GCU BIO-201 Exam 3 With complete verified solutions + Rationales
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
synarthroses
immovable joints, found in places such as the sutures of the skull
Amphiarthrosis
slightly movable joint in places like the innervertebral discs
diarthroses
freely movable joints, found in places such as the shoulder
synovial joints
freely movable joints that connect bones with a sack of fluid to prevent rubbing and breakdown of bone
synchondroses
bones united by hyaline cartilage (cartilaginous joints); are NOT freely moveable; in places such as the epiphyseal line
symphysis
limited movement of joints due to the covering of articular surface of joints with hyaline cartilage. ex. pubis symphysis in os coxa
fibrous joints
consists of inflexible layers of dense connective tissue, holds the bones tightly together (3 Types)
Suture Joints
fuse bones together, such as in the skull
Syndesmosomes
bones connected to ligaments, such as the ligaments that connect the radius and ulna
Gomphoses
peg-in-socket fibrous joint, such as teeth in the alveolar socket
Menisci
Pads of cartilage that lie between the articular surfaces of the bones, especially between the knee and mandible
Bursae
flattened fibrous sacs lined with synovial membrane and containing a thin film of synovial fluid
Tendon Sheaths
Elongated bursa wrapped completely around tendon subjected to friction
Plane/Gliding joints
Flat articular surfaces, bones slide over each other
Usually biaxial joints
Examples: between carpal bones of wrist; between tarsal bones of ankle; also between articular processes of vertebrae
hinge joint
Joint between bones (as at the elbow or knee) that permits motion in only one plane
Pivot joints
Pivot joints allow rotation arround an axis. The forearms have pivot joints.
condyloid joints
