ANSC 312 - Midterm 1 (Lectures 1-4)
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
Hormone
A substance produced by one or more tissues/glands that is transported by the blood to exert a specific effect upon another organ
Peptides, Glycoproteins, Steroids, Prostaglandins
4 Chemical Classes of Reproductive Hormones
Peptide Hormones
Chemical Class of Reproductive Hormones
Amino acid based hormone
Easy and quick to fabricate, just a few aa
Glycoproteins
Chemical Class of Reproductive Hormones
Amino acid based hormone
Polypeptide hormones that contain carbohydrate moieties
Large and complex compared to peptide hormones
More difficult to produce
Need to be intact in order to properly interact with receptors
Steroids
Chemical Class of Reproductive Hormones
Lipid-based hormone
Various forms, but all have common molecular structure = 4 C rings labelled A, B, C, D
Origin/base of these hormones is cholesterol
Goes through a series of enzymatic modifications to produce various types
Prostaglandins
Chemical Class of Reproductive Hormones
Lipid-based hormone
Fairly ubiquitous in biological systems, found throughout the body
Consist of 20 C unsaturated fatty acids that are derived from arachidonic acid
Steroid Pathway
Any steroid starts out as cholesterol and goes through a series of enzymatic reactions
Cholesterol can be converted to Pregnelolone
Pregnelolone converted by enzymes to Progesterone
Progesterone converted to Testosterone
Testosterone (if there are the enzymes present) will be converted to Estradiol
In order to get any of these steroid, the appropriate enzymes need to be present and in place to complete each conversion
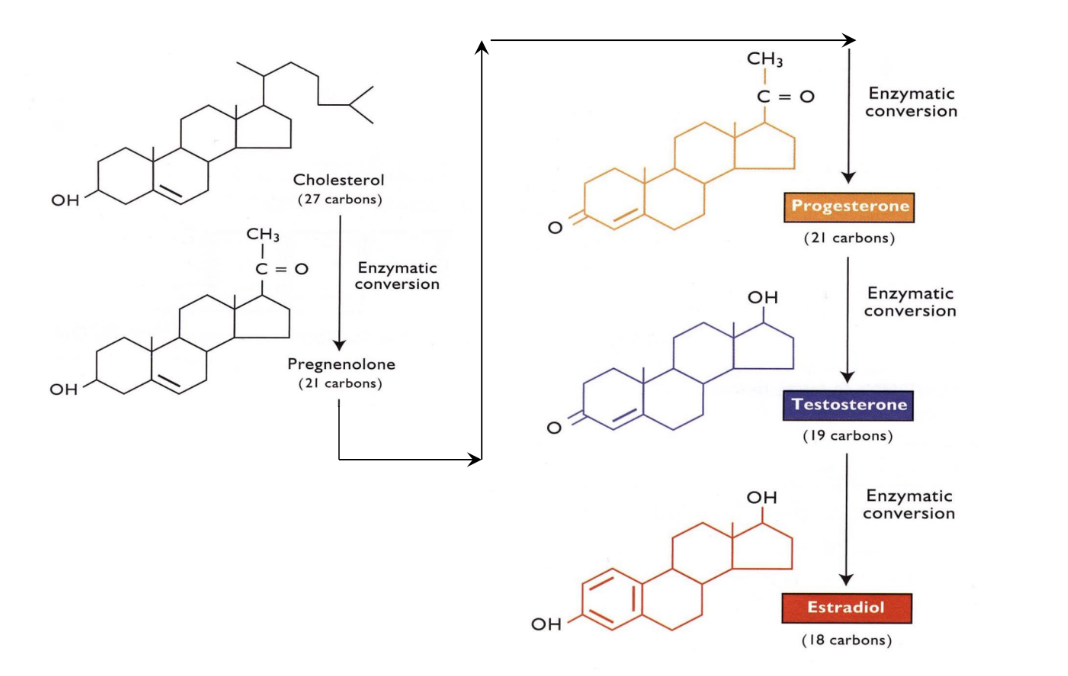
Cholesterol, Pregnenolone, Progesterone, Testosterone, Estradiol
Steroid Pathway
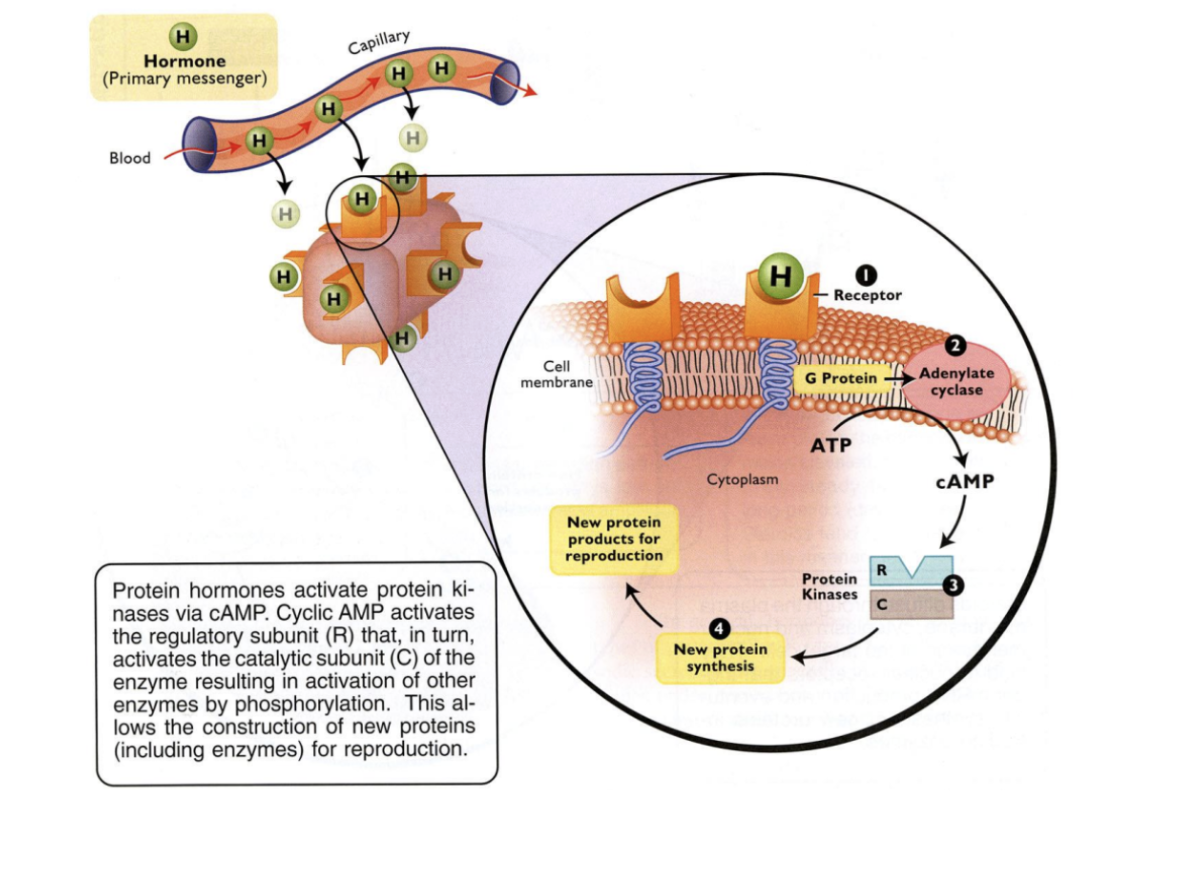
Hormone-receptor binding (surface)
G-protein activation
Adenylate cyclase activation
Protein kinase activation
Synthesis of new product
5 steps of protein hormone action
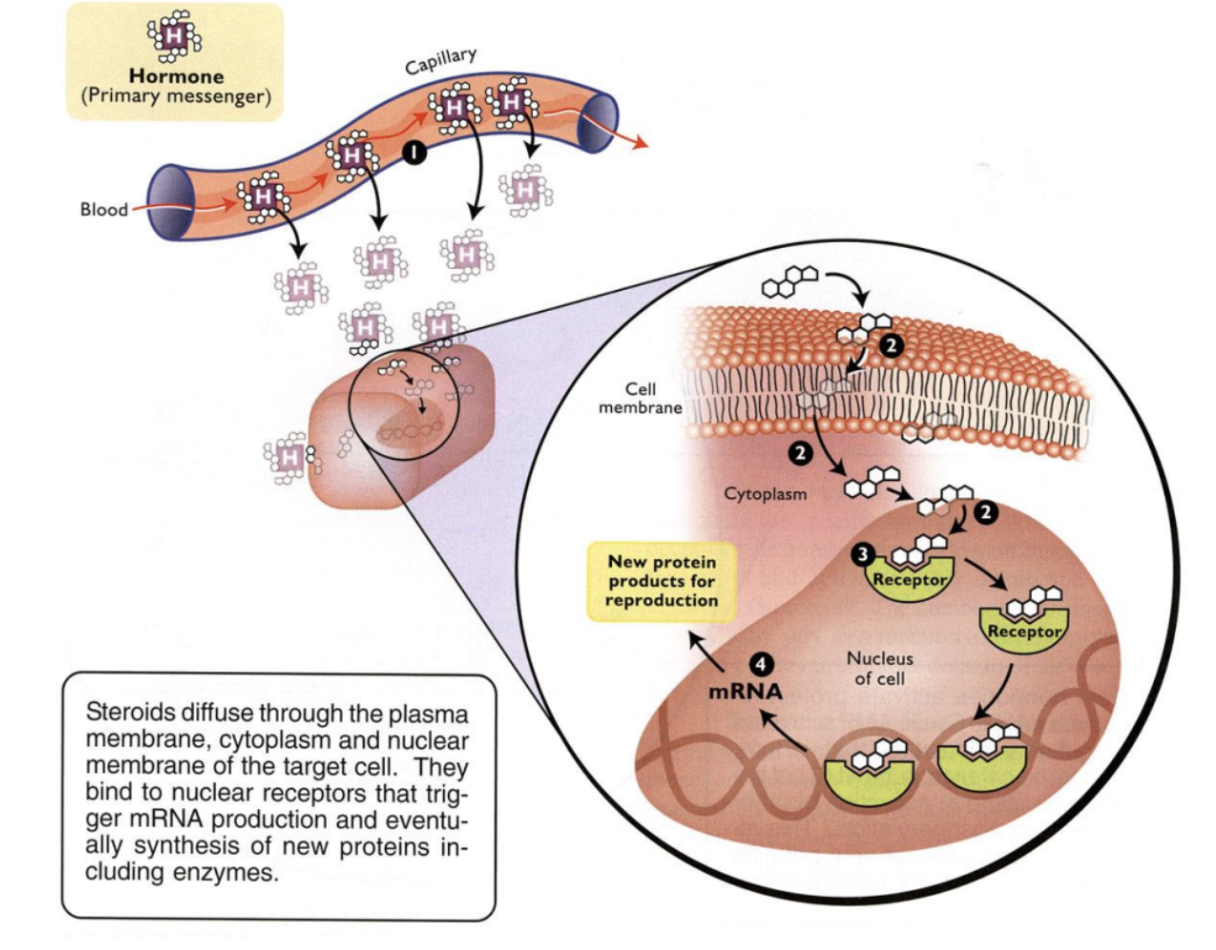
Steroid transport (associated with carrier protein)
Movement through cell membrane and cytoplasm
Binding of steroid to nuclear receptor
mRNA and protein synthesis
4 Steps of Steroid Hormone Action
hypothalamus, pituitary, gonads, uterus, placenta
5 main sources of reproductive hormones
