Atomic Models, Characteristic of a Wave
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
crest
highest point of the wave
through
lowest point of the wave
wavelength
distance from one crest/through to the next (m)
wave height
height from through to crest
wave steepness
ration of wave height to wavelength (height : wavelength)
amplitude
distance from the center of wave to the bottom of the through
wave period
time for one full wavelength to pass a given point
John Dalton’s Atomic Theory
matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. an atom is the smallest unit of an element that can participate in a chemical change.
an element consists only one type of atom, which has a mass that is characteristic of the element and is the same for all atoms of that element.
atoms of one element differ in properties from atoms of all other elements.
a compound consists of atoms of two or more elements combined in a small, whole-number ratio. in a given compound, the numbers of atoms of each of its elements are always present in the same ratio.
atoms are neither creator nor destroyed during a chemical change (instead, rearranged to yield substances that are different from those present before the change)
in chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged
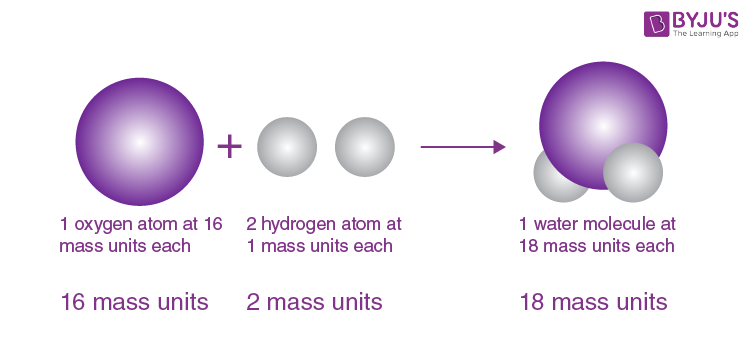
JJ Thomson’s Plum Pudding Model
atom consists of a sphere of positive matter within which electrostatic forces determined the positioning of the negatively charged corpuscles.
explains the overall neutral charge of atom
negatively charged swims in positively charged sea
