Psychology - Research Methods
4.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:19 PM on 5/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
1
New cards
Experimental Method
Involves the manipulation of an independent variable (IV) to measure the effects on the dependent variable (DV). Experiments may be laboratory, field, natural or quasi
2
New cards
Aim
A general statement of what the researcher intends to investigate, the purpose of the study
3
New cards
Hypothesis
A clear, precise, testable statement that states the relationship between the variables to be investigated. Stated the outset of any study
4
New cards
Directional Hypothesis
States the direction of the difference or relationship
5
New cards
Non-Directional Hypothesis
Does not state the direction of the difference or relationship
6
New cards
Variables
Any ‘thing’ that can vary or change within an investigation. Variables are generally used in experiments to determine if changes in one thing result in changes to another
7
New cards
Independent Variable (IV)
Some aspects of the experimental situation that is manipulated by the researcher so the effect on the DV can be measured
8
New cards
Dependent Variable (DV)
The variable that is measured by the researcher. Any effect on the DV should be caused by the change in the IV
9
New cards
Operationalisation
Clearly defining variables in terms of how they can be measured
10
New cards
Extraneous Variables (EV)
Any variable other than the independent variable (IV) that may affect the dependent variable (DV) if it is not controlled
11
New cards
Confounding Variables
A kind of EV but the key feature is that a confounding variable varies systematically with the IV. Therefore we can’t tell if any change in the DV is due to the IV or the confounding variable
12
New cards
Demand Characteristics
Any cue from the researcher or from the research situation that may be interpreted by participants as revealing the purpose of an investigation. This may lead to a participant changing their behaviour within the research situation
13
New cards
Investigator Effects
Any effect of the investigator’s behaviour on the research outcome (DV). This may include everything from the design of the study to the selection of, and interaction with, participants during the research process
14
New cards
Randomisation
The use of chance methods to control for the effects of bias when designing materials and deciding the order of experimental conditions
15
New cards
Standardisation
Using exact;y the same formalised procedures and instructions for all participants in a research study
16
New cards
Experimental Design
The different ways in which participants cam be organised in relation to the experimental conditions
17
New cards
Independent Group Design
Participants are allocated to different groups where each group represents one experimental condition
18
New cards
Repeated Measures
All participants take part in all conditions of the experiment
19
New cards
Matched Pairs Design
Pairs of participants are first matched on some variable that may affect the dependent variable. One member is assigned to Condition A and the other to Condition B
20
New cards
Random Allocation
An attempt to control for participant variables in an independent group design which ensures that each participant has the same chance of being in one condition as any other
21
New cards
Counterbalancing
An attempt to control for the effects of order in a repeated measures design: half the participants experience the conditions in one order, and the half in the opposite order
22
New cards
Lab Experiment
An experiment that takes place in a controlled environment within the researcher manipulates the IV and records the effect on the DV whilst maintaining struct control of extraneous variables
23
New cards
Field Experiment
An experiment that takes place in a natural setting within which the researcher manipulates the IV and records the effect on the DV
24
New cards
Natural Experiment
An experiment where the change in the IV is not brought about by the researcher but would have happened even if the researcher had not been there. The researcher records the effect on a DV they have decided on
25
New cards
Quasi-Experiment
A study that is almost an experiment but lacks key components. The IV has not been determined by anyone
26
New cards
Population
A group of people who are the focus of the researcher’s interest, from which a smaller sample is drawn
27
New cards
Sample
A group of people who take part in a research investigation. The sample us drawn from a (target) population and is presumed to be representative of that population
28
New cards
Sampling Bias
When certain groups are under/over represented which limits the extent of generalisation that can be made to the target population
29
New cards
Generalisation
The extent to which findings and conclusions from a particular investigation can be broadly applied to the population. This is possible if the sample of participants is representative of the target population
30
New cards
Random Sampling
Is a sampling technique where every member of the target population has an equal chance of being selected
* Potentially biased
* Difficult and time consuming
* Potentially biased
* Difficult and time consuming
31
New cards
Systematic Sampling
I a sampling technique that uses a predetermined system to select the participants from a target group
* Objective
* Time-consuming
* Objective
* Time-consuming
32
New cards
Stratified Sampling
Researchers divided subjects into subgroups called strata based on characteristics that they share
* Representative sample
* Does not account for individual differences
* Representative sample
* Does not account for individual differences
33
New cards
Opportunity Sampling
Uses the knowledge and attributes of the researcher to identify a sample
* Convenient and cheaper
* Unrepresentative sample
* Convenient and cheaper
* Unrepresentative sample
34
New cards
Volunteer Sampling