3rd ventricle in the middle of the brain, above the pituitary
Location of hypothalamus
Sella turcica
Location of pituitary gland
Portal vessels
Hypothalamus and pituitary are separated by _______
Allows for connection/communication network to allow hypothalamus to control the anterior pituitary and create hormones that end up in the posterior pituitary and are released from there
Hypothalamic-Hypophyseal System
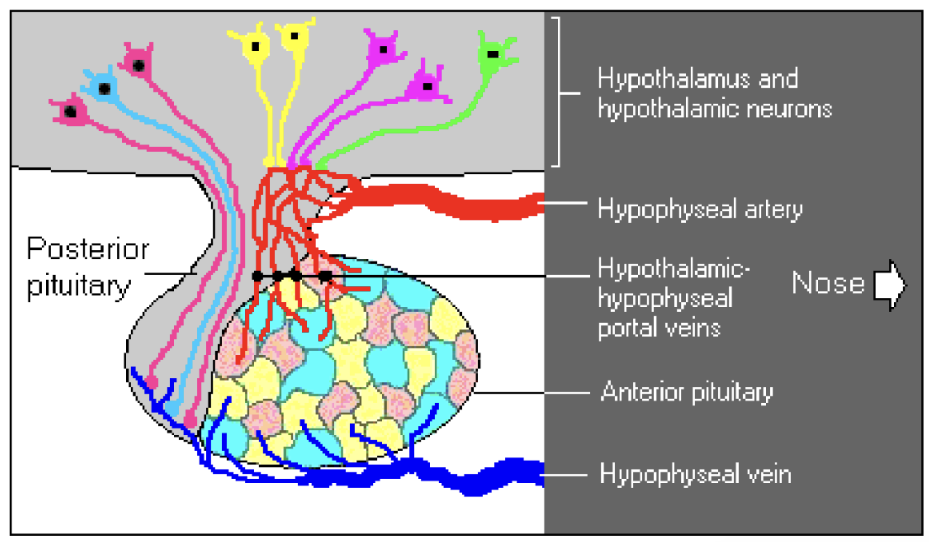
Hypophyseal artery
Transports blood coming in close to the hypothalamic neuron and hypothalamus and extending down into anterior pituitary
Hypothalamus interacts with centers in the brain to detect what is going on in and around the body and in response will produce releasing hormones that go through ___________ into anterior pituitary
Hypophyseal vein
Associate with anterior and posterior pituitary and carry blood/secretions away from those glands
Releasing hormones stimulate other hormone production in the anterior pituitary which will be released, at the appropriate time, through the ____________ to the body
Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GnRH)
Reproductive Hormone
Gland: hypothalamus
Chemical class: Neuropeptide
Target Tissues: Anterior Pituitary
Action: Release of FSH and LH from anterior pituitary
Hypothalamus
Neuropeptide
Anterior Pituitary
Release of FSH and LH from anterior pituitary
Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GnRH)
Gland:
Chemical class:
Target Tissues:
Action:
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Reproductive Hormone
Gland: anterior pituitary
Chemical class: Glycoprotein
Target Tissues: Male - Testis (Sertoli cells)
Female - Ovary (Granulosa cells)
Action: Male - Testis (Sertoli cell function)
Female - Ovary (Follicle growth and Estradiol synthesis)
Anterior pituitary
Glycoprotein
Male - Testis (Sertoli cells)
Female - Ovary (Granulosa cells)
Male - Testis (Sertoli cell function)
Female - Ovary (Follicle growth and Estradiol synthesis)
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Gland:
Chemical class:
Target Tissues:
Action:
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
Reproductive Hormone
Gland: anterior pituitary
Chemical class: Glycoprotein
Target Tissues: Male - Testis (Leydig cells)
