The American Revolution
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:42 PM on 12/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
1
New cards
Lexington & Concord
Shot heard around the world - Beginning of the American Revolution
2
New cards
Bunker Hill
Actually took place at Breed's Hill
A moral victory for Americans - Over 700 British dead
A moral victory for Americans - Over 700 British dead
3
New cards
Brandywine Creek
Washington forced to retreat - British take Philadelphia
4
New cards
Saratoga
Great victory for the Americans - French will pledge military support - turning point of the revolution
5
New cards
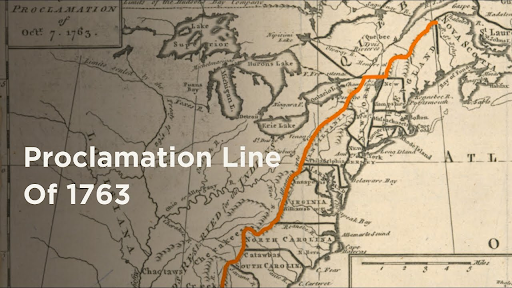
Proclamation line of 1763
Passed after Pontiac's Rebellion - Banned colonial settlement beyond App. Mts
King didn't want to pay for the protection of the colonists on the frontier
Colonists are upset! Not happy with how the King was just now telling them how to live their lives
MANY COLONISTS IGNORED THIS BAN
King didn't want to pay for the protection of the colonists on the frontier
Colonists are upset! Not happy with how the King was just now telling them how to live their lives
MANY COLONISTS IGNORED THIS BAN
6
New cards

The Sugar Act of 1764
Placed a tax on Sugar and Molasses.
Caused the price of Rum to go up! Main ingredient in Rum is Molasses.
Upset the colonists!
Taxation without representation!
Caused the price of Rum to go up! Main ingredient in Rum is Molasses.
Upset the colonists!
Taxation without representation!
7
New cards

The Stamp Act - Passed in 1765
Tax on anything made of paper.
Required colonists to purchase a stamp before purchasing something made of paper,
Colonists HATED this Act and riots started in some colonial cities
Required colonists to purchase a stamp before purchasing something made of paper,
Colonists HATED this Act and riots started in some colonial cities
8
New cards

The Quartering Act - 1765
Soldiers were housed in the private homes of colonists so the crown could save money
9
New cards

Colonists form the Sons of Liberty
Group of Patriots (people against taxation without representation) that started in Boston.
Encouraged protests and boycotts.
Sometimes used violence like tar and feathering tax collectors.
Encouraged protests and boycotts.
Sometimes used violence like tar and feathering tax collectors.
10
New cards
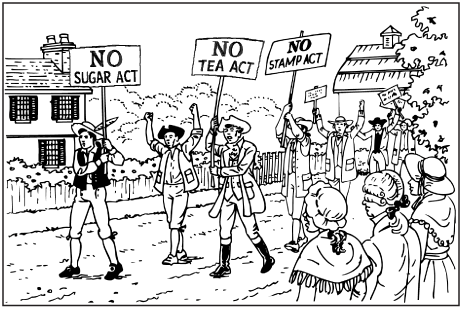
Cause: Patriots protesting against taxation without representation
Effect: 1766 - Stamp act repealed by Parliament
11
New cards
Townshend Acts of 1767
Acts that introduced the British Parliament to imposing duties on glass, lead, paints, paper, and tea that was imported
Massive boycotts begin
Smuggling increases
Massive boycotts begin
Smuggling increases
12
New cards
Patriot
Name for a colonist that was angry about British Taxation policies and thought the colonies should tax and govern themselves. - Many in cities like Boston & Philadelphia
13
New cards
Loyalist
Colonist that was loyal to England and the King. Looked upon Patriots as traitors. Many more in Southern Colonies
14
New cards
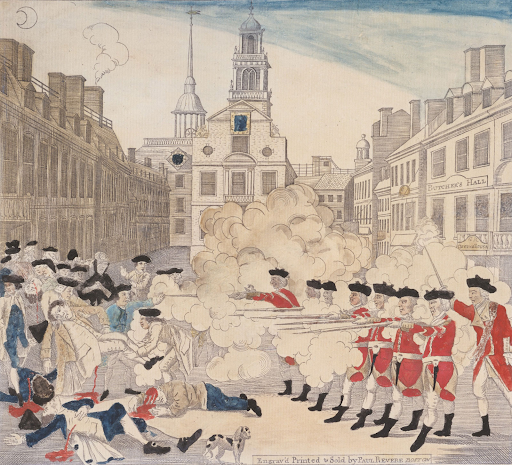

Boston Massacre - 1770
Angry mob of colonists were protesting and things turned violent.
British redcoats fired and 5 colonists were killed
The Image here was created as propaganda and spread around the colonies.
Many loyalists turned “patriot” after this event.
British redcoats fired and 5 colonists were killed
The Image here was created as propaganda and spread around the colonies.
Many loyalists turned “patriot” after this event.
15
New cards