Oval articular surface of one bone fits into a complementary depression in another; found in the joint at the metacarpals and proximal phalanx.
saddle joints
Only one pair exists and is between the thumb and wrist; biaxial
ball and socket joint
shoulder and hip; multiaxial joints
origin bone
the proximal end of bone where a muscle attaches. It cannot move.
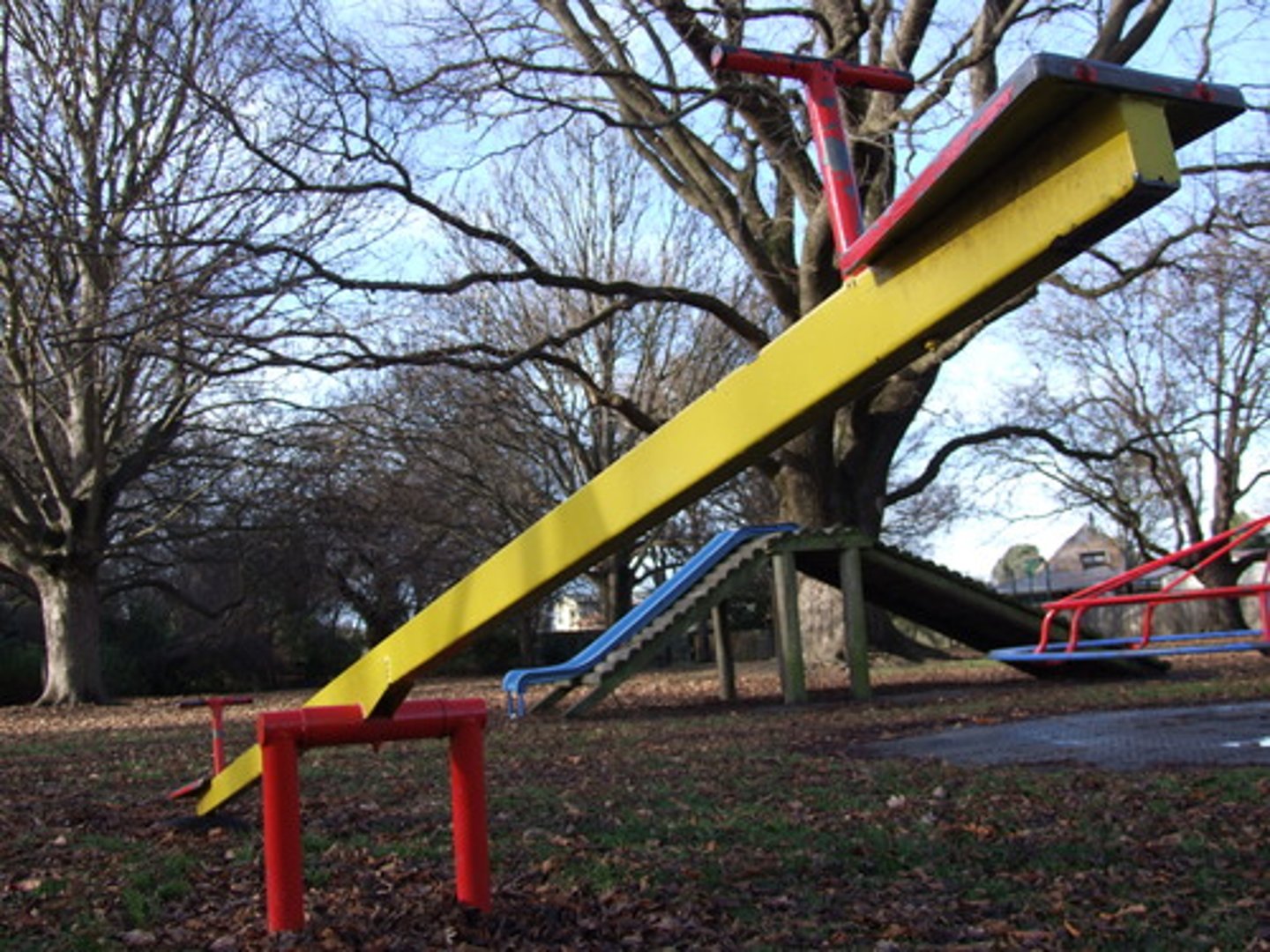
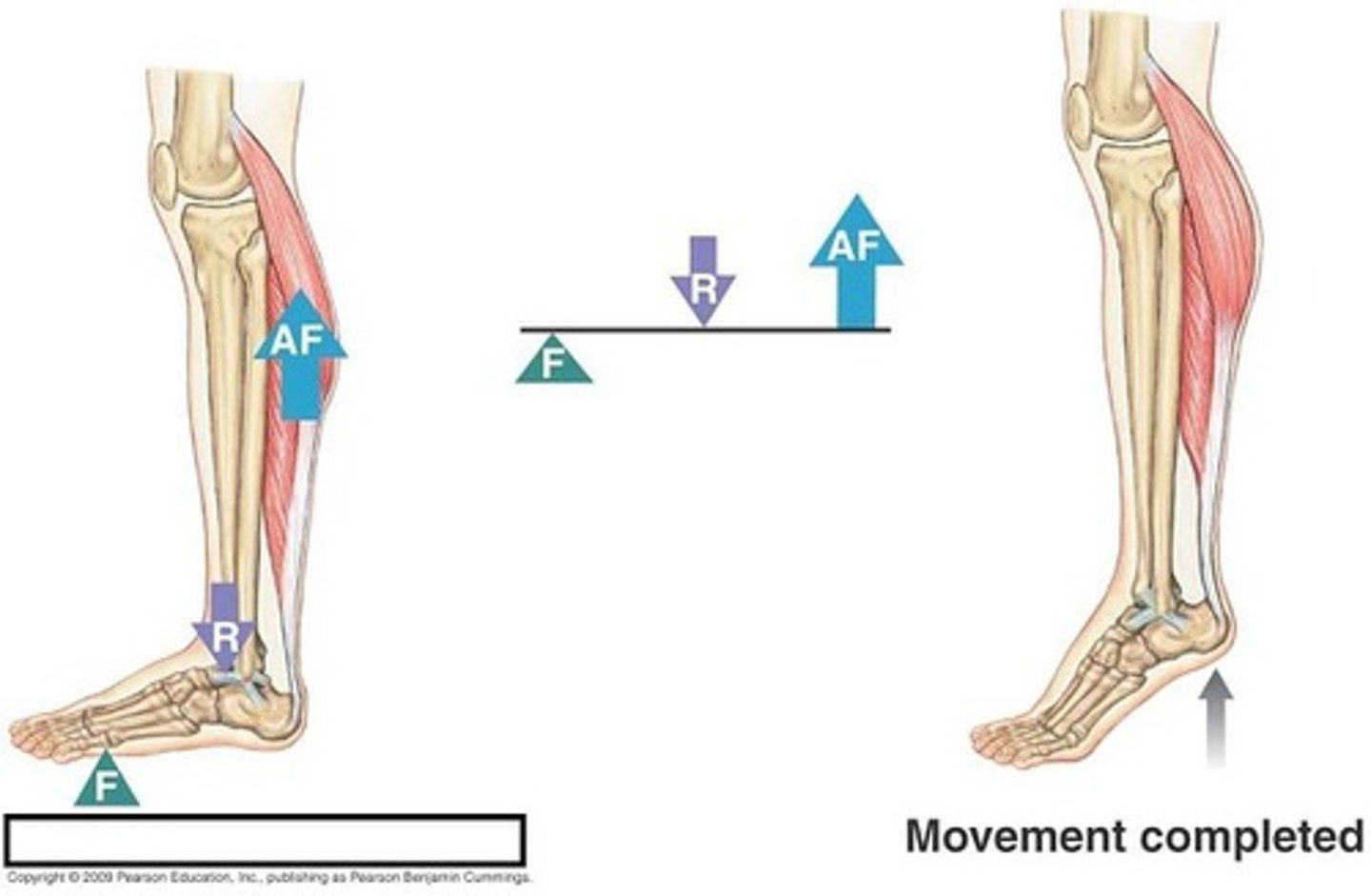
first class lever
The fulcrum is positioned between the effort and resistance

second class lever
the load is between the fulcrum and the effort
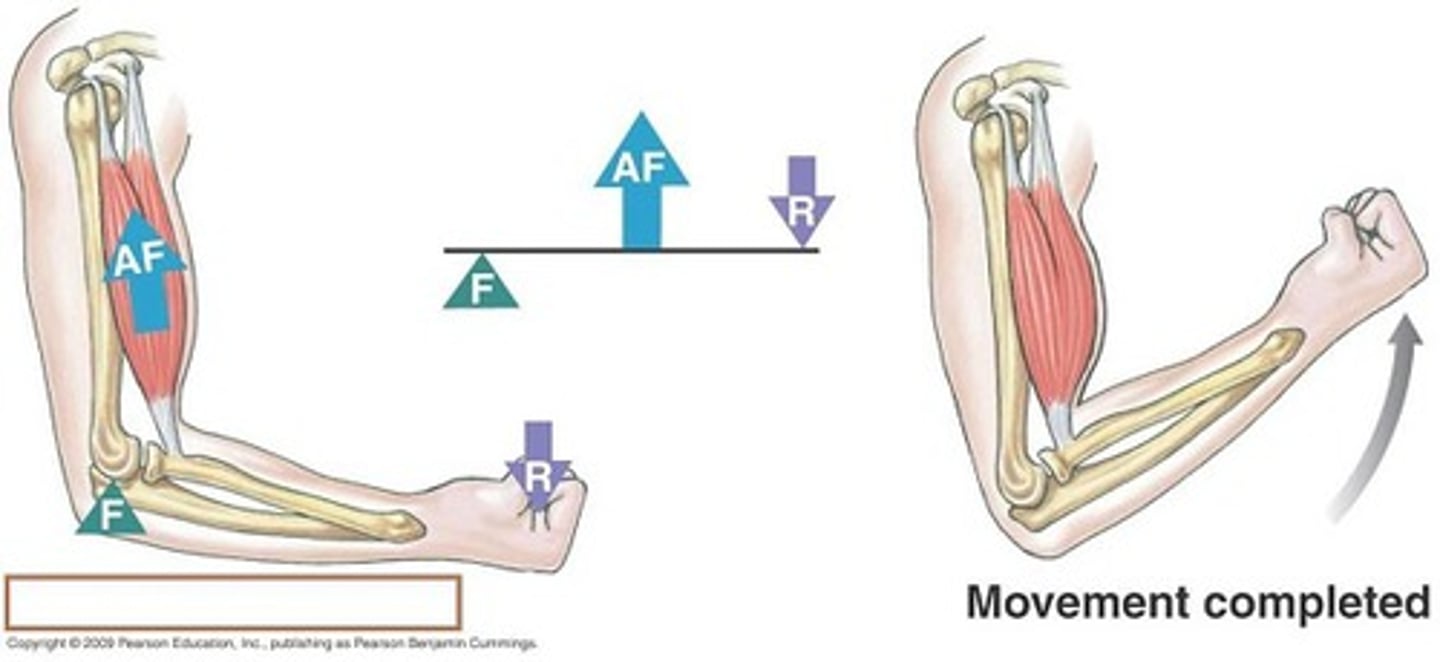
third class lever
the input force is between the fulcrum and the load
sprain
An injury in which the ligaments holding bones together are stretched too far and risk tearing
strain
A condition resulting from damaging a muscle or tendon
Meniscal injury