Female - Ovary (Theca and Luteal cells)
Action: Male - Testosterone synthesis
Female - Ovulation and Progesterone synthesis
Anterior pituitary
Glycoprotein
Male - Testis (Leydig cells)
Female - Ovary (Theca and Luteal cells)
Male - Testosterone synthesis
Female - Ovulation and Progesterone synthesis
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
Gland:
Chemical class:
Target Tissues:
Action:
Prolactin
Reproductive Hormone
Gland: anterior pituitary
Chemical class: Peptide
Target tissues: Mammary Glands
Action: Lactation and Maternal Behaviour
Anterior pituitary
Peptide
Mammary Glands
Lactation and Maternal Behaviour
Prolactin
Gland:
Chemical class:
Target Tissues:
Action:
Oxytocin
Reproductive Hormone
Gland: posterior pituitary
Chemical class: Neuropeptide
Target Tissues: Male - Testicular (stimulates seminiferous tubules)
Female - Uterus and Mammary
Action: Male - Sperm Transport (by causing contractions)
Female - Uterine contractions and Mammary cell growth and Milk letdown
Posterior pituitary
Neuropeptide
Male - Testicular (stimulates seminiferous tubules)
Female - Uterus and Mammary
Male - Sperm Transport (by causing contractions)
Female - Uterine contractions and Mammary cell growth and Milk letdown
Oxytocin
Gland:
Chemical class:
Target Tissues:
Action:
Glandular
Anterior pituitary has more ______ tissue
Neural
Posterior pituitary has more ______ tissue
Gonadotroph Cells
Cells of anterior pituitary
respond to GnRH and produce FSH and LH
Lactotroph cells
Cells of anterior pituitary
Produce prolactin
Herring Bodies
Within posterior pituitary
store and release oxytocin
Estradiol (E2)
Reproductive Hormone
Gland: ovaries
Chemical class: Steroid
Target Tissues: Hypothalamus, Reproductive Tract, Mammary Gland
Action: Female Sexuality
- ↑ Sexual Behaviour
- ↑ GnRH Production
- ↑ Uterine Activity
- Mammary
Development
Ovaries
Steroid
Hypothalamus, Reproductive Tract, Mammary Gland
Female Sexuality
- ↑ Sexual Behaviour
- ↑ GnRH Production
- ↑ Uterine Activity
- Mammary
Development
Estradiol (E2)
Gland:
Chemical class:
Target Tissues:
Action:
Progesterone (P4)
Reproductive Hormone
Gland: Ovaries, Placenta
Chemical class: Steroid
Target Tissues: Hypothalamus, Uterine endothelium and myometrium, Mammary Gland
Action: Pregnancy Maintenance
- ↓ Sexual Behaviour
