Chapter 5 - Linkage, Recombination, Remapping
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is genetic linkage?
The tendency of genes located close together on the same chromosome to be inherited together.
What is linkage group?
A group of genes located on the same chromosome that tend to be inherited together due to genetic linkage.
What is a recombinant gamete?
A gamete that contains a new combination of alleles not found in the parent due to crossing over.
What is a nonrecombinant gamete?
A gamete that carries the same combination of alleles as found in the parent (also called parental gamete).
What is a recombinant progeny?
Offspring that have a different combination of traits than either parent due to recombination during meiosis.
What is the recombination frequency and how is it calculated?
(number of recombinant progeny / total number of progeny) * 100%
What is the maximum recombination frequency and why?
50% because crossing over between two loci can occur in up to half of all meioses.
What unit is used to express distances on a genetic map?
centiMorgan (cM), where 1 cM = 1% recombination frequency.
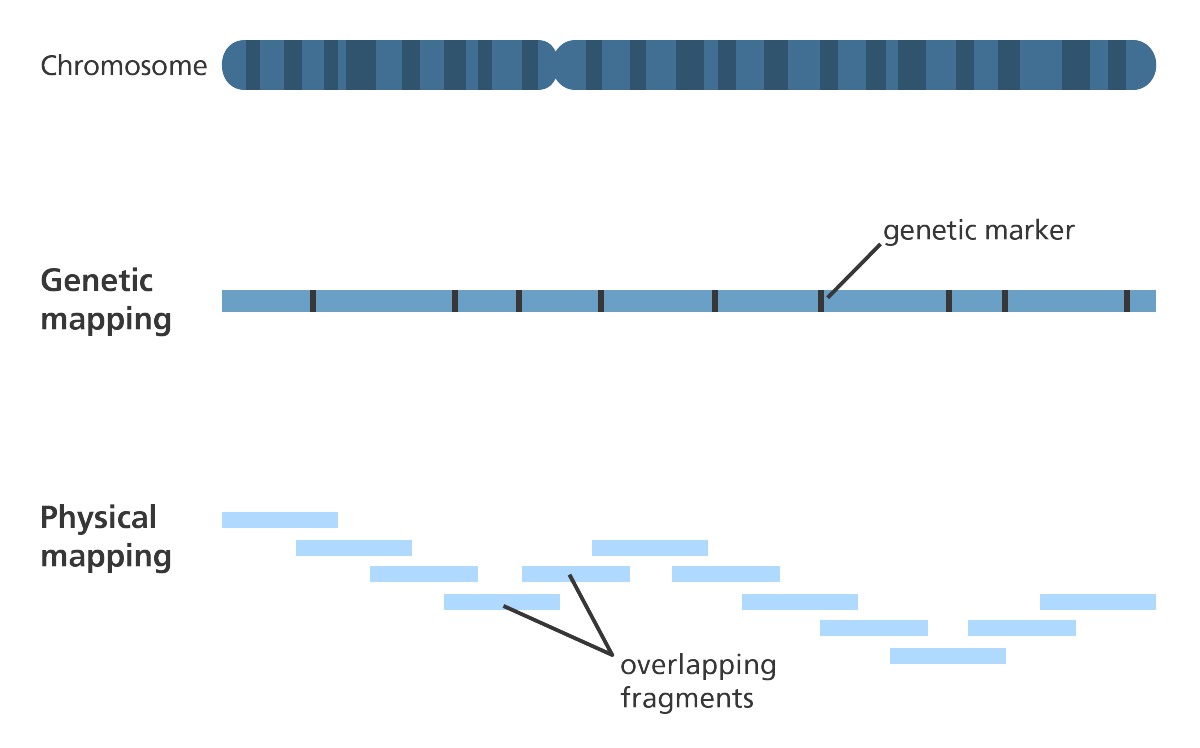
What is the difference between a genetic map and physical map?
A genetic map is based on recombination frequencies, while a physical map shows actual base pair distances between loci.
What does it mean when genes are in cis (coupling) configuration?
Wild type alleles are on one chromosome and mutant alleles are on the homologous chromosome.
What does it mean when genes are in trans (repulsion)?
Each chromosome has one wild-type and one mutant allele.
What is complete linkage?
A condition where genes are so close together on the chromosome that no crossing over occurs between them.
Why did Mendel not observe genetic linkage in his experiments?
The genes he studied were either different chromosomes or far apart on the same chromosome, so they assorted independently.
How can you test for linkage between two genes?
By performing a testcross with a double heterozygote and observing if recombinant progeny occur at frequencies lower than 50%.
What is the purpose of a three-point testcross?
To map the order and distances between three genes and to detect double crossovers.
Why does a two-point testcross underestimate distances between far-apart genes?
Because it fails to detect double crossovers that restore parental combination.
What is incomplete linkage?
When two genes on the same chromosome undergo crossing over in some, but not all, meiotic events.
How do recombination frequencies relate to physical distances on a chromosome?
Higher recombination frequencies usually indicate that genes are farther apart on the chromosome.
What does a three-point testcross allow that a two-point testcross does not?
Determination of gene order and more accurate estimation of distances, including detection of double crossovers.
In notation for linked genes, what does “AB/ab” represent?
A heterozygote with dominant alleles A and B on one chromosome and recessive alleles a and b on the homologous chromosome.
In a complete linkage testcross, what gametes are produced by a heterozygote with genotype MD/md?
Only MD and md gametes (nonrecombinant).
If only MD and md progeny are observed in a testcross involving genes M and D, what does this suggest?
The genes are completely linked and no crossing over occurred.
In a cross involving incomplete linkage, which gametes would be recombinant for a heterozygote with genotype AB/ab?
Ab and aB
If two genes are 20 cM apart, what proportion of gametes are expected to be recombinant?
20%
Given recombination frequencies of A–B = 10%, B–C = 5%, and A–C = 15%, what is the gene order?
A – B – C
In a testcross, 70 progeny are nonrecombinant (MD and md) and 30 are recombinant (Md and mD). What is the recombination frequency?
30 / (70 + 30) = 30%; recombination frequency = 30%
What is the genotype of a heterozygous F₁ individual from a cross between MM DD and mm dd parents?
MD/md