Science midterm
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
What type of magma is associated with volcanoes at divergent boundaries
Basaltic magma
What happens when an ocean plate and continental plate collide
The ocean plate subducts beneath the continental plate
What are contour lines on a map
lines that connect points of equal elevation on a map
How does the distance from an epicenter affect earthquake wave arrival times
The farther away from the epicenter, the bigger the difference in wave arrival times
What station is closer to the epicenter if Station A has a P-S interval of 3m 20s and Station B has 5m 40s?
Station A is closer
What is subduction in plate tectonics
subduction is the process where one tectonic plate moves under another and sinks into the mantle
What is the difference between oceanic and continental plates
Ocean plates are denser and thinner than continental plates, while continental plates are thicker and less dense
What is a deep-sea trench
A deep-sea trench is a long, narrow, and deep depression in the ocean floor, formed by subduction
What are the primary types of earthquake waves
P-waves (primary waves) and S-waves (secondary waves)
What is the Richter scale
Logarithmic scale used to measure the magnitude of earthquakes
What is the focus of an earthquake
the focus is the point within the earth where an earthquake originates
What is the epicenter of an earthquake
The point on earths surface directly above the focus of an earthquake
What is a volcanic eruption
A volcanic eruption is the release of magma, gas, and ash from a volcano
what is the role of tectonic plates in earthquakes
Tectonic plates move and interact at their boundaries, causing stress that can lead to earthquakes
What is the force behind the movements of the plates
Convection currents
What is the movement of plates along a divergent boundary
Pulling away from eachother
When an oceanic plate and a continental plate meet, we can expect to see:
A deep-sea trench
At a transform boundary, what would we most likely find
Earthquakes
What is most likely to occur at a divergent boundary
Mid-ocean ridges
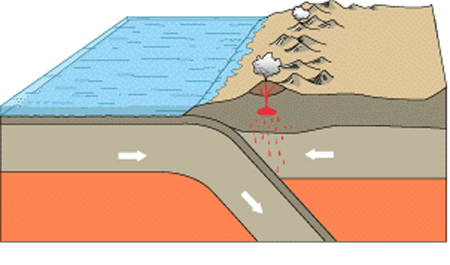
What is the name of the plate boundary in the picture
Convergent: oceanic-continental
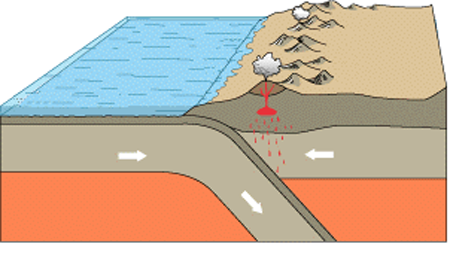
Why does the oceanic plate subduction instead of the continental plate
It is composed of basalt, a more dense rock
On which layer of the earth do tectonic plates “float”
Mantle
Think about CONVECTION. Cool areas within the atmosphere are_________
Contracting and sinking
At which type of plate boundary does sea floor spreading occur along
Divergent
what technology was used to help scientists discover the theory of seafloor spreading
SONAR
Who was the first scientists who proposed the idea that “the Earths continents were once joined as a single landmass that broke apart and sent the continents adrift”
Alfred Wagner
What evidence was used to support the idea the continents were once joined together as a supercontinent
Rock formations, fossils, ancient glacial deposits
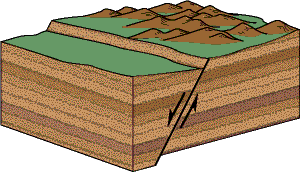
Which fault block is the footwall in the picture below
The block on the right
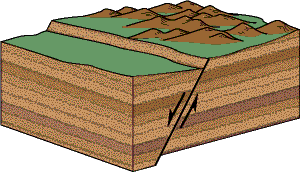
What type of fault is shown below
Normal fault
What type of stress creates a normal fault
Tension
What type of plate boundary is associated with a normal fault
Divergent

