Ch. 9 Lec: Articulations (Joints)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/200
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
201 Terms
1
New cards
\-Structural (Anatomy)
\-Functional (Range of motion)
\-Structure determines function
\-Functional (Range of motion)
\-Structure determines function
Joint Classification
2
New cards
\-Fibrous
\-Cartilaginous
\-Bony
\-Synovial
\-Cartilaginous
\-Bony
\-Synovial
Structural classifications
3
New cards
\-Synarthrosis
\-**Amphiarthrosis**
\-Diarthrosis
\-**Amphiarthrosis**
\-Diarthrosis
Functional classifications
4
New cards
Immovable joint
Synarthrosis
5
New cards
Slightly movable joint
Amphiarthrosis
6
New cards
Freely movable joint
Diarthrosis
7
New cards
–Very strong
–Edges of bones may touch or interlock
–Can be fibrous or cartilaginous
\-4 types (Synarthrotic)
–Edges of bones may touch or interlock
–Can be fibrous or cartilaginous
\-4 types (Synarthrotic)
Synarthrosis
8
New cards
•Suture
•Gomphosis
•Synchondrosis
•Synostosis
•Gomphosis
•Synchondrosis
•Synostosis
Types of Synarthrotic Joints
9
New cards
•Found only between bones of skull
•Edges of bones interlock
•Bound by dense fibrous connective tissue
•Edges of bones interlock
•Bound by dense fibrous connective tissue
Suture
10
New cards
•Binds teeth to bony sockets
•Fibrous connection (periodontal ligament)
•Fibrous connection (periodontal ligament)
Gomphosis
11
New cards
•Rigid cartilaginous bridge between two bones
