1.1.3 Demand, Supply and the market equilibrium
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Theory of Demand
At higher prices, a lower quantity will be demanded than at lower prices, and vice versa.
Determinants of Demand
Income
Prices of complements and substitutes
Tastes and fashions
Advertising
Population
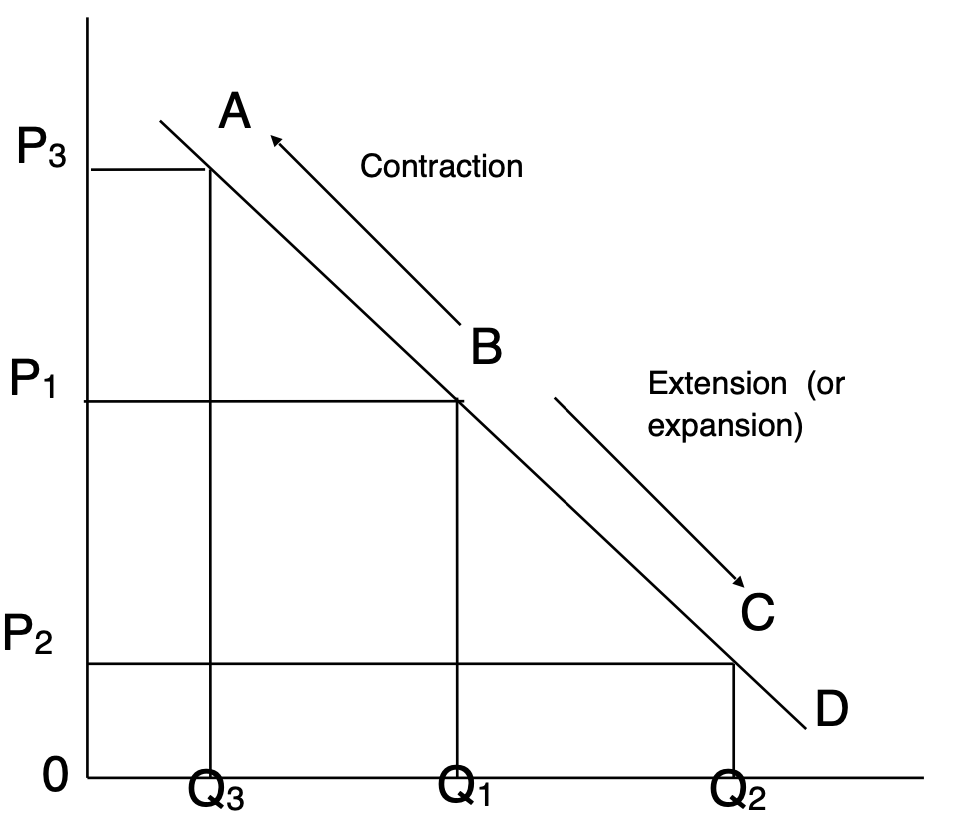
Cause of movements along a Demand Curve
Price determinants
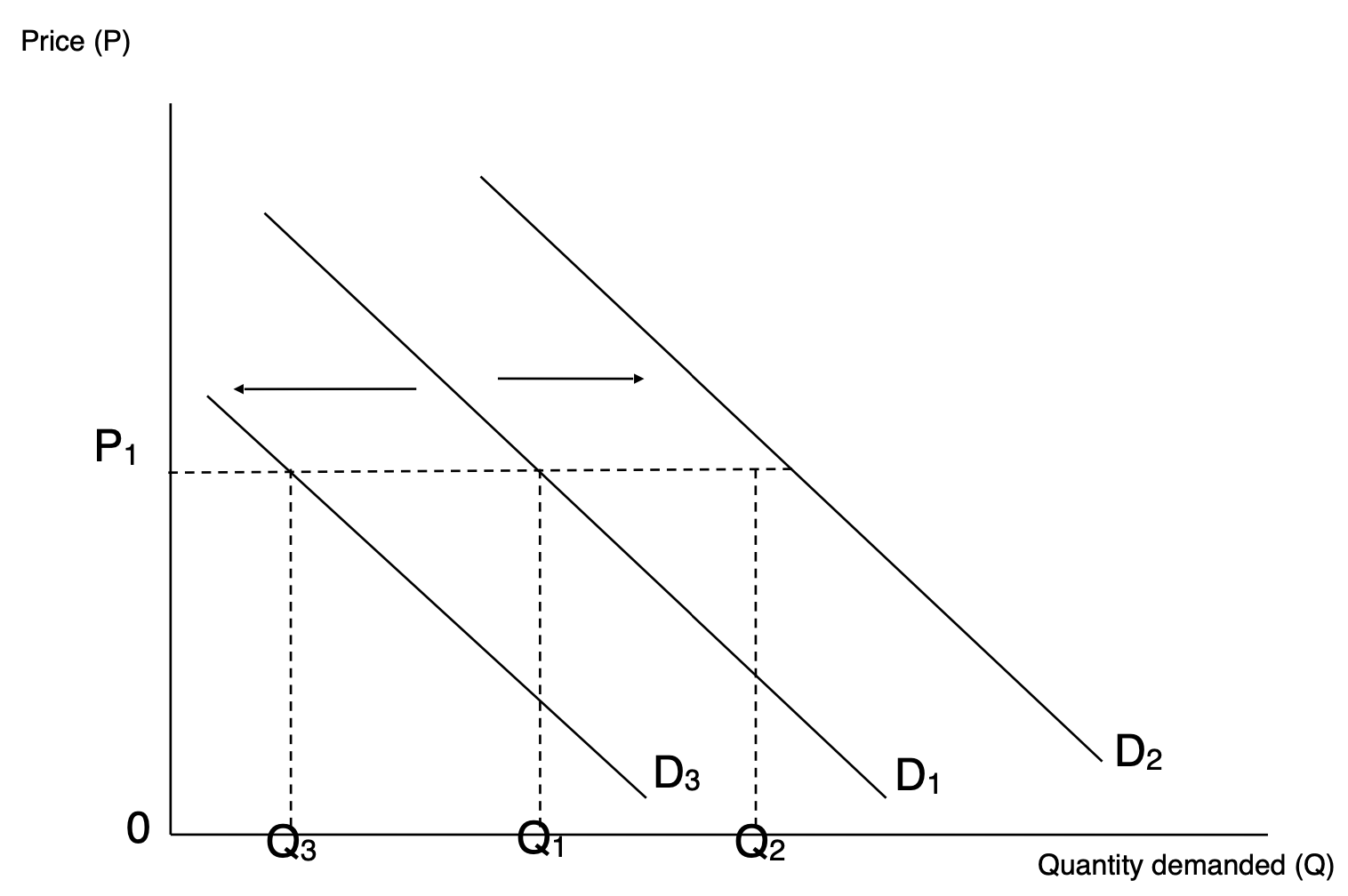
Cause of shifts along a Demand Curve
Non-price determinants - will cause the quantity demand to change
