Repro Lab Practical #1
0.0(0)Studied by 1 person
Card Sorting
1/147
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:33 PM on 3/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
148 Terms
1
New cards
What is the main structural difference observed in cow and mare ovaries? Explain.
Relative location of the cortex vs. the medulla:
* In cow, cortex is on outside and in mare cortex in on inside.
* Mare must ovulate through the ovulation fossa whereas cows can ovulate over the whole surface of the ovary.
* In cow, cortex is on outside and in mare cortex in on inside.
* Mare must ovulate through the ovulation fossa whereas cows can ovulate over the whole surface of the ovary.
2
New cards
How are boars housed at the Swine Educational Unit, and why are they managed this way?
Boars are housed **individually** or in **group** **pens**, depending on their **age** and **whether they display aggressive behavior** towards the other boars
3
New cards
A piece of gauze was placed on top of the collection cup prior to semen collection. What is the purpose of the gauze?
To collect the gel fraction of the ejaculate/prevents the gel fraction from entering the semen collection cup
4
New cards
At what age will the NCSU Swine Educational Unit start to use a boar’s semen for breeding?
When the boar is 8 months of age
5
New cards
Which type of gloves were preferred during semen collection in boars? Why that type?
Vinyl gloves - reduce the chance of killing sperm cells
6
New cards
What prevents boars from being collected using an artificial vagina?
To ejaculate, boars require pressure in addition to the proper temperature. The amount of pressure on the boars glans penis can not be achieved with an artificial vagina, thus we collect via a gloved hand.
7
New cards
Identify the following acronyms:
a. GnRH
b. LH
c. E2
d. P4
e. PGF2a
a. GnRH
b. LH
c. E2
d. P4
e. PGF2a
a. Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone
b. Luteinizing Hormone
c. Estrogen or Estradiol
d. Progesterone
e. Prostaglandin F2alpha
b. Luteinizing Hormone
c. Estrogen or Estradiol
d. Progesterone
e. Prostaglandin F2alpha
8
New cards
Provide the Brand Name of the hormone or chemical you would use in the following scenario:
Inducing puberty in prepubertal gilts
Inducing puberty in prepubertal gilts
PG-600 or Matrix
9
New cards
Provide the Brand Name of the hormone or chemical you would use in the following scenario:
Superovulating embryo transfer donors in cattle
Superovulating embryo transfer donors in cattle
FSH-P, Super-OV, FollitropinV
10
New cards
Provide the Brand Name of the hormone or chemical you would use in the following scenario:
Controlling out-of-season or early-season breeding in mares
Controlling out-of-season or early-season breeding in mares
Regumate
11
New cards
Provide the Brand Name of the hormone or chemical you would use in the following scenario:
inducing luteolysis regression in cattle
inducing luteolysis regression in cattle
Lutalyse, Prostamate
12
New cards
Provide the Brand Name of the hormone or chemical you would use in the following scenario:
increasing intensity of uterine contractions during labor
increasing intensity of uterine contractions during labor
Oxytocin, Pinocin
13
New cards
Provide the Brand Name of the hormone or chemical you would use in the following scenario:
treating ovarian cystic follicles in cattle
treating ovarian cystic follicles in cattle
Cystorelin, Feragyl, Facteral
14
New cards
Provide the Brand Name of the hormone or chemical you would use in the following scenario:
Blocking ovarian function in cattle
Blocking ovarian function in cattle
CIDR, MGA, Progesterone
15
New cards
Provide the Brand Name of the hormone or chemical you would use in the following scenario:
Increasing milk yield
Increasing milk yield
Posilac
16
New cards
How would you interpret the results of weekly progesterone assays with following profile? (L=low, M=medium, H=high)
\
L-H-H
\
L-H-H
Ovulated approximately 14 days ago, retest in 7 days to determine pregnant or open
17
New cards
How would you interpret the results of weekly progesterone assays with following profile? (L=low, M=medium, H=high)
\
M-L-H
\
M-L-H
had subfunctional CL, it regressed & ovulated in past 7 days
18
New cards
How would you interpret the results of weekly progesterone assays with following profile? (L=low, M=medium, H=high)
\
L-L-L
\
L-L-L
Anestrous, non-functioning ovary, not ovulating
19
New cards
How would you interpret the results of weekly progesterone assays with following profile? (L=low, M=medium, H=high)
\
H-H-H
\
H-H-H
Anestrous, but pregnant
20
New cards
How would you interpret the results of weekly progesterone assays with following profile? (L=low, M=medium, H=high)
\
L-M-L
\
L-M-L
Ovulated, but had a subfunctional CL and it regressed
21
New cards
How would you interpret the results of weekly progesterone assays with following profile? (L=low, M=medium, H=high)
\
L-L-H
\
L-L-H
Recently ovulated in past 7 days
22
New cards
What other body fluids could be used for monitoring hormones?