Occurs when researchers seek volunteers to participate in studies
* Requires minimal researcher input - less time consuming
* Volunteer bias
* Requires minimal researcher input - less time consuming
* Volunteer bias
35
New cards
Informed Consent
Participants can enter research freely (voluntarily) with full information about what it means for them to take part, and they give consent before they enter the research
36
New cards
Deception
Deliberately misleading or withholding information from participants ay any stage of the investigation
37
New cards
Protection From Harm
Participants should not be placed at any more risk than they would be in their daily lives and should be protected from physical and psychological harm
38
New cards
Privacy and Confidentiality
Participants have the right to control information about themselves
39
New cards
Pilot Study
A small scale version of an investigation that takes place before the real investigation is conducted. The aim is to check that procedures, materials, measuring scales, etc, work. The aim is also to allow the researcher make changes or modifications as necessary
40
New cards
Single-Blind Procedure
A type of clinical trial in which only the researcher doing the study knows which treatment or intervention the participant is receiving until the trial is over
41
New cards
Double-Blind Study
A type of clinical trial in which neither the participants nor the researcher knows which treatment or intervention participants are receiving until the clinical trial is over
42
New cards
Naturalistic Observation
Watching and recording behaviour in the setting within which it would naturally occur
43
New cards
Controlled Observation
Watching and recording behaviour within a structured environment
44
New cards
Covert Observation
Participants behaviour is watched and recorded without their knowledge or consent
45
New cards
Overt Ovservation
Participants behaviour is watched and recorded with their knowledge and consent
46
New cards
Participant Observation
The researcher becomes a member if the group whose behaviour he/she is watching and recording
47
New cards
Non-Participant Observation
The researcher remains outside of the group whose behaviour he/she is watching and recording
48
New cards
Behavioural Categories
When a target behaviour is broken up into components that are observable and measurable (operationalisation)
49
New cards
Event Sampling
A target behaviour or event is first established then the researcher records this event every time it occurs
50
New cards
Time Sampling
A target individual or group is first established then the researcher records their behaviour in a fixed time frame
51
New cards
Observer Bias
To make data recording more objective and unbiased, observations should be carried out by at least 2 researchers. Then data from different observers is compared to check for consistency
52
New cards
Self-Report Technique
A method in which participants provide information about their thoughts, feelings, or behaviours through direct questioning or structured interviews.
53
New cards
Questionnaire
A research tool is used to collect data from participants by asking a set of standardized questions
54
New cards
Structured Interview
Participants are asked the same set of questions in a standardized manner. Used to ensure fairness and objectivity in the interview process
55
New cards
Unstructured Interviews
Works like a conversation, there is no set questions just a general aim and a certain topic discussion
56
New cards
Semi-Structured Interview
A list of questions that have been worked out in advance but interviewers are free to ask follow up questions
57
New cards
Acquiescence Bias
The tendency to agree with items on a questionnaire regardless of the content of the question
58
New cards
Social Desirability Bias
Tendency to give socially acceptable responses instead of truthful ones due to fear of judgement or desire to please others
59
New cards
Open Questions
Questions for which there is no fixed choice of response and respondents can answer in any way they wish
60
New cards
Closed Questions
Questions for which there is a fixed choice of responses determined by the question setter
61
New cards
Questionnaire Types:
* Likert Scale
* Rating Scale
* Fixed-Choice Option
* Rating Scale
* Fixed-Choice Option
62
New cards
Correlation
A mathematical technique in which a researcher investigates an association between 2 variables, called co-variables
63
New cards
Co-Variables
Factors that are related to each other and can affect the outcome of an experiment or study. They are often controlled or measured to ensure accurate results
64
New cards
Qualitative Data
Data that is expressed in words and non-numerical
65
New cards
Quantitative Data
Data that can be counted
66
New cards
Primary Data
Information collected directly from its source is called Primary Data. It is original and new data collected through surveys, experiments, or observations
67
New cards
Secondary Data
Definition: Data that has already been collected by someone else for a different purpose. Can be obtained from sources such as government agencies, research institutions, or commercial data providers
68
New cards
Meta-Analysis
A statistical technique that combines results from multiple studies to draw a conclusion about the overall effect size, providing a more accurate estimate of the true effect than any single study alone
69
New cards
Measures of Central Tendency
The general term for any measure of the average value in a set of data
70
New cards
Mean
The arithmetic average calculated by adding up all the values in a set of data and dividing by the numbers of values
71
New cards
Median
The central value in a set of data when values are arranged from lowest to highest
72
New cards
Mode
The most frequently occurring value in a set of data
73
New cards
Measures of Central Tendency
A statistical measure that represents the center of a distribution of data. It includes mean, median, and mode.