Which fault block is the footwall?
The right block

What type of fault is this? What type of stress creates it? What plate boundary is associated with it ?
Reverse fault. It is created by compression stress. Associated with convergent boundaries
What can we learn by studying seismic waves
The earthquakes measurement of the Richter scale, distance to the epicenter, and the layers of earths interior
The p waves arrive at a seismic station 7 mins and 40 seconds before the S waves, how far away is the station from the epicenter(use travel time graph)
5800 km
A seismogram is located 4800 kilometers away from the epicenter of an earthquake, what is the difference in time between when the P-waves reach the seismogram and the S-waves reach the seismogram?(use travel time graph)
6 min 40 sec
How many seismic stations do you need to locate the epicenter of an earthquake
3
Aluminum is extracted from the mineral bauxite, to make a variety of items from profit. Bauxite would be an example of an_______
Ore
A mineral that breaks along a rough surface is called a fracture; true or false
True
Fluorescence and magnetism are considered a minerals luster; true or false
False
The least useful property for identifying minerals is_______
Color
The color of a mineral when powdered is ________
Streak
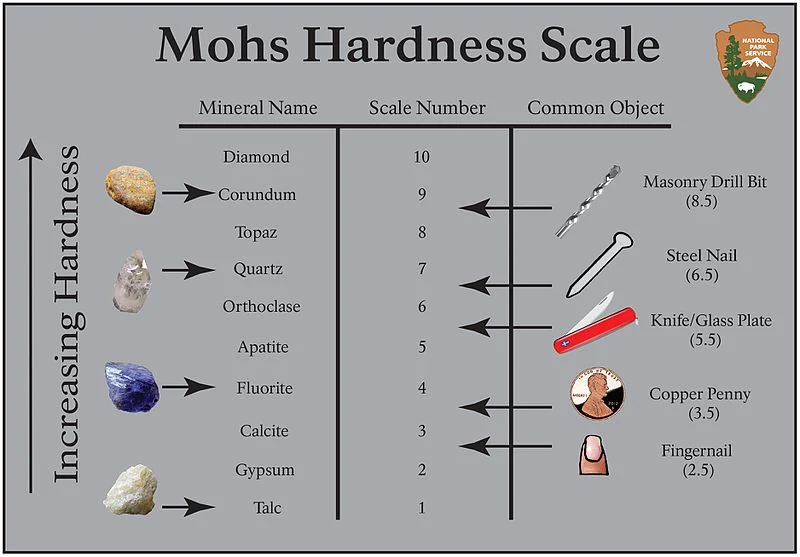
An unknown mineral scratches feldspar and is scratched by corundum. What can you conclude about this minerals hardness
1-2
When describing luster, which two terms do we use?
Metallic or non-metallic
What do copper , gold, silver, sulfur, and graphite have in common
They are all native elements/ minerals
What is the best way to determine if a mineral sample is calcite or quartz
Place a drop of acid on the mineral
Where is magma located
Below the earths surface
Igneous rocks that cool quickly on the earths surface are ______
Extrusive igneous rocks

What is the texture and name of this igneous rock
Vesicular; pumice
If a volcano forms where the pacific plate and the North American plate meet, what type of magma will you expect it to erupt
Andesetic
If a volcano forms at an oceanic hot spot, which type of volcano would you expect to form
Shield
If a volcano forms where plates spread apart, what kind of eruption will you expect to see
Quiet/flowy
Where do most volcanoes form
At plate boundaries
hot spot(continental ) zone
Forms far from plate boundaries, creates rhyloric magma and explosive eruptions
Which magma type do we have if it is 50-60 percent silica
Andesetic
Rhyolitic (crust type, zone, magma temp, silica content, viscosity, eruption,)
Continental crust. Hotspot zone. Low magma temp. High silica content. High viscosity. Explosive.
Andesetic(crust type, zone, magma temp, silica, viscosity, eruption)
Oceanic + Continental crust, convergent zone, medium magma temp, medium viscosity, medium silica. Moderately explosive eruptions
What process is this: When the weight of overlying layers squeezes the sediments together
Compaction
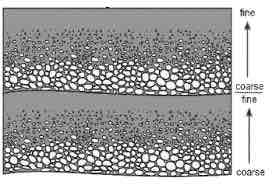
What bedding does this show
Graded bedding
varve
Annual sediment layer

