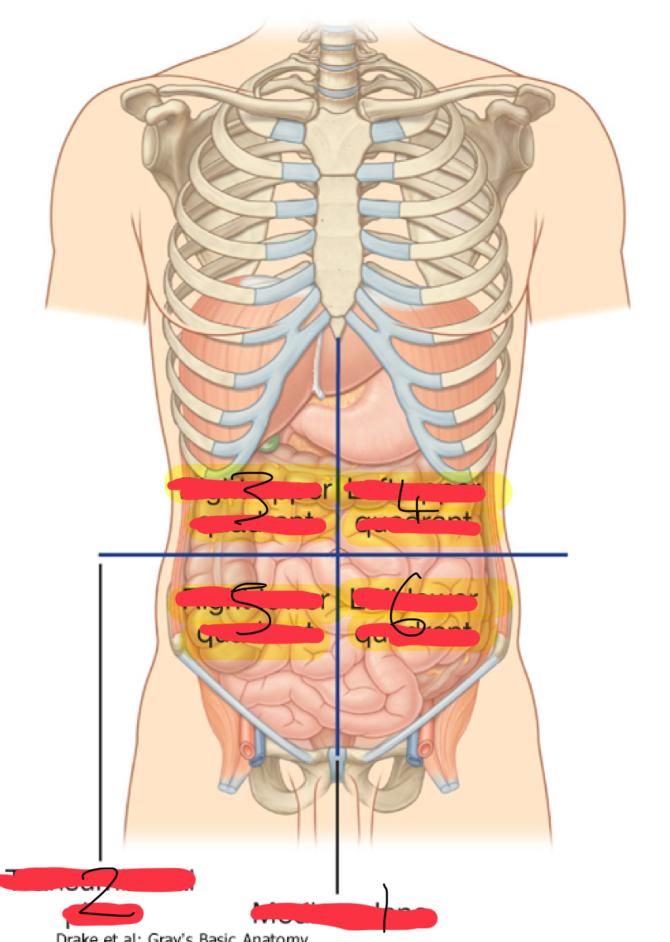
3
right upper quadrant
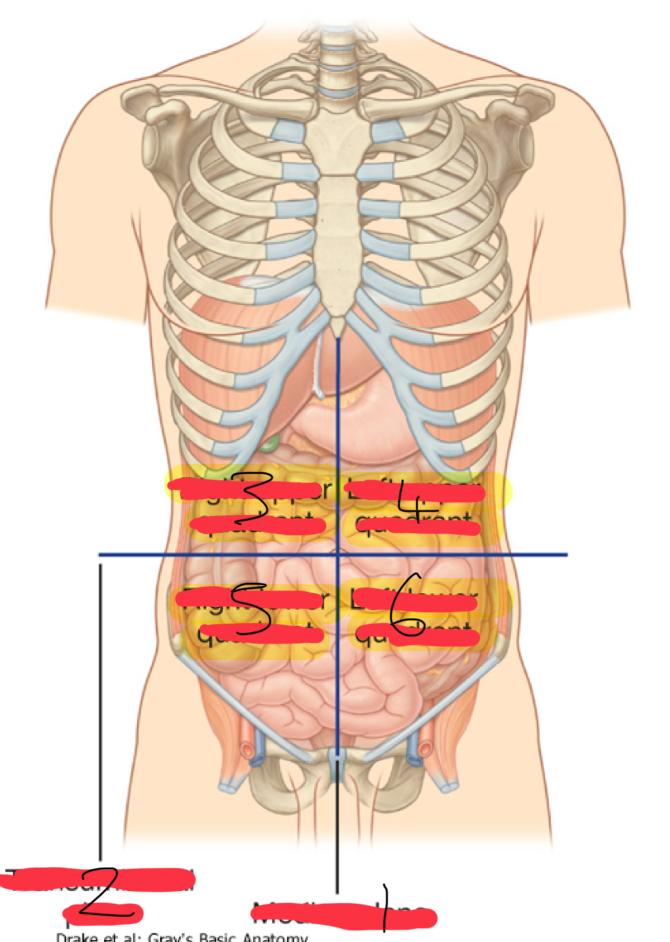
4
left upper quadrant
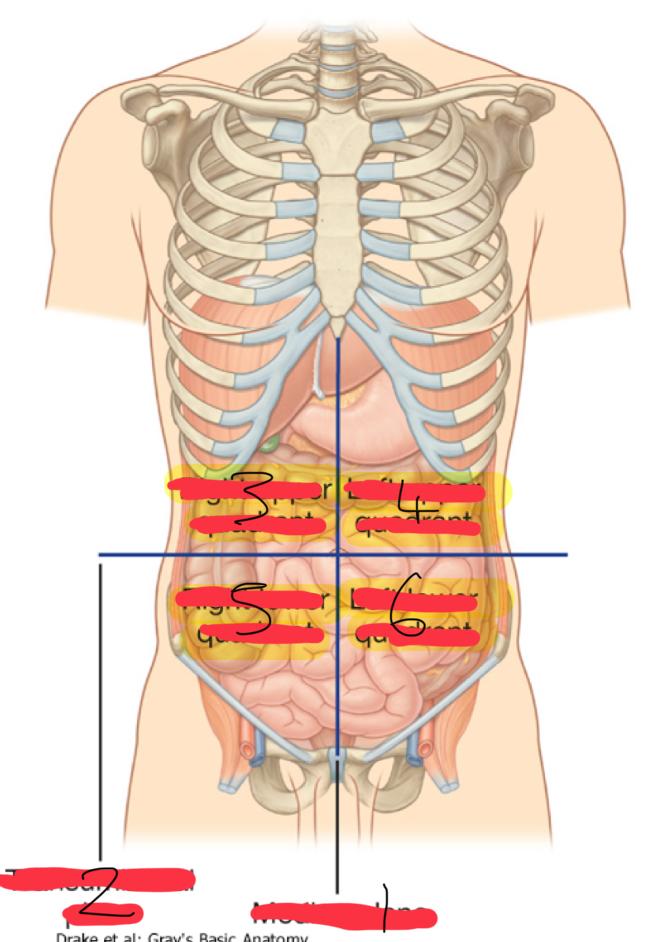
5
right lower quadrant
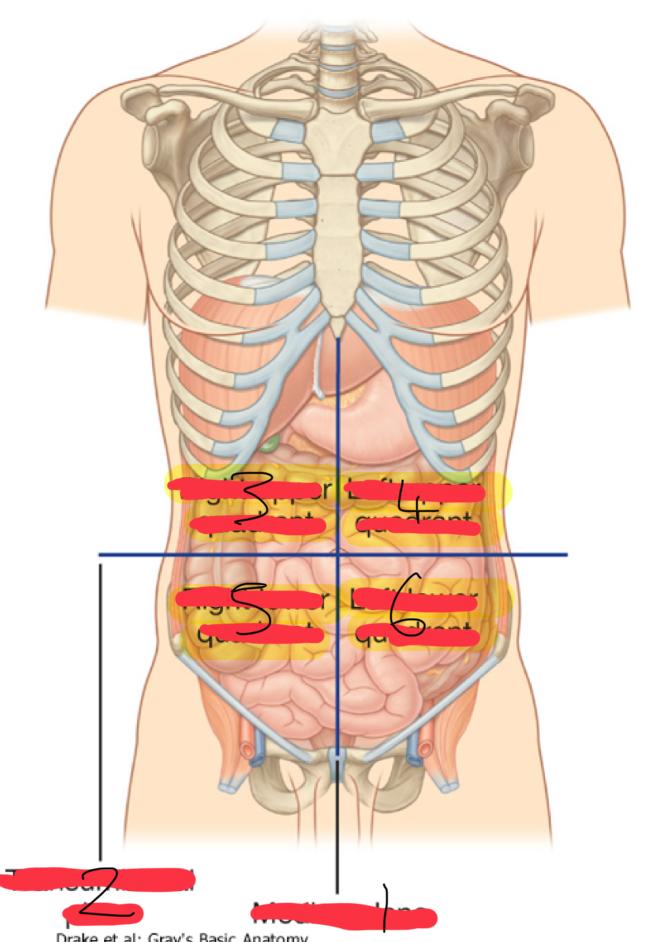
6
left lower quadrant
what are the organs in the Right Upper Quadrant (6)
right lobe of liver
gallbladder
right kidney
portion of stomach
small and large intestine
what are the organs in the Left Upper Quadrant (6)
left lobe of the liver
stomach
pancreas
left kidney
spleen
portion of the large intestine
what are the organs in the right lower quadrant (5)
cecum
appendix
portion of small intestine
reproductive organs (right part)
right ureter
what are the organs in the left lower quadrant (4)
most of small intestine
portion of large intestine
left ureter
reproductive organs (left part)
if there was pain in the Right Lower Quadrant what disease would u suspect
appendicitis