a tear is incurred upon the meniscus, especially at the knee joint
luxation
total dislocation of a joint
subluxation
partial dislocation of a joint
Bursitis
inflammation of a bursa
Tendonitis
inflammation of a tendon sheath due to overuse
Insertion
The attachment of a muscle tendon to a moveable bone or the end opposite the origin
Actin
thin filaments
Myosin
thick filament
Myofiber
entire muscle cell
Myofibril
tightly packed filament bundles found within skeletal muscle fibers
Sarcoplasm
cytoplasm of a muscle cell
Sarcolemma
muscle cell membrane
sarcoplasmic reticulum
specialized endoplasmic reticulum of muscle cells that stores calcium for muscle movement
T (transverse) tubules
membranous channel that extends inward toward sarcoplasmic reticulum
terminal cisternae
dilated end-sacs of SR which cross the muscle fiber from one side to the other
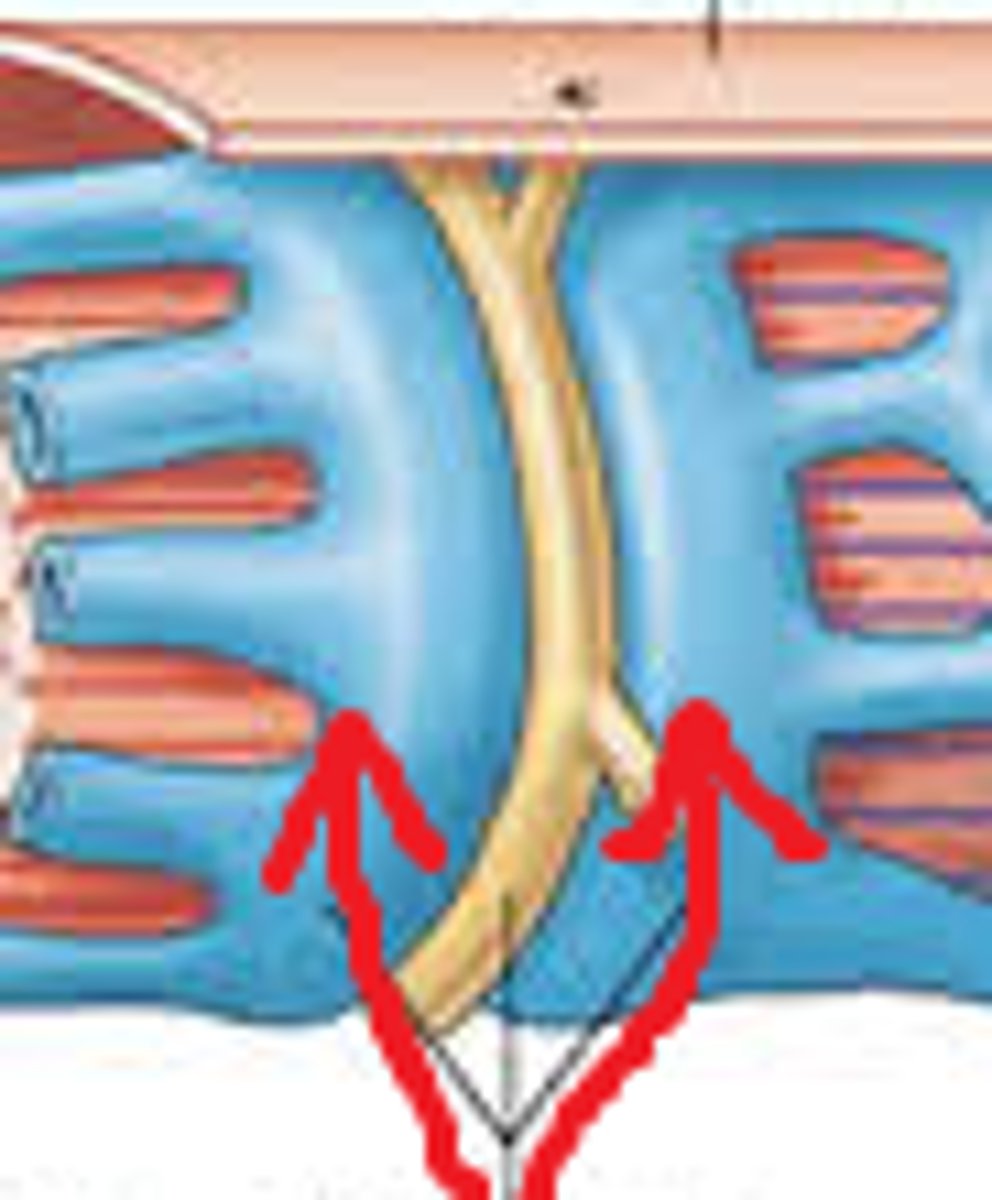
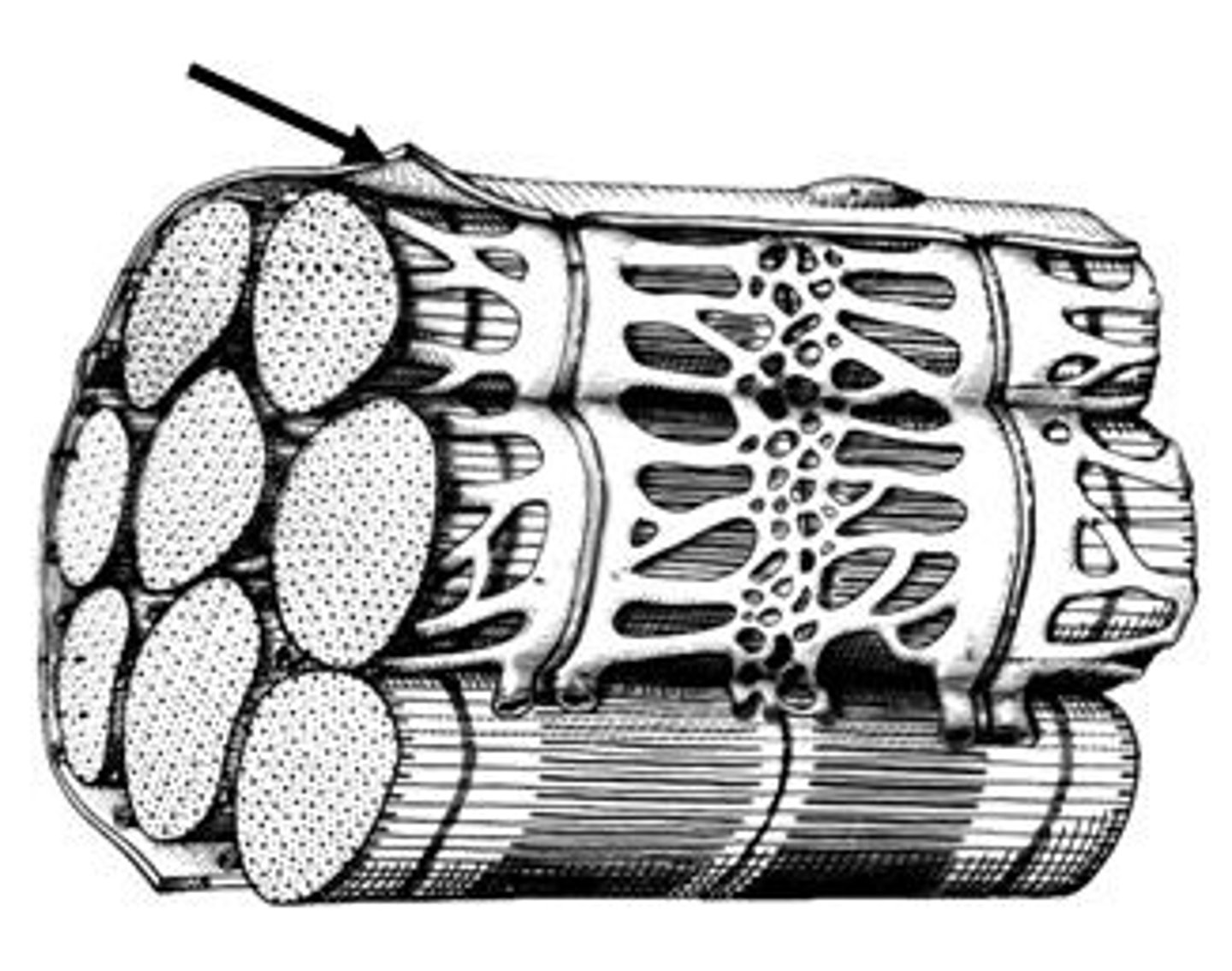