The Tea Act - 1773
NOT A TAX ON TEA!!
Boycotts against British tea were working. Britain had too much tea!
Gave the sale of tea to the colonies to one company. That company lowered the price to “trick” the colonists into buying (still was taxed)
Colonists were highly offended and this lead to further boycotts and eventually the Boston Tea Party
Boycotts against British tea were working. Britain had too much tea!
Gave the sale of tea to the colonies to one company. That company lowered the price to “trick” the colonists into buying (still was taxed)
Colonists were highly offended and this lead to further boycotts and eventually the Boston Tea Party
16
New cards

The Boston Tea Party - 1773
A result of taxes on Tea and the Tea Act
Sons of Liberty dressed as Indians boarded a shipping boat and threw 342 chests of tea into the Boston Harbor.
!!! The King was furious and punished Boston and the colonies with the Intolerable Acts !!!
Sons of Liberty dressed as Indians boarded a shipping boat and threw 342 chests of tea into the Boston Harbor.
!!! The King was furious and punished Boston and the colonies with the Intolerable Acts !!!
17
New cards

The Intolerable Acts of 1774
England’s response to The Boston Tea Party.
Originally called the Coercive Acts
Closed the Port of Boston (Image above)
Stopped the Massachusetts Legislature (Democratic, elected body that makes laws)
Suspended Town Meetings (democratic local government)
Increased the power of the Royal Governor
New Quartering Act
These Acts UNITED the colonists.
18
New cards
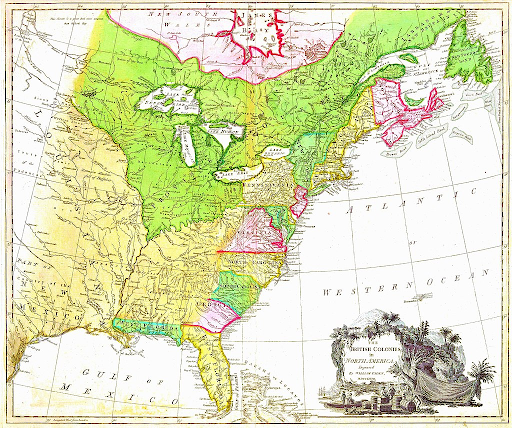
The Quebec Act - 1774
Another response to civil unrest in Boston and other colonial cities
England took away western lands that belonged to the colonies and made it part of Canada (See green area on map)
Very much angered the colonists (They helped win this land in the F&I War)
19
New cards

1st Continental Congress - 1774
Colonial response to the Intolerable Acts
12 of the 13 colonies sent delegates to Philadelphia - created a list of demands for King George III:
1. Repeal the Intolerable Acts!
2. Agree that the colonists have the right to govern and tax themselves
3. Inform the King that the Colonies will begin to train militia troops
4. Agree to new boycotts of British goods
12 of the 13 colonies sent delegates to Philadelphia - created a list of demands for King George III:
1. Repeal the Intolerable Acts!
2. Agree that the colonists have the right to govern and tax themselves
3. Inform the King that the Colonies will begin to train militia troops
4. Agree to new boycotts of British goods
20
New cards

1775 - King George III sends thousands of troops to the colonies
He looked at the training of militia troops as an “act of war”
21
New cards

“The Shot Heard Around the World.”
April 19th, 1775 - hundreds of British troops leave Boston to capture Sam Adams and John Hancock
After being warned by Paul Revere and William Dawes (Midnight ride) - The men of Lexington MA, stood in the village green to block the British.
Someone Fired! (Shot Heard Around the World)
The British opened fire and 7 colonists were killed.
The British marched on to Concord where colonists resisted. Hundreds of British are killed as they march back to Boston as the “Minute Men” rise up.
After being warned by Paul Revere and William Dawes (Midnight ride) - The men of Lexington MA, stood in the village green to block the British.
Someone Fired! (Shot Heard Around the World)
The British opened fire and 7 colonists were killed.
The British marched on to Concord where colonists resisted. Hundreds of British are killed as they march back to Boston as the “Minute Men” rise up.
22
New cards

The 2nd Continental Congress meets
Olive branch petition - one last chance at peace
Decide to put into words why war is necessary (committee formed to write reasons)
Levy (tax) money to raise a formal army
Appoint George Washington as Commander of the Continental Army
Decide to put into words why war is necessary (committee formed to write reasons)
Levy (tax) money to raise a formal army
Appoint George Washington as Commander of the Continental Army
23
New cards

Thomas Paine publishes “Common Sense”
Published in early 1776 to explain in plain english why Americans should resist British control.
Sold thousands of copies throughout the colonies
Helped turn people toward the Patriot cause
Sold thousands of copies throughout the colonies
Helped turn people toward the Patriot cause
24
New cards

July - 1776 - Declaration of Independence is written
Declared Independence from England
All men are created equal with certain rights that cannot be taken away. (Life, Liberty, and the pursuit of Happiness)
Governments are created among men to protect those rights. Government gets its power from the people.
If government does not protect those rights - people should put a new government in place
All men are created equal with certain rights that cannot be taken away. (Life, Liberty, and the pursuit of Happiness)
Governments are created among men to protect those rights. Government gets its power from the people.
If government does not protect those rights - people should put a new government in place
25
New cards
Trenton & Princeton
2 victories inspire americans
Many join or re-enlist in the army
Many join or re-enlist in the army