Bio 3.4 - Microbiology
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
How can bacteria be distinguished from each other?
size
shape
staining characteristics
metabolic features
antigenic features
genetic features
What are the three shapes of bacteria?
Bacillus
Coccus
Spirillum
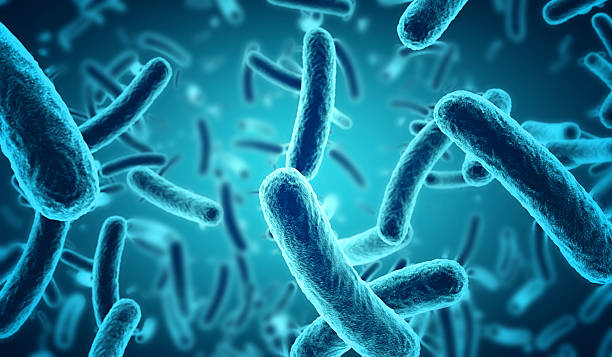
What shape is bacillus?
Rod shaped
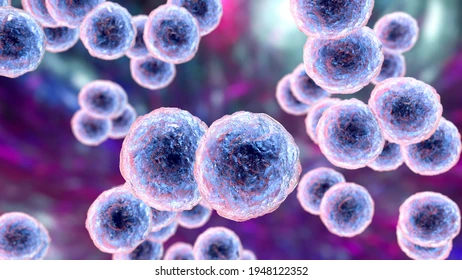
What shape is coccus?
Spherical
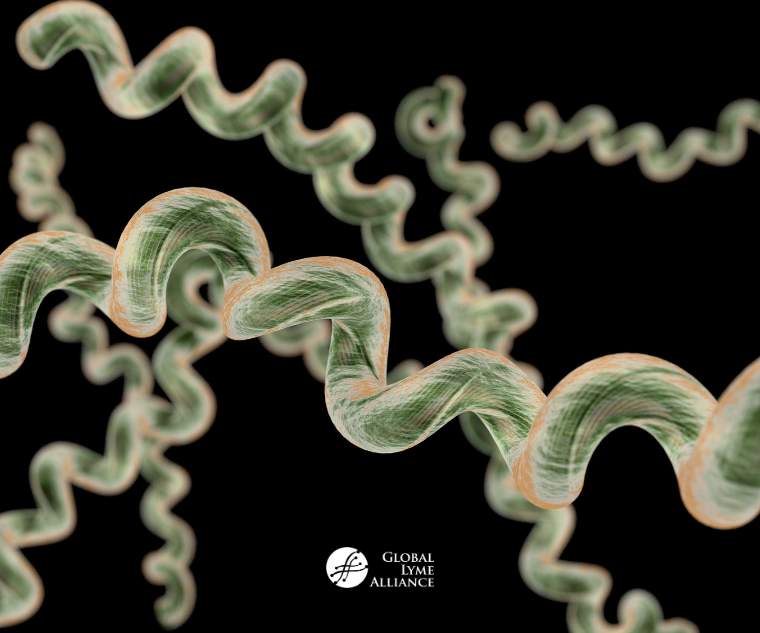
What shape is spirillum?
Spiral/corkscrew
How are bacteria grouped?
singly
in pairs
in chains
in clusters
Using cell structure, what are the two types of bacteria?
Gram positive
Gram negative
How do you distinguish between gram positive and negative bacteria?
Using gram stain
What colour does gram positive bacteria stain after using gram stain?
purple
What colour does gram negative bacteria stain after using gram stain?
red
What are the 4 stages of gram staining?
crystal violet (purple) - stain/dye
Lugol’s iodine - mordant
Ethanol - decolouriser
Safranin (red) - counter stain
What is the effect of the reagent crystal violet?
Binds to the peptidoglycan cell
all cells will appear purple
What is the effect of the reagent Lugol’s iodine?
Helps bind the crystal violet to peptidoglycan cell wall strongly
What is the effect of the reagent ethanol?
Removes any unbound crystal violet stain and also the outer lipopolysaccharide layer
gram positive = purple
gram negative = colourless
What is the effect of the reagent safranin?
Binds to the peptidoglycan wall
gram positive = purple
gram negative = red
Explain the composition of the cell wall in gram positive bacteria linking it to why they stain purple?
They retain the crystal violet/iodine complex
Walls have a thick layer of peptidoglycan/murein
Gram stain can easily reach it
Peptidoglycan layer retains the crystal violet/iodine complex when washed with alcohol
Do not have an additional lipopolysaccharide layer or protein layer
Why are gram positive bacteria susceptible to antibiotics such as penicillin?