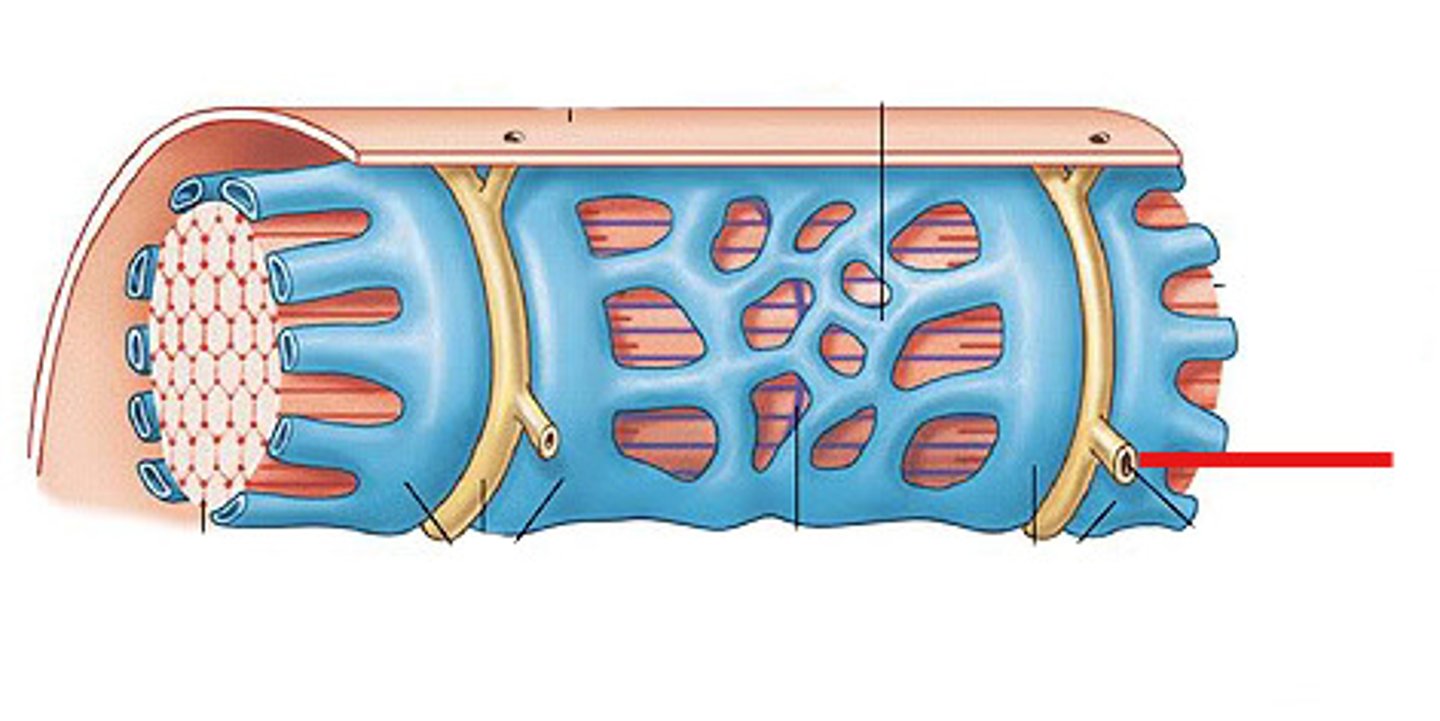
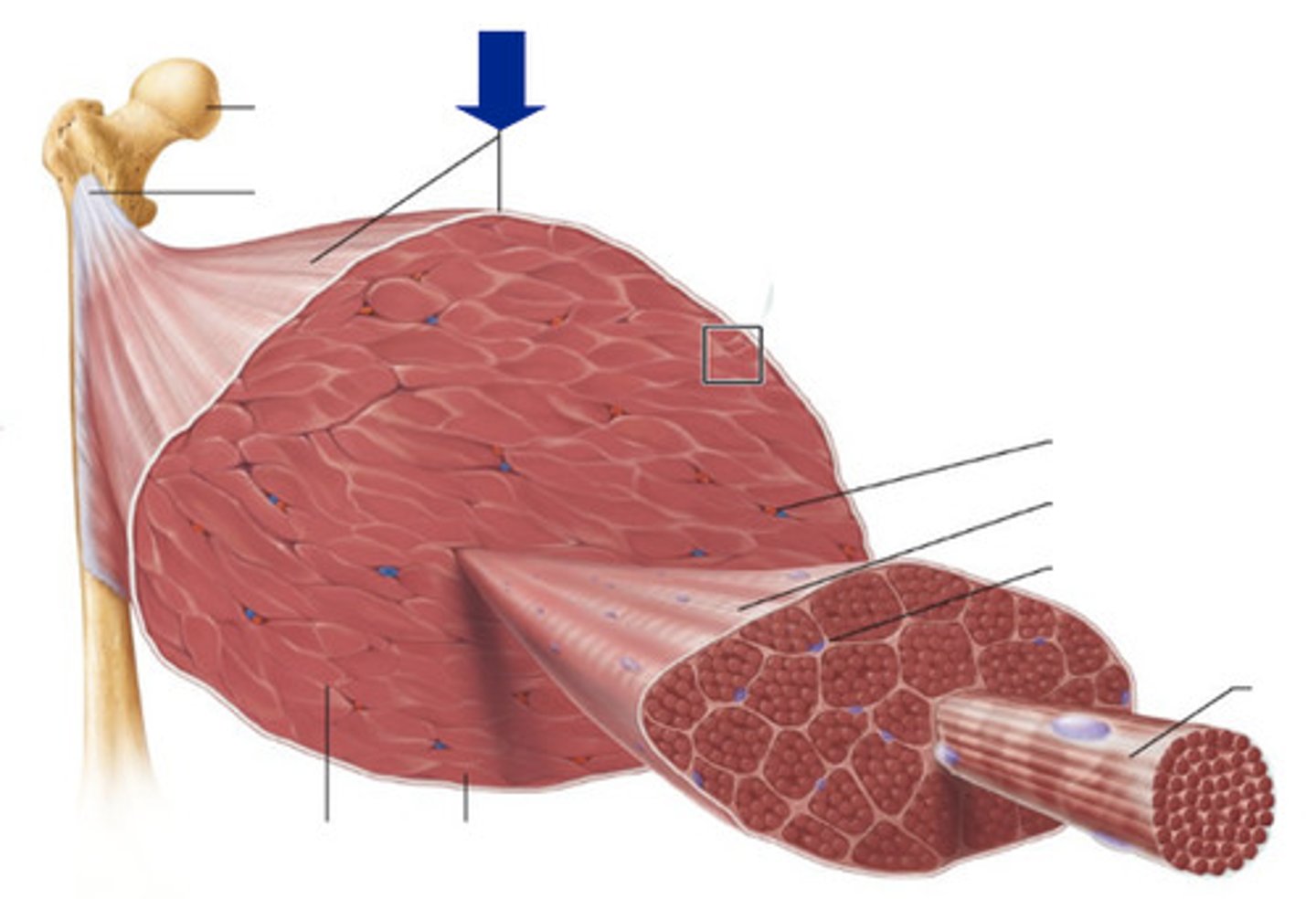
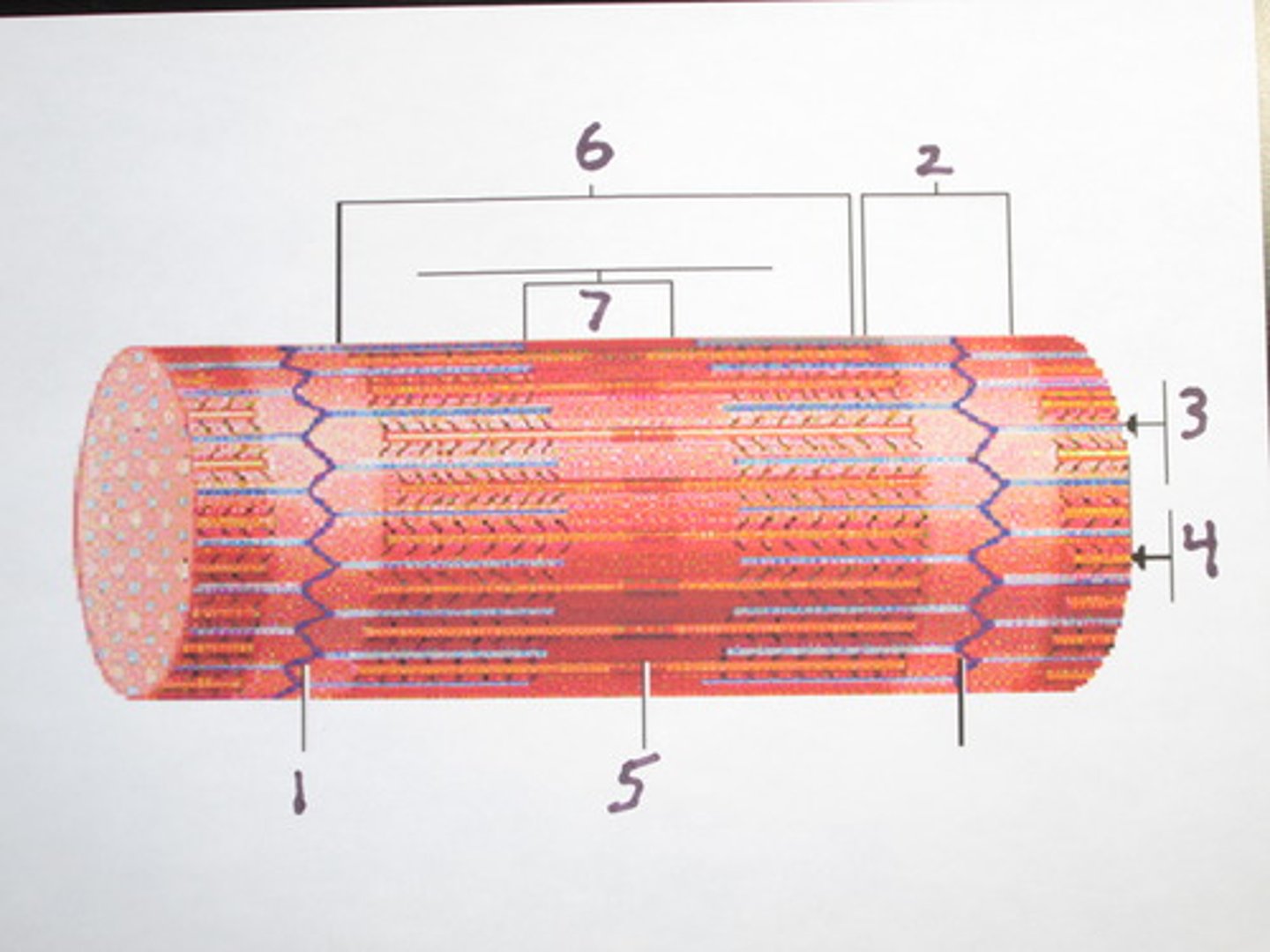
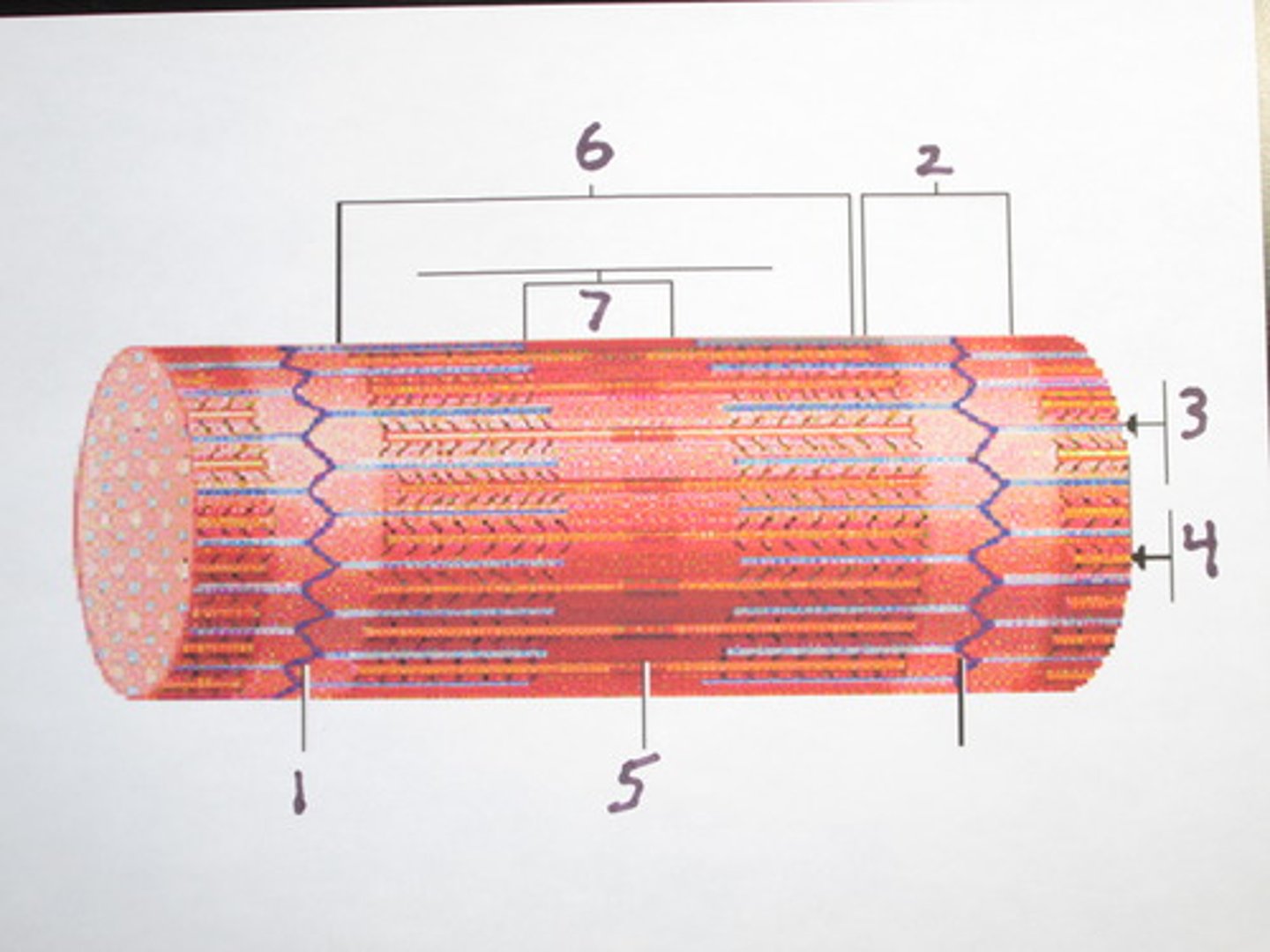
Endomysium
Surrounds individual muscle fibers
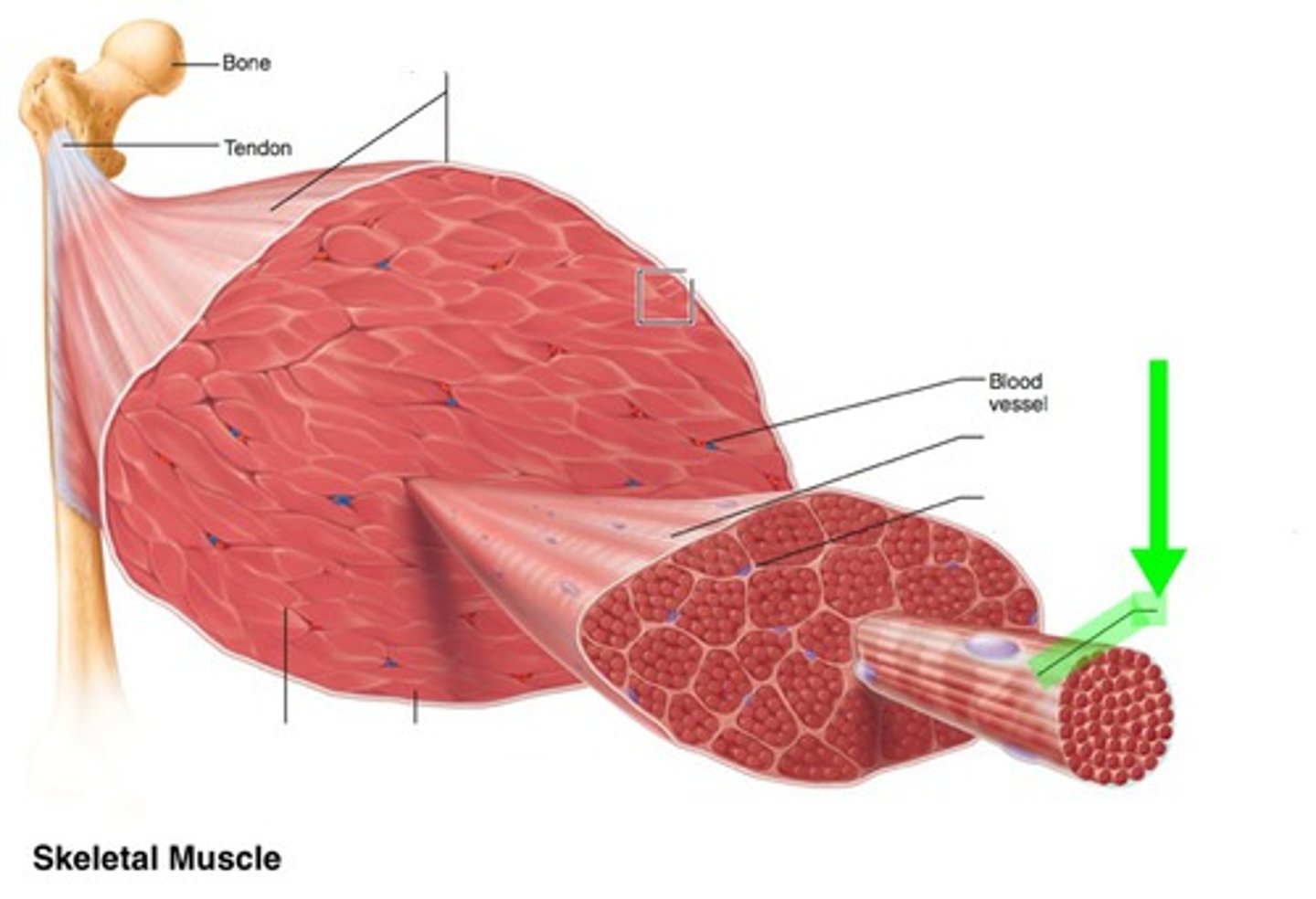
Perimysium
Connective tissue surrounding a fascicle
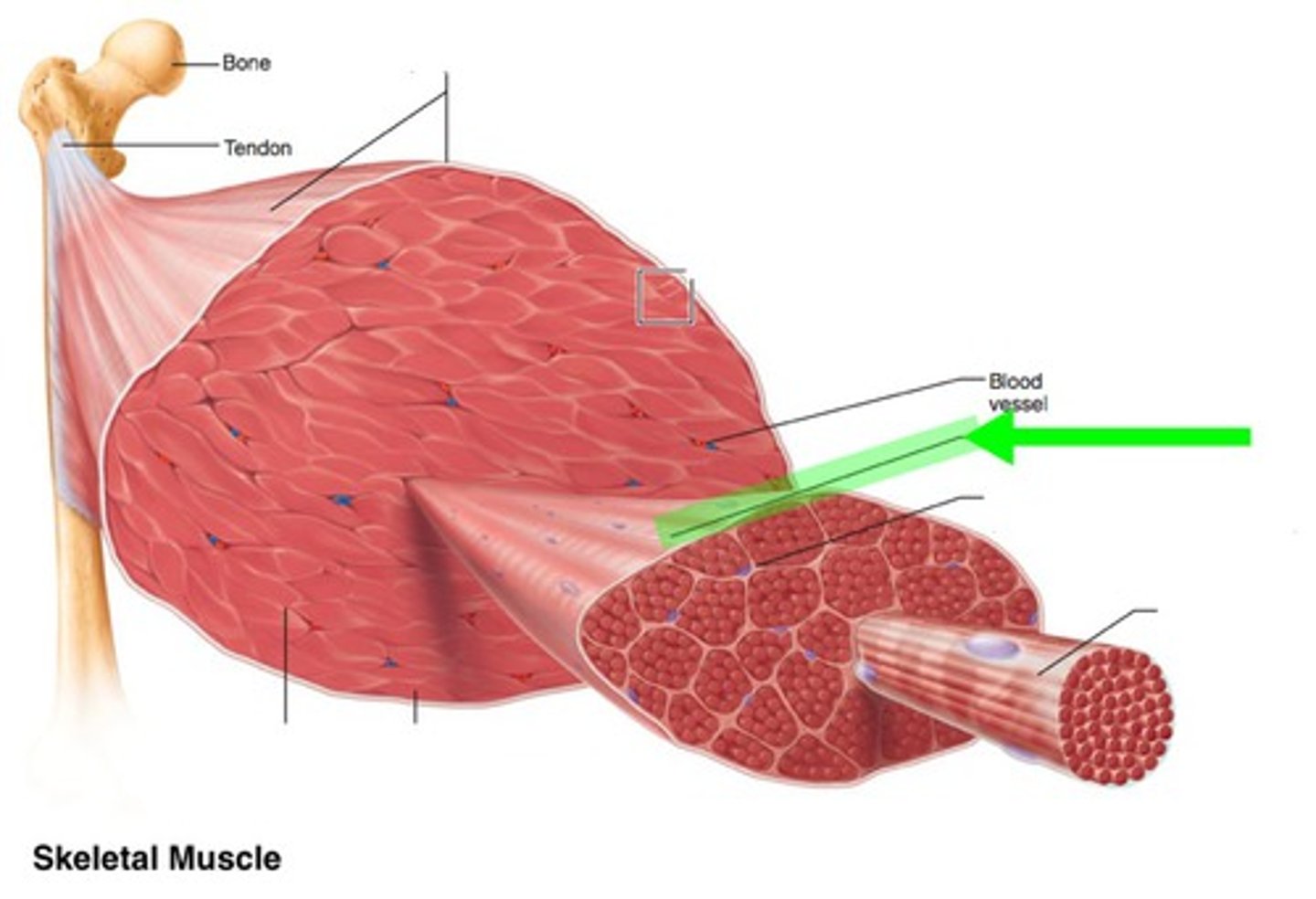
Epimysium
covers the entire skeletal muscle
aponeurosis
a sheet-like tissue that functions as a tendon, connecting muscle to bone. it is sheet-like, compared to a coil-like tendon
Sarcomere
contractile unit of a muscle fiber
cross bridges
myosin head, which connects thick filaments and thin filaments during a contraction
titin protein
spans from tip of thick filament to Z line; helps maintain alignment
Z line
A dark thin protein band to which actin filaments are attached in a striated muscle fiber, marking the boundaries between adjacent sarcomeres.