-↓ GnRH Production
-↓ Uterine Activity
- Lactation
Ovaries, Placenta
Steroid
Hypothalamus, Uterine endothelium and myometrium, Mammary Gland
Pregnancy Maintenance
- ↓ Sexual Behaviour
-↓ GnRH Production
-↓ Uterine Activity
- Lactation
Progesterone (P4)
Gland:
Chemical class:
Target Tissues:
Action:
Testosterone (T)
Reproductive Hormone
Gland: Testis
Chemical class: Steroid
Target Tissues: Hypothalamus
Reproductive Tract
Muscle
Action: Male Sexuality
- ↑ Sexual Behaviour
- ↓ GnRH Production
- Spermatogenesis
- ↑ Muscle
Development
Testis
Steroid
Hypothalamus
Reproductive Tract
Muscle
Male Sexuality
- ↑ Sexual Behaviour
- ↓ GnRH Production
- Spermatogenesis
- ↑ Muscle
Development
Testosterone (T)
Gland:
Chemical class:
Target Tissues:
Action:
Prostaglandin (E2)
Reproductive Hormone
Gland: Uterus
Chemical class: Prostaglandin
Target Tissues: Ovary
Action: ↑ Progesterone Production
Uterus
Prostaglandin
Ovary
↑ Progesterone Production
Prostaglandin (E2)
Gland:
Chemical class:
Target Tissues:
Action:
Prostaglandin (F2a)
Reproductive Hormone
Gland: Uterus
Chemical class: Prostaglandin
Target Tissues: Ovary
Uterine myometrium
Action: ↓ Progesterone Production
Stimulates Uterine Contractions (Parturition)
Uterus
Prostaglandin
Ovary
Uterine myometrium
↓ Progesterone Production
Stimulates Uterine Contractions (Parturition)
Prostaglandin (F2a)
Gland:
Chemical class:
Target Tissues:
Action:
Equine Chorionic Gonadotropin (eCG - horse)
Reproductive Hormone
Gland: Placenta
Chemical class: Glycoprotein
Target Tissues: Ovary
Action: Maintains Progesterone Production
**(FSH like activity in other species)
Placenta
Glycoprotein
Ovary
Maintains Progesterone Production
**(FSH like activity in other species)
Equine Chorionic Gonadotropin (eCG - horse)
Gland:
Chemical class:
Target Tissues:
Action:
Pineal Gland
Located above the hypothalamus between the hemispheres of the brain
Plays a role in reproduction, particularly in livestock
Sensitive to environmental light and senses changes in photoperiod
Releases melatonin in response to dark
_______ via melatonin regulates breeding activity in seasonal breeder (ex. sheep, goats, horses)
Broad Ligament
Structure of the Female Reproductive Tract
Supports and houses the vascular supply, lymphatic drainage and nerves for the female tract