pain in the right upper quadrant what disease would u suspect
gallbladder or liver problems
what method of locating internal organs is more precise
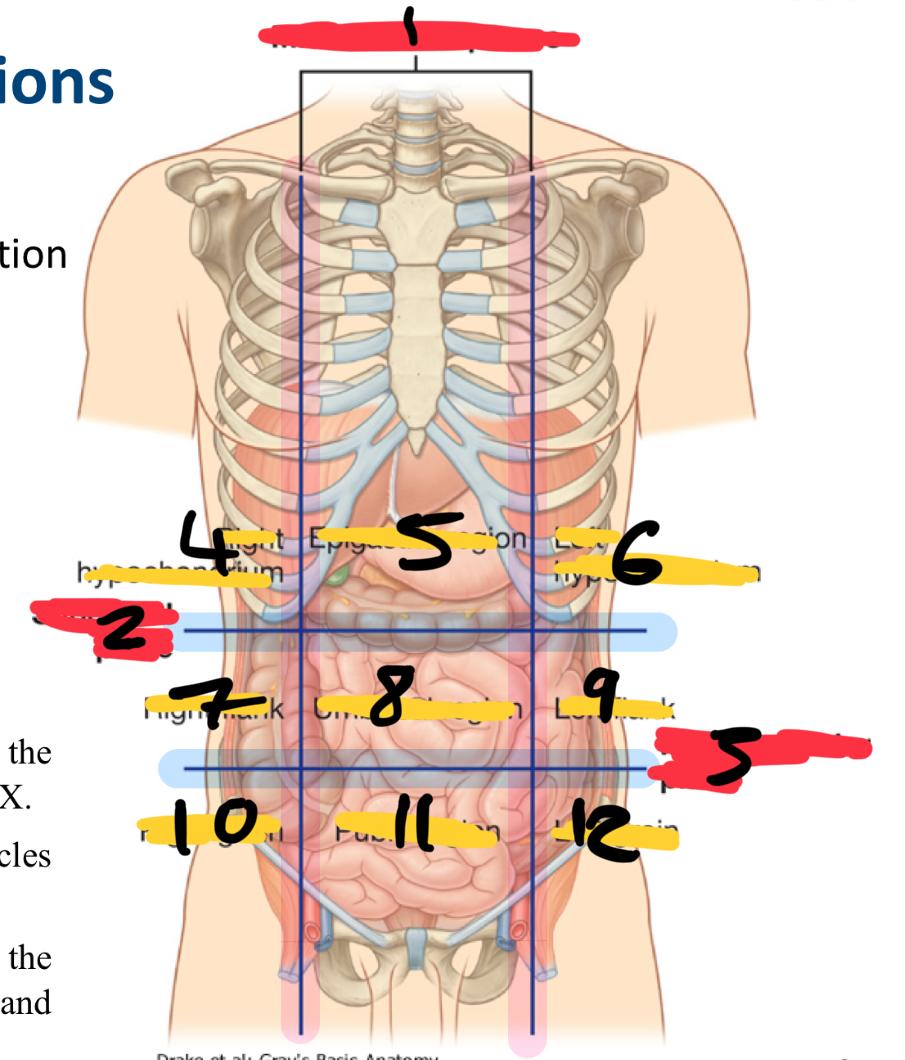
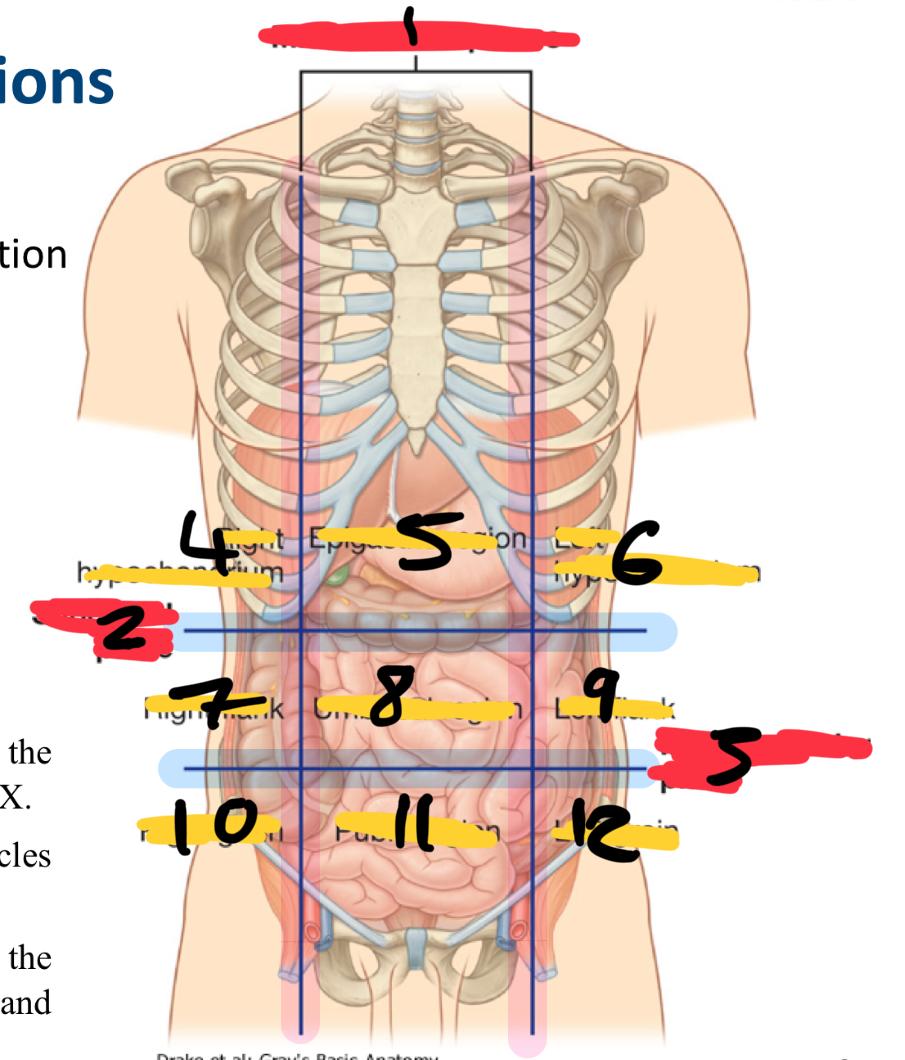
Nine-region pattern
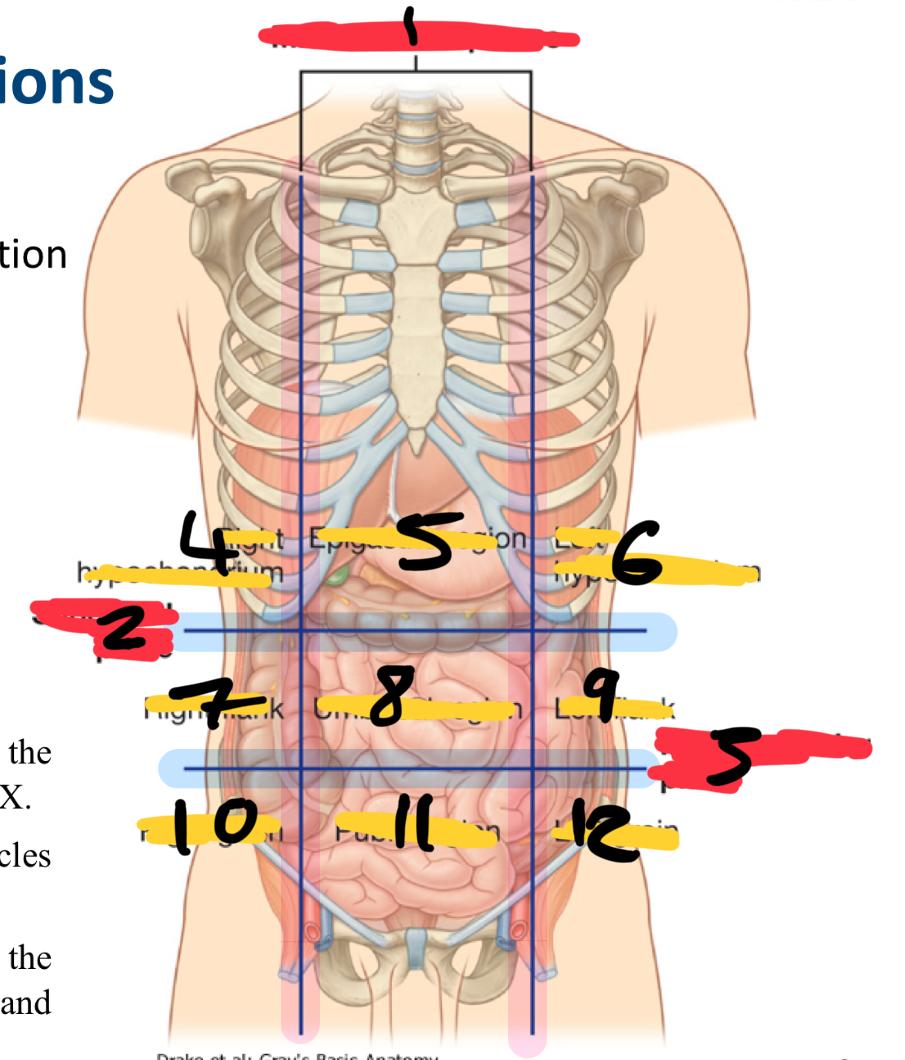
1
midclavicular planes (verticle)
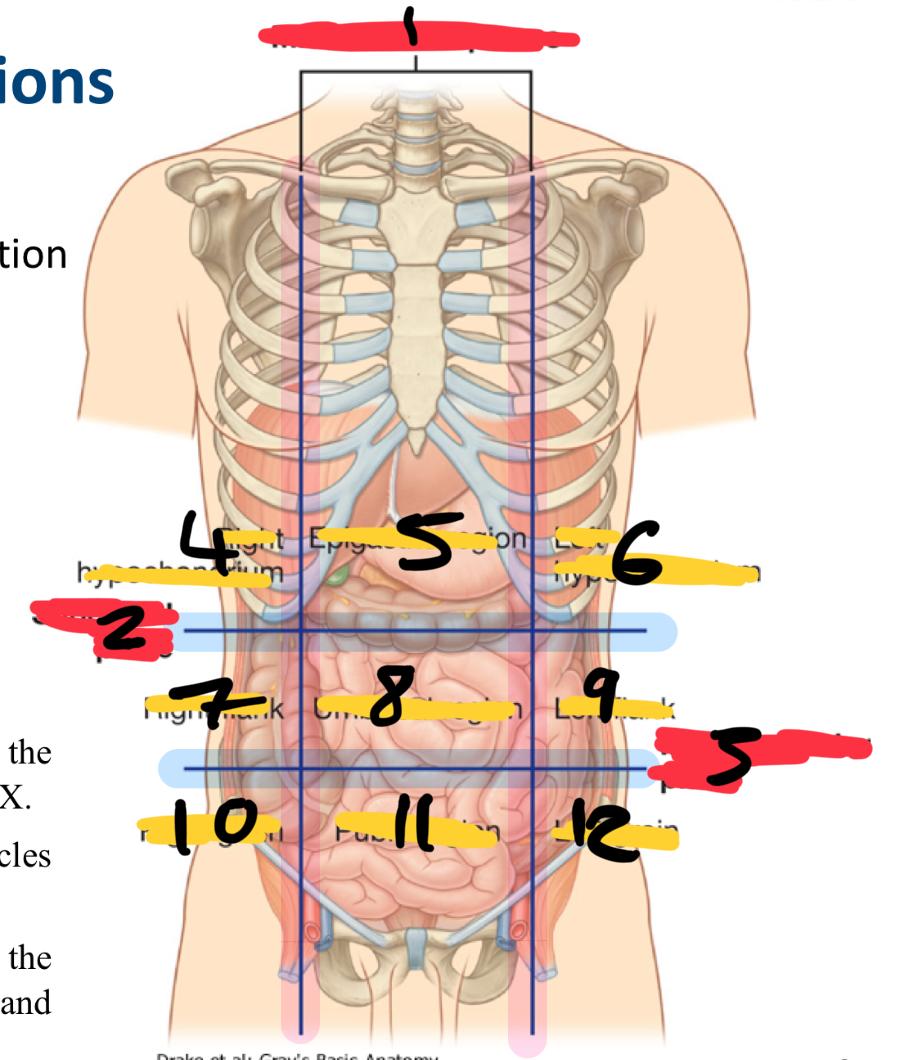
2
subcostal plane (horizontal)
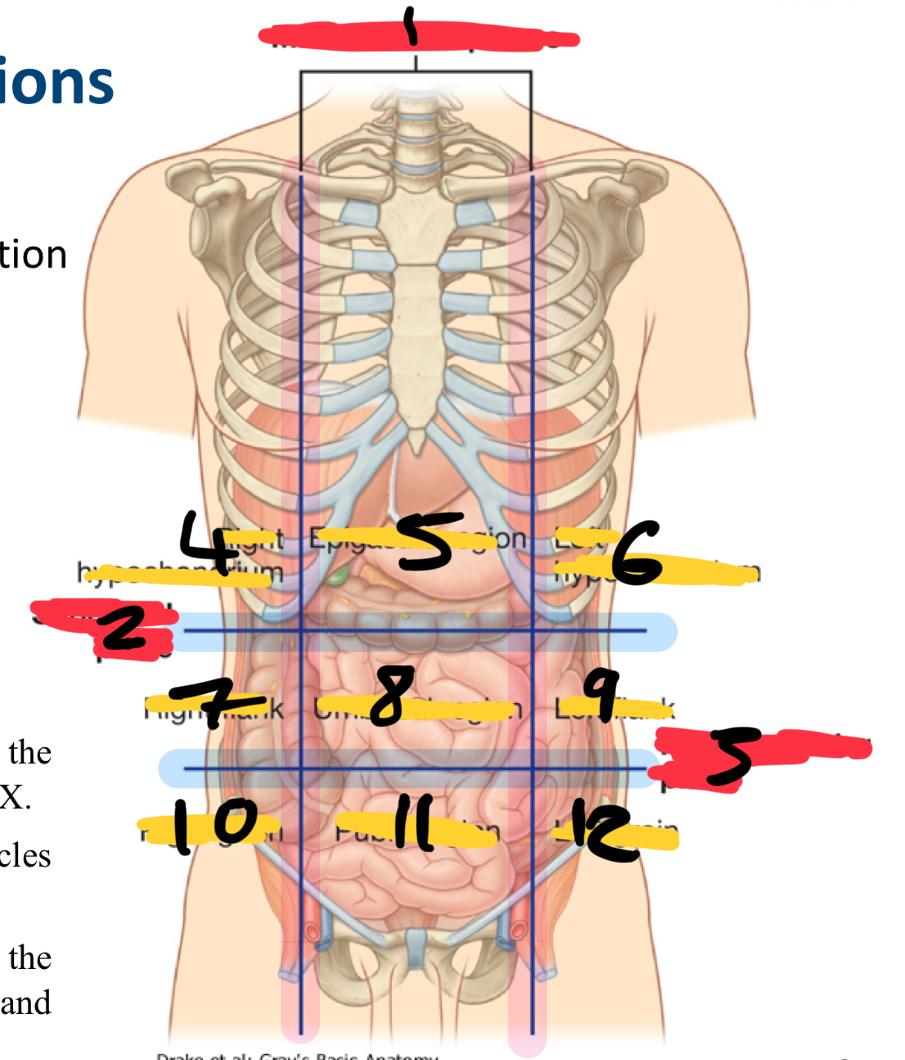
3
intertubercular plane (verticle)
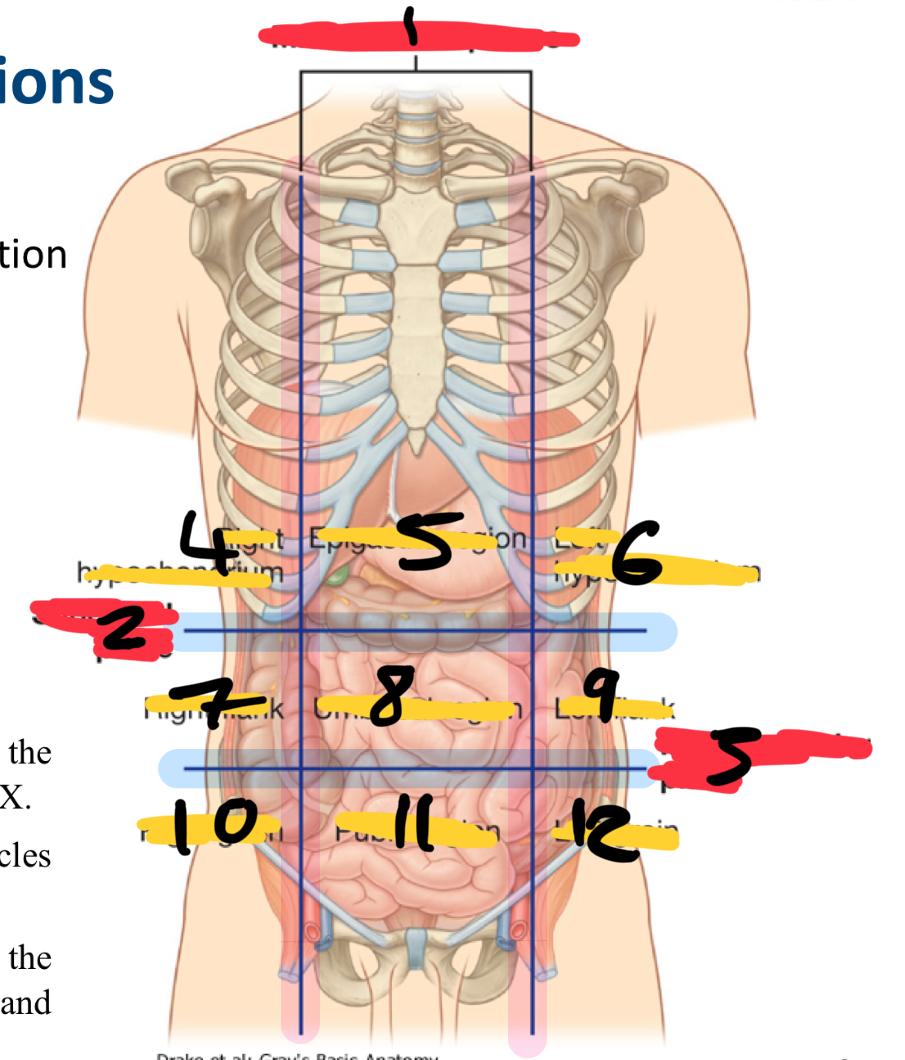
4
right hypochondrium
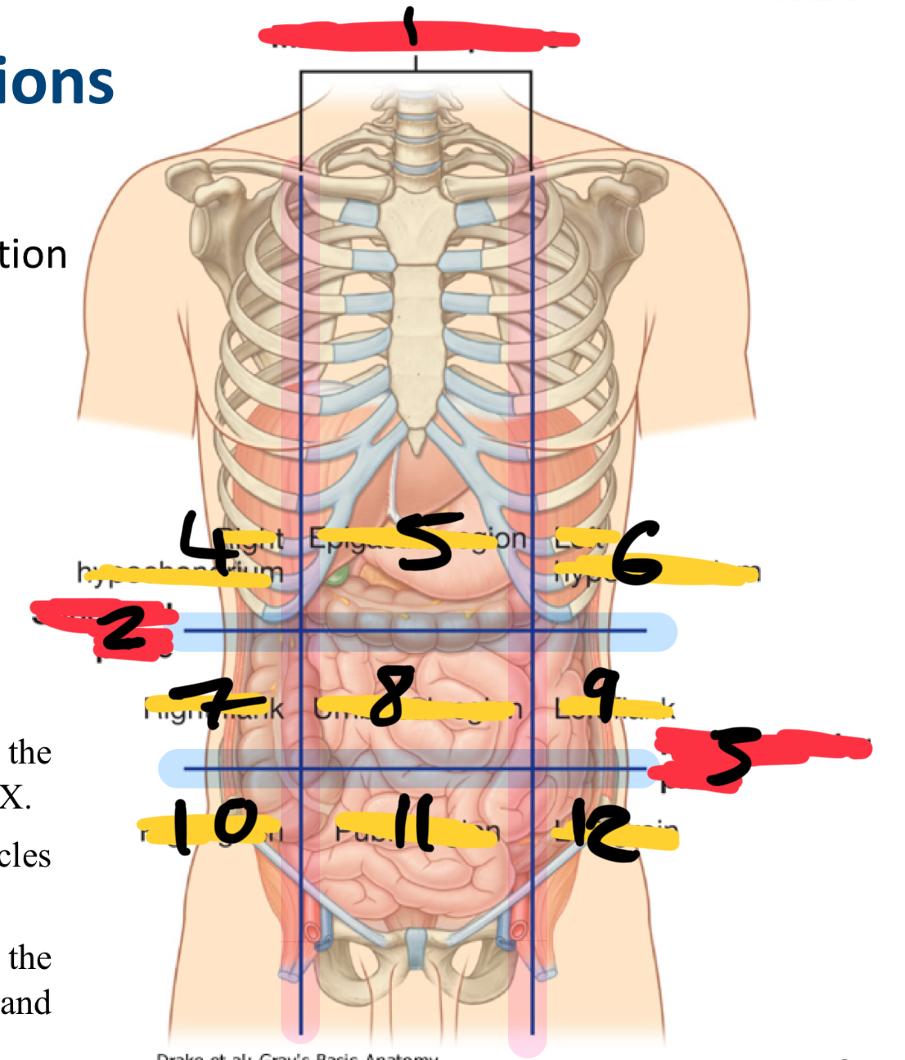
5
epigastric region
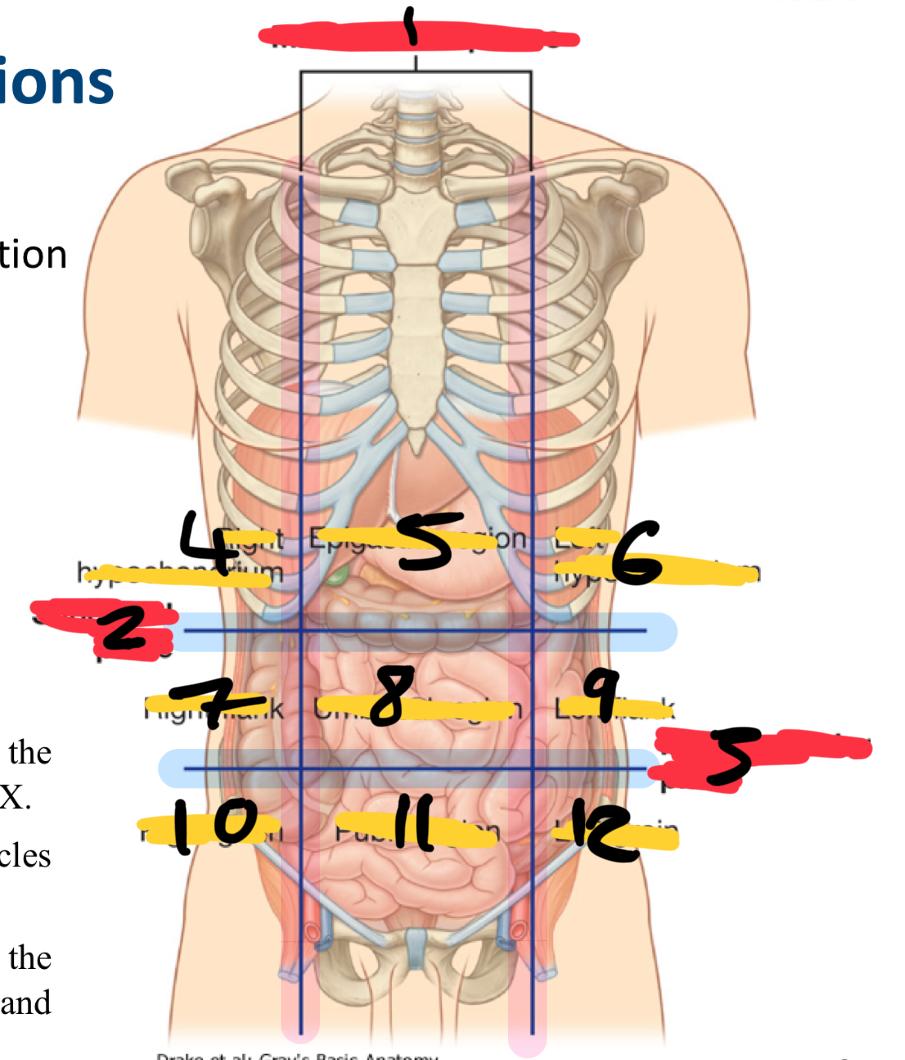
6
left hypochondrium
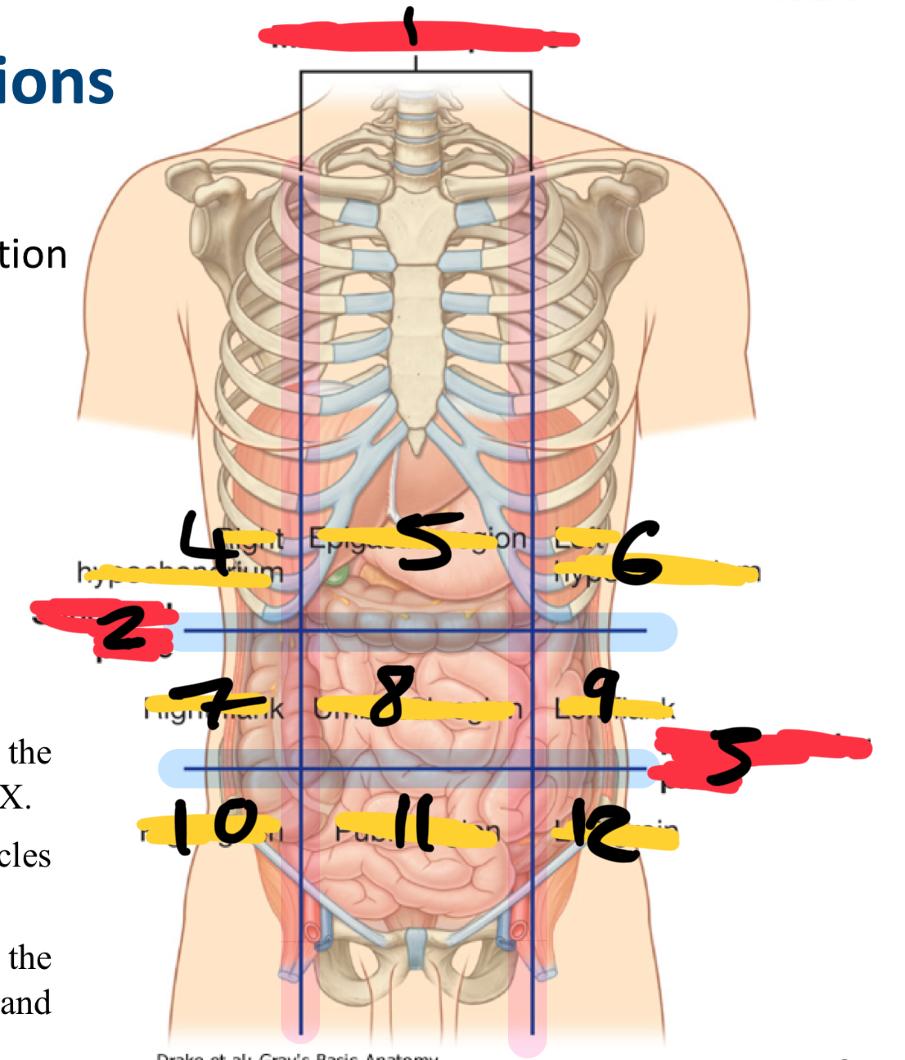
7
right flank
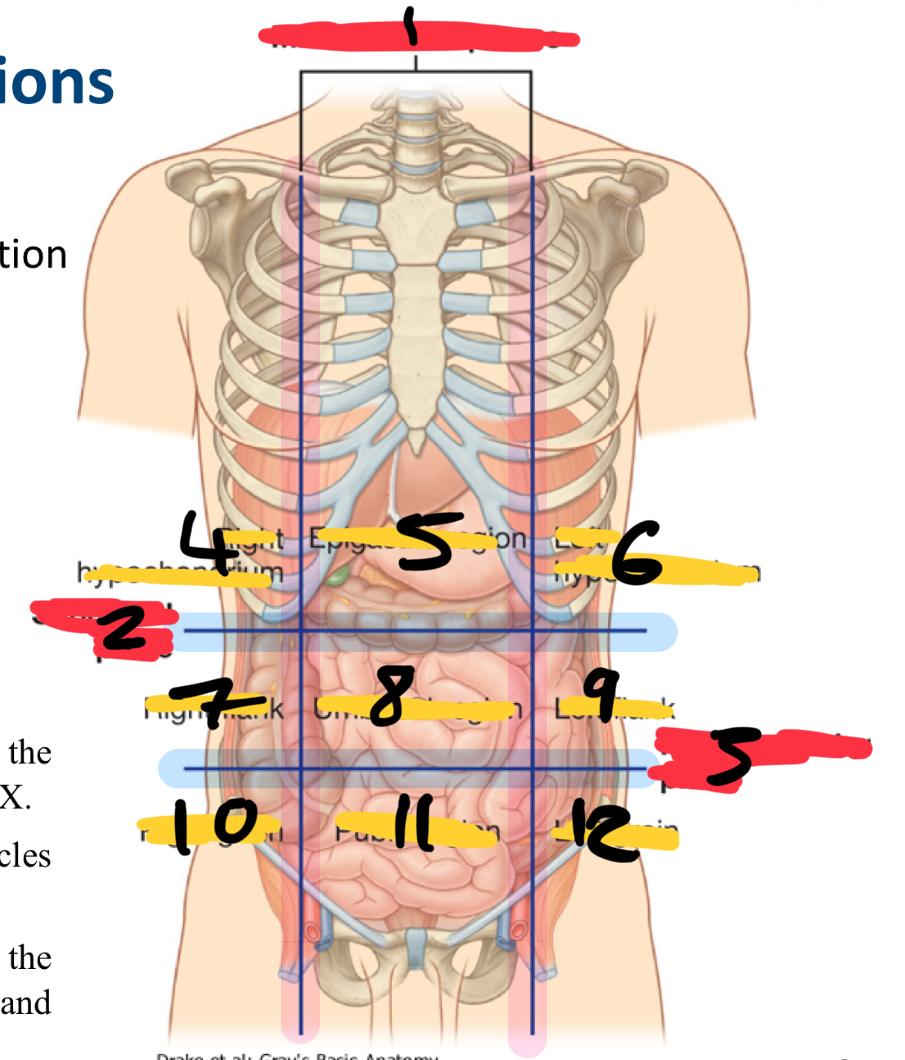
8
umbilical region
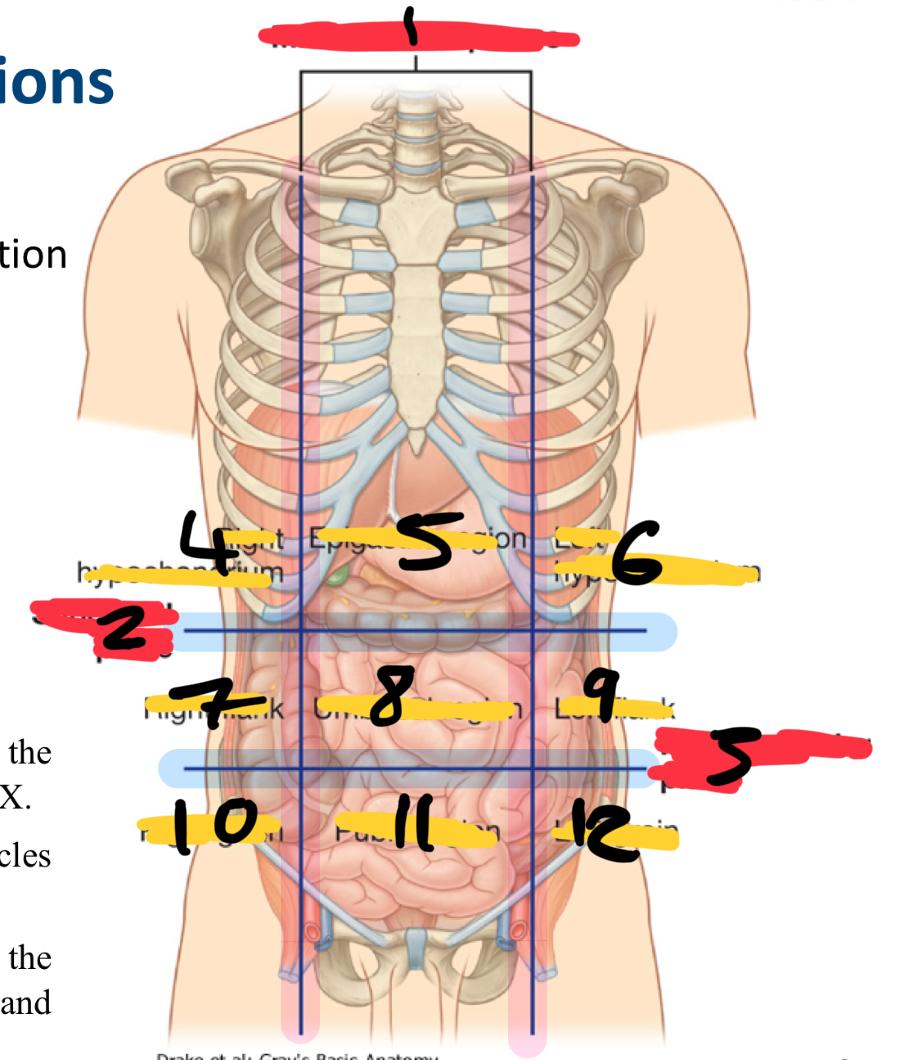
9
left flank
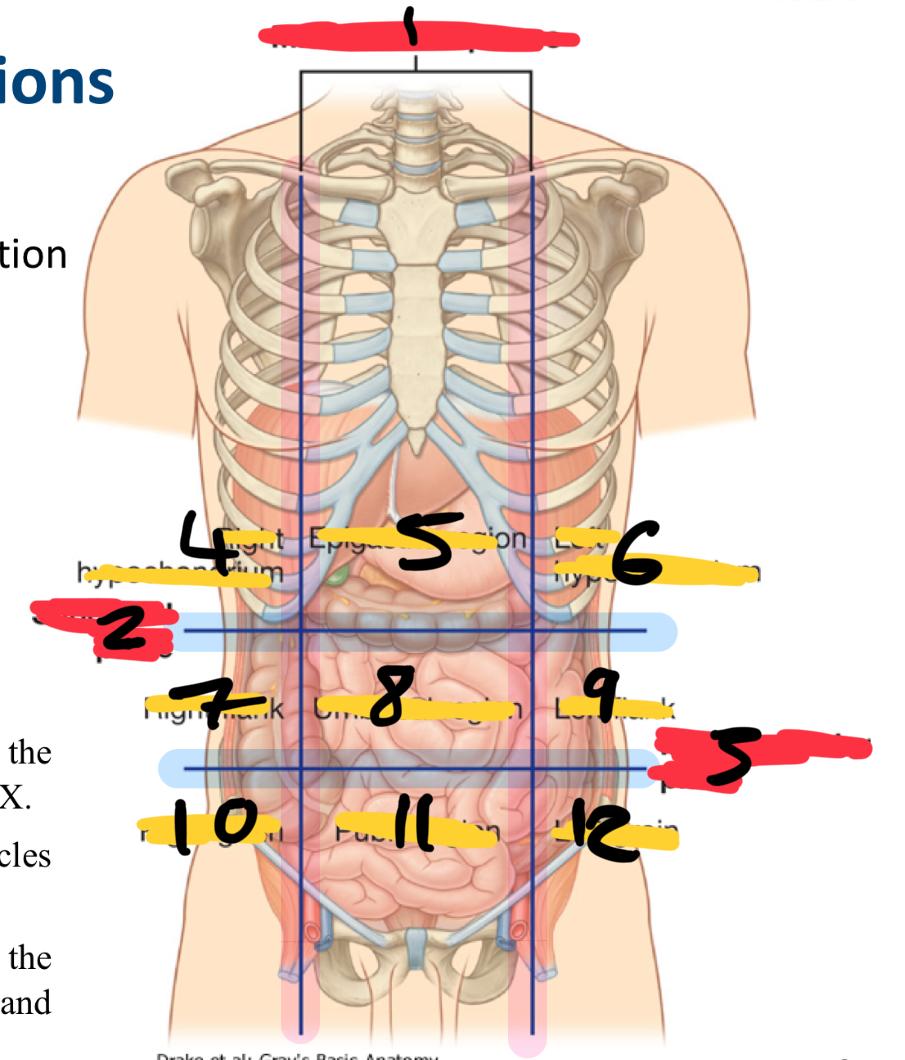
10
right groin
11
pubic region
12