•Found between vertebrosternal ribs and sternum
•Also, epiphyseal cartilage of growing long bones
•Found between vertebrosternal ribs and sternum
•Also, epiphyseal cartilage of growing long bones
Synchondrosis
12
New cards
•Created when two bones fuse
•Example: metopic suture of frontal bone
•And epiphyseal lines of mature long bones
•Example: metopic suture of frontal bone
•And epiphyseal lines of mature long bones
Synostosis
13
New cards
–More movable than a synarthrosis
–Stronger than a diarthrosis
–Can be fibrous or cartilaginous
\-2 types (Amphiarthroses)
–Stronger than a diarthrosis
–Can be fibrous or cartilaginous
\-2 types (Amphiarthroses)
Amphiarthrosis
14
New cards
\-Syndesmosis
\-Symphysis
\-Symphysis
Types of Amphiarthroses
15
New cards
Bones connected by a ligament
Syndesmosis
16
New cards
Bones connected by fibrocartilage
Symphysis
17
New cards
\-Synovial joints (Diarthroses)
Diarthrosis
18
New cards
–Freely movable joints
–At ends of long bones
Surrounded by **joint capsule** (**articular capsule)**
–At ends of long bones
Surrounded by **joint capsule** (**articular capsule)**
Diarthroses
19
New cards
–Synovial fluid from synovial membrane
–**Articular cartilage** covers articulating surfaces
–**Articular cartilage** covers articulating surfaces
Diarthroses
20
New cards
Contains synovial membrane
J**oint capsule** (**articular** **capsule**)
21
New cards
Fills joint cavity
Synovial fluid
22
New cards
Prevents direct contact between bones