Like the scaffolding that holds the female tract in position in the abdomen
Mesovarium
Portion of the Broad Ligament
Supports the ovary
Houses the vascular supply, lymphatic drainage and nerves for the ovary
Forms the ovarian stem = hilus
Hilus
Ovarian stem
Part of the mesovarium of the broad ligament
Mesosalpinx
Portion of the Broad Ligament
Not very prominent
Connects to oviduct
Thin, transparent segment of the BL that supports the oviduct
Forms a pouch around the ovary = bursa
Bursa
Pouch around ovary
Part of the mesoalpinx of the broad ligament
Mesometrium
Portion of the Broad Ligament
Majority of tissue
Suspends uterus in abdomen from dorsal wall
Largest portion of the BL
Supports the uterine horns – suspended from the dorsal body wall
Utero-ovarian ligament
Attaches the ovary and uterus, but is not a part of the BL
Ovaries
Structure of the Female Reproductive Tract
Production of oocytes (female contribution to embryo)
Production of Estradiol
Production of Progesterone
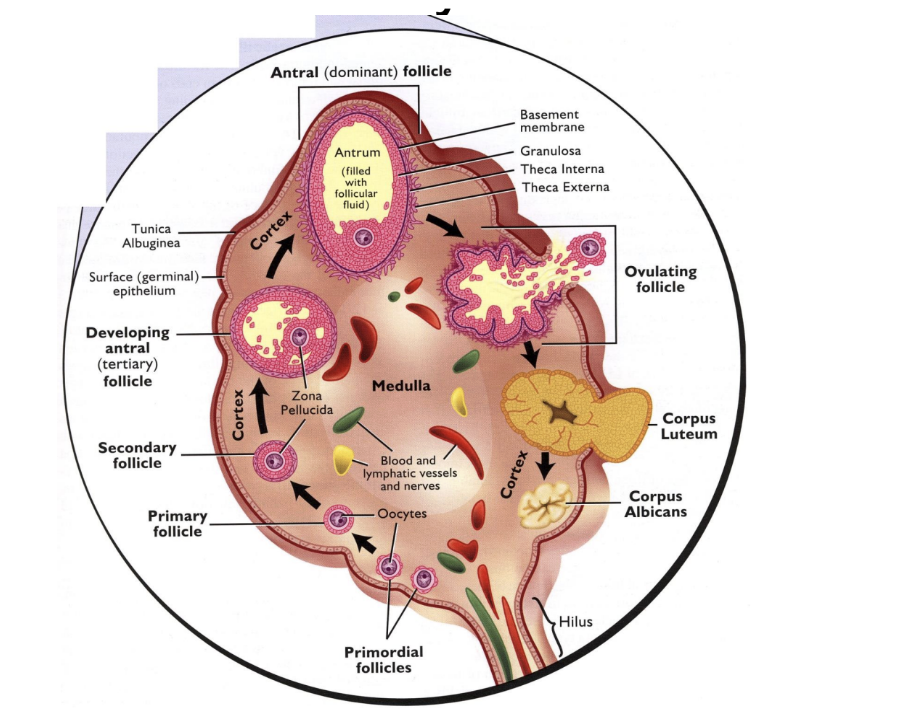
primordial follicle, primary follicle, secondary follicle, tertiary follicle, antral (preovulatory) follicle, corpus luteum, corpus albicans
Order of follicle structures in development in ovary
Medulla
Center of ovary = _____
Cortex
Outside of ovary = ______
Theca cells respond to LH and produce testosterone
Testosterone migrates to granulosa cells
Granulosa cells respond to FSH and converts testosterone to estradiol
Steps of Estradiol (E2) Production by the Ovaries
Theca externa
Granulosa cells
Antrum
Theca interna
Basement membrane
Corona radiata
Oocyte
Cumulus oophorus
Label the parts of a mature pre-ovulatory (antral) follicle
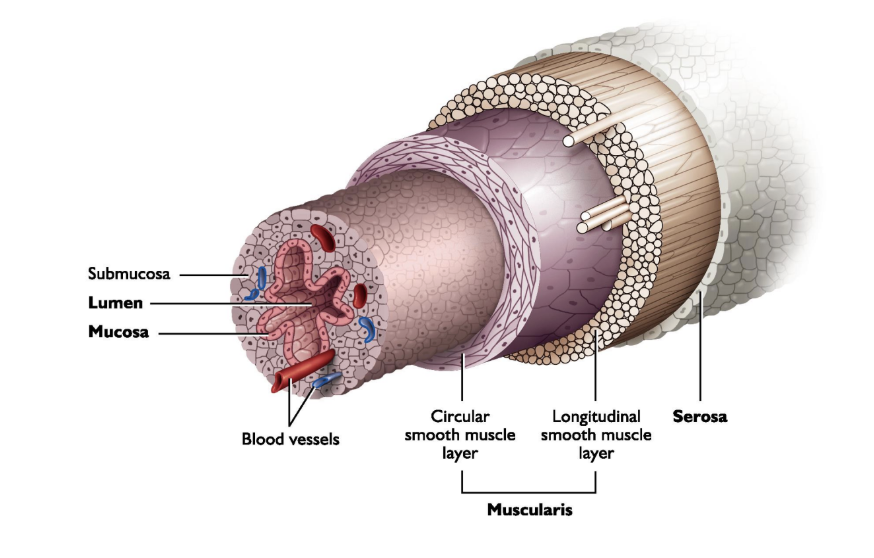
serosa, muscularis (longitudinal, circular), submucosa, mucosa
Layers of the female tract (from outside to inside)
Serosa
Layer of the Female Tract
Outer layer
“Skin” of the tract
Single layer of flatten cells that cover the female tract (like its skin)
Muscularis
Layer of the Female Tract
2nd layer
Double layer of smooth muscles
Outer longitudinal layer
Inner circular layer
Allows tissues to contract (transport - sperm, oocyte, embryos)
Submucosa
Layer of the Female Tract
3rd layer
Houses blood vessels, nerves and lymphatics
Supporting layer for the mucosa
Mucosa
Layer of the Female Tract
