Anatomy Skeletal System Textbook
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/292
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:36 PM on 11/30/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
293 Terms
1
New cards
composed of bones, cartilages, and ligaments joined tightly to form a strong, flexible framework for the body
Skeletal system
2
New cards
joint surfaces in the mature skeleton
Cartilage location
3
New cards
A cord or band of tough collagenous tissue binding one organ to another, especially one bone to another
ligaments
4
New cards
soft bloody or fatty material enclosed in the bones
bone marrow
5
New cards
support
protection
movement
blood formation
storage
protection
movement
blood formation
storage
functions of skeletal system
6
New cards
limbs and vertebral column support the body
mandible and maxilla support the teeth
mandible and maxilla support the teeth
Support function
7
New cards
bones enclose and protect the brain, spinal cord, lungs, heart, and pelvic viscera
Protection Function
8
New cards
movements of the limbs, and other movements such as breathing, are produced by the action of muscles on bones
Movement Function
9
New cards
Red Bone marrow is the major producer of blood cells
Blood Formation Function
10
New cards
skeleton stores calcium and phosphorus
fatty bone marrow has fuel
fatty bone marrow has fuel
Storage Function
11
New cards
affects blood sugar regulation, fertility, and brain function in mammals
other functions of the skeleton
12
New cards
osseous tissue, a connective tissue with a hard, calcified matrix
bone
13
New cards
compact (dense) bone
spongy bone
spongy bone
2 forms of bone
14
New cards
consists of a solid matrix
compact (dense) bone
15
New cards
porous lattice honeycombed with spaces
spongy bone
16
New cards
interior of bone
where is spongy bone found
17
New cards
osseous tissue
organ (femur)
organ (femur)
2 meanings for bone
18
New cards
osteogenic
osteoblasts
osteocytes
osteoclasts
osteoblasts
osteocytes
osteoclasts
Four kinds of bone cells
19
New cards
bone surface, beneath the fibrous connective tissue membrane that covers a bone
osteogenic cells location
20
New cards
give rise to osteoblasts
only bone cells that divide and make more bone cells
only bone cells that divide and make more bone cells
osteogenic cells function
21
New cards
lie in a single layer on the bone surface, somewhat resembling a cuboidal epithelium
osteoblasts location
22
New cards
bone-forming cells that synthesize the organic matter of the bone and promote its mineralization
osteoblasts function
23
New cards
reside in cavities called lacunae, which are connected to each other by channels called canaliculi
Osteocyte locations
24
New cards
pass nutrients and chemical signals
pass metabolic wastes
orchestrate bone remodeling
maintenance of bone density
sense mechanical stress
secrete signals that adjust bone shape and density
pass metabolic wastes
orchestrate bone remodeling
maintenance of bone density
sense mechanical stress
secrete signals that adjust bone shape and density
Osteocyte function
25
New cards
90%
how much of bone cells are osteocytes
26
New cards
osteoblasts become trapped in the matrix the deposit
how are osteocytes made
27
New cards
lie one the bone surface
lie in pits that they have eroded
lie in pits that they have eroded
osteoclasts location
28
New cards
bone-dissolving cells that develop from a separate line of bone marrow stem cells
osteoclasts function
29
New cards
stony matter that surrounds the osteocytes and lacunae
matrix of osseous tissue
30
New cards
bones being soft and bending easily
deficient in minerals can cause
31
New cards
childhood mineral deficiency
rickets
32
New cards
adulthood mineral deficiency
osteomalacia
33
New cards
flexibility
collagen gives bones
34
New cards
consists of porous lattice of slender rods and plates called trabeculae
spongy (cancellous) bone
35
New cards
bone marrow and small blood vessels
spaces of spongy tissue are filled with
36
New cards
forms the hard outer shell of the bone. Prevents bone marrow from seeping out and provides a solid attachment surfaces for muscles, tendons, and ligaments
compact (dense) bone
37
New cards
A structural unit of compact bone consisting of a central canal surrounded by concentric cylindrical layers of matrix
osteons
38
New cards
A little plate or layer in compact bone that arranges around a central canal
lamellae
39
New cards
long bones
what are the most important bone for movement
40
New cards
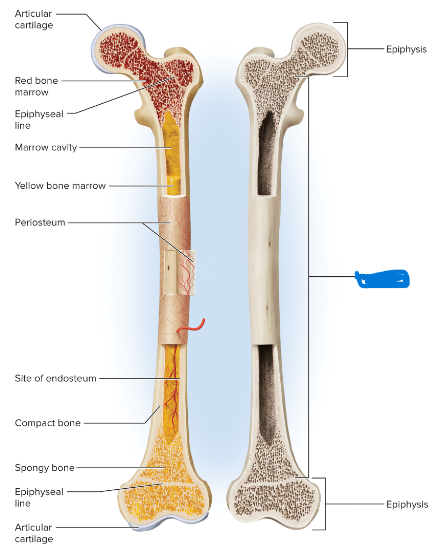
The shaft of a long bone (elongated midsection)
diaphysis
41
New cards
The head of a long bone (expanded end)
epiphysis
42
New cards
provides leverage
shaft function
43
New cards
strengthen a joint and provide added surface area to for the attachment of tendons and ligaments
head function
44
New cards
A thin layer of hyaline cartilage covering the articular surface of a bone at a synovial joint
articular cartilage
45
New cards
serving to reduce friction and ease joint movement
articular cartilage function
46
New cards
spongy bone
what is the head and shaft filled with
47
New cards
marrow (medullary) cavity of the shaft and spaces between the spongy bone
where is bone marrow occupying
48
New cards
the line marking the site of an epiphyseal plate that has has stopped growing and become ossified.