74
New cards
Measures of Dispersion
Used to describe the degree of variation or spread of data in a dataset. Examples include range, variance, and standard deviation
75
New cards
Range
A simple calculation of the dispersion in a set of scores which is worked out by subtracting the lowest score from the highest score and adding 1 as a mathematical correction
76
New cards
Standard Deviation
Measure of the spread of data from its mean. It indicates how much the data deviates from the average value. A low SD indicates data is clustered around the mean, while a high SD indicates data is more spread out
77
New cards
Statistical Testing
A method used to determine if the difference between two groups is due to chance or a real effect
78
New cards
Peer Review
A process where experts in a field review and evaluate a piece of work to ensure its quality and accuracy. It helps to identify errors, gaps, and strengths in the work
79
New cards
Publication Bias
The tendency of researchers and journals to only publish studies with positive or significant results, leads to an incomplete and potentially biased representation of the research on a particular topic
80
New cards
Case Studies
An in-depth investigation, description and analysis of a single individual group, institution or event
81
New cards
Content Analysis
A research technique that enables the indirect study of behaviour by examining communications that people produce
82
New cards
Coding
The stage of cintent analysis in which the communication to be studied is analysed by identifying each instance of the chosen categories
83
New cards
Thematic Analysis
An inductive and qualitative approach to analysis that involves identifying implicit or explicit ideas within the data. Themes will often emerge once the data has been coded
84
New cards
Reliability
Refers to how consistent a measuring device is - and this includes psychological tests or observations which assess behaviour
85
New cards
Test-Retest Reliability
A method of assessing reliability of a questionnaire or psychological test by assessing the same person on two separate occasions. This shows to what extent the test produces the same answers
86
New cards
Inter-Observer Reliability
The extent to which there is agreement between two or more observers involved in observations of a behaviour. This is measured by correlating the observations of a behaviour. This is measured by correlating the observations of two or more observers
87
New cards
Validity
The extent to which an observed effect is genuine
88
New cards
Face Validity
A basic form of validity in which a measure is scrutinised to determine whether it appears to measure what it is supposed to measure
89
New cards
Concurrent Validity
The extent to which a psychological measure relates to an existing similar measure
90
New cards
Ecological Validity
The extent to which findings from a research study can be generalised to other settings and situations. A form of external validity
91
New cards
Temporal Validity
The extent to which findings from a research study can be generalised to other historical times and eras. A form of external validity
92
New cards
Internal Validity
Refers to whether the effects observed in an experiment are due to the manipulation of the independent variable and not some other factor
93
New cards
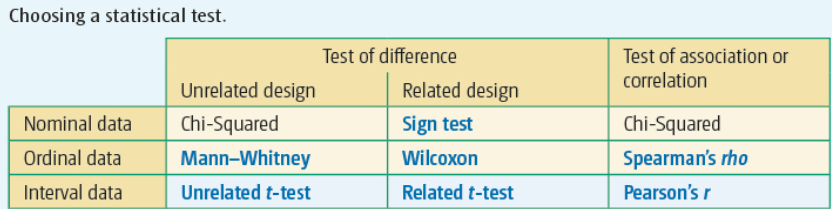
Choosing a Statistical Test
1. Difference or correlation
2. Experimental design
3. Levels of measurement
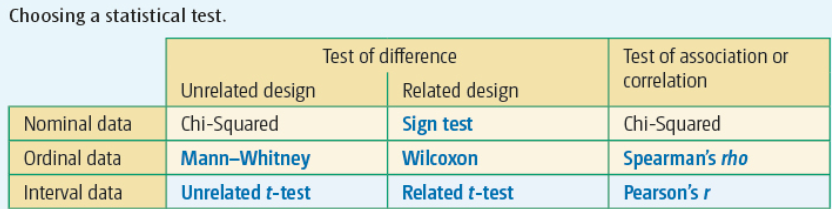
94
New cards
Statistical Test Mnemonic
Carrots Should Come Mashed With Swede Under Roast Potatoes
95
New cards
Probability
A measure of the likelihood that a particular event will occur where 0 indicates statistical impossibility and 1 statistical certainty
96
New cards
Significance
A statistical terms that tells us how sure we are that a difference or correlation exist. A ‘significant’ result means that the researcher can reject the null hypothesis
97
New cards
Critical Value
When testing a hypothesis, the numerical boundary or cut-off point between acceptance and rejection of the null hypothesis
98
New cards
Type 1 Error
The incorrect rejection of a true null hypothesis (a false positive)
99
New cards
Type 2 Error
The failure to reject a false null hypothesis (a false negative)
100
New cards
Level of Significance
Equal or less than 5%