Milk, Urine, Salvia, CNS fluid, Feces, Blood, Sweat
23
New cards
What are the advantages of using this type of kit to determine when to breed your cows?
Determine cyclic animals, Identify short cycles, better management of animals estrous cycle
24
New cards
What are the disadvantages of using this type of kit to determine when to breed your cows?
Cost, Time, inconsistent testing, may claim an animal is pregnant when she is not (false positives)
25
New cards
Draw a graph that illustrates the bovine estrous cycle. Make sure you include the following hormones: progesterone, estrogen, and PGF2α.
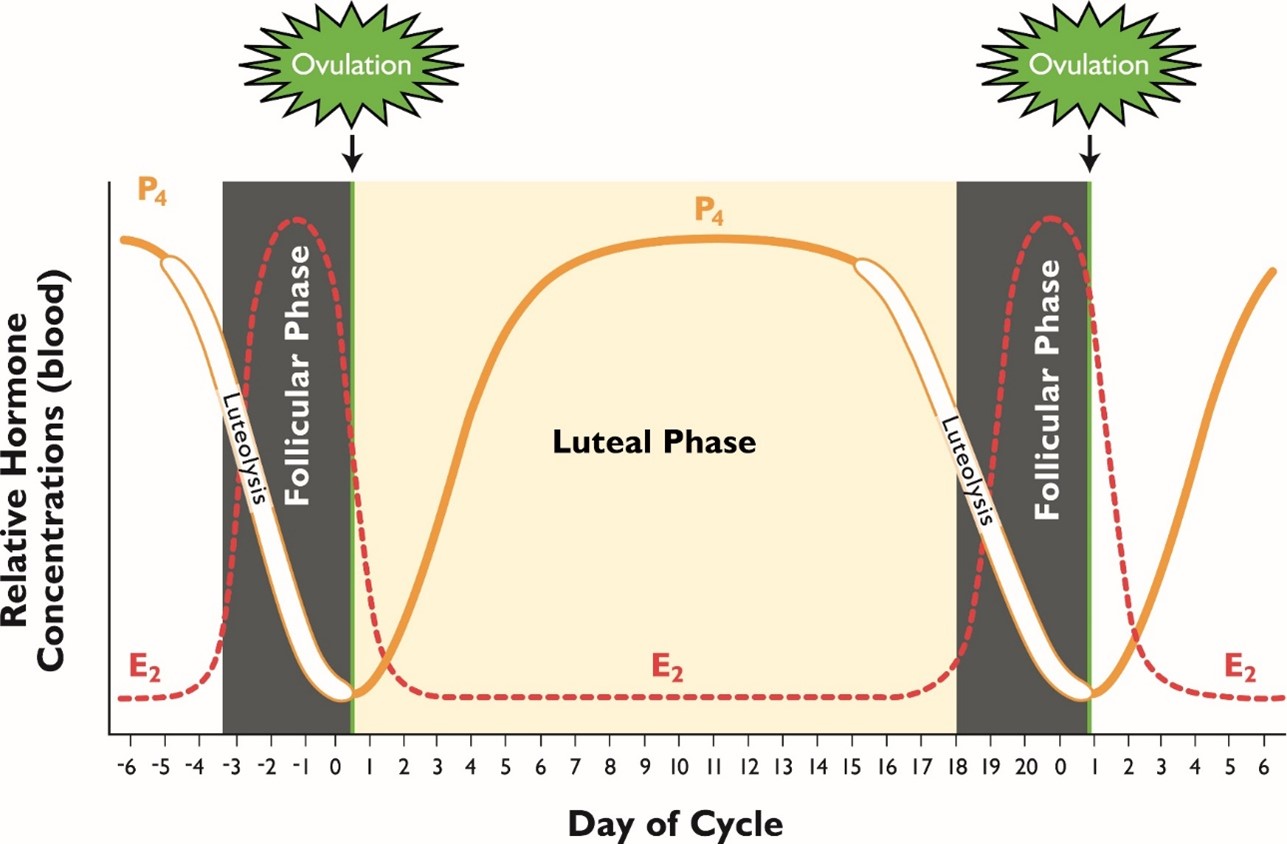
26
New cards
What are the two exogenous reproductive hormones used in the NC Synch protocol.
* Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (Factrel)
* Prostaglandin F2a (Lutalyse)
* Prostaglandin F2a (Lutalyse)
27
New cards
What is the length of the goat estrous cycle, and when do these animals generally display estrus?