Supply Curve
How much of a product sellers are willing to supply at different prices
(between price and quantity supplied)
Factors affecting Supply
Prices of factors of production
Technology
Taxes
Subsidies
Labor productivity
Number of firms in an industry
Natural factors (e.g. weather)
Cause of movements along a Supply Curve
Price variations
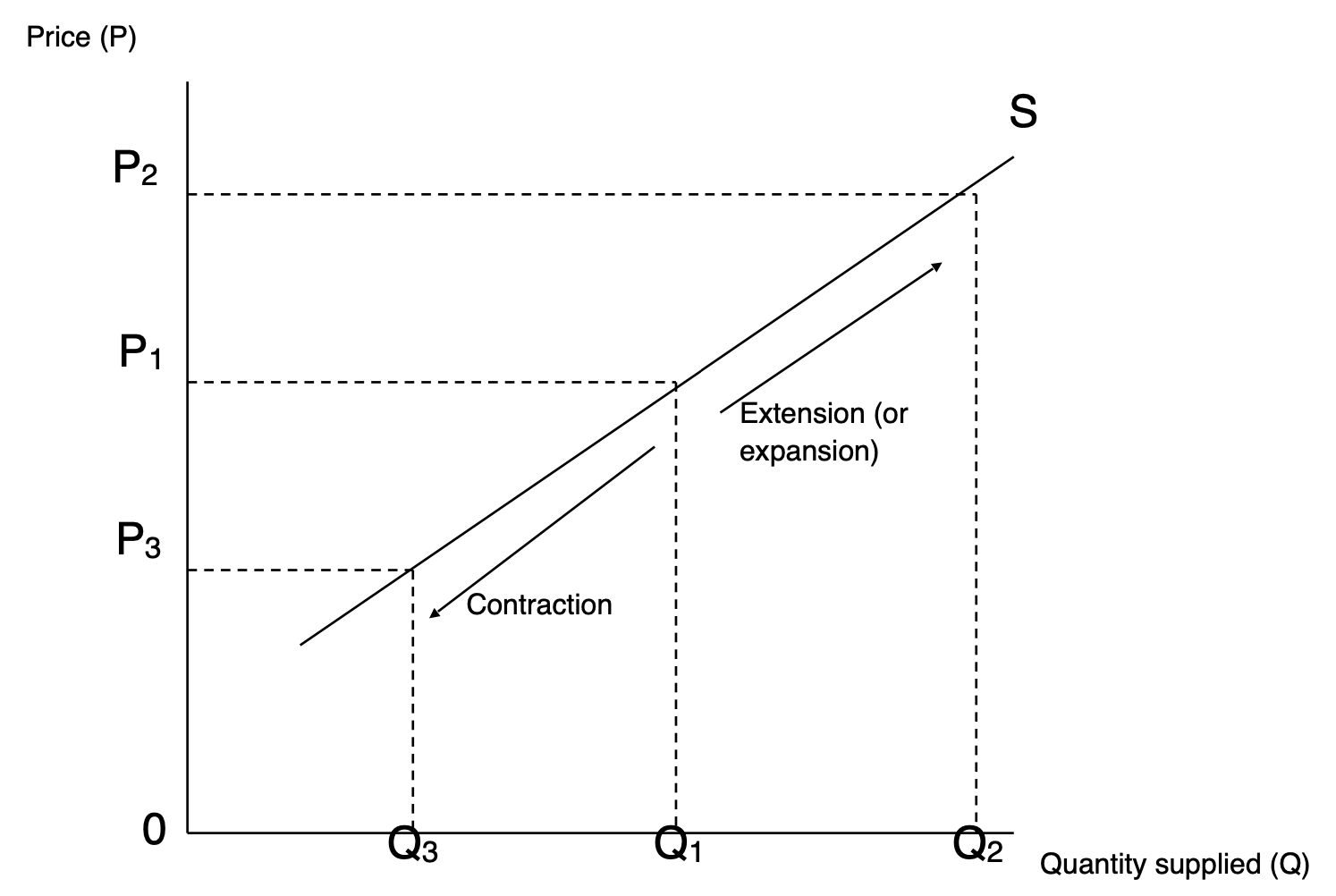
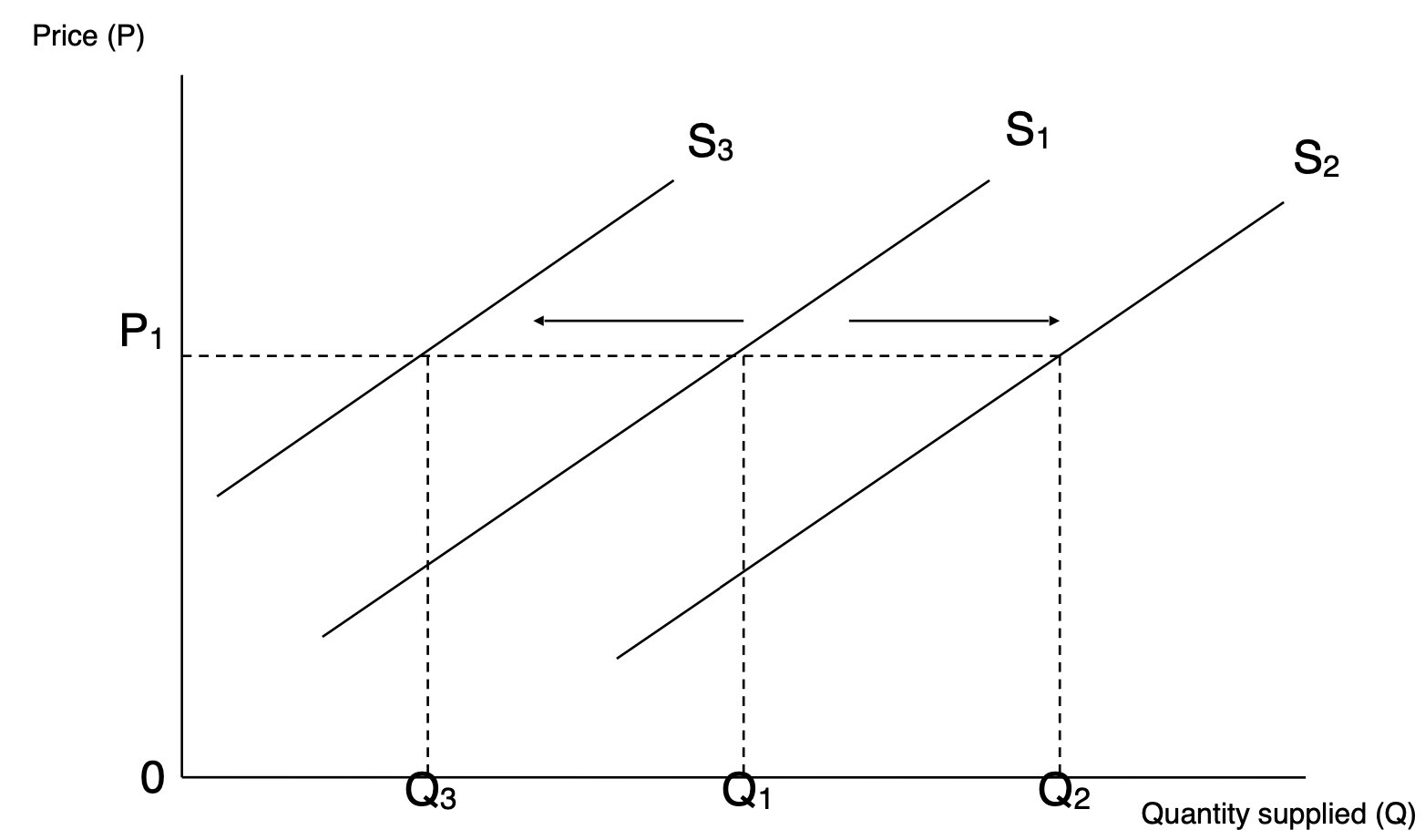
Cause of shifts of a Supply Curve
Alterations in non-price determinants (like technology, costs and labor productivity)