left groin
what organs are in the right hypochondriac region
right lobe of the liver
gallbladder
large intestine
small intestine (partially)
Epigastric region organs
stomach
left lobe of liver
duodenum
adrenal glands
left hypochondriac organs
spleen
stomach
pancreas
large intestine
right flank organs
large intestine
small intestine
right kidney
umbilical region
small intestine
umbilical cord (in foetus)
pancreas
reproductive organs
left flank organs
large intestine
small intestine
left kidney
right groin organs
cecum
appendix
small intestine (ileum)
right reproductive organs
right ureter
pubic region organs
small intestine (ileum)
colon
urinary bladder
reproductive organs
left groin organs
large intestine
small intestine
left reproductive organs
left ureter
do the abdominal muscle flash cards
done
where are the anterolateral muscles
in the abdominal wall
how many muscles in the anterolateral wall
5
what are the 3 flat muscles
external oblique
internal oblique
transversus abdominis
what are the 2 vertical muscles that are near the midline and are enclosed within a tendinous sheath by the aponeuroses of the flat muscles
rectus abdominis
pyramidalis
what are the functions of he anterolateral muscles
keep organs in place
posture
protection
quiet and forced expiration
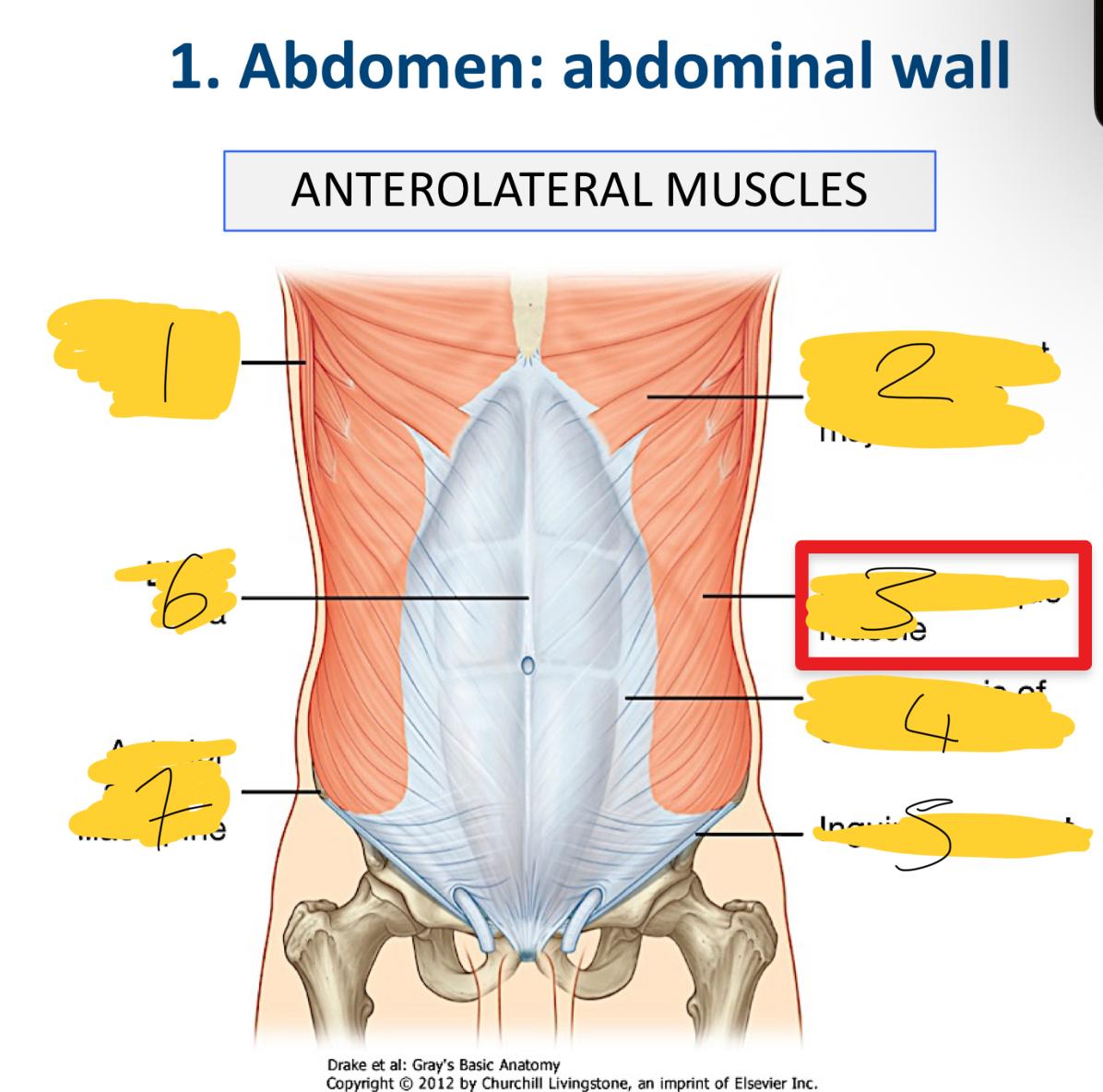
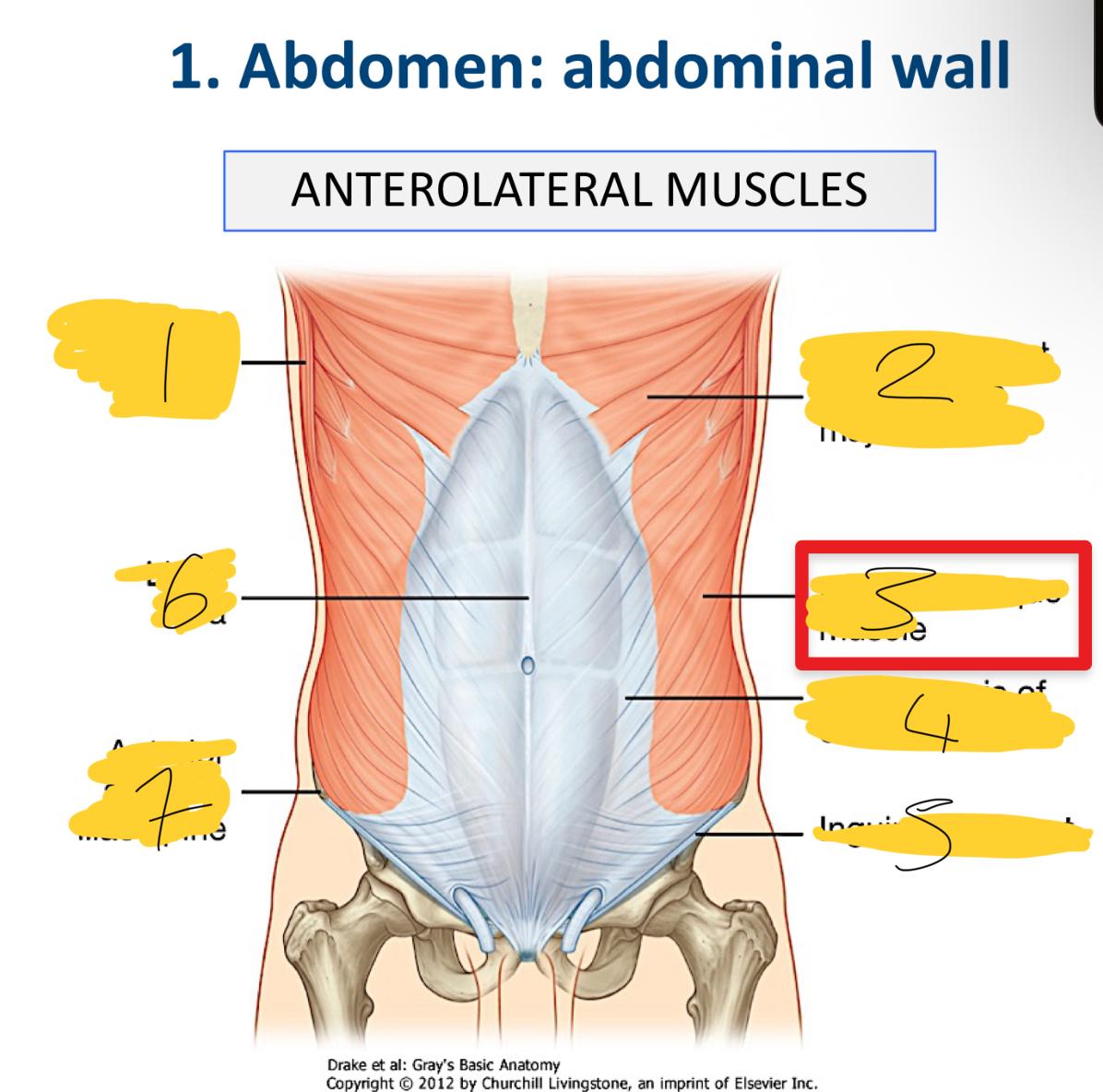
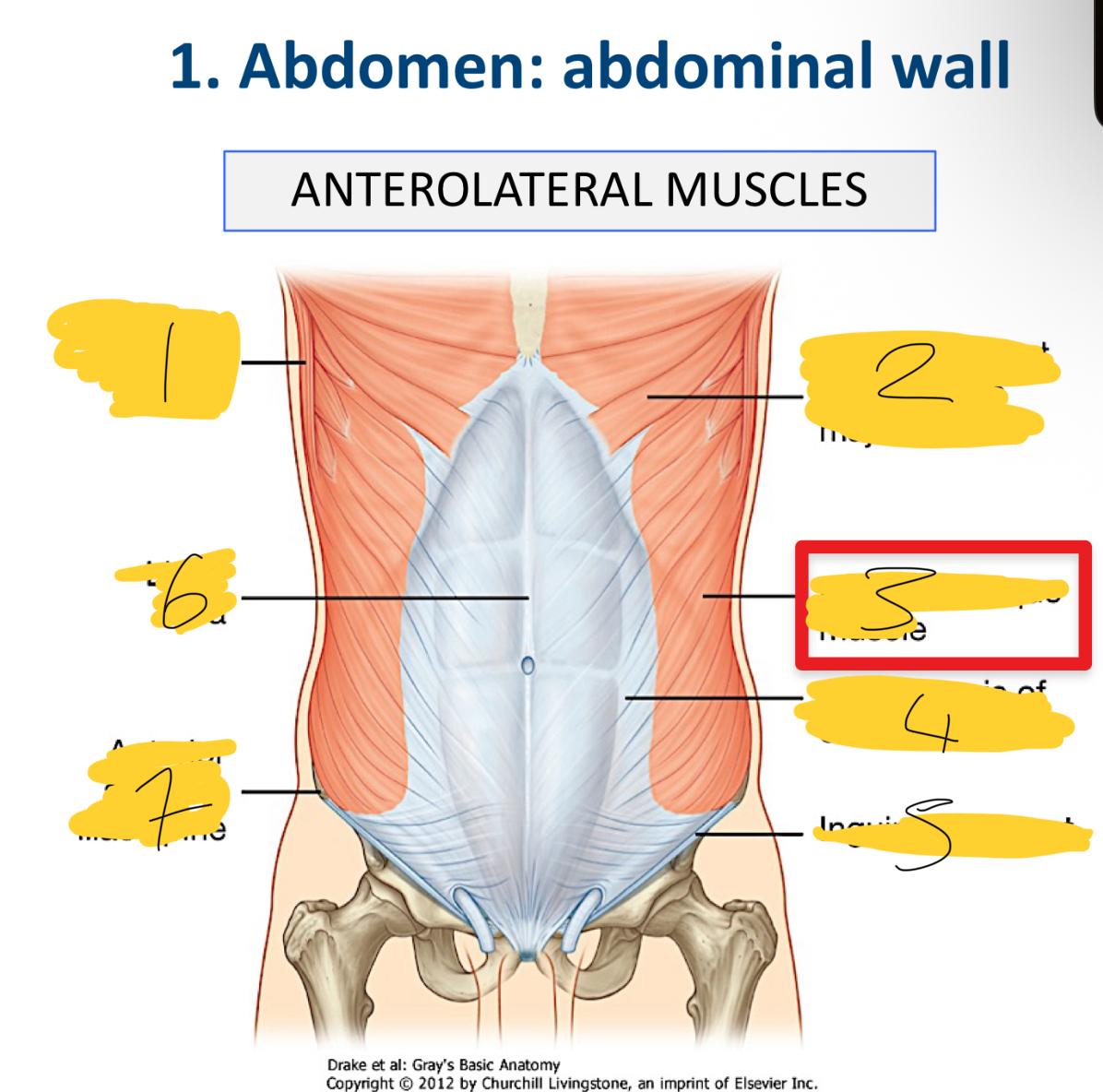
external oblique muscles are … muscles
flat and the most superficial and horizontal
1
latissimus dorsi muscle
2
abdominal part of pectoralis major muscle
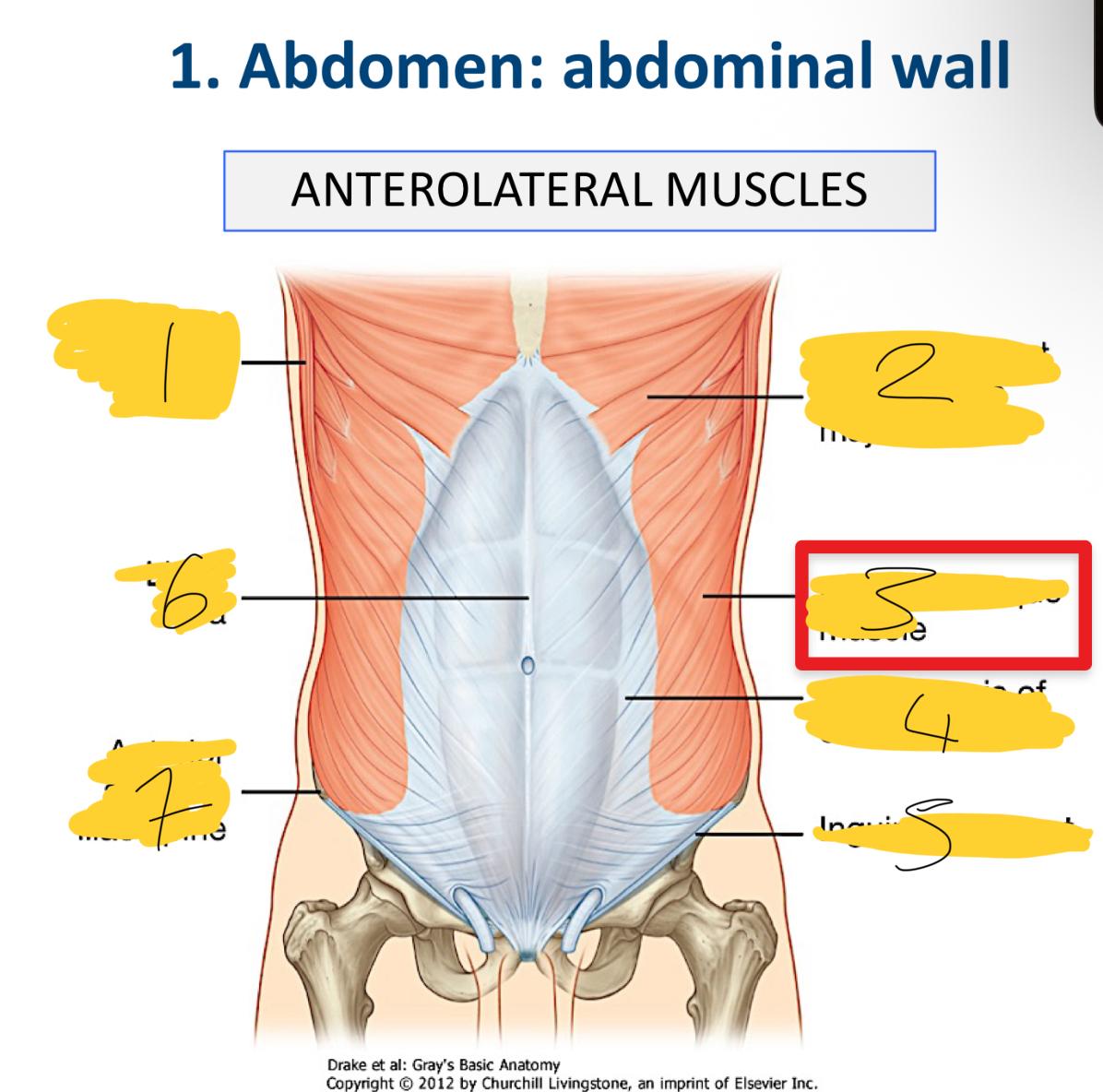
3
external oblique muscle
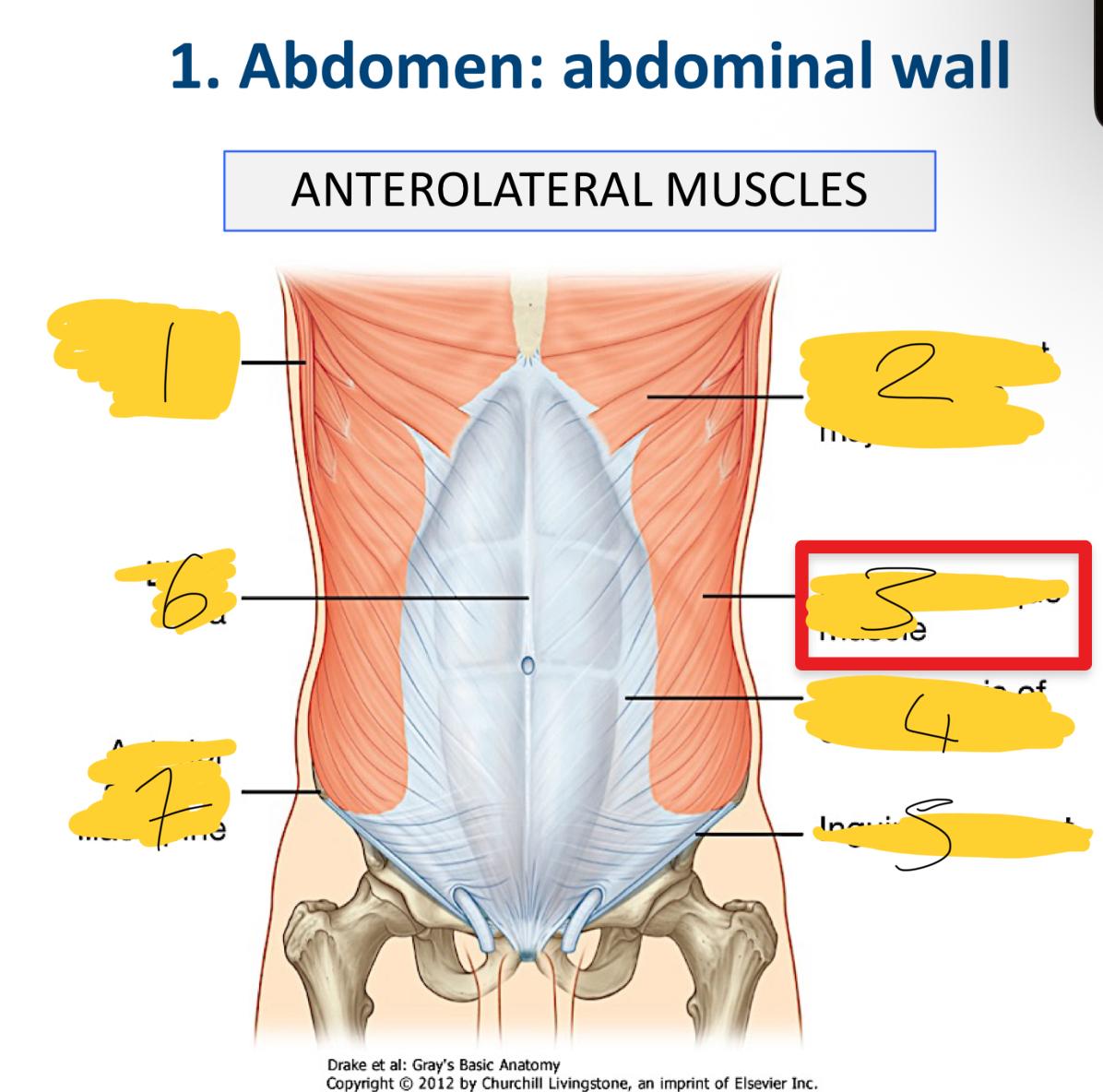
4
aponeurosis of external oblique
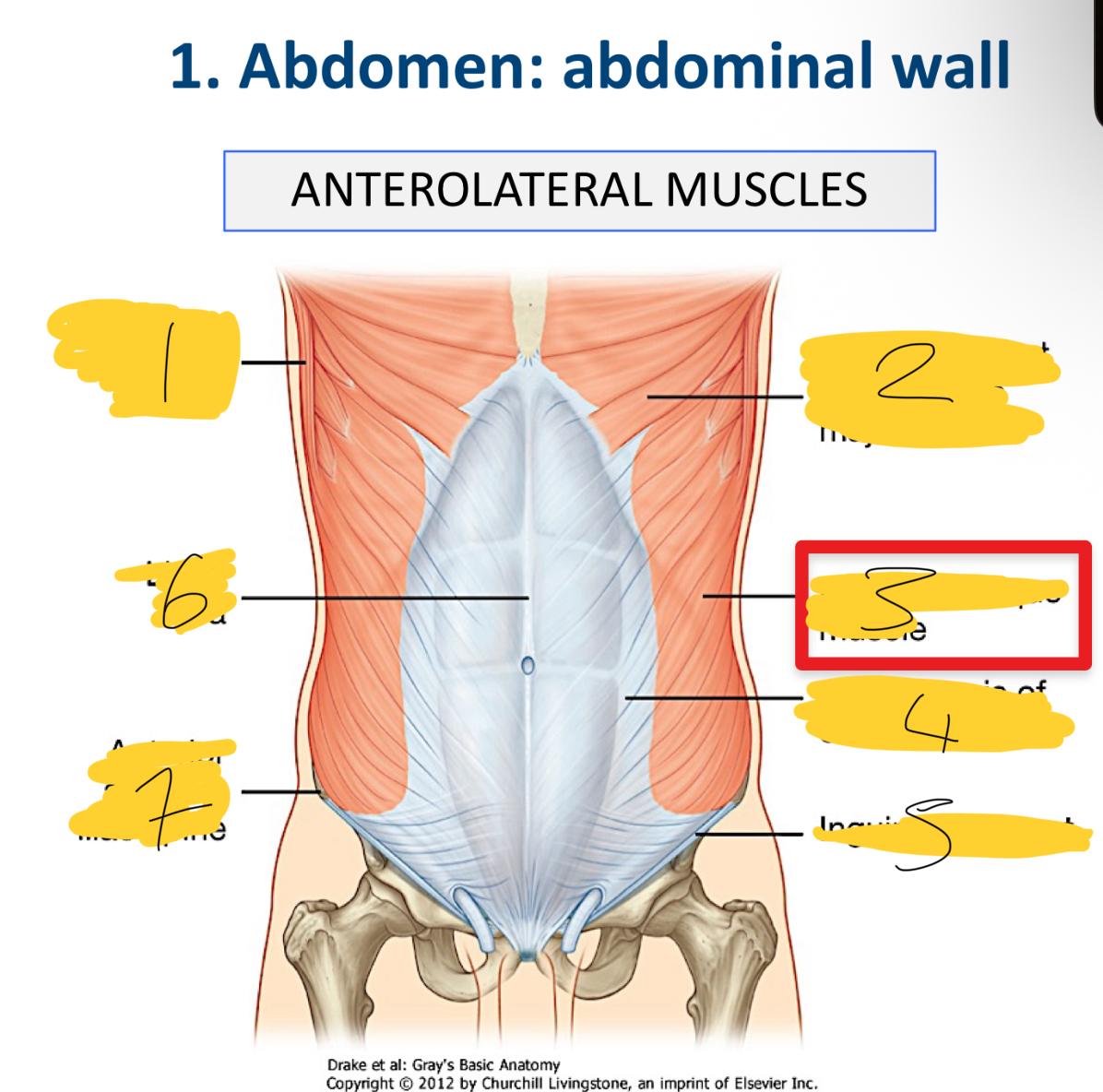
5
inguinal ligament
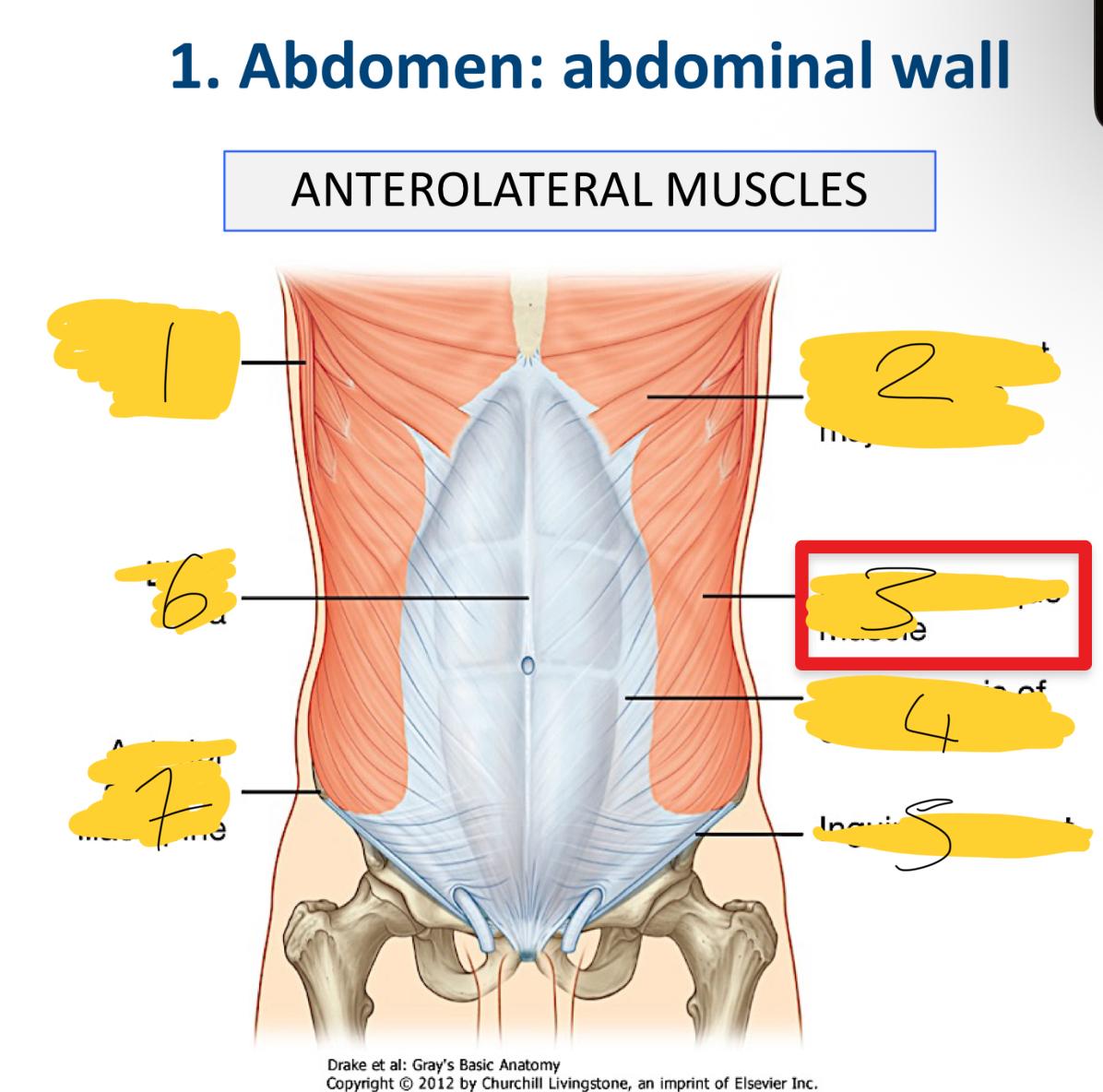
6