Estrous Cycle Length – 21 days
Seasonal Breeders – display estrus in Fall
Seasonal Breeders – display estrus in Fall
28
New cards
What are two signs/symptoms that a doe is in estrus?
* Interest in buck
* Raised tail
* Vocalizations
* Red/swollen vulva
* Sometimes mucus from the vagina is present
* Raised tail
* Vocalizations
* Red/swollen vulva
* Sometimes mucus from the vagina is present
29
New cards
What is the site of semen deposition by AI and natural service in the doe?
AI – Uterine Body
Natural Service - Vagina
Natural Service - Vagina
30
New cards
What are the advantages of using artificial insemination in small ruminants?
\
* Introduce new genetics
* Introduce new breeds
* Small herd and don’t want to mess with a buck
* Introduce new genetics
* Introduce new breeds
* Small herd and don’t want to mess with a buck
31
New cards
What are the disadvantages of using artificial insemination in small ruminants?
* Requires more labor
* More invasive
* Requires more equipment
* More invasive
* Requires more equipment
32
New cards
What is the flushing effect?
Increase the amount of feed prior to breeding, mostly increasing energy, about 1 month before introducing bucks.
* Hope to increase body weight, ovulation rate, and therefore litter size
* Hope to increase body weight, ovulation rate, and therefore litter size
33
New cards
What are the restrictions in place when using the flush effect? When will it work/not work?
* Must continue through breeding season and for 30-40 more days.
* Doesn’t work in does that are too fat (BCS 4-5) or too thin (BCS 2 or less)
* Doesn’t work in does that are too fat (BCS 4-5) or too thin (BCS 2 or less)
34
New cards
What is the “buck effect”?
Strategic exposure of does to intact males will result in the doe displaying estrus approximately 7 to 10 days after the introduction of the buck.
35
New cards
What are the restrictions in place when using the buck effect? Where does the buck need to be?
* Bucks need to be isolated from does for this procedure to be effective.
* Buck must be out of the doe’s line of sight and sense of smell for an extended period of time, perhaps as long as several months
* Buck must be out of the doe’s line of sight and sense of smell for an extended period of time, perhaps as long as several months
36
New cards
What is the purpose of conducting a breeding soundness exam (BSE) on bulls?
The purpose is to identify bulls that are capable of breeding and to identify individuals that may be injured and unable to breed females.
37
New cards
How often should a BSE exam be done?
A BSE should be conducted 30 to 60 days before very breeding season.
38
New cards
What is the main purpose of collecting heifer pelvic measurements?
Screening tool to identify heifers likely to have calving difficulties
39
New cards
What is the minimum scrotal circumstance size a yearling bull must have to pass its breeding soundness exam at the Beef Educational Unit?
32 cm
40
New cards
Name at least 1 factor that a breeding soundness exam in bulls doesn’t test for.
Libidio
41
New cards
What is the name of the tool used to take heifer pelvic measurements?
Pelvimeter
42
New cards
What is a good male-to-female ratio for the average bull?
For young bulls a ratio of 1 bull to 12 females.
For mature bulls a ratio of 1 bull to 36 females
For mature bulls a ratio of 1 bull to 36 females
43
New cards
Number of females should equal the number of months old the bull is.
Assuming they are in good health and pass the BSE
44
New cards
How do you calculate the measurement for the total heifer pelvic area?
Multiply the measurement for the height by the width measurement, this gives the square area (cm^2)
45
New cards
When is the best time to take hiefer pelvic measurements? What is the minimum pelvic measurement that is recommended?
It is recommended to do this 4-6 weeks before breeding season. No less than 140 cm^2
46
New cards
Should heifer pelvic measurements be used as a screening tool or a selection tool?
A screening tool - If you use it as a selection tool you will simply be picking your larger framed animals. Ideally, you should identify the animals with abnormally small pelvic measurements and cull them.
47
New cards
Describe the the estrous scale used at the Equine Educational Unit. Be sure to inclde what each number represents
0 = Violent Behavior
1 = Indifferent Behavior
2 = Slightly Interested
3 = Interested, Winking, may urinate
4 = Greatly interested, Urinating, Squatting, and will lean into stallion
1 = Indifferent Behavior
2 = Slightly Interested
3 = Interested, Winking, may urinate
4 = Greatly interested, Urinating, Squatting, and will lean into stallion
48
New cards
How often should you tease mares to determine when they are ready to breed?
Everyday or every other day
49
New cards
Mares are classified as what type of breeders and when do they display estrus?
Long day breeder, only display estrus when daylight is increasing
50
New cards
How many progressively motile sperm should be in an on the farm breeding dose?