4th/innermost layer
Lines the lumen
Secretory layer of epithelium in lumen of the reproductive tract
Properties and role varies for each segment of the tract and depending on the endocrine environment
Oviducts
Structure of the Female Reproductive Tract
Connection between the ovaries and the rest of the reproductive tract
Gamete/Embryo Transport
Site of Fertilization
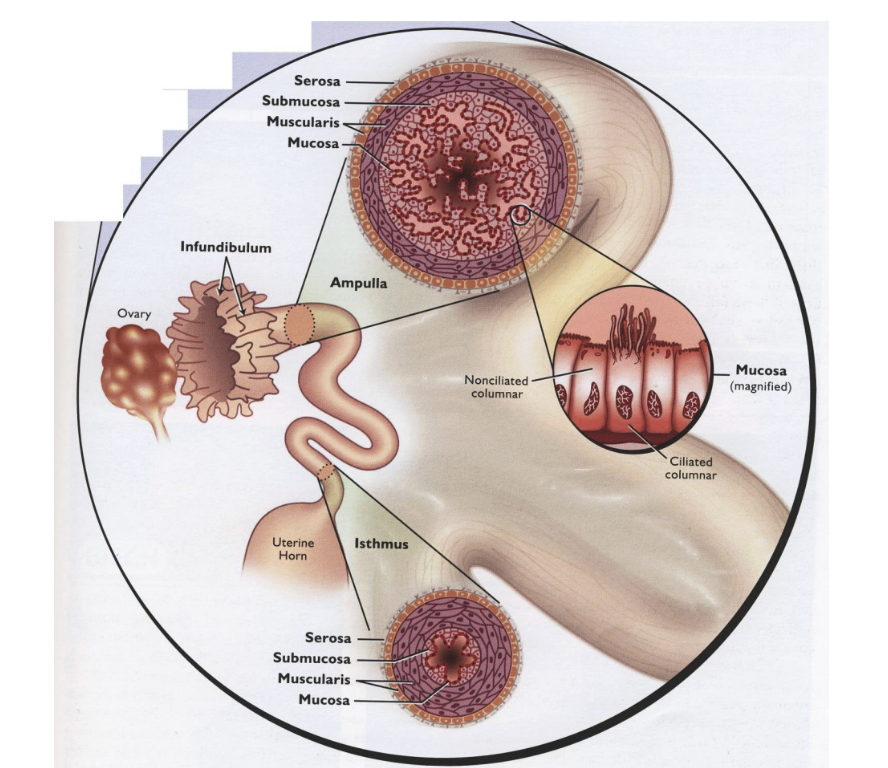
infundibulum, ampulla, ampullary-isthmic junction, isthmus, uterotubal junction
Segments of the Oviduct (from closer to the ovary to further)
Infundibulum
Segment of the Oviduct
Thin funnel shaped opening closes over the ovary
Forms “pocket” around the ovary (helps to cover ovary)
When ovary have oocytes that ovulate, end up in this pocket
Fimbriae “finger-like projects sweep oocytes toward the oviduct"
Tissue that interacts with ovary and helps to intercept any oocytes that are ovulated
Ampulla
Segment of the Oviduct
“Upper-half” of the oviduct
Large diameter and ciliated mucosa to transport oocytes to the point of fertilization
Ampullary-isthmic junction
Segment of the Oviduct
Transition between ampulla and isthmus
Site of Fertilization
Oocyte doesn’t sit and wait here for fertilization, fertilization will occur at some point when moving from ampulla to isthmus
Isthmus
Segment of the Oviduct
“Lower-half” of the oviduct attached to the uterus
Small diameter tube that transports sperm to AIJ & transports embryos to the uterus
Uterotubal junction (UTJ)
Segment of the Oviduct
Junction of the uterus & oviduct
Sperm reservoir
Uterus
Structure of the Female Reproductive Tract
Sperm transport
Maintains and nourishes embryo and fetus
Role controlled by stage of the female cycle (dynamic, and susceptible to endocrine events)
Sperm transport to the oviduct
Maintain pre-implantation embryo
Maternal portion of placenta – transfer of nutrients to fetus
Expulsion of fetus and fetal placenta
Perimetrium
Uterine Tissue Layer - Serosa
External layer that connects to the mesometrium of the broad ligament
Myometrium
Uterine Tissue Layer - Muscularis
Muscle layers of the uterus
Facilitates uterine contractions
Sperm transport (post-coital)
Expulsion of fetus & placenta (parturition)
Endometrium
Uterine Tissue Layer - Submucosa and Mucosa
Cells lining the uterine lumen
