the protestant and counter reformations
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
what challenges did Christians face in the 1st century? how did that change by the 4th century?
they were originally persecuted, but after Emperor Constantine granted religious freedom in the Roman Empire, Emperor Theodosius was able to make it the official religion in 380
what two groups did the Church divide into?
Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox Churches
*temporarily worked together during the Crusades
John Wycliffe
attacks the Church through writings and sermons
encourages people to read and interpret the Bible for themselves instead of believing whatever the Church told them
led to many people claiming they were the Pope (split in Western church)
given a posthumous (after death) “execution”
from England + translates Bible into English
Jan Hus
he supports John Wycliffe’s ideas
the Church calls him a heretic, or a disbeliever who holds views that go against the Church
the Church burns him at the stake for his views
from Bohemia, held services in the vernacular
what problems did the Church experience from the 11th century to the 15th century?
split into Eastern and Western Churches (1054)
western Church splits even more due to Wycliffe
Church is questioned
Pope loses power
enemies of the Church are being killed
people like Wycliffe + Hus believed that the Church wasn’t the ultimate authority, the Bible was
protestant
a person who challenges something (could be an idea, person, etc).
reformation
the process of reshaping or remaking something (taking the challenged idea and renewing it).
what were some of the Church’s abuses?
become more secular
increase marriage/baptism fees
indulgences
sermons + Bible were in Latin
printing press
allowed Reformation ideas to be spread much quicker and more efficiently
what is humanism, and how may it have led to the Protestant reformation?
humanism is the study of human potential, reasoning, and achievements (people started recognizing that God wasn’t always the highest authority– people were; they read Greek + Roman texts).
once people were exposed to humanist ideas, they realized they had been blindly following the Church
they started believing in human reasoning
fought for reform
started wondering how they, as humans, could have a relationship with God
causes of the Reformation
100 Years War and Black Death
clergy was uneducated (didn’t have education)
church was busy with worldly (politics, economics) affairs – not doing spiritual work
scientific advances which contradicted the Catholic Church
indulgences – paying $$ for a pardon of sins or reward for good behavior
Catholic Church hierarchy
1. God
2. Pope
3. Cardinals
4. Archbishops
5. Bishops
6. Priests and Monks
7. Laity - not in the church, regular church attendees
what did Erasmus do?
he translated the New Testament into Italian
Martin Luther
German monk who was upset with the Church, main teachings and beliefs included:
salvation by faith alone, not good works
Bible is the ultimate authority and we should base our teachings off of it only
all people are = before God
people should read + interpret Bible themselves
his opposition to the Church started when he joined the monastery; realized the Church was corrupt and wouldn’t save him
what were some of Luther’s issues with the Church?
Tetzel (a friar) was selling indulgences
merchants want usury (lending money + charging interest); this is wrong in the Bible
Church’s wealth + power
Italian domination (angered Germans + English)
Luther’s 95 Theses
posted on All Saint’s Church in Wittenberg, Germany (1517), 95 reasons he opposes the Church, criticized:
indulgences
Pope’s power
Church’s wealth
*gained support, was aided through printing presses
Pope Leo X Medici
Pope during the height of religious corruption
ordered Luther to give up his beliefs (1520)
Luther burned the order and was excommunicated in 1521
who summoned Luther to trial?
Charles V - Trial was in Worms, Germany
1518: wanted him to redact his Theses, Luther refused —> excommunication (1521)
Edict of Worms
Luther is declared an outlaw + heretic by Charles V
banned his writings
demanded his arrest
anyone who helped him would be punished
anyone who killed him wouldn’t be punished
led to the formation of Lutherans
Luther had to hide in Wartburg Castle to stay safe (friends helped him)
in 1524, what do peasants want an end to? what is Luther’s reaction?
peasants want an end to serfdom and revolt in 1524
Luther does not support the revolt and the princes of Germany massacre 100,000 people
who declared war against Protestants?
Charles V
t or f: Luther had no support from princes
f: had support from Northern German princes
*other princes joined together against Luther
Peace of Augsburg
religion of each German state would be decided by its ruler (1555)
King Henry VIII
devout Catholic
he and Catherine of Aragon had a daughter Mary, but no male heir
Henry wanted a divorce
the Pope could annul (set aside) a marriage, but refused (not a legitimate reason to annul)
Henry called on Parliament to pass laws ending Pope’s power in England and legalize his divorce
in 1534, Henry breaks from the Catholic Church and declared himself head of the Church Of England
STARTS REFORMATION IN EUROPE!
