Honors Chemistry Unit 4-5 Test WCHS Mrs. Herrick
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Dalton’s Atomic Theory
Matter is made of tiny atoms; atoms of the same element are identical, atoms of different elements are different. Atoms combine in whole-number ratios to form compounds, and chemical reactions rearrange atoms without creating or destroying them
Billiard Ball Model
John Dalton’s model of the atom, which describes atoms as solid, indivisible spheres— like tiny billiard balls— that make up matter
What subatomic particle did Thompson discover?
Electron
What subatomic particle did Rutherford discover?
Proton
What subatomic particle did Chadwick discover?
Neutron
Plum Pudding Model
J.J. Thompson’s model of the atom, which describes the atom as a positively charged “pudding” with negatively charged electrons (plums) scattered throughout
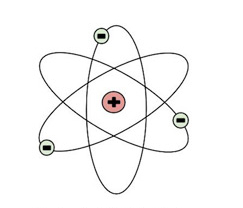
Bohr Planetary Model
Niels Bohr’s model of the atom, where electrons orbit the nucleus in fixed energy levels, like planets orbiting the sun
Quantum Mechanical Model (Schrodinger)
The modern atomic model where electrons are found in regions called orbitals, and their positions are based on probabilities rather than fixed paths
Democritus
An ancient Greek philosopher who first proposed that matter is made of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms (no experimental testing)
Aristotle
An ancient Greek philosopher who believed that all matter was made of four elements— earth, water, fire, and air— and rejected the idea of atoms (no experimental testing)
Joseph Priestley
A scientists who discovered oxygen and studied gases, helping to advance chemistry
Antoine Lavoisier
Known as the “Father of Modern Chemistry”, he named oxygen and hydrogen, proved the Law of Conservation of Mass, and helped transform chemistry into a quantitative science
What type of electron configuration is listed?: 1s² 2s² 2p⁴
Full version
What type of electron configuration is listed?: [He] 2s² 2p⁴
Noble Gas (shorthand) version
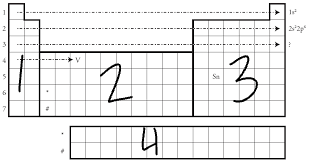
Label the sublevels
S-block
D-block
P-block
F-block

Which sublevel orbital is pictured?
S-block
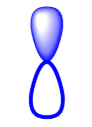
Which sublevel orbital is pictured?
P-block

Which sublevel orbital is pictured?
D-block
Hund’s Rule
Electrons will fill empty orbitals of the same energy singly before pairing up, and all singly-filled orbitals have parallel spins
Pauli Exclusion Principle
No two electrons in the same atom have the same set of four quantum numbers, meaning each orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons with opposite spins
Aufbau Principle
Electrons fill orbitals starting with the lowest energy level first before moving to higher energy levels
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
It is impossible to know both the exact position and exact momentum of an electron at the same time— the more precisely one is known, the less precisely the other can be known
Excited State
When an electron absorbs energy and moves to a higher energy level than its ground state
Ground State
The lowest energy state of an atom, where all electrons are in their normal, lowest-energy orbitals
Flame Test
A test where light is emitted when electrons in an atom absorb energy, jump to a higher energy level, and then return to the ground state, producing characteristic colors for different elements
Spectroscopy
A technique that analyzes the light emitted or absorbed by atoms or molecules to identify elements and determine their energy levels
What is represented by this symbol?: λ
Wavelength
Wavelength
The distance between two consecutive peaks or troughs of a wave
What is represented by this symbol?: ν
Frequency
Frequency
The number of wave cycles that pass a point per second
Planck’s Constant
A fundamental constant that relates to the energy of a photon to its frequency (E=hν)
Speed of Light
The constant c = 3.00 × 10⁸ m/s, which is the speed at which light travels in a vacuum
Emission Spectrum
A spectrum of light emitted by excited electrons as they return to lower energy levels, showing specific colors or lines unique to each element
Absorption Spectrum
A spectrum showing dark lines where light has been absorbed by electrons, indicating the specific wavelengths absorbed as electrons jump to higher energy levels
Continuous Spectrum
A spectrum that contains all wavelengths of light without gaps, producing a smooth rainbow of colors
The order of all types of waves (longest wavelength, lowest energy →shortest wavelength, highest energy)
Radio Waves
Microwaves
Infrared (IR)
Visible Light (red has the longest wavelength, violet has the shortest)
Ultraviolet (UV)
X-rays
Gamma Rays
Relationship between wavelength, frequency, and energy
Wavelength and frequency are inversely proportional: c=λν
Energy and frequency are directly proportional to frequency: E=hν
Energy is inversely proportional to wavelength: E=hc/λ
Quantum of Energy
The smallest amount of energy that can be absorbed or emitted by an atom, corresponding to one photon of light
How are isotopes of the same element the same and different?