**Articular cartilage**
23
New cards
\-Synovial fluid
\-5 accessory structures
\-Mobile but relatively weak
\-5 accessory structures
\-Mobile but relatively weak
Synovial joint
24
New cards
–Has the consistency of egg yolk
–Contains proteoglycans
–3 primary functions
–Contains proteoglycans
–3 primary functions
Synovial fluid
25
New cards
•Lubrication
•Nutrient distribution
•Shock absorption
•Nutrient distribution
•Shock absorption
Primary functions: Synovial fluid
26
New cards
–Cartilages
\-Fat pads
–Ligaments
–Tendons
–Bursae
\-Fat pads
–Ligaments
–Tendons
–Bursae
Accessory structures: Synovial joint
27
New cards
Fibrocartilage pad between opposing bones
Meniscus
28
New cards
Made of cartilage
Meniscus
29
New cards
–Adipose tissue covered by synovial membrane
–Protect articular cartilages
–Protect articular cartilages
Fat pads
30
New cards
–Support and strengthen joints
**-Sprain**
**-Sprain**
Ligaments
31
New cards
Ligament with torn collagen fibers
Sprain
32
New cards
Attach to muscles around joint
Tendons
33
New cards
–Small pockets of synovial fluid
–Cushion areas where tendons or ligaments rub against other tissues
–Cushion areas where tendons or ligaments rub against other tissues
Bursae
34
New cards
•Collagen fibers of joint capsule and ligaments
•Shapes of articulating surfaces and menisci
•Other bones, muscles, or fat pads
•Tendons attached to articulating bones
•Shapes of articulating surfaces and menisci
•Other bones, muscles, or fat pads
