Genetics Midterm 1 Vocabulary
1/182
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
183 Terms
true-breeding lines
a variety that produces the same trait across generations (pure bred)
single-factor cross
a cross in which an experimenter observes one character
monohybrids
Parents that are heterozygous for one character.
reciprocal cross
same outcome
Dominant
Appears in F1
Recessive
Trait that is hidden in F1
Alleles
Different forms of a gene
Can a gene have more than two more than two alleles in the alleles in the population? In an population? In an individual?individual?
Yes in a population
BUT no, an individual can only have two alleles for a given gene because they inherit one allele from each parent
laws of segregation
two alleles for each trait must separate when gametes are formed then reunite at random, one from each parent at fertilization
Punnent Square Method
can be used to predict outcome of a cross or self fertilization experiment
product rule of probability
The chance of two or more independent events occurring together
sum rule of probability
the probability that exclusive events will occur is equal to the sum of their individual probabilities
What is the probability that both A and B will occur?
product rule
What is the probability of A or B occurring?
sum rule
Homoezygous
Have 2 identical alleles; can be both dominant and both recessive
Heterozygous
An organism that has two different alleles for a trait
Genotype
genetic composition of an individual
Phenotype
Observable traits of an organism.
Test cross
a mating in which an individual showing the dominant phenotype (but unknown genotype Y-) is crossed with an individual with the recessive phenotype
dihybrid cross
A cross between individuals that have different alleles for the same gene
Results of Mendel's dihybrid cross F2
contained both parental types and recombinant types
Results of Mendel's dihybrid cross alleles
assort independently and appear in any combination in the offspring
law of independent assortment
during gamete formation, different pairs of alleles segregate independently of each other
monohybrid ratio
3:1
dihybrid ratio
9:3:3:1
Probability Formula
number of individuals with a given phenotype /total number of individuals
Loci Assort Independently
we can look at each locus independently to get the answer
heterozygous incross
binomial expansion equation
probability of an unordered combination of outcomes

Pedigrees
a chart that shows a trait in a family and how it is inherited
Symbols of a pedigree
-circle: female
-square: male
-shaded: trait present/affected by trait
-1/2 shaded: carrier of trait
-not shaded: not affected by trait
vertical pattern of inheritance indicates
rare dominant trait
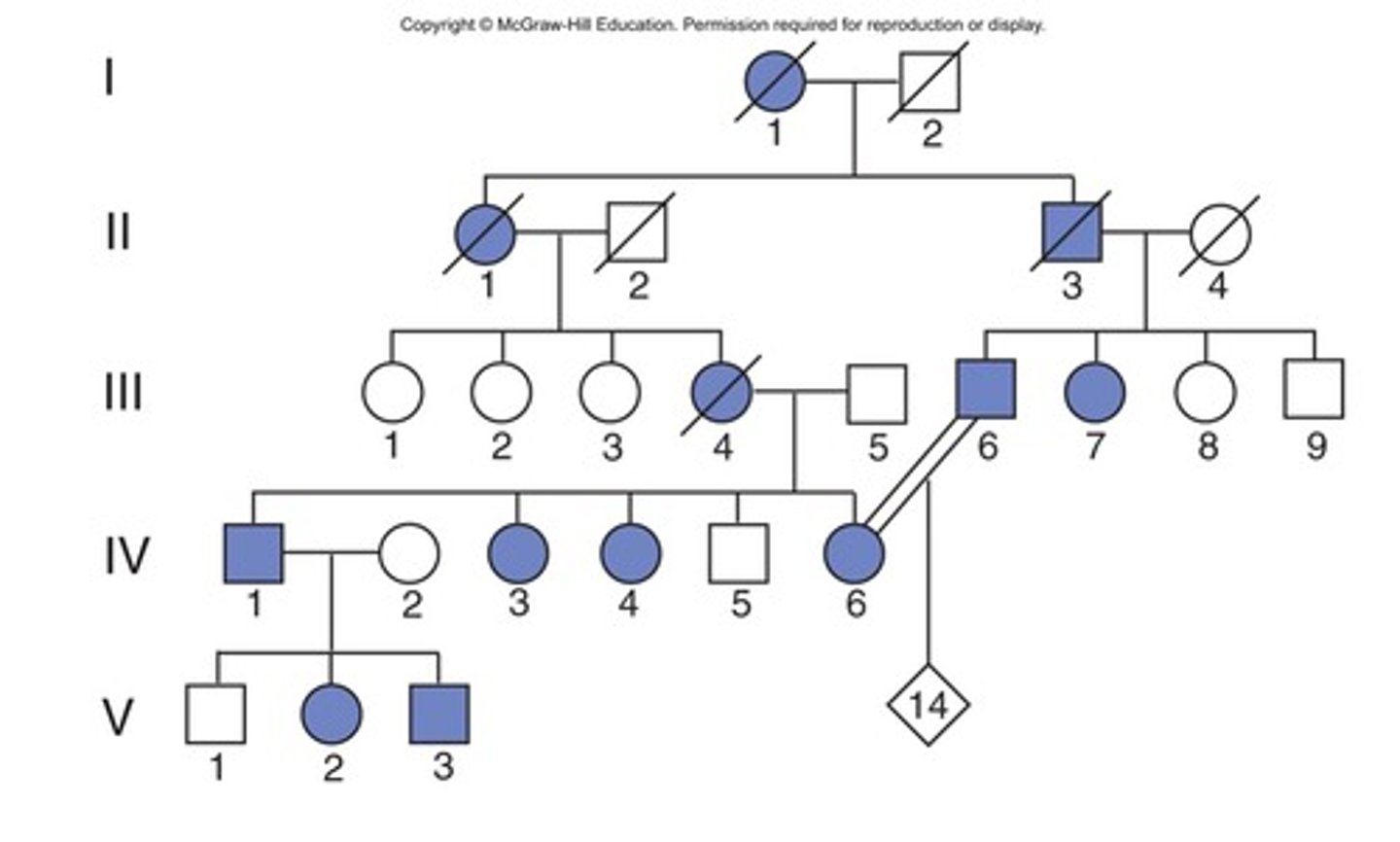
vertical pattern pedigree trait example
huntington disease
Huntington's disease
a hereditary disease marked by degeneration of the brain cells and causing progressive dementia.