They have the same protons and are the same element, but have different neutrons and mass
What is the difference between a cation and an anion?
A cation is a positively charged ion (loses electrons), and an anion is a negatively charged ion (gains electrons)
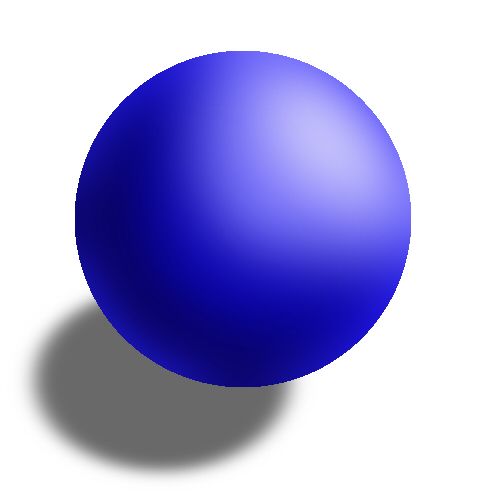

Which model is shown and who created it?
Billiard ball model created by Dalton
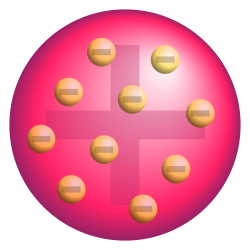
Which model is shown and who created it?
Plum pudding model created by Thompson
Who created this atomic model?
Rutherford
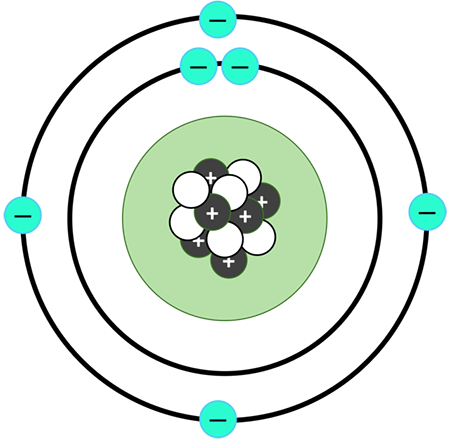
Who created this atomic model?
Chadwick
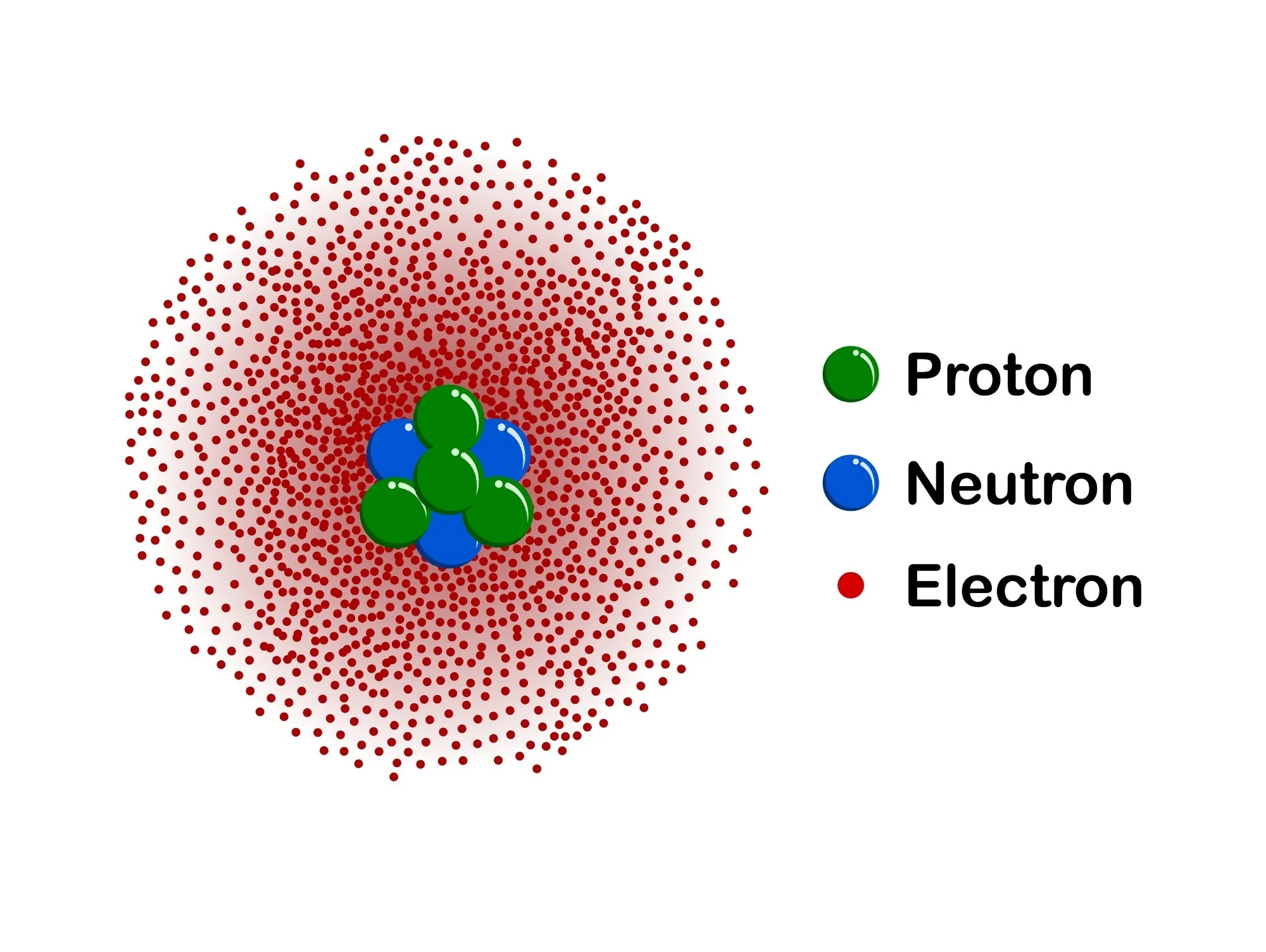
What is this atomic model and who created it?