•Tendons attached to articulating bones
S**tabilize synovial joints**
–Prevent injury by limiting the range of motion
–Prevent injury by limiting the range of motion
35
New cards
\# of Synovial Joint Movements
19
36
New cards
\-Flexion
\-Extension
\-Hyperextension
\-Extension
\-Hyperextension
Synovial Joint Movements
37
New cards
\-Abduction
\-Adduction
\-Circumduction
\-Rotation
\-Adduction
\-Circumduction
\-Rotation
Synovial Joint Movements
38
New cards
\-Pronation
\-Supination
\-Inversion
\-Eversion
\-Supination
\-Inversion
\-Eversion
Synovial Joint Movements
39
New cards
\-Dorsiflexion
\-Plantar flexion
\-Opposition
\-Reposition
\-Plantar flexion
\-Opposition
\-Reposition
Synovial Joint Movements
40
New cards
\-Protraction
\-Retraction
\-Depression
\-Elevation
\-Retraction
\-Depression
\-Elevation
Synovial Joint Movements
41
New cards
Decreases angle between articulating bones
Flexion
42
New cards
Increases angle between articulating bones
Extension
43
New cards
Extension past anatomical position
**Hyperextension**
44
New cards
Movement away from longitudinal axis
Abduction
45
New cards
Movement toward longitudinal axis
Adduction
46
New cards
Complete circular movement without rotation
**Circumduction**
47
New cards
Movements made about the longitudinal axis and in the transverse plane
Rotation
48
New cards
•Rotates forearm so that radius rolls across ulna
•Results in palm facing posteriorly
•Results in palm facing posteriorly