linea alba
7
anterior superior iliac spine
what does he aponeuroses cover
anterior part of the abdominal wall o the Linea alba
what are the associated ligaments to the external obliques
inguinal ligament
lacunar ligament
internal oblique muscles are …. muscles
flat and smaller and thinner and horizontal
how are internal oblique muscles
superomedial direction (facing up)
what does the aponeuroses do
blends into the Linea alba
transversus abdonminis muscles are …….
horizontal
flat
deep to the internal oblique muscle
the rectus abdomins muscle is a ….. muscle
flat, vertical
the rectus abdominis is intersected by …
3-4 transverse tendons
pyramidalis muscles are …
flat vertical muscles
pyramidalis muscle are ….. to the rectus abdominis muscle
anterior
always present (pyramidalis muscle) true/false
FALSE
where is the pyramidalis muscle
from pubis to the linea alba
which part of the rectus sheath covers the upper ¾ rectus abdominis
external oblique - covers all anterior (top)
internal oblique - half covers anterior(top) and half posterior(bottom)
transversus abdominis - covers all posterior (bottom)
which part of the rectus sheath covers the inferior ¼ of the rectus abdominis
external oblique, internal oblique and transversus abdomins covers all the anterior
does the inferior ¼ of the rectus abdominis have a posterior sheath
no - making it weaker
what is the arcuate line
it marks he lower limit of the posterior wall of the rectus sheath
located between your belly button and pubic bone
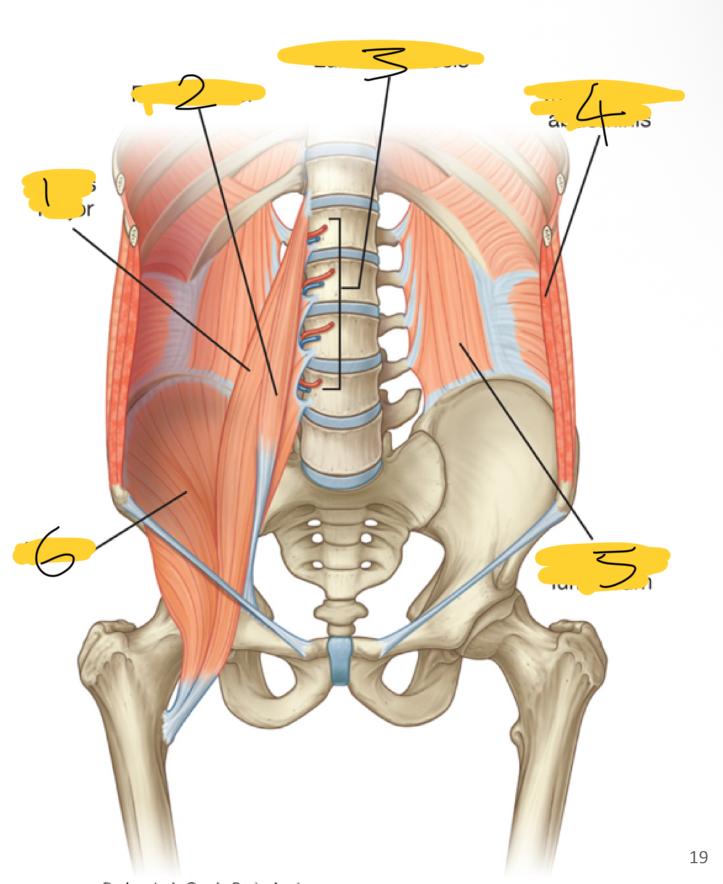
1
psoas major
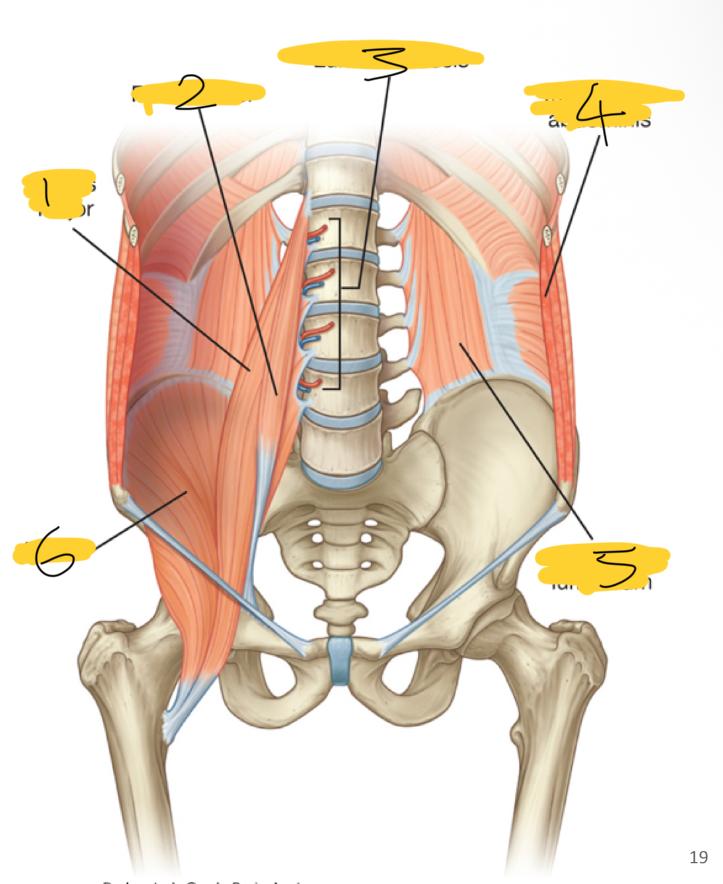
2
psoas minor
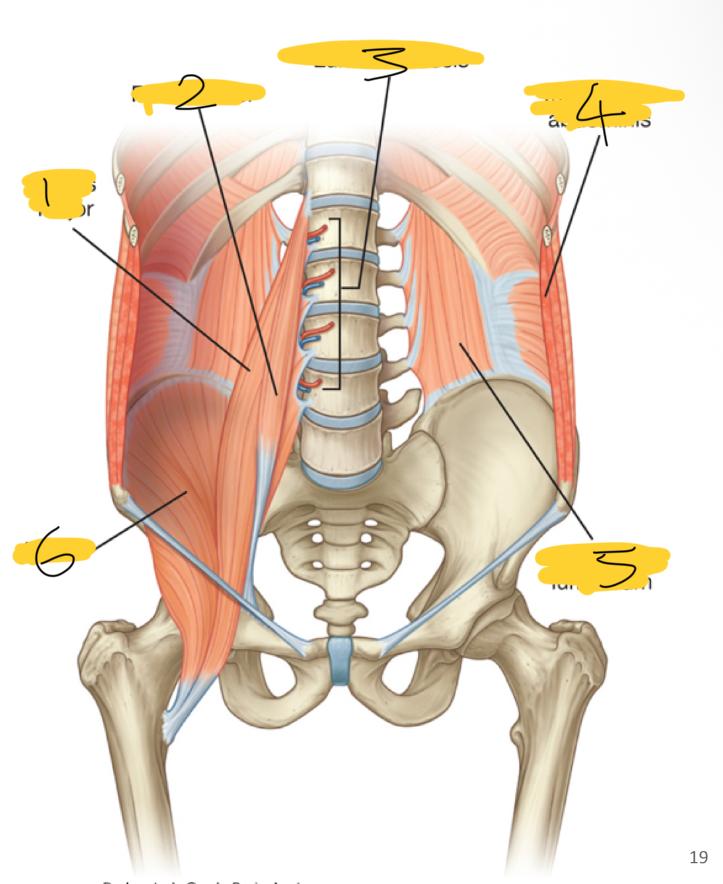
3
lumbar vessels
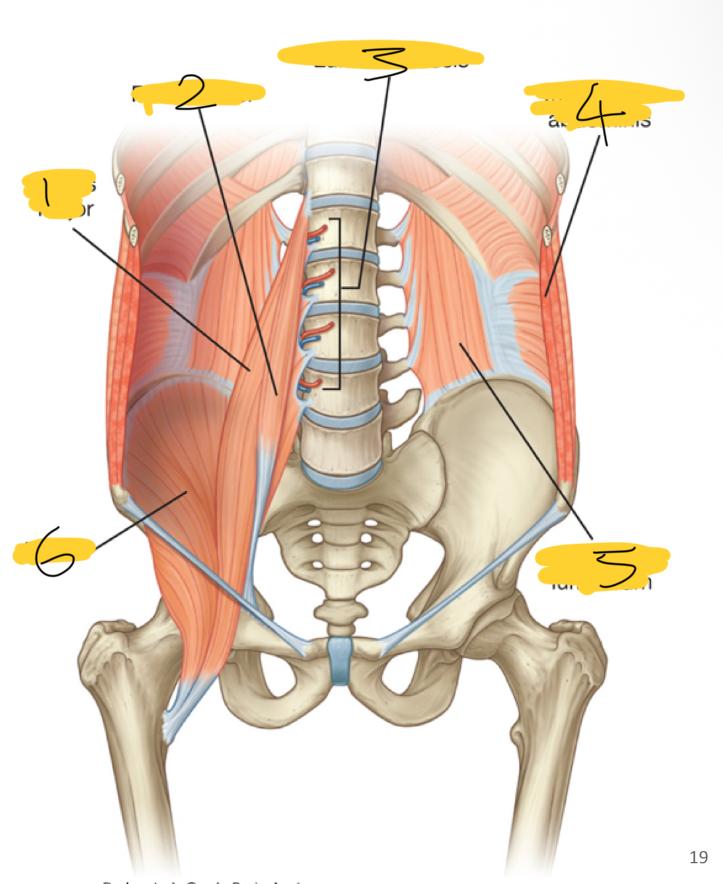
4
transversus abdominis
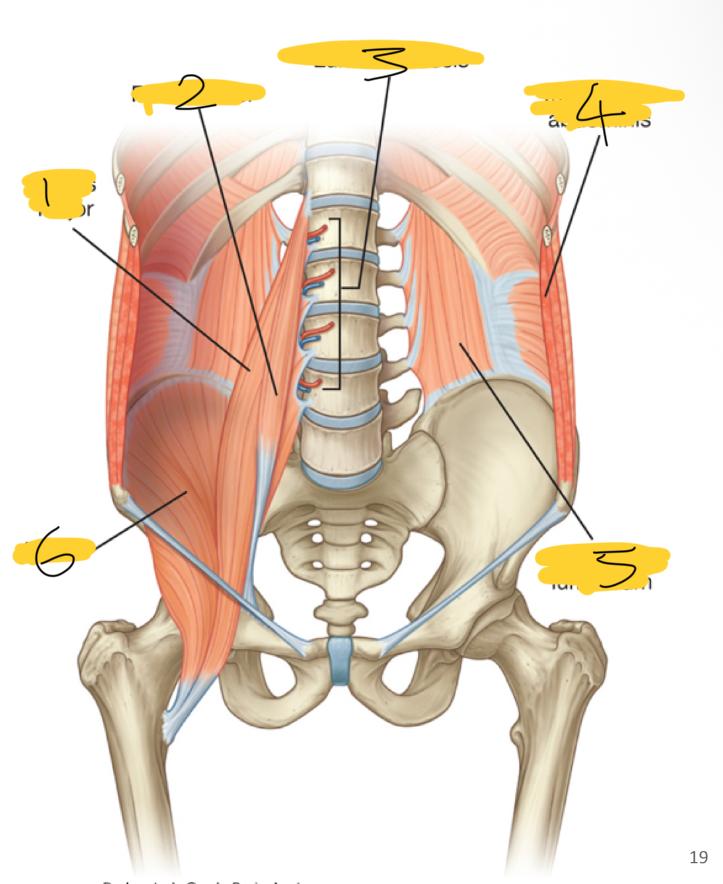
5
quadratus lumborum