500 Million
51
New cards
How many progressively motile sperm should be in a shipping dose?
1 Billion
52
New cards
Name 2 things that we look for in a semen evaluation.
Color and Volume of the ejaculate
Sperm Concentration
Sperm Motility
Sperm Viability
Sperm Morphology
Sperm Concentration
Sperm Motility
Sperm Viability
Sperm Morphology
53
New cards
What kills sperm?
Everything kills sperm
54
New cards
What type of artifical vagina is used at the Equine Educational Unit and why is this type prefered?
Used to use the Colorado as it maintains temperature and pressure better; have now switched to the Missouri as it is **lighter**
55
New cards
Free teasing
Stallion comes up to fence, mares are loose OR stallion in a small pen, mares are loose in pasture around him
56
New cards
In hand teasing
Stallion comes up to fence, mares are walked up individually
57
New cards
Stall Teasing
stallion walked up down barn aisle, mares are in stalls
58
New cards
Cystorelin, Fertagyl, Factrel Hormone + Structure
GnRH (peptide)
59
New cards
Cystorelin, Fertagyl, Factrel Use
Treatment of Cystic Ovaries, stimulate LH and FSH
60
New cards
Cystorelin, Fertagyl, Factrel Species
Cattle (dairy)
61
New cards
Oxytocin Use
Stimulates Milk letdown, Stimulates uterine contractions
62
New cards
Oxytocin Species
ALL - Cattle, Horses, Swine, Sheep, Dogs
63
New cards
Lutalyse, Prostamate Hormone/Structure
Prostaglandins (PGF2a)
64
New cards
Lutalyse, Prostamate Use
Regress CL to control the onset of estrus, induce parturition
65
New cards
Lutalyse, Prostamate Species
Cattle, Horses, Swine
66
New cards
pLH Hormone/Structure
Gonadotropins (LH) - protein
67
New cards
pLH use
Induction of ovulation
68
New cards
pLH Species
ALL
69
New cards
Follutein, Pregnyl Hormone/Structure
Gonadotropins (hCG) - protein
70
New cards
Follutein, Pregnyl Use
Treatment of Cystic Ovaries, Induce ovulation
71
New cards
Follutein, Pregnyl Species
Cattle
72
New cards
FSH-p, Folltropin-V, Super-OV Hormone/Structure
Gonadotropins (FSH) - protein
73
New cards
FSH-p, Folltropin-V, Super-OV Use
Superovulation of embryo donors
74
New cards
FSH-p, Folltropin-V, Super-OV Species
Cattle, Horses, Swine, Sheep, Dogs
75
New cards
Gestyl Hormone/Structure
Gonadotropins (PMSG) - protein
76
New cards
Gestyl Use
Superovulation, stimulatation of estrus during anestrous
77
New cards
Gestyl Species
Cattle
78
New cards
P.G. 600 Hormone/Structure
Gonadotropins (PMSG+hCG) - protein
79
New cards
P.G. 600 Use
Induction of estrus in anestrous gilts and sows
80
New cards
P.G. 600 Species
Swine
81
New cards
Posilac Hormone/Structure
Somatotropin (bGH or bST) - protein
82
New cards
Posilac Use
Increase milk production
83
New cards
Posilac Species
Cattle
84
New cards
Regumate Hormone/Structure
Progestogens (Progesterone) - steroid
85
New cards
Regumate Use
Synchronize estrus in mares or cyclic pigs, suppress foal heat
86
New cards
Regumate Species
Swine, horses
87
New cards
Melengesterol Acetate Hormone/Structure
Progestogens (Progesterone) - steroid
88
New cards
Melengesterol Acetate Use
Suppress or Synchronize heat
89
New cards
Melengesterol Acetate Species
Cattle
90
New cards
Megestrol Acetate (Ovaban) Hormone/Structure
Progestogens (Progesterone) - steroid
91
New cards
Megestrol Acetate (Ovaban) Use
Prevention of estrus
92
New cards
Megestrol Acetate (Ovaban) Species
Dogs, Cats
93
New cards
Depo-Provera Hormone/Structure
Progestogens (Progesterone) - steroid
94
New cards
Depo-Provera Use
Prevention of estrus
95
New cards
Depo-Provera Species
Dogs, cats
96
New cards
Fluorogesterone Acetate Sponges Hormone/Structure
Progestogens (Progesterone) - steroid
97
New cards
Fluorogesterone Acetate Sponges Use
Synchronize estrus
98
New cards
Fluorogesterone Acetate Sponges Species
sheep/goats
99
New cards
CIDR Hormone/Structure
Progestogens (Progesterone) - steroid
100
New cards
CIDR Use
Synchronize estrus