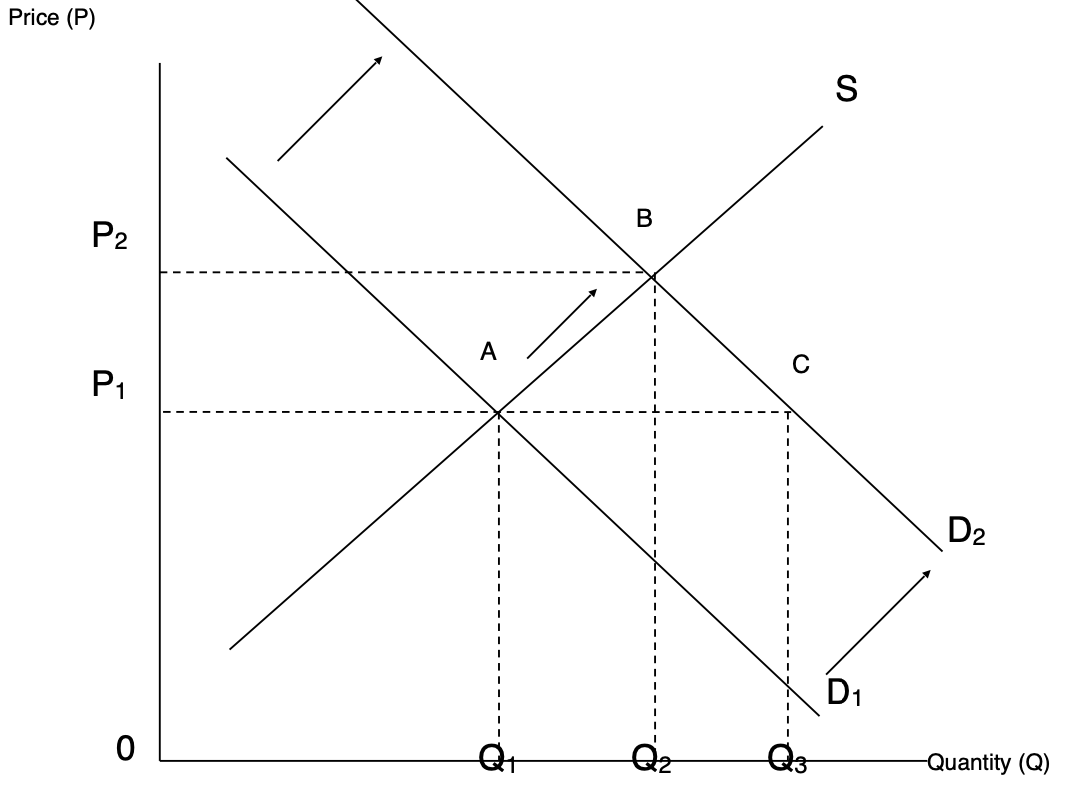
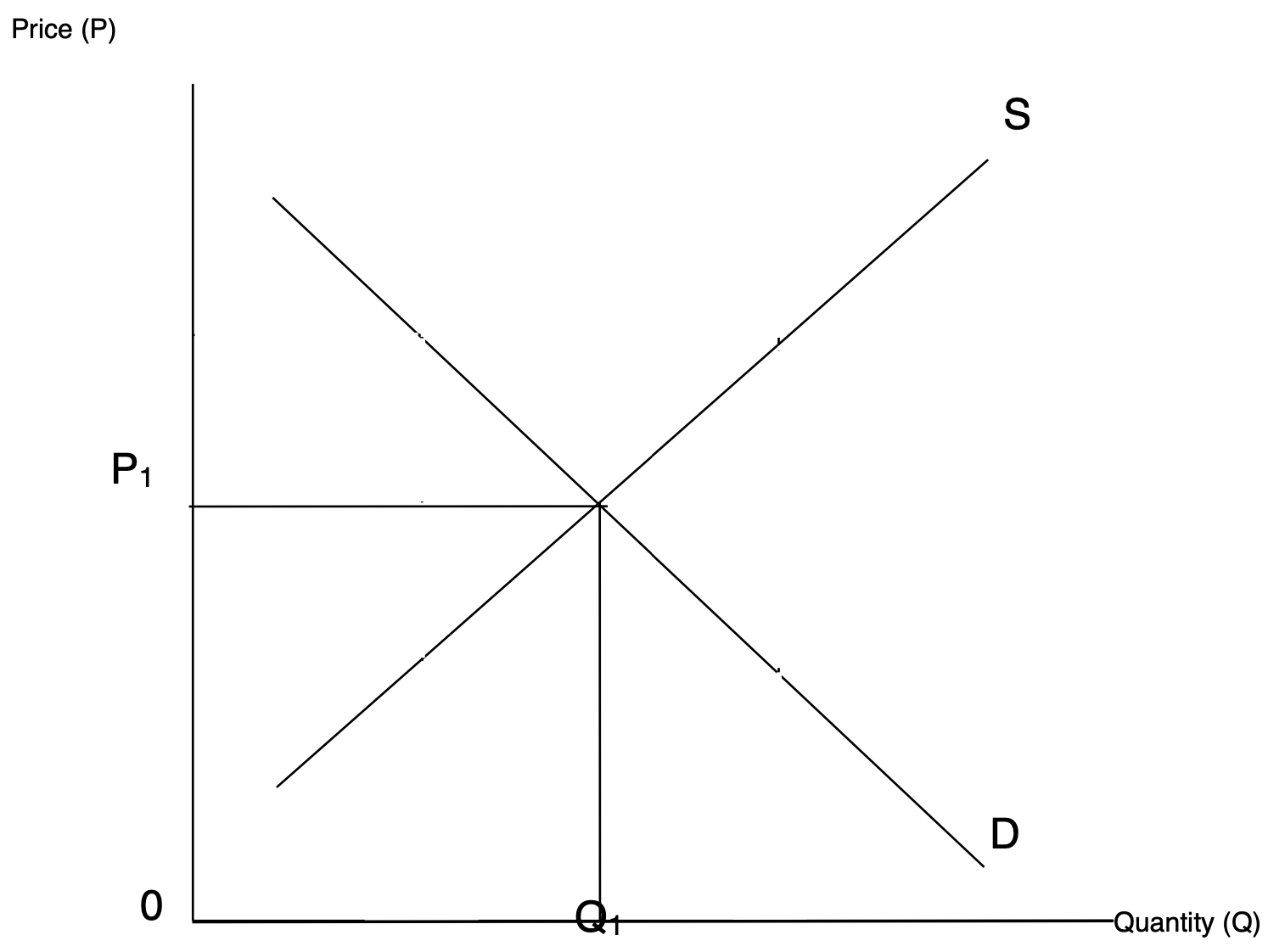
Equilibrium Price
The price where supply equals demand, leading to a state of ‘rest’ in the market, determined by the intersection of the demand and supply curves.