Roles vary with female cycle
Secretions that enhance sperm and embryo survival
Signals if pregnancy has been achieved
Maternal portion of placenta & transfer of nutrients to fetus
Duplex uterus
Type of Uterus
2 cervical entries
In rabbit - cervical entry for each uterine horn, can have sperm from 1 buck on one side, and another on the other side
Marsupials - branched cervix leading up to uterine horn
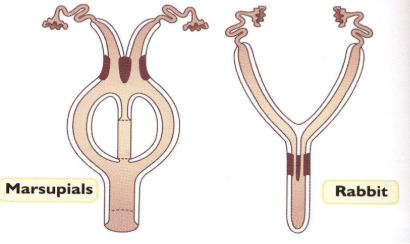
Bicornate uterus
Type of Uterus
Distinct uterine horns
Can be poor to moderately developed or highly developed
Very long and developed uterine horns in litter-bearing species compared to monocorpus species
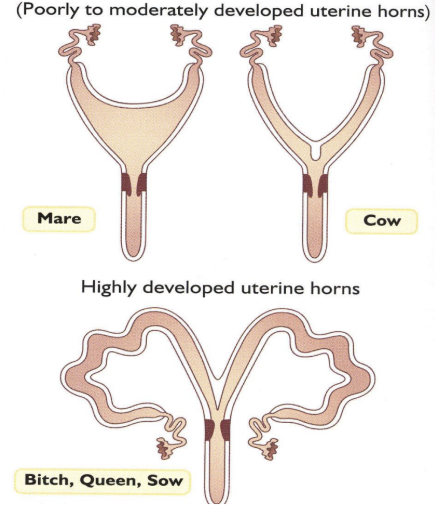
Simplex uterus
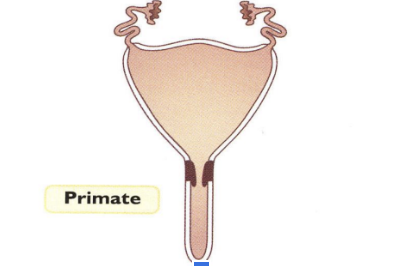
Type of Uterus
No defined uterine horns
Simply uterine body
Primates
Caruncles
Variation in Endometrium
in ruminants, points of attachment of uterus to placenta
On surface of endometrium
Endometrial folds
Variation in Endometrium
creates increased surface area that placenta interacts with
Cervix
Structure of the Female Reproductive Tract
Thick walled segment of female system that separated the internal tract (sterile portion) from the external tract (non-sterile)
Transition tissue between uterus and vagina
Prevents microbial contamination of uterus (considered sterile)
Site of semen deposition (sow, mare)
Semen reservoir/sperm transport
Single Fold | Bitch and Queen |
Multiple Folds | Sow, Ewe, Cow, and Mare |
Functions:
Copulation
Reservoir/Barrier to sperm transport (make sure only better sperm get in)
Site of semen deposition
Pregnancy
Mucus plug conserves the sterile uterine environment (without plug, concerns for infection)
Vagina
Structure of the Female Reproductive Tract
Organ of copulation
Site of semen deposition (cows, ewes, queen, bitch)
Birth canal
External portion of the reproductive tract
Copulatory organ of the female
Site of semen deposition (Cow, Ewe, Bitch & Queen)
Thickness & Secretions of the mucosa influenced by estrus cycle
Whether dominant steroid is progesterone or estradiol that will cause secretions by the mucosa that acts as a lubricant
When animal is copulating - there will be high levels of estradiol
Lubricate and protect the vaginal wall
lower abdomen, below rectogenital pouch