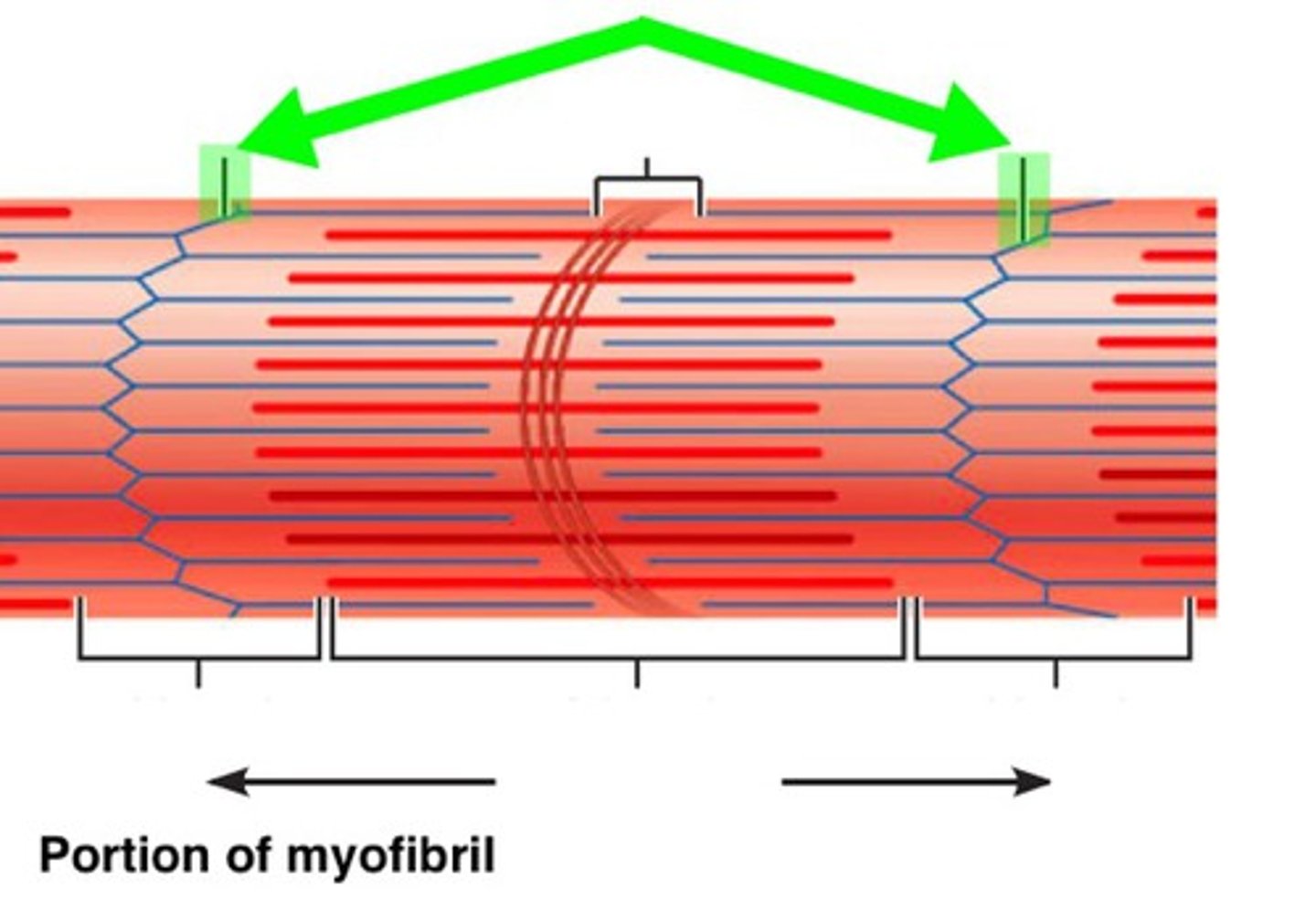
I band
thin filaments only (#2 on picture)
A band
dark area; extends the length of the thick filaments (#6 on picture)
H zone
thick filaments only
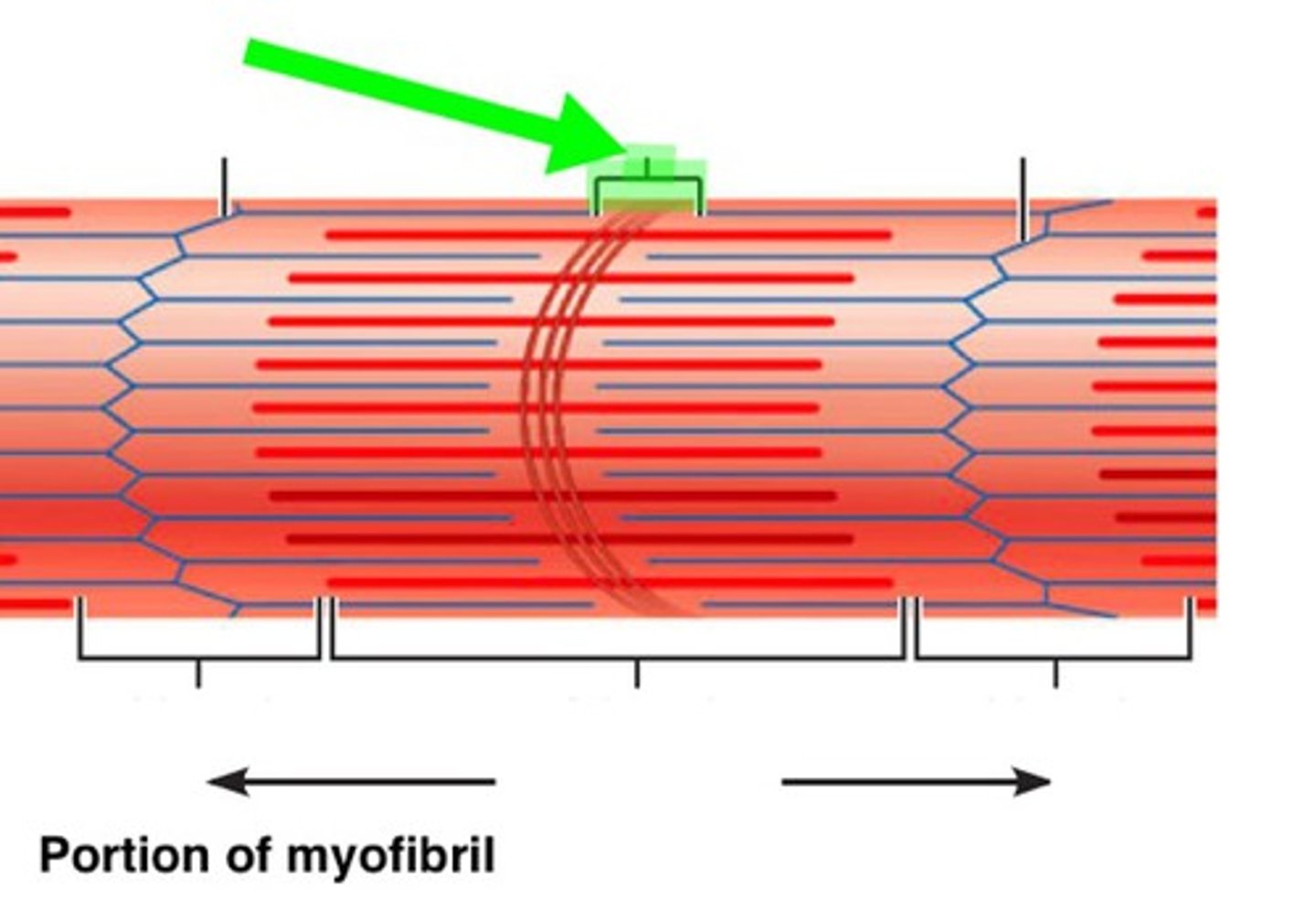
M line
supporting proteins that hold the thick filaments together in the H zone
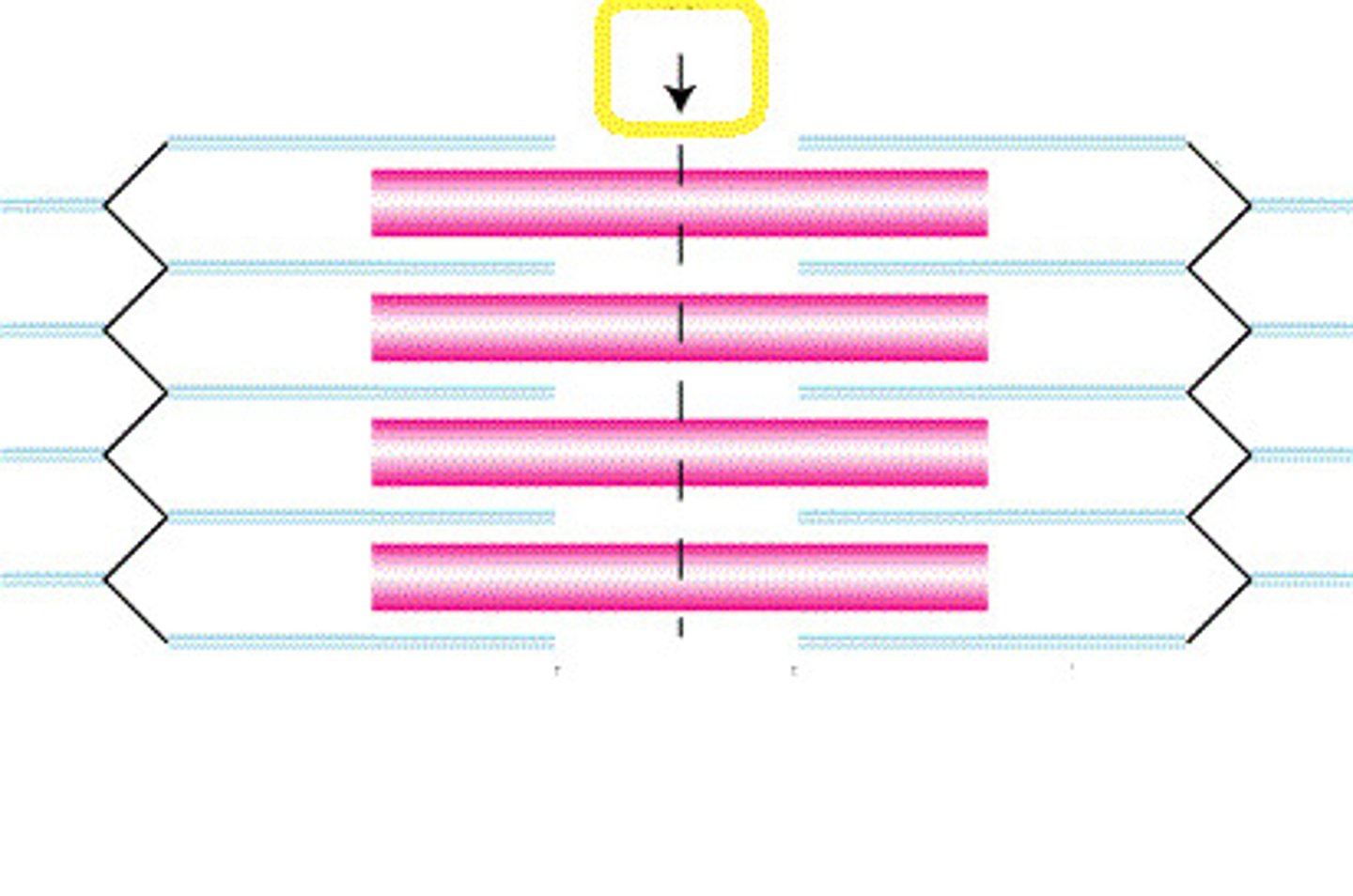
motor unit
A motor neuron and all of the muscle fibers it innervates
fine control
small motor units contain as few as 20 muscle fibers per nerve fiber (ex. eye muscles)
strength control
large motor units where up to 1,000 connect to a muscle (ex. gastrocnemius)
Recruitment (Muscle)
It is the process of increasing the number of motor units contracting within a muscle at a given time.