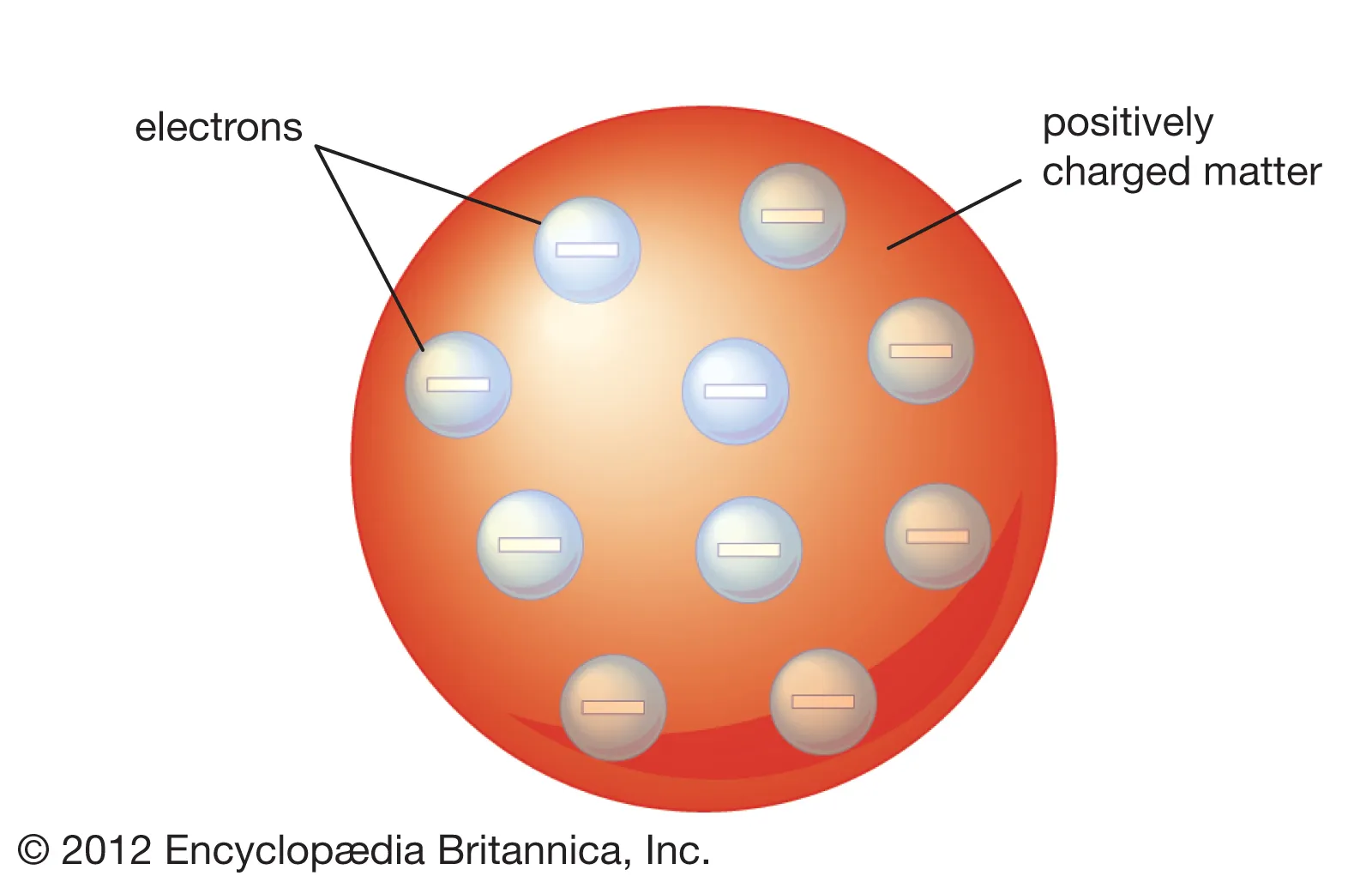
Rutherford’s Nuclear Atom Model (Alpha Scattering Experiment; Rutherford Planetary Model)
positively-charged particles and most of the mass of an atom was concentrated in an extremely small volume. nucleus (positively charged core) is the region of the atom.
negatively-charged electrons surround the nucleus of an atom. electrons surrounding the nucleus revolve around it with very high speed in circular paths called orbits.
electrons being negatively charged and nucleus being a densely concentrated mass of positively charged particles are held together by a strong electrostatic force of attraction.
mass of an atom is concentrated in the nucleus
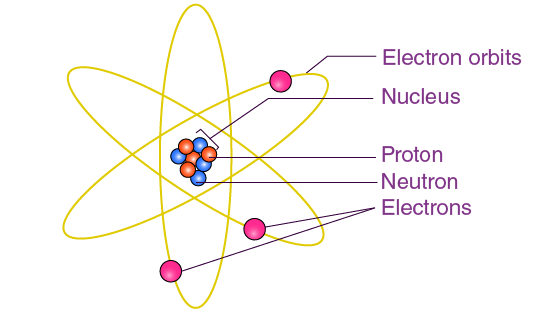
Bohr’s Solar System Model of the Atom
electrons assume only certain orbits around the nucleus. these orbits are stable and called stationary orbits.
each orbit has energy associated with it.
e.g., orbit closest to the nucleus has an energy E1, the next closest E2, and so on
light is emitted when an electron jumps from a higher orbit to lower orbit and absorbed when it jumps from a lower to higher orbit
emitted (higher to lower)
absorbed (lower to higher)
energy and frequency of light emitted or absorbed is given by the difference between the two orbit energies.
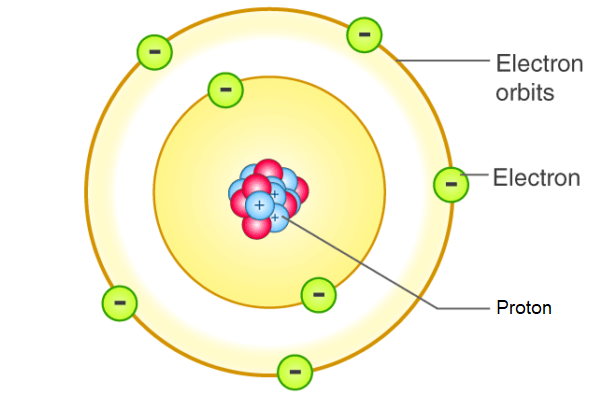
Erwin Schrödinger’s Quantum or Wave-Mechanical Model
electrons are not in a circular orbits around the nucleus.
electrons are in a 3-D region around the nucleus called atomic orbitals.
atomic orbital describes the probable location of the electron.