Pronation
49
New cards
•Turns palm anteriorly
•Forearm is supinated in anatomical position
•Forearm is supinated in anatomical position
Supination
50
New cards
Twists sole of foot medially
Inversion
51
New cards
Twists sole of foot laterally
Eversion
52
New cards
Flexion at ankle (lifting toes)
Dorsiflexion
53
New cards
Extension at ankle (pointing toes)
**Plantar flexion**
54
New cards
Movement of thumb toward palm or other fingers
**Opposition**
55
New cards
Opposite of opposition
**Reposition**
56
New cards
Anterior movement in horizontal plane (forward)
Protraction
57
New cards
Opposite of protraction (pulling back)
**Retraction**
58
New cards
Moving a structure inferiorly (down)
**Depression**
59
New cards
Moving a structure superiorly (up)
Elevation
60
New cards
\-Plane (gliding)
\-Hinge
\-Condylar (ellipsoid)
\-Hinge
\-Condylar (ellipsoid)
Classification: Synovial Joints
61
New cards
\-Saddle
\-Pivot
\-Ball-and socket
\-Pivot
\-Ball-and socket
Classification: Synovial Joints
62
New cards
–First two cervical vertebrae are joined by a synovial joint
–Synovial joints lie between adjacent articular processes
–Adjacent vertebral bodies form symphyses
–Synovial joints lie between adjacent articular processes
–Adjacent vertebral bodies form symphyses
**Intervertebral joints**
63
New cards
Separates vertebral bodies
**Intervertebral disc**
64
New cards
–**Anulus fibrosus**
–**Nucleus pulposus**
–**Vertebral end plates** of cartilage
