Nursing Fundamentals NCLEX
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
RN Delegation
RNs DO NOT delegate tasks that involve Evaluation, Assessment, or Teaching (EAT).
Sodium range (mEq/L)
135-145
Potassium lab range (mEq/L)
3.5-5.0
Total Calcium lab range (mg/dL)
9.0-10.5
Magnesium lab range (mg/dL)
1.3-2.1
Phosphorus lab range (mg/dL)
3.0-4.5
BUN range (mg/dL)
10-20
Creatinine range in males (mg/dL)
0.6-1.2
Creatinine range in females (mg/dL)
0.5-1.1
HgbA1c range
<6.5%
WBC range mm3
5,000-10,000
RBC range in men million/mm3
4.7-6.1
RBC range in women million/mm3
4.2-5.4
Hemoglobin range in men g/100 mL
14-18
Hemoglobin in women g/100 mL
12-16
Hematocrit range in men
42-54%
Hematocrit range in women
37-47%
Platelet range /mm3
150,000-400,000
Normal PT and Normal INR ranges (seconds)
11-12.5 for PT and 0.7-1.8 for INR
What is the therapeutic INR range? (seconds)
2-3
What does PT/INR asses?
How well the blood clots and the effectiveness of anticoagulant therapy
Normal PTT range (seconds)
30-40
What is the therapeutic PTT range?
1.5 – 2 x normal or control values
What does PTT assess?
How long it takes blood to clot
Glucose range (mg/dL)
70-105
Digoxin therapeutic range (ng/mL)
0.5-2.0
Lithium therapeutic range (mEq/L)
0.8-1.4
Dilantin therapeutic range (mcg/mL)
10-20
Theophylline therapeutic range
10-20
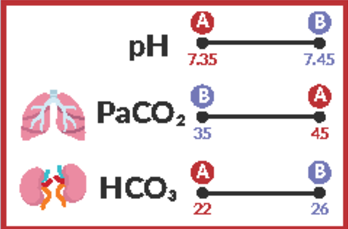
Normal pH range
7.35-7.45
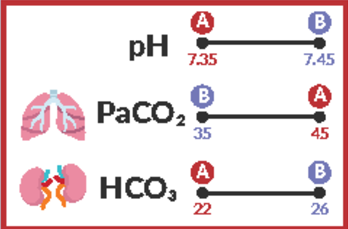
Normal PaC02 range (mmHg)
35-45
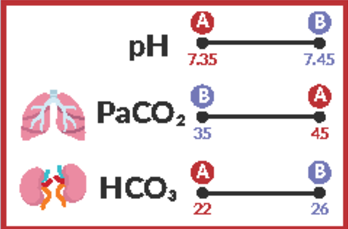
Normal HC03 range (mmol/L)
22-26
Normal P02 range (mmHg)
80-100
People allergic to these foods may also be allergic to latex
Bananas, apricots, chestnuts, kiwis, passion fruit, avocados, tomatoes, cherries, peaches, and/or grapes.
What’s the order of a typical assessment?
IPPA- Inspection, palpation, percussion, auscultation
What is the order of an abdominal assessment?
IAPP- Inspection, auscultation, percussion, palpation
How do you walk with a cane?
COAL- Cane opposite affected leg.
How to walk with a walker?
Walker with affected leg
How do you walk with a crutch?
Crutch underarm, step with unaffected leg first
How do you go upstairs with a crutch?
good leg up first followed by the crutches and the bad leg
How do you go downstairs with a crutch?
Crutches and bad leg followed by good leg,
An RN should NOT delegate what they can ____.
EAT- Evaluate, assess, teach
What illnesses cause a patient to be placed on airborne precautions?
Measles, chicken pox, herpes zoster, TB
What illnesses cause a patient to be placed on droplet precautions?
Sepsis, scarlet fever, strep, pertussis, pneumonia, parvovirus, influenza, diphtheria, epiglottitis, rubella, mumps, adenovirus
What illnesses cause a patient to be placed on contact precautions?
MRSA, VRSA, RSV, skin infections, wound infections, enteric infections (c.diff), eye infections (conjunctivitis)
What is the management for airborne precautions?
Negative pressure room, private room, mask (N95 for TB)
What is the management for droplet precautions?
Private room and mask
What is the management for contact precautions?
Gown, gloves, goggles, private room, and hand hygiene
What are some skin infections that would cause someone to be put on contact precautions?
Cutaneous diphtheria, herpes zoster, impetigo, scabies, staph, pediculosis