epiphyseal line
49
New cards
shieldlike plates that protect delicate organs
flat bones
50
New cards
sternum- heart
cranial bones- brain
cranial bones- brain
organs flat bones protect
51
New cards
bones that don't fit the description of flat and long bones
short and irregular bones
52
New cards
A layer of fibrous connective tissue covering the surface of a bone.
periosteum
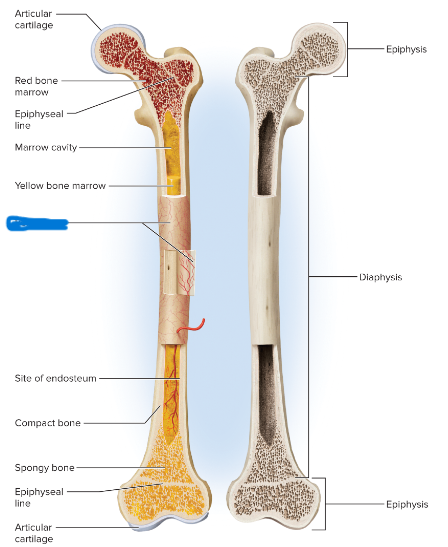
53
New cards
provides strong attachment and continuity from muscle to tendon to bone
periosteum function
54
New cards
a thin layer of reticular connective tissue separating the bone from the bone marrow (internal surface)
endosteum
55
New cards
red bone marrow
yellow bone marrow
yellow bone marrow
2 types of bone marrow
56
New cards
serves to produce blood cells and platelets, fills nearly every bone of a child's skeleton, but is more distribution in adults
red bone marrow
57
New cards
fatty bone marrow that dominates the long limb bones of adults
yellow bone marrow
58
New cards
formation of bone
ossification
59
New cards
intramembranous
endochondral
endochondral
2 types of ossificaiton
60
New cards
A process in which a sheet of mesenchyme becomes calcified to form a bone, employed primarily for the production of flat bones such as those of the cranium.
intramembranous ossification
61
New cards
fontanels
another name for gaps
62
New cards
A process in which a hyaline cartilage precursor (model) is replaced by calcified tissue to form a bone; employed for the production of most bones of the body except for flat bones of the skull and part of the clavicle.