–**Nucleus pulposus**
–**Vertebral end plates** of cartilage
**Intervertebral disc: Components**
65
New cards
\-Tough outer layer of fibrocartilage
\-Attaches disc to vertebrae
\-Attaches disc to vertebrae
**Anulus fibrosus**
66
New cards
•Elastic, gelatinous core
•Absorbs shocks
•Absorbs shocks
**Nucleus pulposus**
67
New cards
Cover superior and inferior surfaces of disc
**Vertebral end plates** of cartilage
68
New cards
\-Bulging disc
\-Herniated disc
\-Herniated disc
**Intervertebral disc: Damage**
69
New cards
•Bulge in anulus fibrosus
•Invades vertebral canal
•Invades vertebral canal
Bulging disc
70
New cards
•Nucleus pulposus breaks through anulus fibrosus
•Compresses spinal nerves
•Compresses spinal nerves
Herniated disc
71
New cards
\-Flexion
\-Extension
\-Lateral flexion
\-Rotation
\-Extension
\-Lateral flexion
\-Rotation
Vertebral movements
72
New cards
Elbow joint is what type of joint?
Hinge joint
73
New cards
\-Humerus
\-Radius
\-Ulna
\-Radius
\-Ulna
Elbow joint: Articulations involved
74
New cards
–Complex hinge joint
–Transfers weight from femur to tibia
–3 articulations
–Transfers weight from femur to tibia
–3 articulations
Knee joint
75
New cards
\-2 femur, tibia articulations (At medial and lateral condyles)
\-1 between patella and patellar surface of femur
\-1 between patella and patellar surface of femur
Knee joint: Articulations
76
New cards
–Ball-and-socket diarthrosis
–Between head of humerus and glenoid cavity of scapula