Position of reproductive tract
Monotocous
Term for animals that produce a single offspring at birth
Polytocous
Term for animals that produce multiple offspring at birth (litter-bearing)
Ectoderm
Embryonic Germ Layer
Reproductive Tract
- ♀ vagina (external) or ♂ penile sheath
- ♀ clitoris or ♂ penis
Nervous System
- hypothalamus
- anterior & posterior pituitary
Oral cavity
Nasal cavity
Mesoderm
Embryonic Germ Layer
Reproductive System
- gonads (ovaries/testes)
- ♀ uterus, cervix, vagina(internal)
- ♂ epididymus, ductus deferens, ♂ accessory sex glands
Urinary System
Skeletal System
Blood Vessels
Muscle
Endoderm
Embryonic Germ Layer
Digestive System
Respiratory System
Glandular Systems
Development of hypothalamic-hypophyseal systems
Migration of primordial germ cells from the yolk sac
Sex cords development in the gonad & mesonephric renal system regression/transformation
Sexual Differentiation - Sex becomes evident from structures
Development of female tract and ovaries
Formation of the broad ligament
6 major events of embryonic development of the female reproductive system
280-290 days / 9.5 months
Cattle Gestation Period
145-150 days / 5 months
Sheep Gestation Period
114 days / 3 months, 3 weeks, 3 days
Swine Gestation Period
60-65 days / 9 weeks
Dog Gestation Period
63-67 days / 9 weeks
Cat Gestation Period
Rathke’s pouch
Anterior pituitary develops from the _________ during embryonic development
Infundibulum
Posterior pituitary develops from the _________ during embryonic development
pronephros → mesonephros → metanephros
3 embryonic renal systems in order
Pronephros
First Embryonic Renal System
Most primitive form of kidney found in the developing embryo – limited function & eventually degenerates
Mesonephros
Second Embryonic Renal System
These early kidneys (pick up from pronephros) of early mammalian embryo eventually regresses and gives way to the Metanephros
Remnants of the regressing _______ renal system become portions of the reproductive tracts
When no longer acting as renal system, becomes part of reproductive system
Metanephros
Third/Final Embryonic Renal System
Renal system that will eventually become the functioning kidneys in the adult animal
Paramesonephric/Mullerian ducts
Ducts that develop into the female reproductive tract during embryogenesis