endochondral ossification
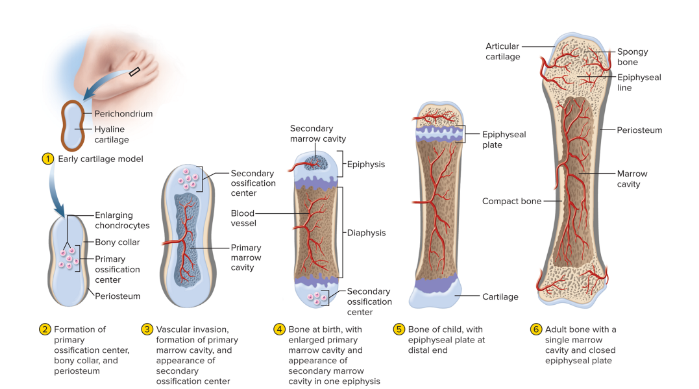
63
New cards
hyaline cartilage covered with pericondrium
Step 1 of Endochondral Ossification
64
New cards
in a primary ossification center chondrocytes enlarge and die. Thin walls calcify. Osteoblasts deposit thin layer of bone around model, forming a collar
Step 2 of Endochondral Ossification
65
New cards
blood vessels pierce the periosteum at the primary ossification center. Osteoclasts digest calcified tissues, hollowing out the shaft and creating the primary marrow cavity. Osteoblasts deposit layers of bone, thickening shaft. Secondary ossification center develops
Step 3 of Endochondral Ossification
66
New cards
secondary ossification center has hollowed out secondary marrow cavity. Another ossification center appears
Step 4 of Endochondral Ossification
67
New cards
epiphyseal plates separates marrow cavities. Plate is a growth zone
Step 5 of Endochondral Ossification
68
New cards
cartilage in epiphyseal plate is depleted
marrow cavities unite into single medullary cavity
bones can no longer grow
marrow cavities unite into single medullary cavity
bones can no longer grow
Final step of endochondral ossification
69
New cards
accommodate changing forces applies to the skeleton
addition of new tissue to the bone surface
addition of new tissue to the bone surface
why do bone change size and shape
70
New cards
stimulates an increase in bone mass
what does tension do to the skeleton
71
New cards
maintenance
growth
remodeling
exchange minerals with extracellular fluid
growth
remodeling
exchange minerals with extracellular fluid
bones functions as an metabolically active organ
72
New cards
calcium and phosphate
skeleton is the body's primary reservoir for
73
New cards
bone structure
component of DNA, RNA, ATP, phospholipids, and other compounds
component of DNA, RNA, ATP, phospholipids, and other compounds
phosphate function
74
New cards
bone structure
muscle contraction, blood clotting, exocytosis, nervous communication, and cellular responses to hormones
muscle contraction, blood clotting, exocytosis, nervous communication, and cellular responses to hormones
calcium function
75
New cards
crystallization process in which osteoblasts extract calcium, phosphate, and other ions from the blood and deposit them in the osseous tissue
mineral deposition
76
New cards
process in which the osteoclasts dissolve bone, releasing minerals into the blood and making them available for other uses
resorption
77
New cards
A deficiency of calcium ions in the blood that causes dysfunctions ranging from muscle tremor to tetanus (inability of the muscle to relax)
hypocalcemia
78
New cards
An excess of calcium ions in the blood that depresses nervous, muscular, and cardiac function
Hypercalcemia
79
New cards
calcitriol
parathyroid hormone
parathyroid hormone
what 2 hormones regulates calcium homeostasis
80
New cards
most active form of vitamin D
promotes calcium absorption in the small intestine
reduces urinary loss of calcium
stimulates osteoclasts to release calcium from the bones
promotes calcium absorption in the small intestine
reduces urinary loss of calcium
stimulates osteoclasts to release calcium from the bones
calcitriol
81
New cards
rickets
low levels of calcitriol result in
82
New cards
secreted by the parathyroid glands
stimulates bone resorption by osteoclasts
promotes calcium reabsorption by kidneys
promotes calcitriol synthesis
stimulates bone resorption by osteoclasts
promotes calcium reabsorption by kidneys
promotes calcitriol synthesis
parathyroid hormone (PTH)
83
New cards
fracture results from an unusual stress on a bone
stress fracture
84
New cards
bone has been weakened by some other condition, and it fractures under a stress that a healthy bone would withstand
pathological fracture
85
New cards
any fracture that breaks through the skin
open fracture
86
New cards
fracture does not break through skin
closed fracture
87
New cards
descriptions of bones that include a variety of ridges, spines, bumps, depressions, holes, and joint surfaces
bone markings
88
New cards
a tubular passage or tunnel in a bone
Canal Bone marking
89
New cards
a rounded knob
condyle Bone marking
90
New cards
a narrow ridge
crest Bone marking
91
New cards
a flare superior to a condyle
epicondyle Bone marking
92
New cards
a smooth joint surface that is flat or only slightly concave or convex
facet Bone marking
93
New cards
a slit through a bone
fissure Bone marking
94
New cards
a hole through a bone, usually round
foramen Bone marking
95
New cards
a shallow, broad, or elongated basin
fossa Bone marking
96
New cards
a cavity within a bone
sinus Bone marking
97
New cards
any bony prominence
process
98
New cards
a sharp, slender, or narrow process
spine Bone marking
99
New cards
a small, rounded process
tubercle Bone marking
100
New cards
a rough surface
tuberosity Bone marking