Queen Elizabeth I
second daughter of Henry VIII and Anne Boleyn
combined Catholic styles w/ Protestant teaching to please both religions
was a Protestant, but wanted peace
makes the Anglican Church the official church of all of Great Britain
John Calvin
his ideas hit the church with a POW:
P: predestination; God chooses who goes to heaven, you don’t get there by good works
salvation through predestination
decided at birth
O: our moral lives will reveal if God chooses us to go to heaven or hell
W: work ethic, righteous life that honors God (strict, frugal, disciplined lifestyle)
from France, supporter of Luther
published a book in 1536 on his beliefs
John Knox
visited Calvin in Geneva and liked his teachings
returned to his native Scotland and his followers were called Presbyterians
Anabaptists
means “baptize again”
persecuted across Europe
believed in Baptism only for adults who were old enough to decide
what did Luther do while in hiding?
translated the New Testament into German vernacular in order to make the Bible accessible to ordinary citizens. they didn’t have to follow the Church’s interpretations anymore, and could read the Bible and interpret it themselves.
*CHRISTIANITY DIAGRAM*
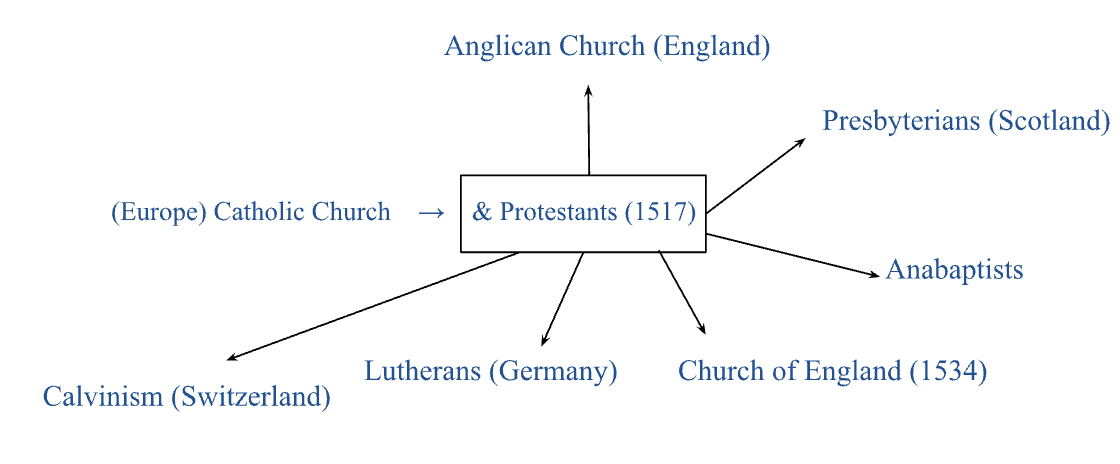
how did the Catholic Church try to win back followers during the Counter-Reformation?
Society of Jesus: missions, schools, seminaries
Council of Trent
“The Index of Forbidden Books”: protect the Church’s teachings + banish those texts
Ignatius
religious leader who created the Society of Jesus
what two new Popes were founded during the Counter-Reformation?
Paul III and Paul IV (had to renew the Church)
Catholic doctrines
Church’s interpretation of the Bible was final
Christians needed good works + faith for salvation
Bible is as powerful as the Church
indulgences were acceptable (false ones were not)
t or f: the Counter-Reformation completely failed
f: were able to reverse some effects of the Protestant Reformation and gain followers
Council of Trent
established rules and guidelines to go against the Protestant Reformation
made of Catholic leaders
killed + tried many Protestants (accused of heresy/dissent)
other effects of Counter-Reformation:
parish schools (increased appreciation for education)
both reformations ended up unifying among themselves
women wanted more rights
pros and cons of Jesuit order
Pros:
many Europeans went back to Catholicism
Jesuit teachers sent around the world on missions
schools, colleges, and seminaries were created
investigated in indulgences and other abuses in the Church
ran charitable organizations (such as one for former prostitutes and one for Jewish people who converted to Catholicism)
Cons:
depending on perspective, converting individuals to Catholicism may be seen as a con
Jesuits had close ties to royal courts and political figures, leading criticism and a worry that they would abuse their influence in govt.
