6. Treatment
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Purpose & types of Colorectal cancer treatments
What is the treatment modality used on most colorectal cancer patients?
Surgery
What is the treatment of choice for colorectal cancer?
Surgery
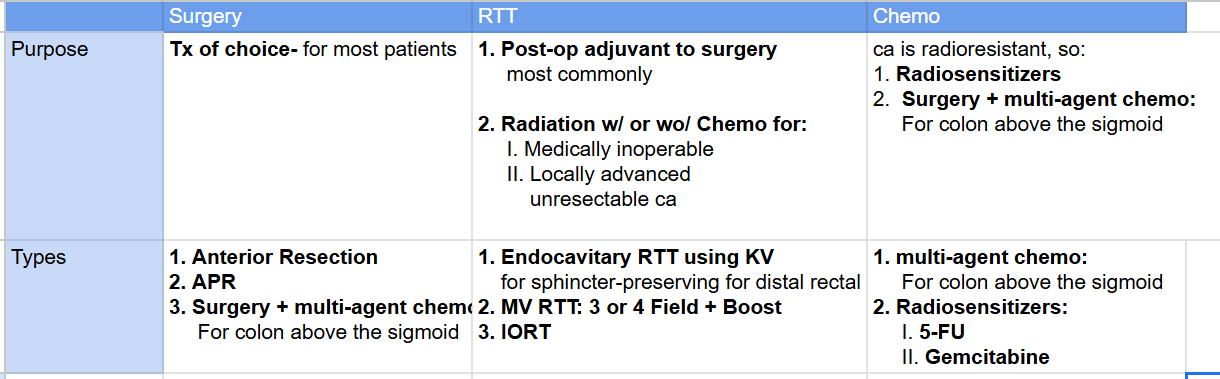
What are the 3 surgery techniques used?
Anterior Resection
APR
Surgery + Multi-agent chemo
What is Anterior Resection?
en bloc tumor removal + lymph node dissection
Bowel is reanastomosed (reattached)- so colostomy is not required
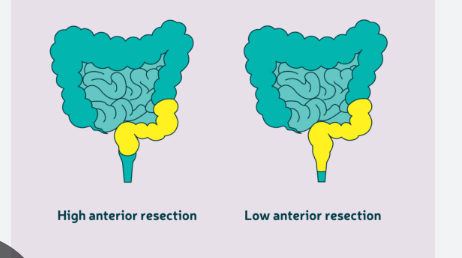
What does APR stand for?
Abdominoperineal Resection
On what patients is APR used?
rectal cancer in lower 3rd of rectum
Removes anus so colostomy required
What is “surgery + multi-chemo agent” used for
colon above the sigmoid
T/F: Colon cancer is chemosensitive
False: its chemoresistant
What type of chemo is given to colorectal patients as a chemosensitizer
5-FU
Gemitabine
What are the 2 purposes of delivering RTT to colorectal cancer patients?
Most commonly as: Post-Op adjuvant to surgery
RTT + Chemo for disease that is:
Medically inoperable
Locally advanced unresectable cancer
What is the major advantage of post-op RTT adjuvant to surgery?
The physician has:
pathologic confirmation &
extent of tumor spread to lymph nodes or distant mets
Types of RTT used:
Endocavitary RTT w/ KV (contact therapy)
MV RTT: 3 or 4 field + Boost
IORT boost
What is the purpose of using Endovacitary RTT?
To possibly offer a sphincter-preserving technique for patients with distal rectal cancers confined to the bowel wall
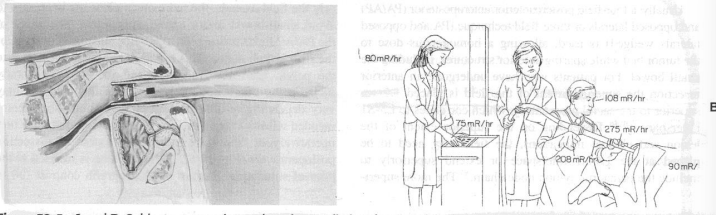
Endocavitary RTT
dose
number of treatments
Dose/ Treatment: 30Gy
# of txs: 4 txs, 2 weeks apart each
FYI:
week 0: 30 Gy
week 2: 30 Gy
week 4: 30Gy
week 6: 30 Gy
For MV treatments to treat colorectal cancer, What areas do we treat?