Planetary model created by Bohr
What is this atomic model and who created it?
Quantum mechanical model by Schrodinger
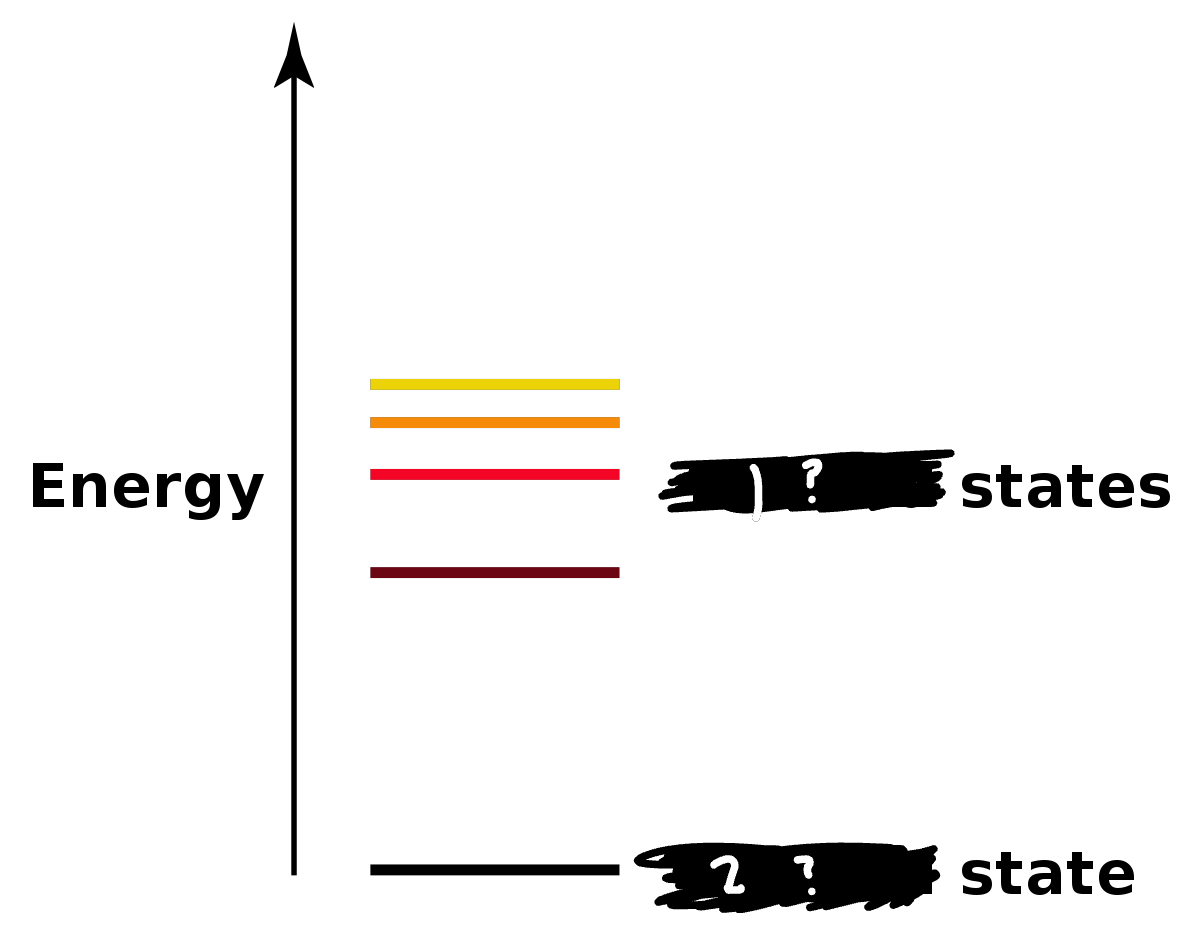
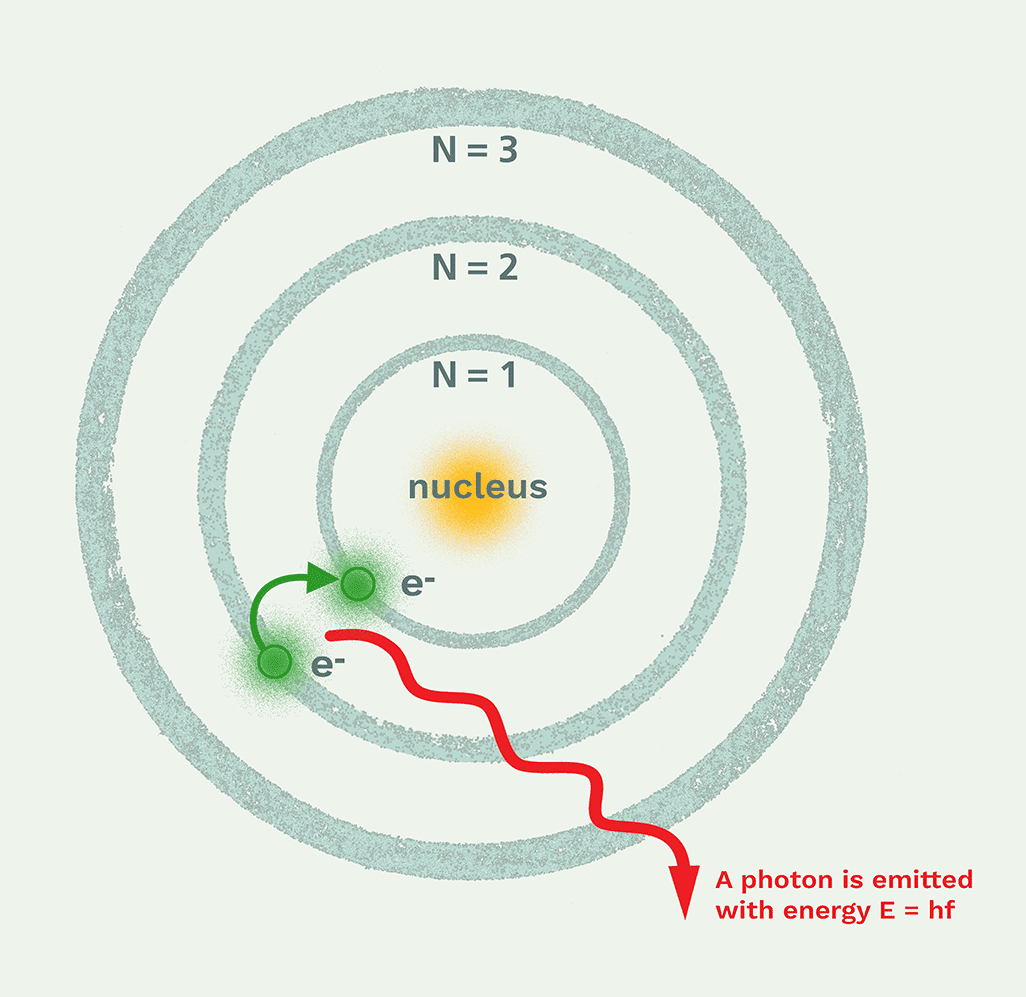
Label the diagram
Excited
Ground
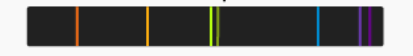
Which spectrum is pictured?
Emission spectrum

Which spectrum is pictured?
Absorption spectrum
Which spectrum is pictured?
Continuous spectrum
Who created the gold foil experiment?
Rutherford
Who didn’t know position/movement of electrons?
Heisenberg
Who developed the complex math of the motion of electrons?
Schrodinger
What are isotopes?
An element with the same number of protons and a different number of neutrons
What does “A” mean?
Atomic mass
What does “Z” mean?
Atomic number
What part of the atom is the most dense?
The nucleus
What are valance electrons?
The electrons in the outermost shell of an atom, which are involved in forming chemical bonds
What is common about the shorten configurations of the elements that are in the same column of the periodic table?
They have the same number of valance electrons
What is an amu?
A unit of mass used for subatomic particles, atoms, and molecules
What parts of the isotope does the amu equal?
The sum of its protons and neutrons