feared that Jesuits would manipulate things in the govt. to work in their favor
centralized structure of the Jesuit order could sometimes lead to internal conflicts and power struggles within the organization
did not allow the religious freedom of the Indigenous cultures
purpose of the Council of Trent
to refute Protestant beliefs and clarify + strengthen Catholic doctrine
how many sessions did the Council of Trent hold over its 18-year duration?
25 (40 bishops total)
which doctrine was reaffirmed during the 13th session of the Council?
transubstantiation
what was the stance of the Council on the selling of indulgences?
it was upheld, but reformed
which of the following was NOT a decree issued by the Council of Trent?
the complete abolition of purgatory (temporary place of punishment)
the two sources of special revelation according to the Council
Holy Scripture and traditions of the church (including the “unwritten traditions”).
*Protestants only believed in Holy scripture
other things established by the Council
Gregorian calendar
decrees on marriage (needs a priest + 2 witnesses), concubinage, divorce (cannot remarry if other partner is alive)
affirmed purgatory’s existence
*quick summary of reformation*
started with Martin Luther + 95 Theses
aided by printing press
new religious denominations
Calvinism: predestination
Anabaptists: adult baptism only, no priests
Anglicans: separation of Church and State
formed by Elizabeth after Henry VIII broke away from church
Lutherans
council of Trent led to Counter-Reformation
Lutheranism
salvation: faith + accept God’s word
sin: apologize and intend on improving yourself
authority: Bible
individal interpretations
provides basis for teachings
teaches way to have a faithful life
worship: mix of Old Catholic and New Lutheran rituals
prayers in German vernacular
altar, crucifix, monster dressed in traditional vestments
2/7 Catholic sacraments: Baptism and Communion
community life: religion starts at home
father’s role: lead + protect
women: get married, have kids, stay in house
Calvinism
salvation: predestination
rules set so that people wouldn’t sin
singing, dancing, card-playing, etc. were banned
authority: Bible
theocracy
rules set to punish sinners (didn’t attend church or commited blasphemy)
worship: met 5x a week
simple life (simple decorations)
long sermons given by minister
men, women, and children sat on different sides
if children were called on and didn’t know the answer, they were shamed
2/7 sacraments: Baptism and Eucharist (blood and body)
only ones listed in Bible
community life: ruled by the Bible
started in Geneva
Christian names
no bars/drinking
in bed by 9
inns had Bibles for guests
no “fun” activities
annual home inspection
banishment for poor behavior
Anabaptism
salvation: only way to be saved was to be isolated from everyone
avoided govt. and wars
didn’t believe in rituals + ceremonies to admit people into their community
sin: no one could go to heaven (sin is everywhere)
authority: Bible
individual interpretation
very minimal role of the Priest
simple life
worship: met in homes, not Churches
absolutely no decorations
Baptism for adults
Eucharist (communion)
no priests
children were in meetings, but couldn’t participate in rituals
community life: secluded and isolated
didn’t want any part of the sinful world
believed they would be attacked by others for their beliefs
had rules to follow:
no involvement in outside world
no govt. involvement
freedom for all (no war)
tolerant of other religions
communities were places of refuge
Anglicanism
sin: people are born sinful (original sin)
baptism washed away sins
salvation: justification by faith, apologizing for sins, and accepting God’s word
didn’t have to do good deeds
authority: King of England —> Head of Church
he interprets the Bible
assistant: Archbishop of Canterbury
bishops + priests spread his teachings
weren’t restricted to a strict interpretation (long process of information being transferred, not going to be perfect)
people needed to obey laws + be loyal to the King
worship: High and Low church
High: Roman Catholic mass, wealthy
Low: preaching from the Bible, middle/low class
services in Churches and monasteries
white buildings w/ 10 Commandments on walls
Church members wrote Book of Common prayer in English
sermons in English
community life: people were obliged to do the right thing
gave each other privacy
everyone lived their best way according to their beliefs
no one type of Anglicanism
just have to be obedient to English law and God