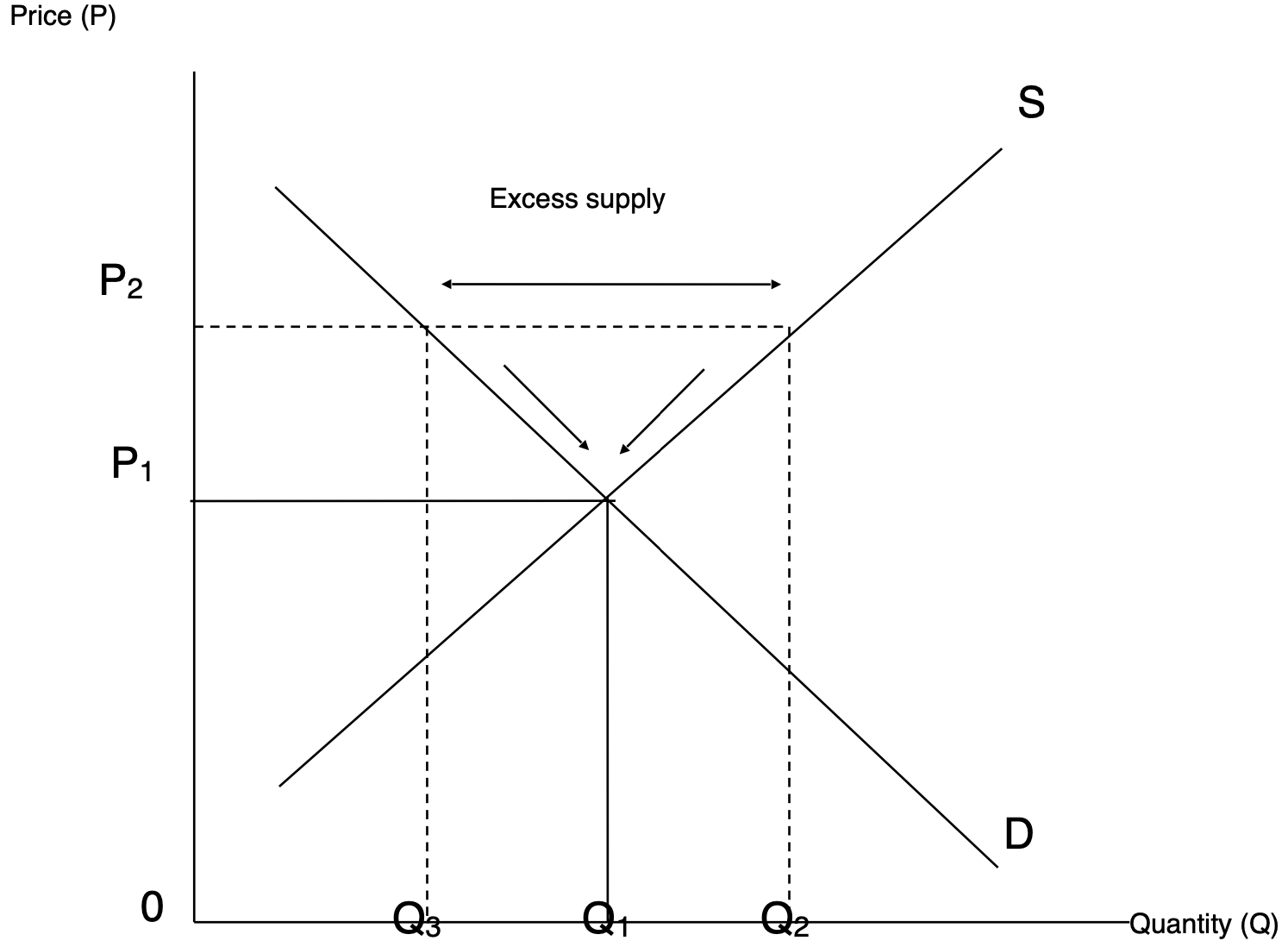
Excess supply on supply and demand diagram - how to fix this
There is a higher supply of the products than there is demand; a surplus
To fix, lower price temporarily (sale) until excess stock is sold
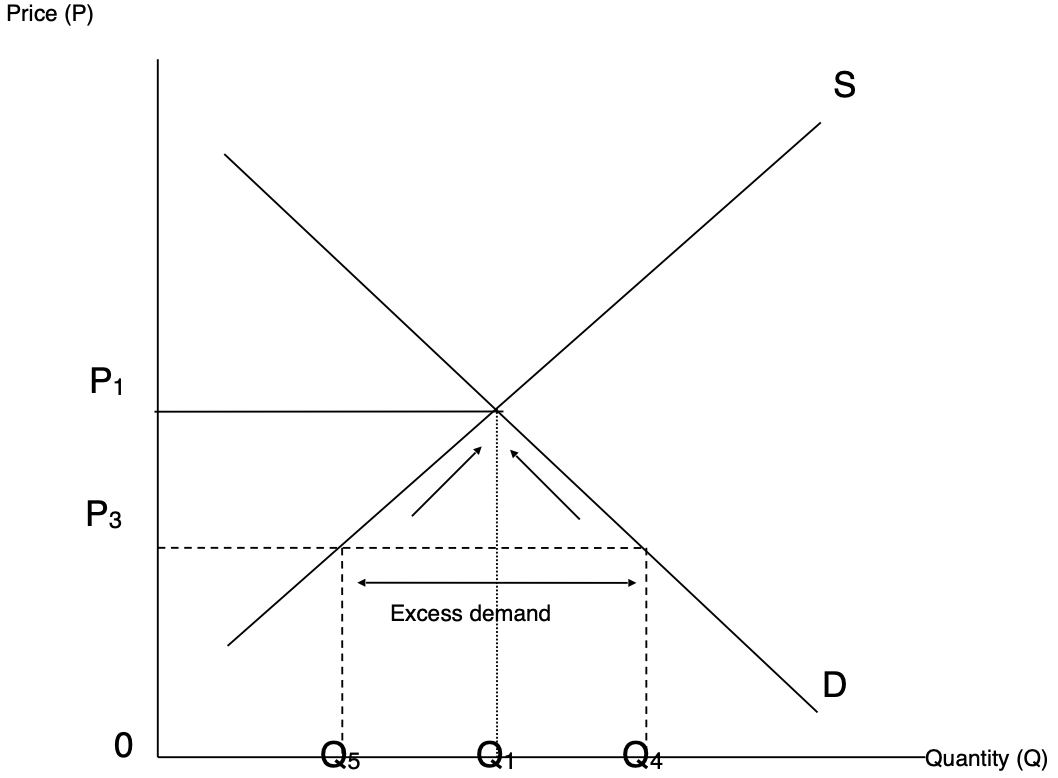
Excess demand on supply and demand diagram - how to fix this
Demand is higher than the amount that can be supplied, to combat:
Raise the price until demand evens out it is justified due to the popularity of the good- people will begin to buy less, and extra revenue is made
Shifts in Supply and Demand
Changes in equilibrium price due to shifts in demand or supply curves, leading to adjustments in price levels to match supply and demand.