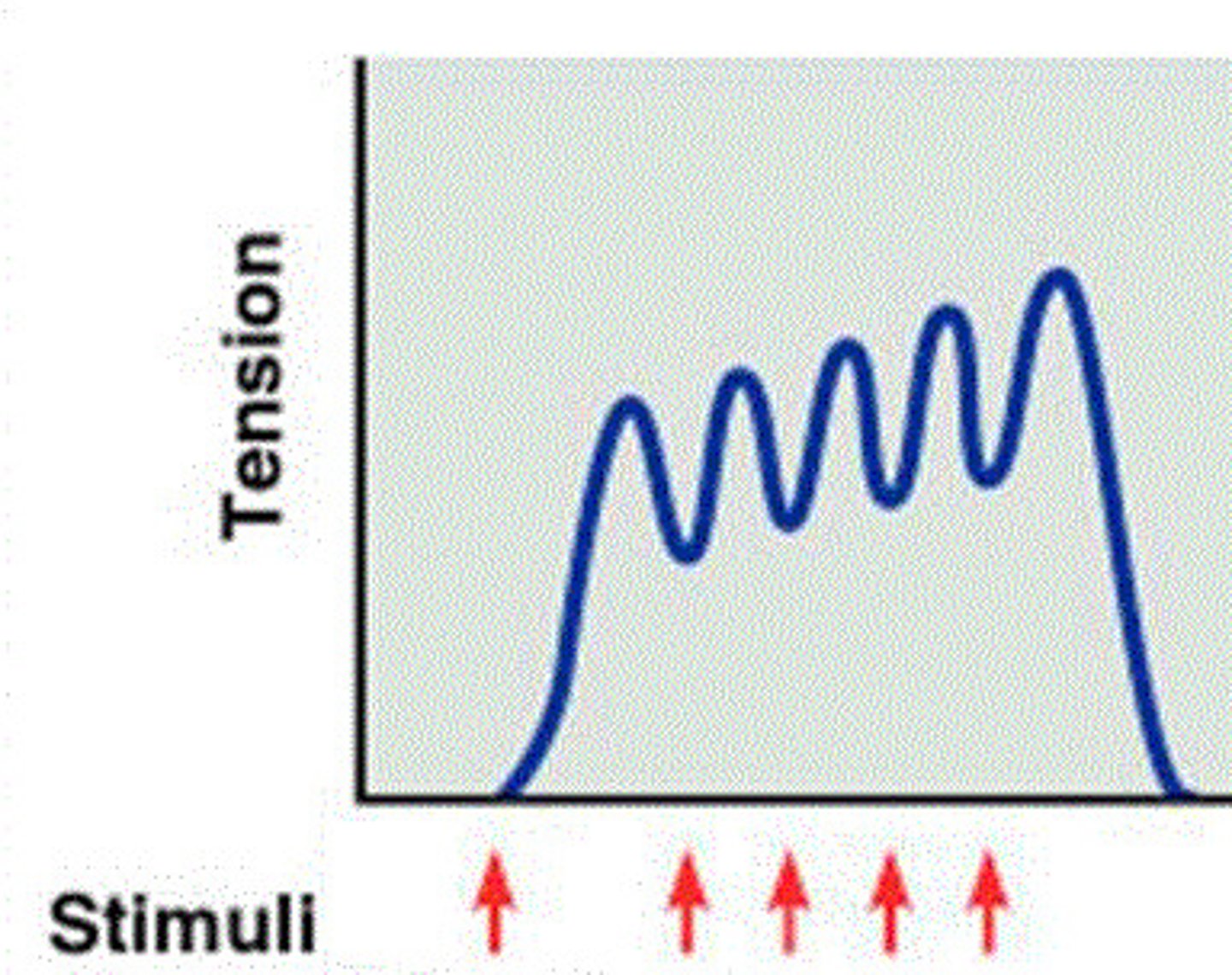
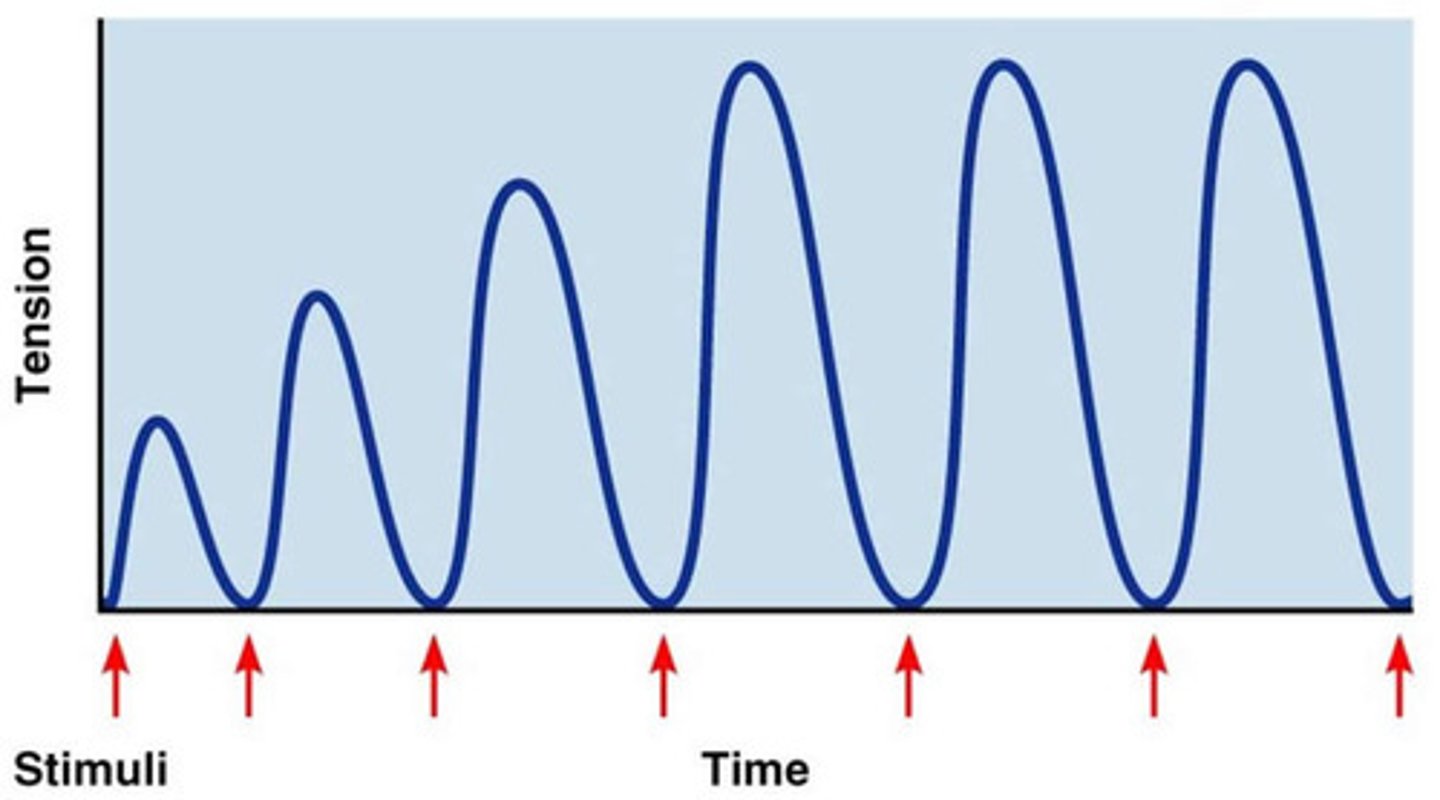
unfused tetanus
type of wave summation with partial relaxation observed between twitches
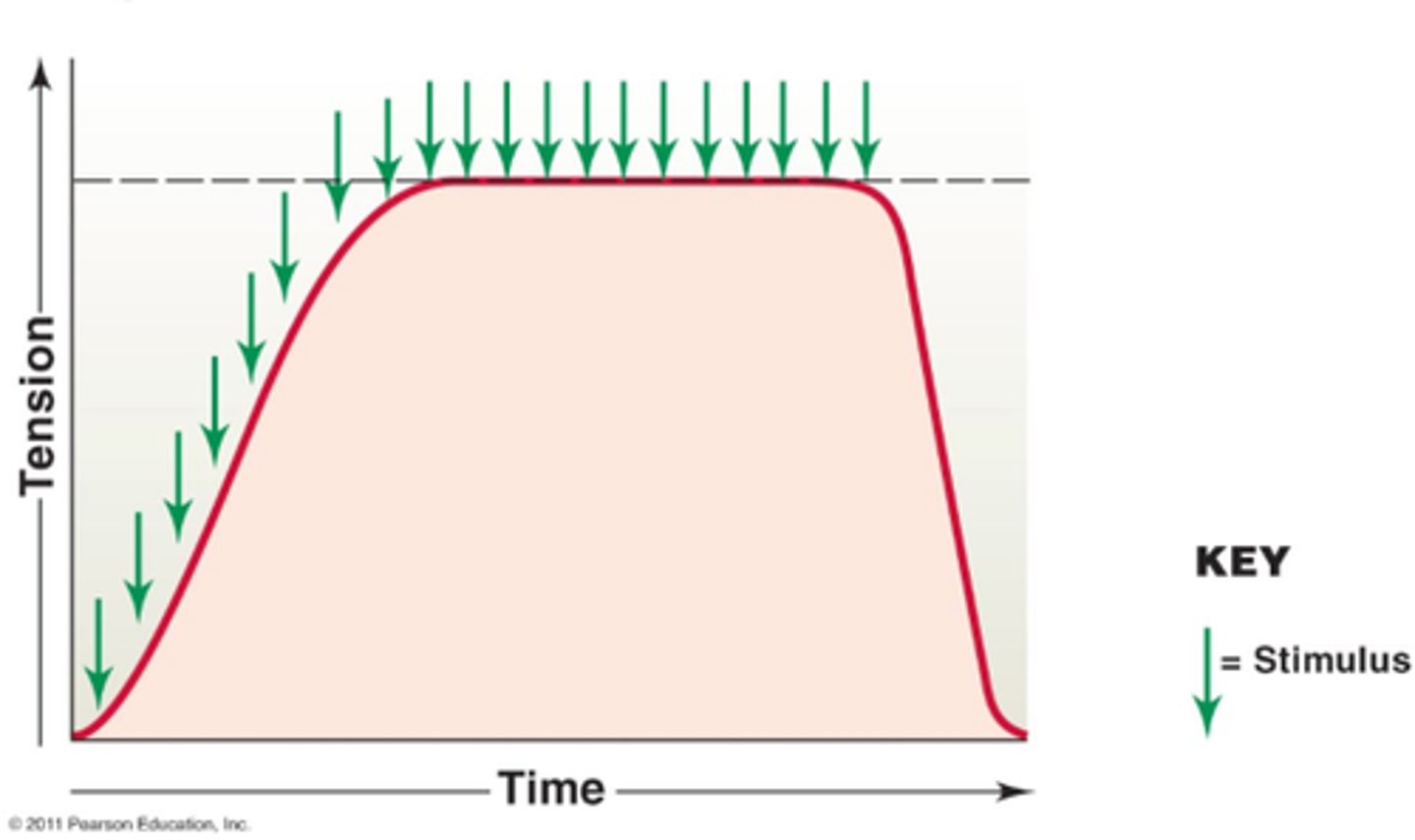
fused tetanus
when stimulus frequency is so high that no muscle relaxation takes place between stimuli
wave summation
One stimulus immediately follows the next; stimulus continually gets hit. Muscles doesn't quite return to resting state.