horizontal pattern of inheritance indicates
rare recessive trait
horizontal pattern of inheritance example
cystic fibrosis
cystic fibrosis
A genetic disorder that is present at birth and affects both the respiratory and digestive systems.
Key aspects of pedigrees with dominant traits
1. affected children have at least one affected parent
2. vertical pattern of inheritance
3. affected parents can produce unaffected children if both parents are heterozygotes
four aspects of pedigrees with recessive traits
1. affected individuals can be children of two unaffected parents
2. all children of affected parents should be affected
3. rare recessive traits show horizontal pattern
4. could show vertical pattern of inheritance if trait is common in the population
single gene inheritance
one gene may determine more than one trait
incomplete dominance
Cases in which one allele is not completely dominant over another
incomplete dominance example
flower Colour in snapdragons
phenotypic ratios are an ____ reflection of the genotypic ratios
exact
Codominance
F1 hybrids display traits of both parents
lentils offer an example of
multiple alleles
A 3:1 ratio in each cross indicates that....
different alleles of the same gene are involved
allele frequency
Number of times that an allele occurs in a gene pool compared with the number of alleles in that pool for the same gene
wild-type allele
most common allele in a population >1%
mutant allele
a rare allele in the same population <1%
monomorphic
a gene with only one common, wild-type allele
polymorphic
a gene with more than common
ABO blood types in humans are determined by...
three alleles of one gene
six genotypes produce ___ blood phenotypes
four
Gene I controls the type of
sugar polymer on surface of red blood cells
Human histocompatibility antigens
an extreme example of multiple alleles
three major genes encode
histocompatibility antigens
histocompatibility antigens gene has
400-1200 alleles each
sickle cell anemia
a genetic disorder that causes abnormal hemoglobin, resulting in some red blood cells assuming an abnormal sickle shape
how many alleles code for sickle cell anemia
multiple alleles, more than 400 so far
pleiotropy
A single gene having multiple effects on an individuals phenotype
HbBs allele
affects more than one trait
phenotype of heterozygote defines the
dominance relationship of two alleles
complete dominance
hybrid resembles one of the two parents
incomplete dominance
hybrid resembles neither parent
Ay allele
Dominant allele causing yellow coat color in mice, recessive lethal allele
Ay is dominant to A for
hair Colour
Ay is recessive to A for
lethality
2:1 ratio indicates
recessive lethal allele
pure breeding yellow (AyAy) mice
cannot be obtained because they are not viable
Pleiotropy
A single gene having multiple effects on an individuals phenotype that are distinct but seem unrelated
pleiotropy in humans
waardenburg syndrome
holt oram syndrome
Penetrance
The percentage of individuals with a particular genotype that shows the expected genotype.
penetrance can be
complete or incomplete
expressivity can be
variable or unvarying
Expressivity
the degree to which a trait is expressed
modifier genes
alter the phenotypes produced by alleles of other genes
modifier gene example
T locus of mice that causes short tails
environmental effects on phenotype #1
Temperature is a common element of the environment that can affect phenotype
coat Colour in siamese cats
phenocopy
A trait that appears inherited but is caused by the environment and not heritable
phenocopy example
phocomelia due to thalidomide
9:3:3:1 in F2
suggest two independently assorting genes for seed coat Colour
2 genes controlling the same trait
function additively in independent pathways
Epistasis
a gene interaction in which one gene mask the effect of another gene allele
epistatic allele
the allele that does the masking
hypostatic gene
gene that is masked
epistasis can be
recessive or dominant
recessive epistasis
9:3:4 ratio
recessive epistasis example
Labrador coat color (Yellow, brown, black)
Gene B determines
black or brown
recessive allele ee of gene E is epistatic to B and determines
yellow
genotype ee mask the effect of
all B genotypes
recessive epistasis in humans with rare blood ttype
bombay phenotype
homozygosity for the h bombay allele is epistatic to the l gene determining
ABO blood types
recessive epistasis in sweet peas
Purple F1 progeny are produced by crosses of two pure-breeding white lines
reciprocal recessive epistasis accounts for ____ flower in sweet peas
purple
Complementation
recessive allele is complemented by a wild type
dihybrid cross generates a ___ ratio in F2 progeny
9:7
reciprocal recessive epistasis
homozygosity for the recessive allele of either gene results in a white phenotype
Two genes work in tandem to produce purple sweet pea flowers
a dominant allele of each gene must be present to produce that color
heterogeneous traits
have the same phenotype but are caused by mutations in different genes