Primary tumor, and
Pelvic nodes
Via a boost field/ shrinking field
Field arrangments for colorectal cancer
Option 1: 3 field prone: 1 PA + 2 lats w/ wedges
Option 2: 4 field: AP, PA, 2 lats
Which field arrangement for colorectal cancer causes more bladder irradiation?
4 field
Field borders for 4 field for colorectal cancer
AP/PA fields
Superior: L4/5 interspace (disc space) or Smoke Stack
Inferior: Just below obturator foramen; 2 cm + margin from the tumor
Lateral: 2cm lateral to pelvic side wall (FY: so you tx iliac nodes)
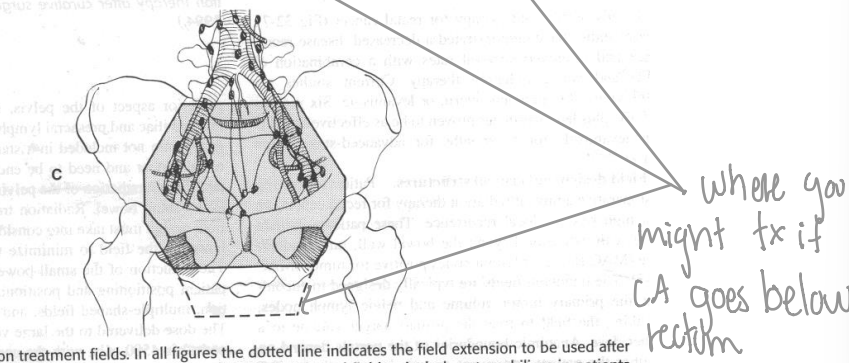
Field borders for 4 field for colorectal cancer
Lateral fields (assuming 3 field technique)
Anterior: symphysis pubis; ensuring tx of external iliac nodes
Posterior: 1.5-2.0 cm behind the anterior bony sacral margin
What organs do we protect using a 3 field technique/
remaining bowel
bladder
bone marrow
SIM markings for colorectal cancer
BB on anal verge- perineal reference
Iodine contrast-soaked tampon- vagina reference
Dose for MV technique for colorectal cancer patients and # of weeks
50-55Gy; higher doses if small bowel can be excluded from field
6-5.5 wks
What does IORT stand for?
Intraoperative Radiation Therapy
What is IORT used for?
Boost technique
What dose is used for IORT for colorectal cancer?
10-20 Gy in a single fraction
T/F:IORT is a better boost than a shrinking field technique
False: it has higher toxicity, does not show improvement in survival, and contraindicated in patients with distant mets
RADIATION SIDE EFFECTS
What is the primary dose-limiting structure for colorectal cancer patients?
small bowel (fyi: causes diarrhea)
If treating lesion in ascending or descending colon, dose-limiting structures include
kidney and small bowel
What are severe effects of RTT to treat colon cancer?
adhesions
enteritis
obstruction
What treatment devices can be used to displace the small bowel?
belly-board
false table-top
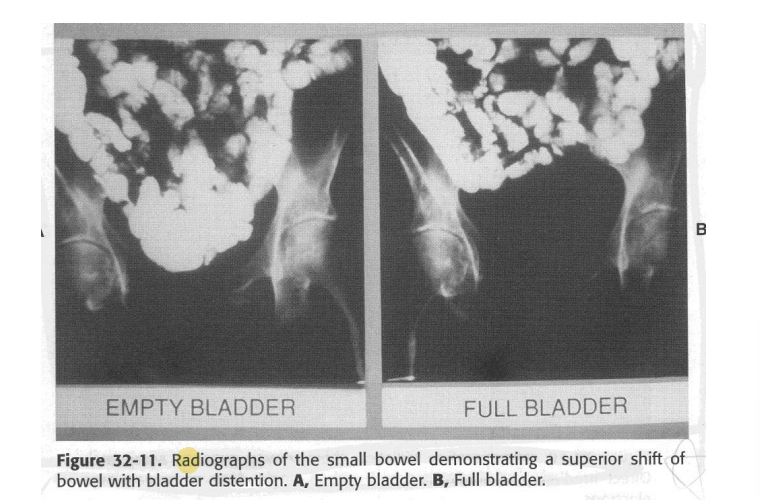
Bladder should be (empty/full) when treating colorectal cancer with RTT. WHy?
full
to displace small bowel
Other side effects when treating colorectal cancer with RTT
Acute/ Brisk erythema in gluteal fold