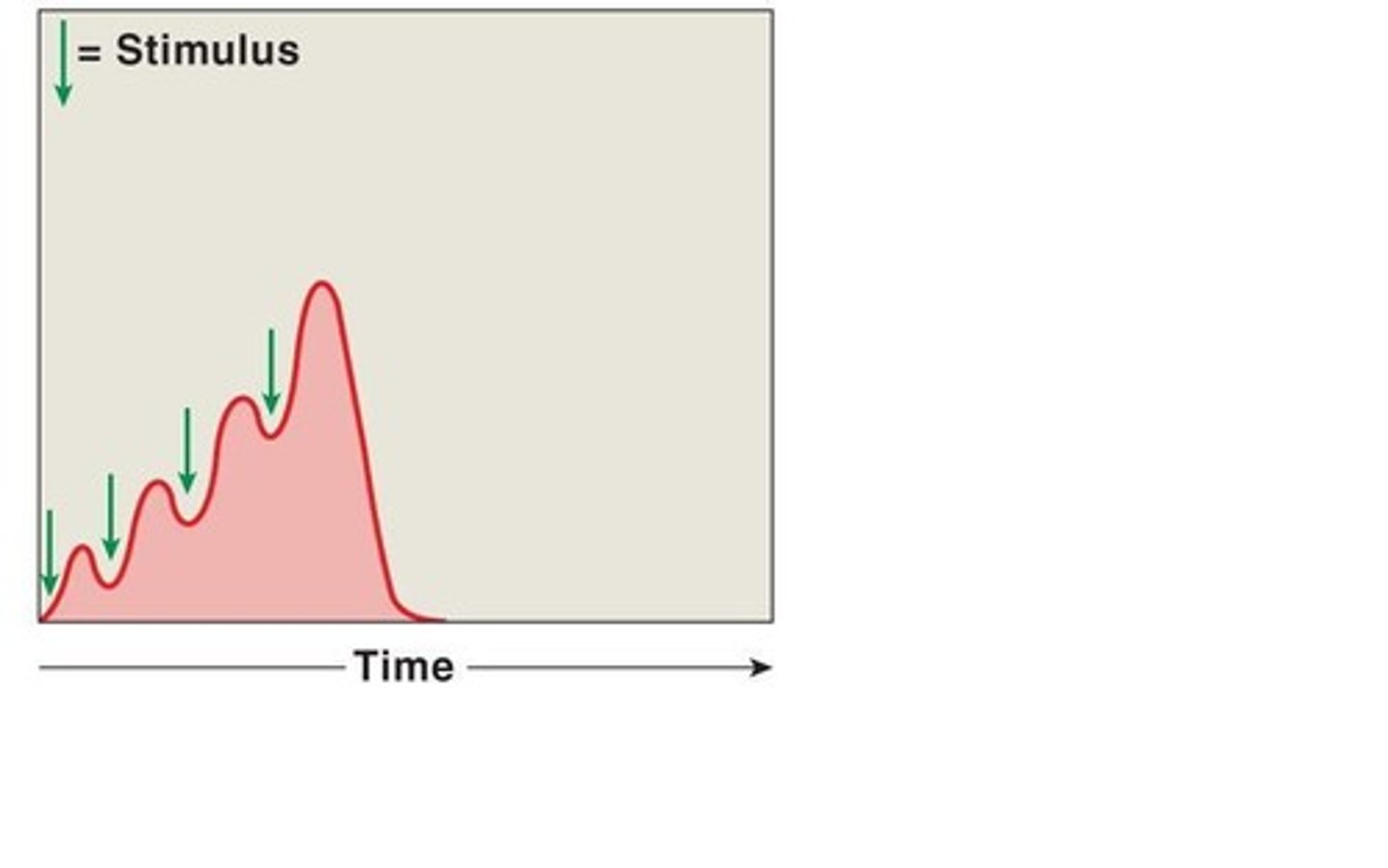
Treppe
Phenomenon in which each successive twitch contracts with similar amount of stimulus before.
isotonic contraction
A muscle contraction that pulls on the bones and produces movement of body parts.
isometric contraction
Muscle contracts but there is no movement, muscle stays the same length
concentric contraction
shortening of muscle ex. flexing biceps
eccentric contraction
muscle lengthens ex. extending biceps
yes
Are skeletal muscles striated?
yes
Are cardiac muscles striated?
No
Are smooth muscles striated?
no
Are cardiac and skeletal muscles regenerative?
yes
Is smooth muscle regenerative?
cardiac muscle
Which muscle type has intercalated discs?
myofibrils stretched too far
does not allow myosin and actin to touch, therefore muscle cannot form cross bridges to contract.
myofibrils too close together
actin and myosin are intertwined deeply, allowing for there to be no tension for muscle to preform contraction movement
phosphagen system
supplies energy very quickly and is the primary source of energy for very high-intensity exercise
myokinase/creatine kinase
transfers Pi from one ADP to another, converting the latter to ATP
anaerobic respiration
Respiration in the absence of oxygen. This produces lactic acid. It is used for short term exercise
aerobic respiration
Respiration that requires oxygen; is used for long term exercise
slow twitch fibers
red muscle fibers that are slow to contract but have the ability to continue contracting for long periods of time (many mitochondria, small diameter)
fast twitch fibers
muscle fibers that contract rapidly and forcefully but fatigue quickly (few mitochondria, large diameter)
calmodulin
A cyoplasmic Ca2+-binding protein. Calmodulin is particularly important in smooth muscle cells, where binding of Ca2+ allows calmodulin to activate myosin light-chian kinase, the first step in smooth muscle cell contraction.
myosin light chain kinase
enables myosin heads to attach to actin
no
does smooth muscle have sarcomeres?
Phosphorylation
The metabolic process of introducing a phosphate group into an organic molecule.
Astrocytes
contributes to and regulates Blood Brain Barrier (BBB); regulates composition of fluid in the brain; converts glucose to lactate for the brain to use as energy; secretes chemicals that stimulate nerve maintenance
Microglia
Act as phagocytes, eating damaged cells and bacteria, act as the brains immune system
Oligodendrocytes
Form myelin sheath in CNS
ependymal cells
produce and circulate cerebrospinal fluid (ciliated for this movement)
satellite cells
protect neuron cell bodies
Schwann cells
produce myelin in PNS
Nissl bodies
RER and free ribosomes that make neurotransmitters
initial segment of axon
Area of the axon having the lowest threshold for stimulation, so the action potentials begin at this point
axoplasm
cytoplasm of axon
Axolemma
plasma membrane of axon
axon collaterals
Side branches of the axon, carry signal to other cells.
Axon telodendria
branches on axon terminal propagating signals towards post synaptic cell
Endoneurium
delicate connective tissue around individual nerve fibers in nerve
Perineurium
surrounds each neuron fascicle
Epineurium
surrounds the entire nerve bundle