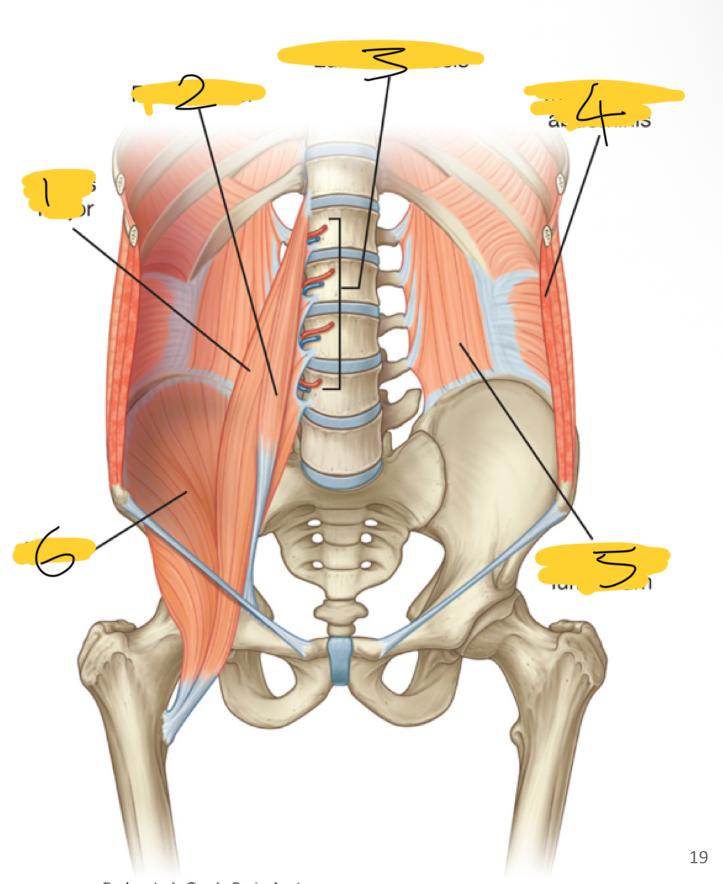
6
iliacus
what posterior wall muscles are medial
psoas major
psoas minor
what posterior wall muscles are lateral
quadratum lumborum muscles
what posterior wall muscles are superior
diaphragm
what superior wall muscles are inferior
iliacus muscles
the psoas minor muscles are always present true/false
false
quadratus lumborum where are they
fill the spaces between ribs XII and iliac crest
are they overlapped by the psoas major muscles
yes overlapped medially
what is the iliopsoas muscle comprised of
inguinal ligament
psoas major muscle
in the inferior of the diaphragm it has 2
left dome
right dome
what are the right and left domes caused by
underlying abdominal contents pushing these lateral areas upwards
what pushes these areas up on the right
liver
right kidney
right suprarenal gland
what pushes these areas up on the left
fundus of the stomach (top bit)
spleen
left kidney
left suprarenal gland
in the inferior diaphragm the right crus is ….
longest and broadest
the right crus is attached to
the bodies of lumbar vertebra (LI to LIII) and intervening intervertebral discs
the left crus is
shorter
the left crus is attached to
lumbar vertebrae (LI and LIII) and associated intervertebral disc
in the diaphragm how many hiatus and foramen?
2 hiatus and 1 foramen
what goes through the Aortic hiatus
aorta artery
azygos vein
what goes through Oesophageal hiatus
Oesophagus
what goes through Caval opening ?
inferior vena cava
right phrenic nerve
does the left phrenic nerve pass through the caval opening
NO - passes through muscular part of the diaphragm
what is the peritoneum
thin membrane lines the walls of the abdominal cavity and viscera
what is the Parietal peritoneum
lines walls of the abdominal cavity
what is the visceral peritoneum
covers the viscera - external surface