–Greatest range of motion of any joint
–Between head of humerus and glenoid cavity of scapula
–Greatest range of motion of any joint
Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint)
77
New cards
–Most frequently dislocated joint
–Supported by skeletal muscles, tendons, and ligaments
–Supported by skeletal muscles, tendons, and ligaments
Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint)
78
New cards
–Between head of femur and acetabulum of hip bone
–Strong ball-and-socket diarthrosis
–Strong ball-and-socket diarthrosis
Hip joint
79
New cards
–Wide range of motion
–Acetabular labrum
–Acetabular labrum
Hip joint
80
New cards
•Rim of fibrocartilage
•Increases depth of joint cavity
•Seals in synovial fluid
•Increases depth of joint cavity
•Seals in synovial fluid
Acetabular labrum
81
New cards
–**Rheumatism**
**-Arthritis (joint inflammation)**
\-__**Osteoarthritis**__
–**Rheumatoid arthritis**
–**Gouty arthritis**
**-Arthritis (joint inflammation)**
\-__**Osteoarthritis**__
–**Rheumatoid arthritis**
–**Gouty arthritis**
Joints: Degenerative changes
82
New cards
Pain and stiffness in musculoskeletal system
**Rheumatism**
83
New cards
All rheumatic diseases that affect synovial joints
**Arthritis (joint inflammation)**
84
New cards
•Caused by wear and tear of joint surfaces, or genetic factors affecting collagen formation
•Generally affects people over age 60
•Generally affects people over age 60
__**Osteoarthritis**__
85
New cards