Penicillin inhibits the formation of cross linkages in the peptidoglycan layer which provides strength
weakens the wall and when water enters by osmosis the cell swells and bursts
especially significant when cells divide
Explain the composition of the cell wall in gram negative bacteria linking it to why they stain red?
Have an additional lipopolysaccharide and protein layer outside the thin peptidoglycan layer
This outer membrane reduces the penetration of the crystal violet stain
On treatment w alcohol the outer layer is lost and thin inner peptidoglycan layer is exposed
Crystal/iodine complex is washed away
Bacteria show counterstain safranin which is red
Why are gram negative bacteria not susceptible to antibiotics such as penicillin?
Thick lipopolysaccharide layer prevents the entry of those molecules
different antibiotics are required
Why do antibiotics not damage human cells as well as bacteria cells?
Human cells do not have a peptidoglycan cell wall
Human cells have 80s ribosomes not 70s - have a different metabolism to bacteria
What conditions need to be considered for culturing bacteria?
Nutrients
Growth factors
Temperature
pH
Oxygen
What nutrients are needed for culturing bacteria?
Supplied in a nutrient media
Cultured in liquid medium - nutrient broth/medium solidified with agar
Provides water
Includes
carbon - energy source (glucose)
nitrogen for amino acids synthesis in organic molecules and in inorganic form e.g. nitrate ions
What growth factors are needed for culturing bacteria?
Vitamins
biotin
mineral salts e.g. Na+, Mg2+, Cl-, SO42-, PO43-
amino acids
purines + pyrimidines
What temperature is needed for culturing bacteria?
Bacterial metabolism is regulated by enzymes
range of 25-45 C is suitable for most bacteria
optimum for mammalian pathogens is 37
suitable for enzyme activity
What pH is needed for culturing bacteria?
favoured by slightly alkaline conditions (pH 7.4)
fungi grow better in neutral to slightly acidic conditions
What is an obligate aerobes?
must have oxygen available
What are obligate anaerobes?
must not have oxygen
What are facultative anaerobes
can grow with or without oxygen but better with oxygen present
What is defined media?
contains only known ingredients/known concentrations
What is undefined media?
not all ingredients/concentrations are known e.g. yeast extract
What is selective media?
allows only certain bacteria to grow e.g. Maconkey agar - allows gram negative agar
What is the advantage of adding glucose rather than lactose to bacteria growing in a fermenter?
All bacteria can ferment/utilise glucose for respiration
Two types of bacteria
lactose - fermenting bacteria - can use lactose
non lactose fermenting bacteria - can’t use lactose - can’t synthesise enzyme needed to hydrolyse lactose into galactose and glucose
What is aseptic technique?
Laboratory practice that maintains sterility in apparatus and prevents contamination of the equipment and the environment
How do you prevent contamination of pure cultures and apparatus by bacteria from the environment?
Sterilise all apparatus and media before use to prevent initial contamination
Handle cultures carefully, flaming necks of culture vessels before opening and closing
Use equipment such as sterile loops to prevent subsequent contamination
How do you prevent contamination by the bacteria being used in experiments?
Sterilise the work surface before and after an experiment using a disinfectant (1% virkon)
Use the correct handling techniques to prevent the contamination of personnel and the immediate environment by the organisms being cultured
Why are petri dishes and nutrient agar sterilised before agar is poured?
To prevent contamination of the culture medium
How is an inoculating loop sterilised?
By heating it to red heat in a bunsen burner blue flame before and after use
Why should the petri dish lid only be slightly lifted?
To prevent microorganisms from the air contaminating the culture and vice versa
How do you secure a petri dish after inoculation?
Lid should be secured with adhesive tape and label it with date and name
Why are inoculated agar plates incubated at 25 degrees for 24-48 hours in schools?
It encourages the growth of the culture without growing harmful or toxic pathogens
What is an autoclave?
A large sealed container like a pressure cooker
What is an autoclave used for?
To sterilise cultures or glass and metal
121 degrees
15 mins
in steam under pressure
How do you dispose of petri dishes after use?
Seal them in an autoclave bag
autoclave at 121 degrees for 15-30 mins
throw them out with general waste
What sterilisation method is used for heat-labile plastics?
Irradiation
When might estimating bacterial population size may be important?
Tissue samples e.g. urine
Water sample
Food samples/drug manufacture e.g. penicillin
What are the two ways the population size of bacteria in liquid culture may be measured?
Directly - counting cells
Indirectly - by measuring turbidity (cloudiness)
What are the two types of direct counts when measuring the population size of bacteria in a liquid?
Viable counts
Total counts
What is a viable count of bacteria?
Describes living cells only
What is a total count of bacteria?
Describes living and dead cells
How is the bacterial growth measured indirectly?
By measuring the turbidity of the culture - light absorption by sample of water gives an indication of the population of bacteria