movement of water through root
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Where and how is water taken up?
By the root hair cells
crosses the cortex and enters the xylem in the centre of the root
root hair cells take up mineral ions by active transport
water potential decreases
water is taken up by osmosis
Three routes through the cortex
apoplast pathway
symplast pathway
vacuolar pathway
Apoplast pathway
travels through cell wall
water can enter the cell wall and move due to the cohesive force of water
water can move directly from cell wall to cell wall
molecules stick together, forming a continuous stream towards xylem
Open structure of cellular wall = little resistance = fastest route
(diffusion not osmosis as water does not cross a membrane)
Symplast pathway
moves through cytoplasm
water moves by osmosis
passes from cell to cell through pores in the cell wall called plasmodesmata
each cell further away from roots has a lower water potential so this is why water is able to move by osmosis
Vacuolar pathway
similar to symplast
water passes through vacuole
slowest as many membrane to cross
Three pathways of water through the root
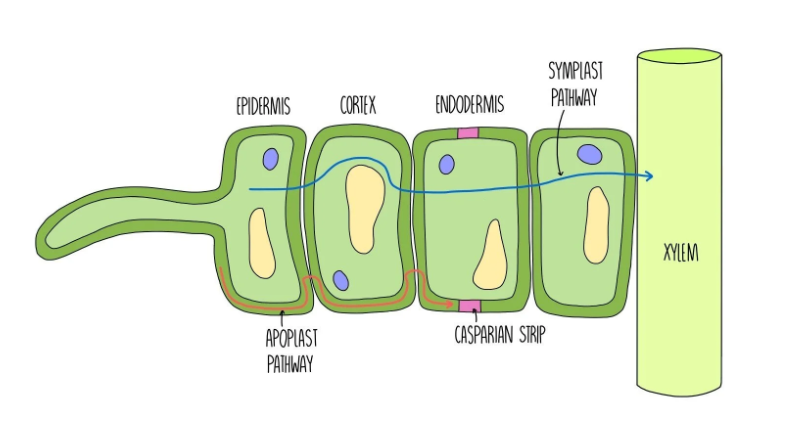
What happens when the water reaches the endodermis during the apoplast pathway?
apoplast pathway is blocked
by a waterproof strip in the cell walls called the Capsarian Strip
this is so water is forced to take the symplast pathway
meaning it will have to pass through a selectively permeable membrane
any toxins in the water will not pass through the membrane
it is a protection mechanism
what is an endodermis
an inner layer of cells in the cortex of a root surrounding a vascular bundle.
Adaptations of root hair cells
microscopic size = penetrate between soil particles
large SA : Vol ratio of hairs and there are thousands
each hair has thin walls = short distance for diffusion and osmosis
conc of solute in cytoplasm maintains water potential gradients
How does the concentration of solute in cytoplasm maintain water potential gradients? (in root hair cells)
soil water has low conc of dissolved mineral
therefore high water potential
cytoplasm in root hair cell - high conc of dissolved mineral
therefore low water potential