•An inflammatory condition
•Immune system attacks joint tissues
•Immune system attacks joint tissues
**Rheumatoid arthritis**
86
New cards
Crystals of uric acid form within synovial fluid
**Gouty arthritis**
87
New cards
–Muscles attach to bones
–Bones are controlled by endocrine system
–Bones are controlled by endocrine system
Other systems interact with skeletal system
88
New cards
–Digestive and urinary systems provide calcium and phosphate minerals to bones for growth
–Skeleton serves as a reserve for calcium, phosphate, and other minerals
–Skeleton serves as a reserve for calcium, phosphate, and other minerals
Other systems interact with skeletal system
89
New cards
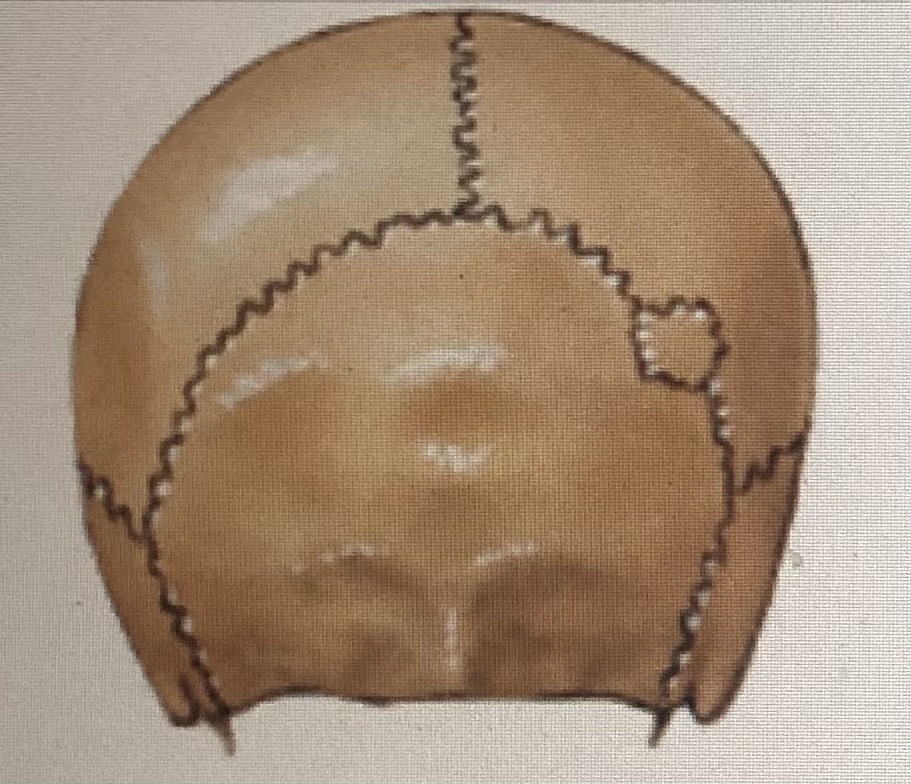
Suture
90
New cards
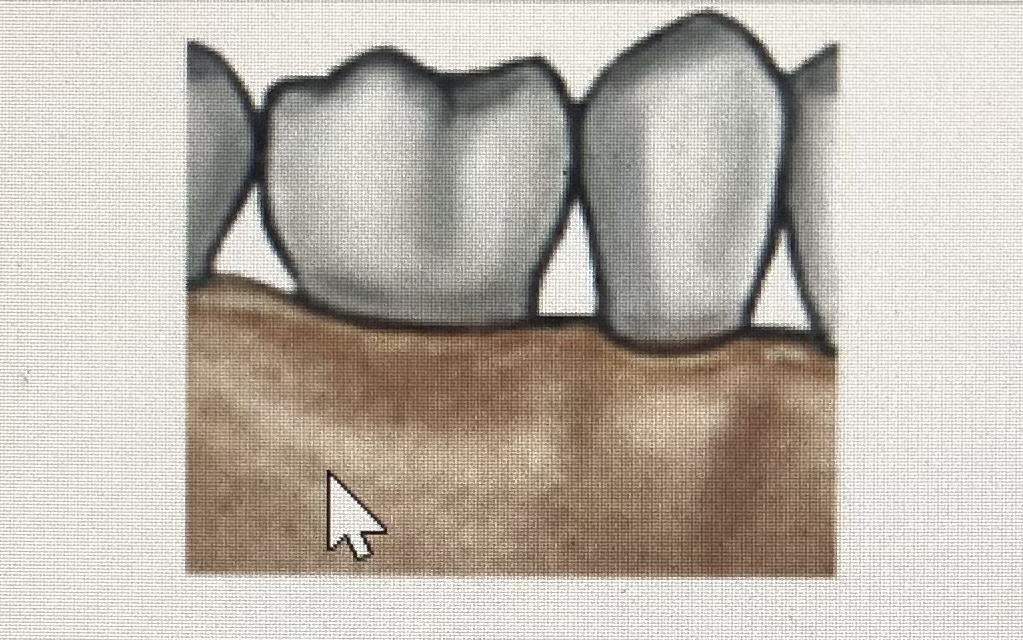
Gomphosis
91
New cards
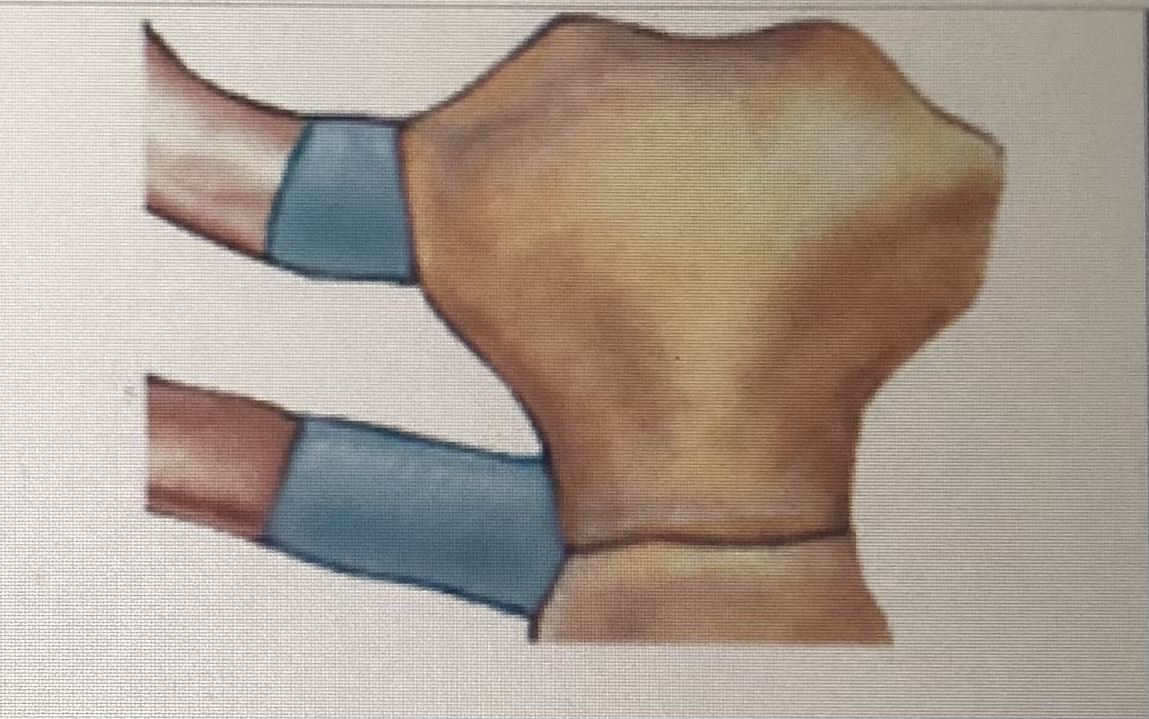
Sychondrosis
92
New cards
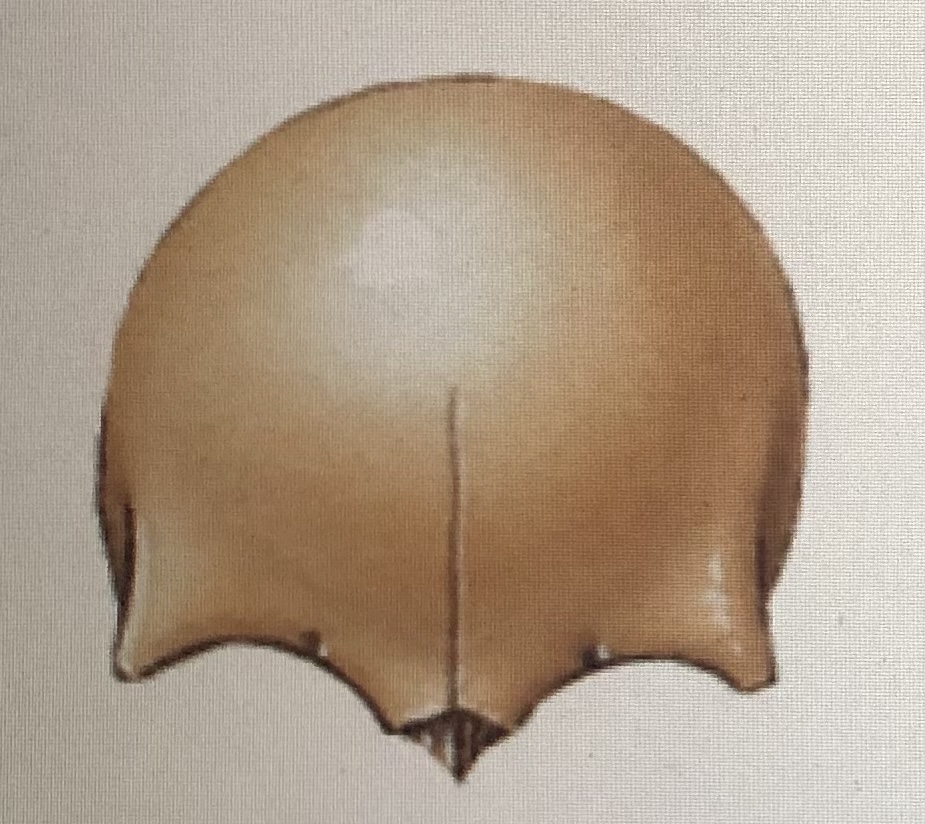
Synostosis
93
New cards
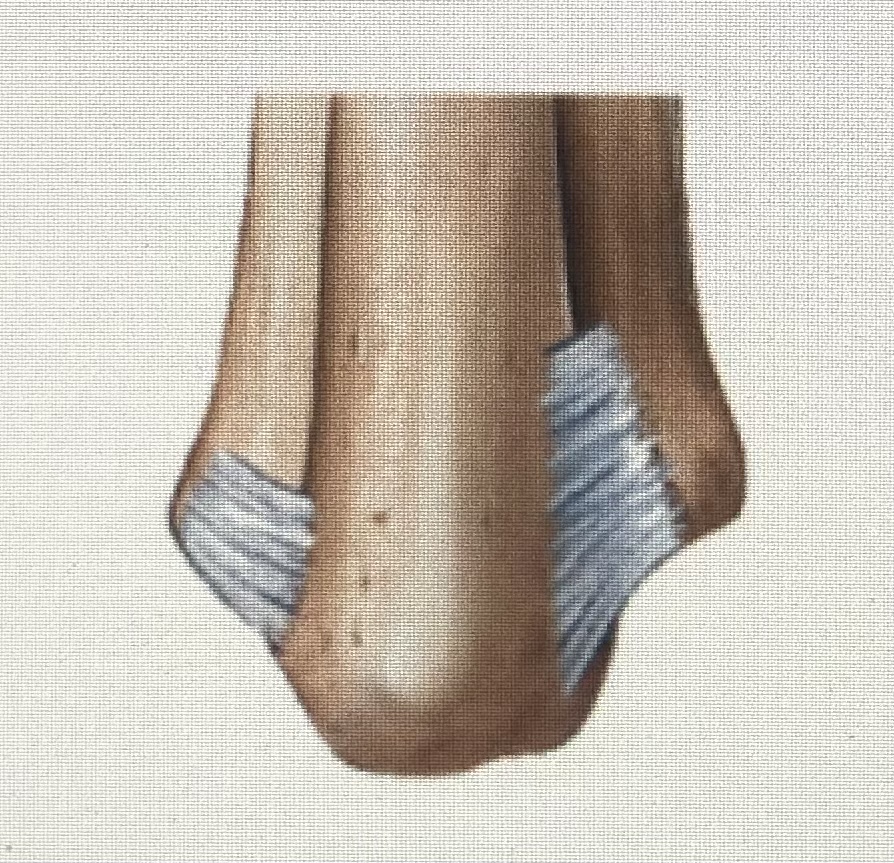
Syndesmosis
94
New cards
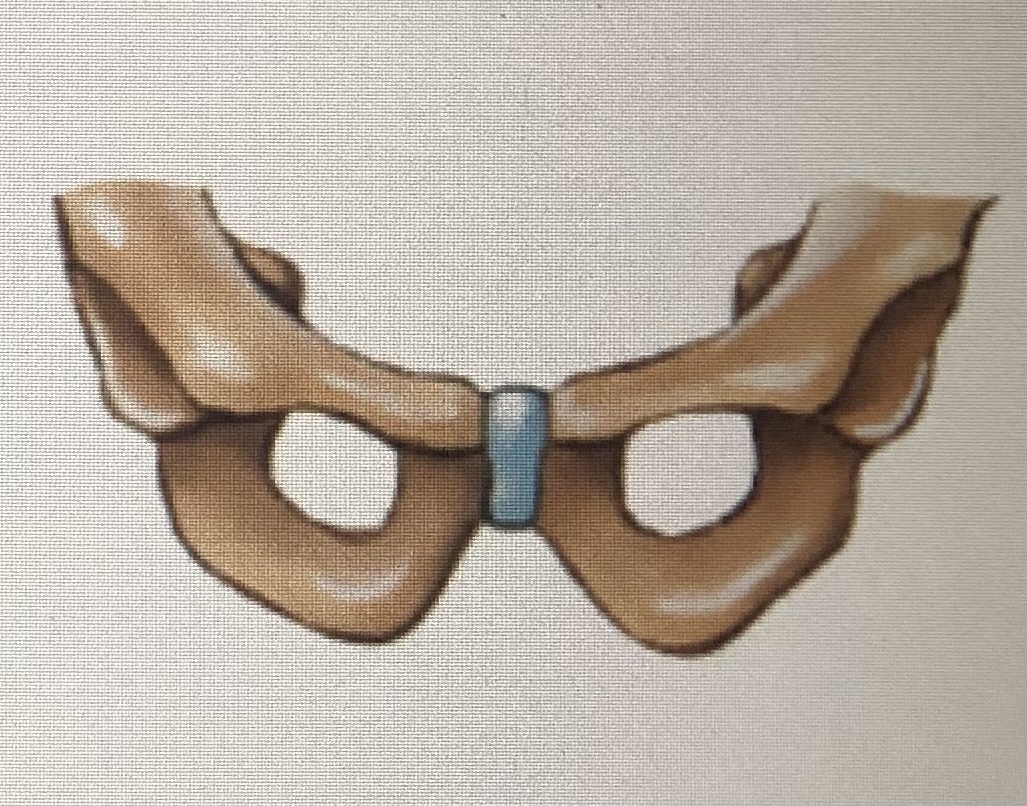
Symphysis
95
New cards
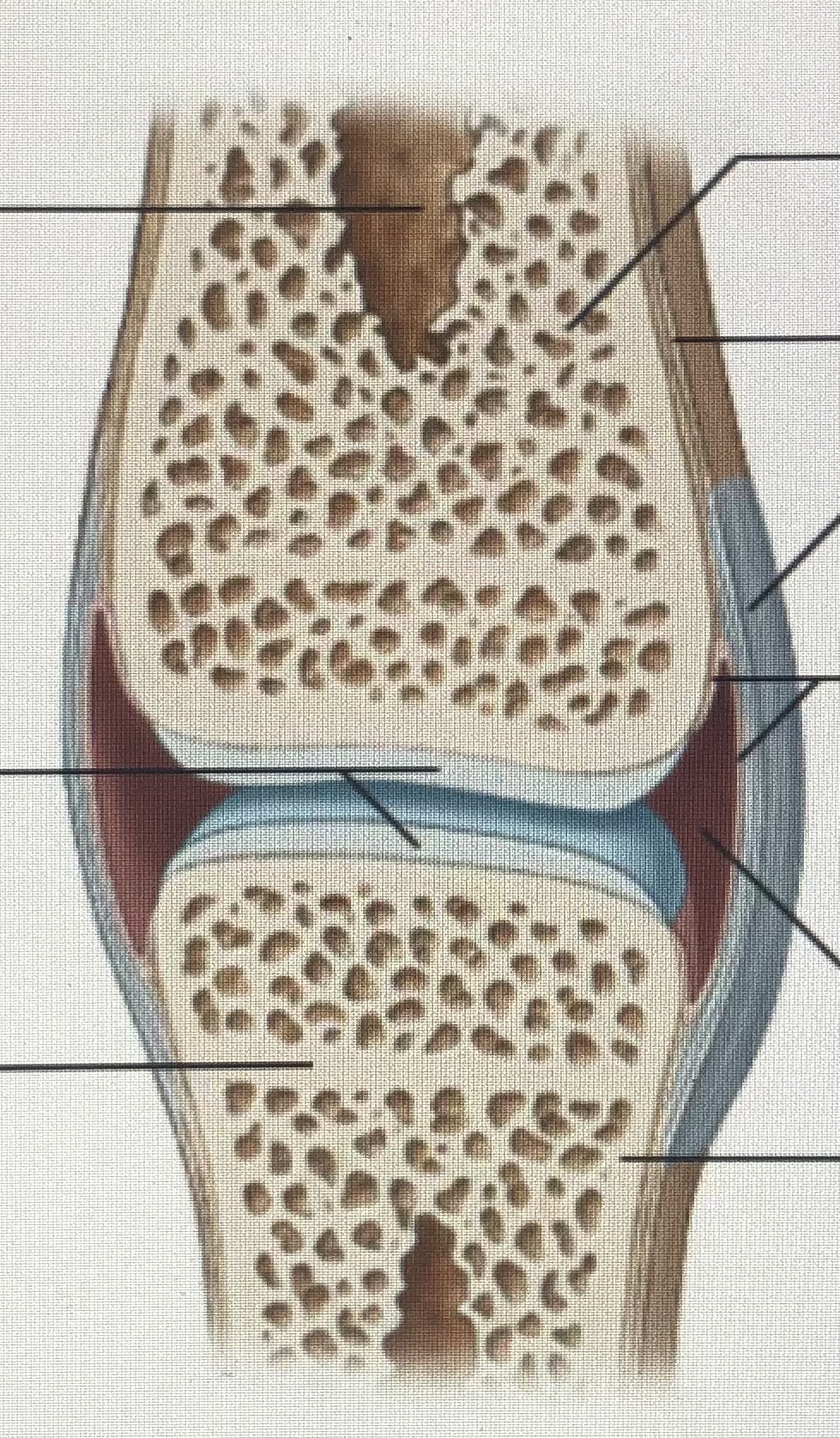
Synovial joint
96
New cards
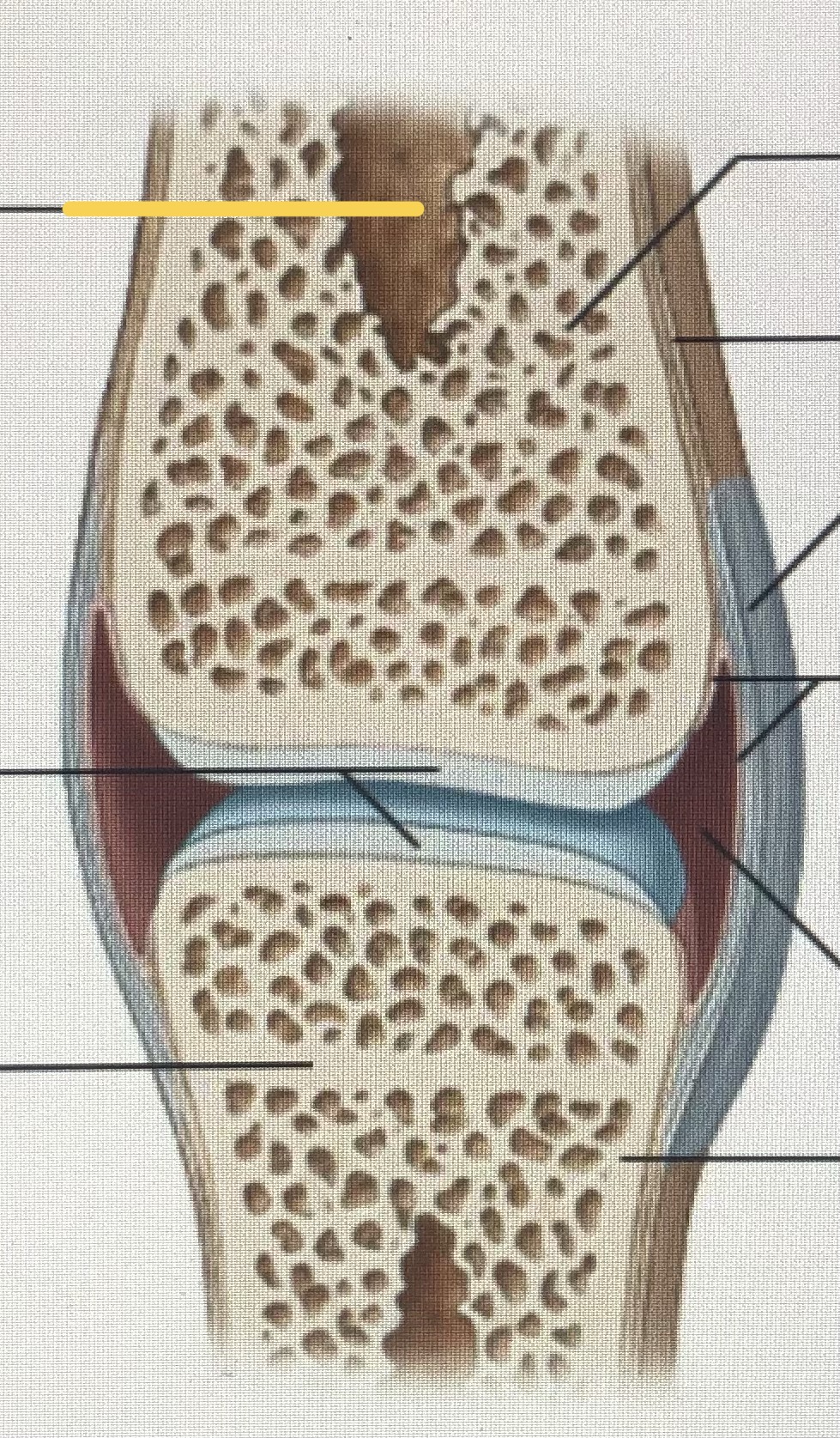
Medullary cavity
97
New cards
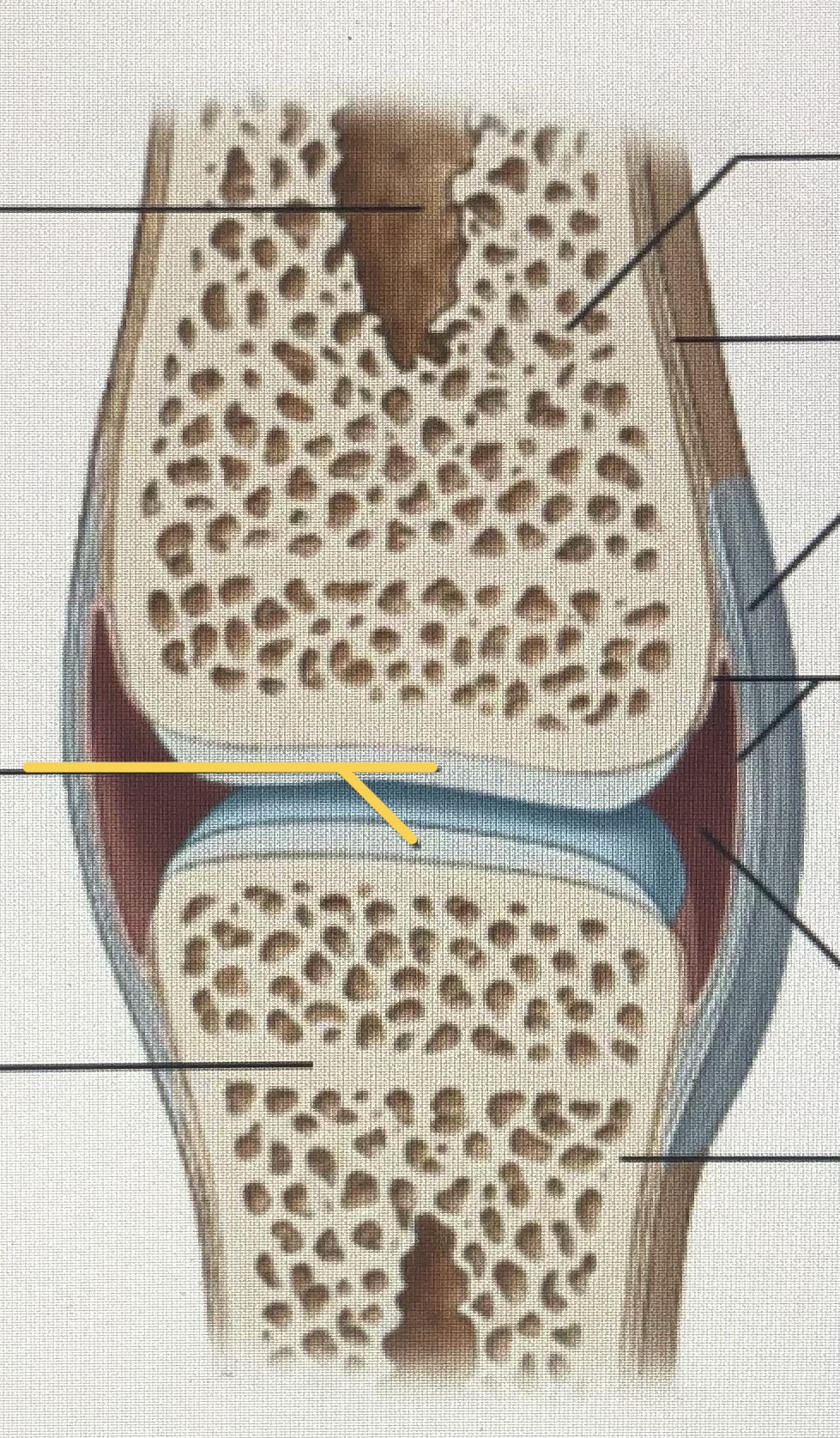
Articular cartilages
98
New cards
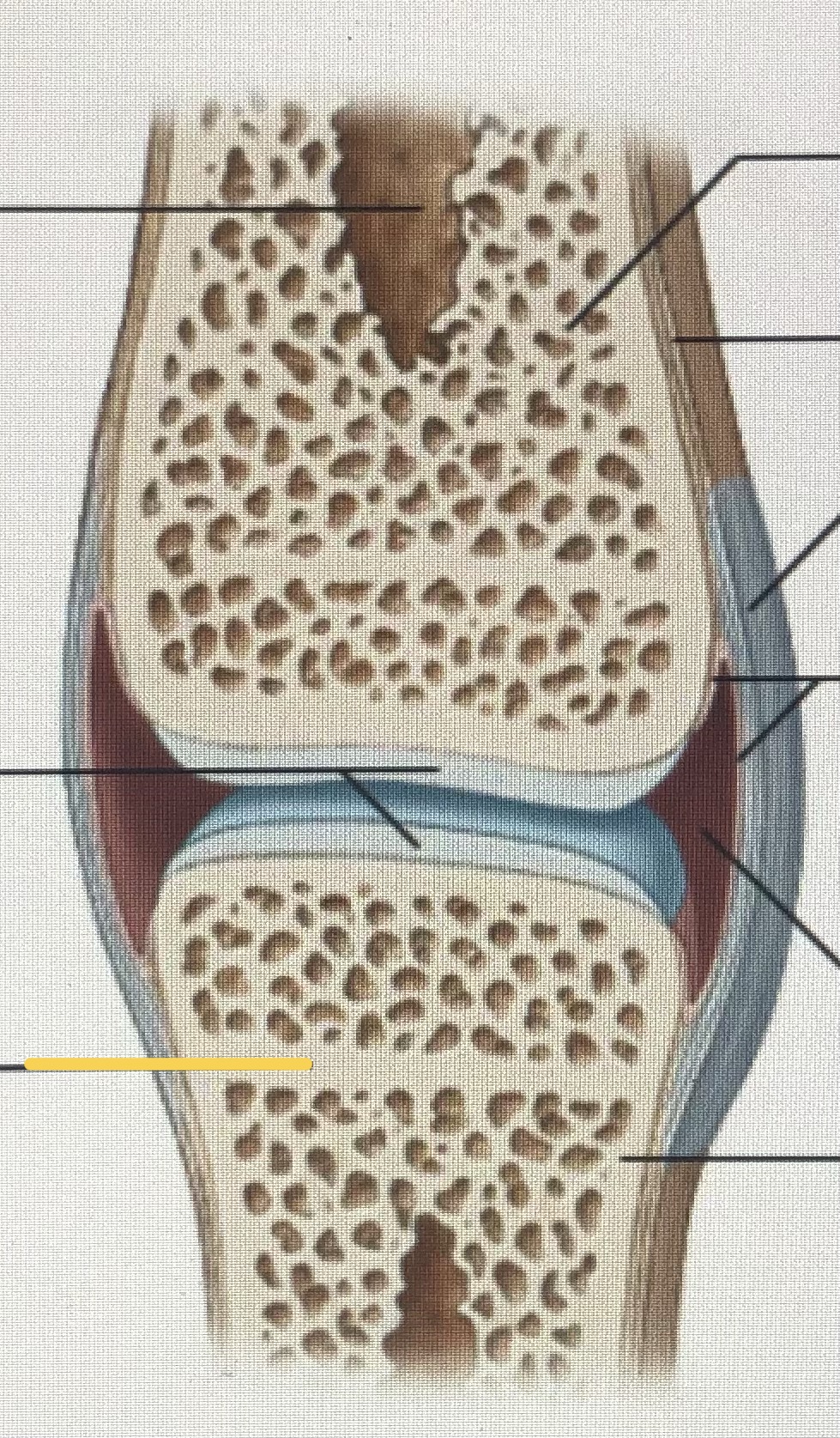
Metaphysis
99
New cards
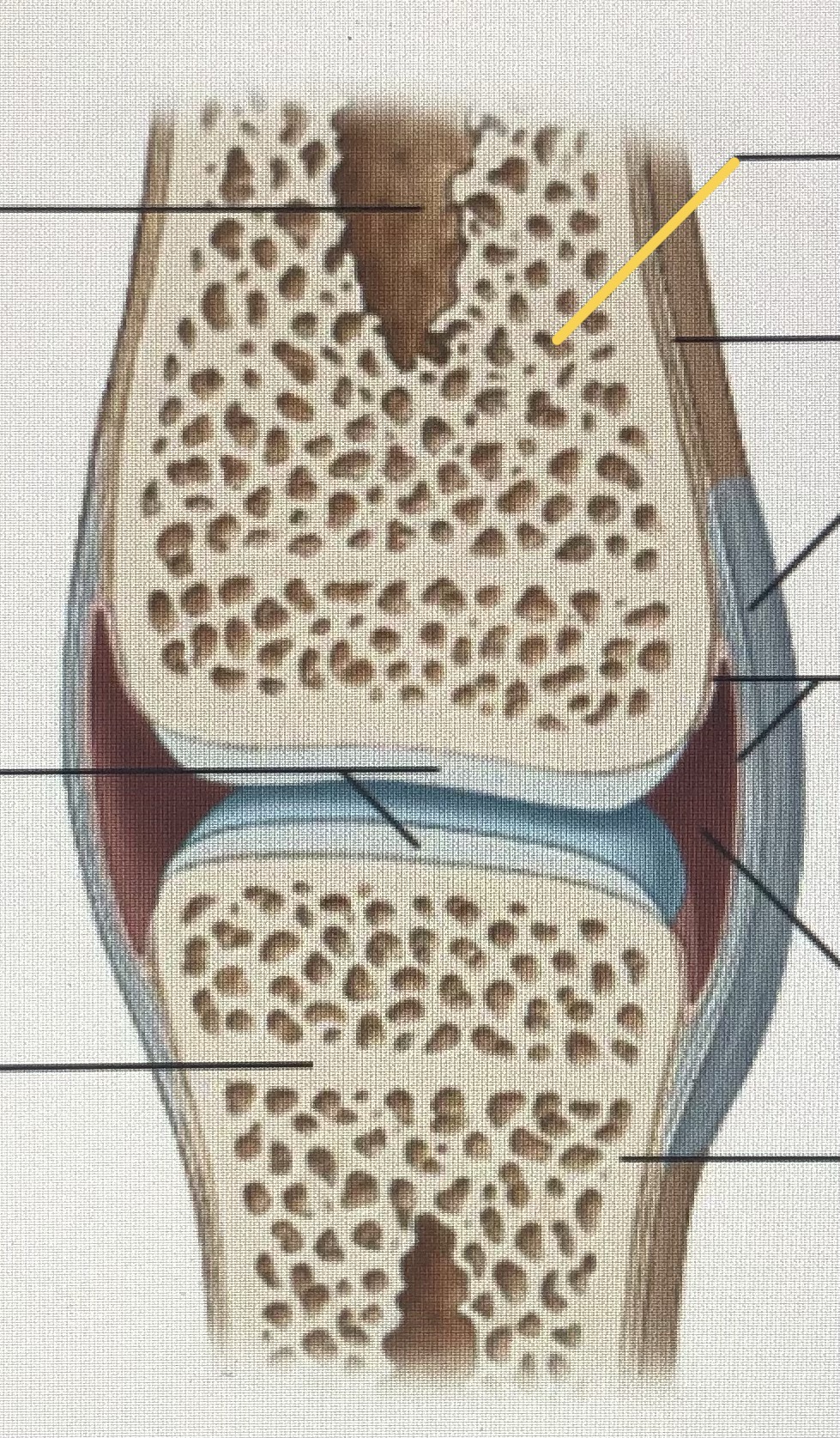
Spongy bone
100
New cards
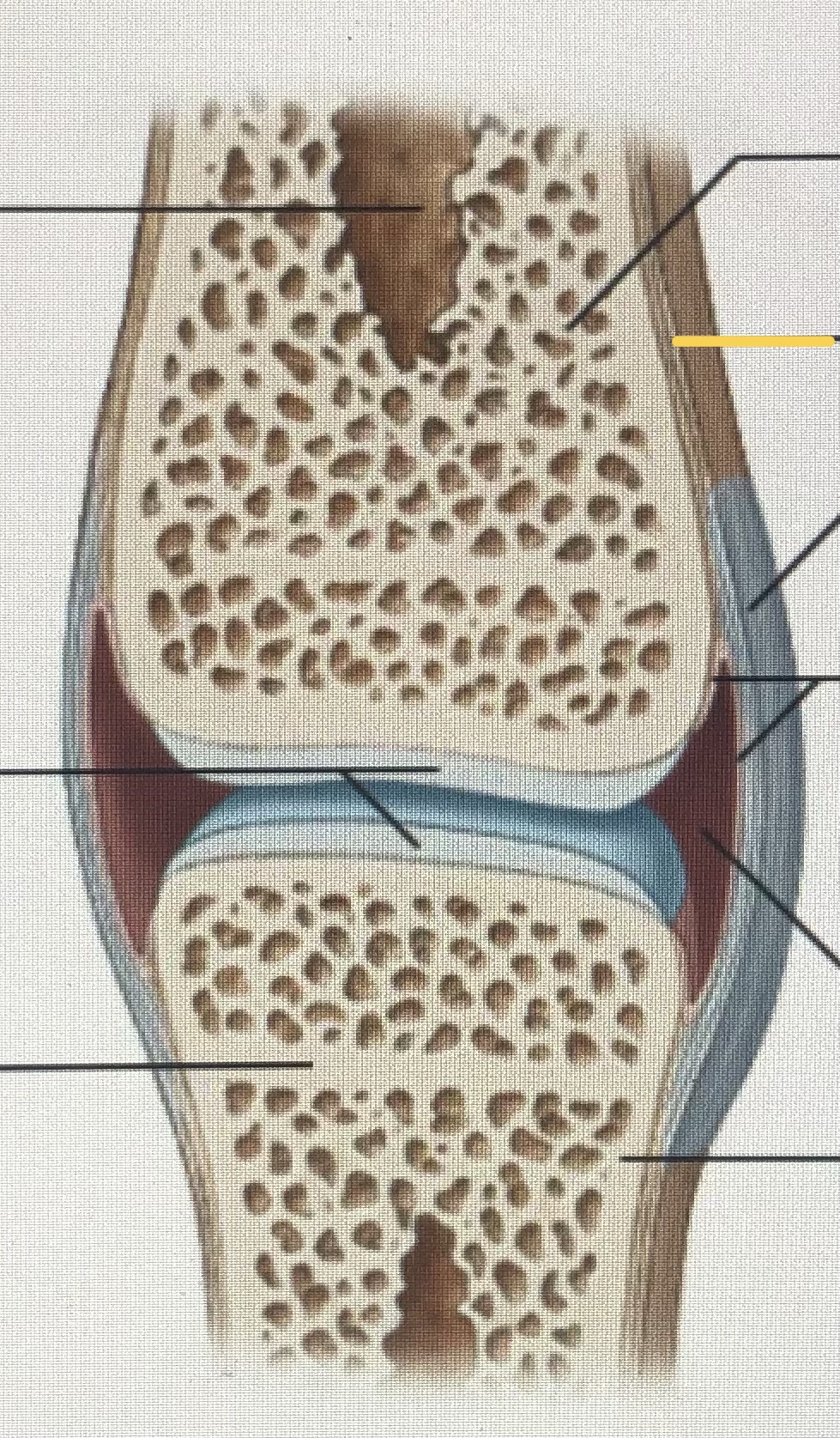
Periosteum