What type of bedding is shown in the picture
Cross bedding
Organic sedimentary rock
Made from organic materials (plants, animals)
Clastic sedimentary rock
Formed from broken pieces of older weathered and eroded rocks
Chemical sedimentary rock
Forms when water traveling through rock dissolves some minerals
Limestone dissolves in rainwater
Chemical weathering
Acid is spilled on a marble counter top
Chemical weathering
The more fractures in a rock, the faster it weathers; true or false
True
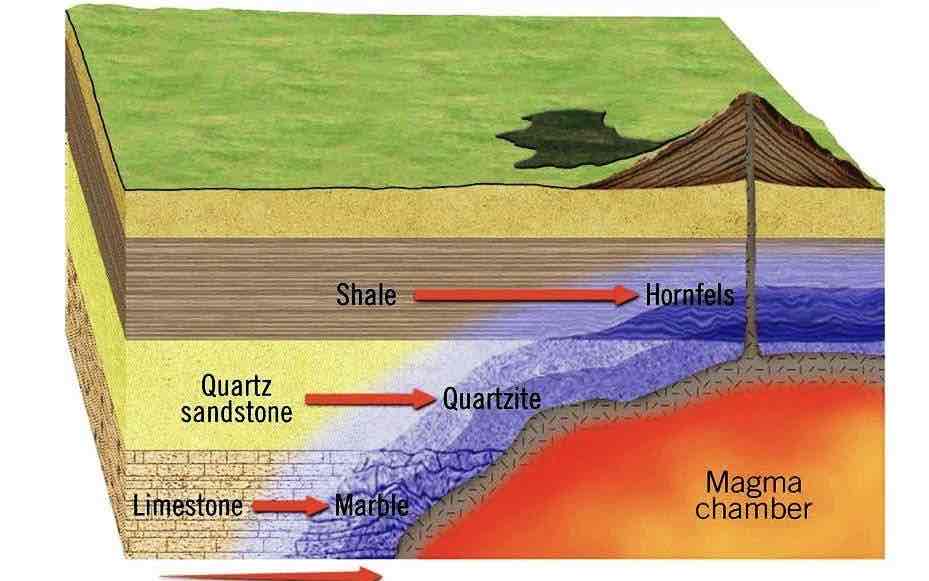
What type of metamorphism is happening in the picture
Contact metamorphism
Regional metamorphism
metamorphism affecting rocks over an extensive area as a result of the large-scale action of heat and pressure.

Which term best describes the texture of this rock
Foliated
The temperature and pressure during formation of metamorphic rock is so great that rock actually melts before becoming the new rock; true or false
False
Which type of rock could become metamorphic
Igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic
What type of earth science: California uses a wide range of renewable energy resources to meet its clean energy goals, and promote sustainable energy use
Environmental science
What type of earth science: stratus clouds are “blanket-like” in their appearance
Meteorology
What type of science: the Milky Way is a spiral galaxy
Astronomy
What type of science: the Labrador current is a cold current in the North Atlantic Ocean which flows from the Arctic Ocean south along the coast of Labrador and passes around Newfoundland, continuing south along the east coast of Canada near Nova Scotia.
Oceanography
What type of science: slicing through the center of Iceland is the mid-Atlantic ridge, this is the boundary between the North American and Eurasian tectonic plates
Geology
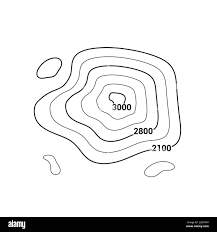
What type of map is shown in the picture
Topographic map
Cinder cone volcanoes
Cinder Cone Volcanoes are steep, conical hills with a bowl-shaped crater at the summit, formed from the accumulation of ejected lava fragments during explosive eruptions. They typically have basaltic magma, leading to fluid lava flows and are often associated with divergent plate boundaries and hot spots.
Composite Volcanoes (Stratovolcanoes)
* Shape: Large, cone-shaped volcanoes with steep slopes and a layered structure. * Formation: Built up by alternating layers of lava flows and pyroclastic deposits (ash, cinders, etc.). * Magma: Andesitic (intermediate silica content), leading to explosive eruptions. * Plate Boundary: Primarily associated with convergent plate boundaries (where plates collide).
What are Shield Volcanoes?
Shield Volcanoes are broad, gently sloping volcanoes with a shield-like appearance, formed by the accumulation of highly fluid basaltic lava flows. They are commonly found at divergent plate boundaries and hot spots.