anatomy chapter 3: tissues
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
histology
study of tissues
tissue
group of cells that work together to perform a particular function
epithelial
protect, absorb, secrete
connective
connects part of the body and helps support and protect
muscle
extract force, contracts, makes movement possible
nervous
receives and carries signals/protects signal conducting cells (communication and control)
simple squamos (epithelial)
flat
simple cubiodal (epithelial)
cube (square)
simple columnar (epithelial)
column (rectangular)
stratified squamos (epithelial)
many layers
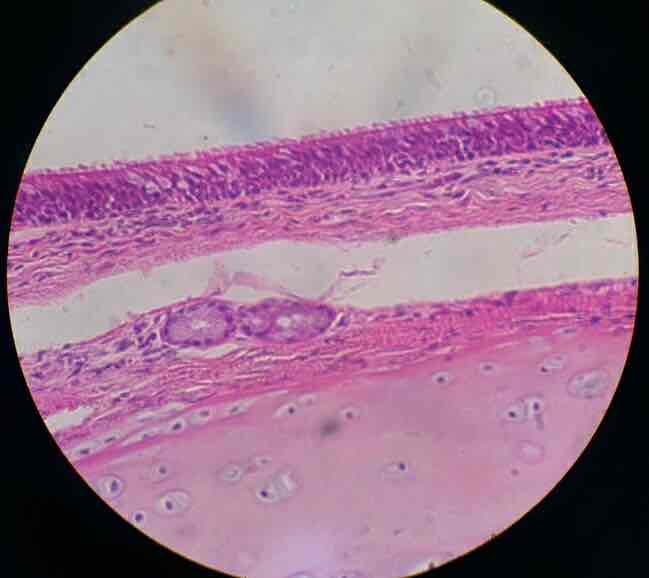
pseudostratified epithelial (epithelial)
consists of one layer of cells different height ; pseudo=false
simple squamos epithelium structure
flat, slightly irregular (lining blood vessels, heart, and lungs)
simple squamos epithelium function
secretes pericardial fluid (fluid surrounds heart) pleural fluid (cells covering lung)
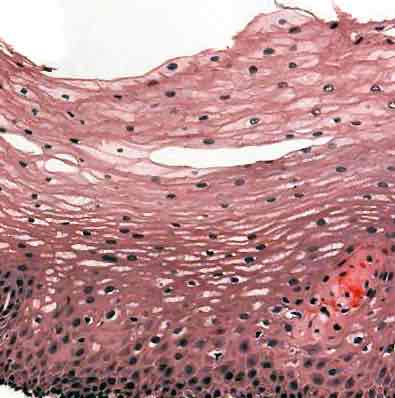
stratified squamos epithelium structure
several layers: tall, cylidrical cells in lowest layer, irregular
stratified squamos epithelial function
shaped flat cells as its approaches surface ; protection of delicate surface from injury
stratified squamos epithelial location
mouth, skin, esophogus, vagina
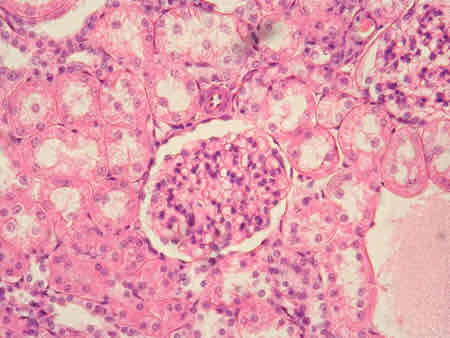
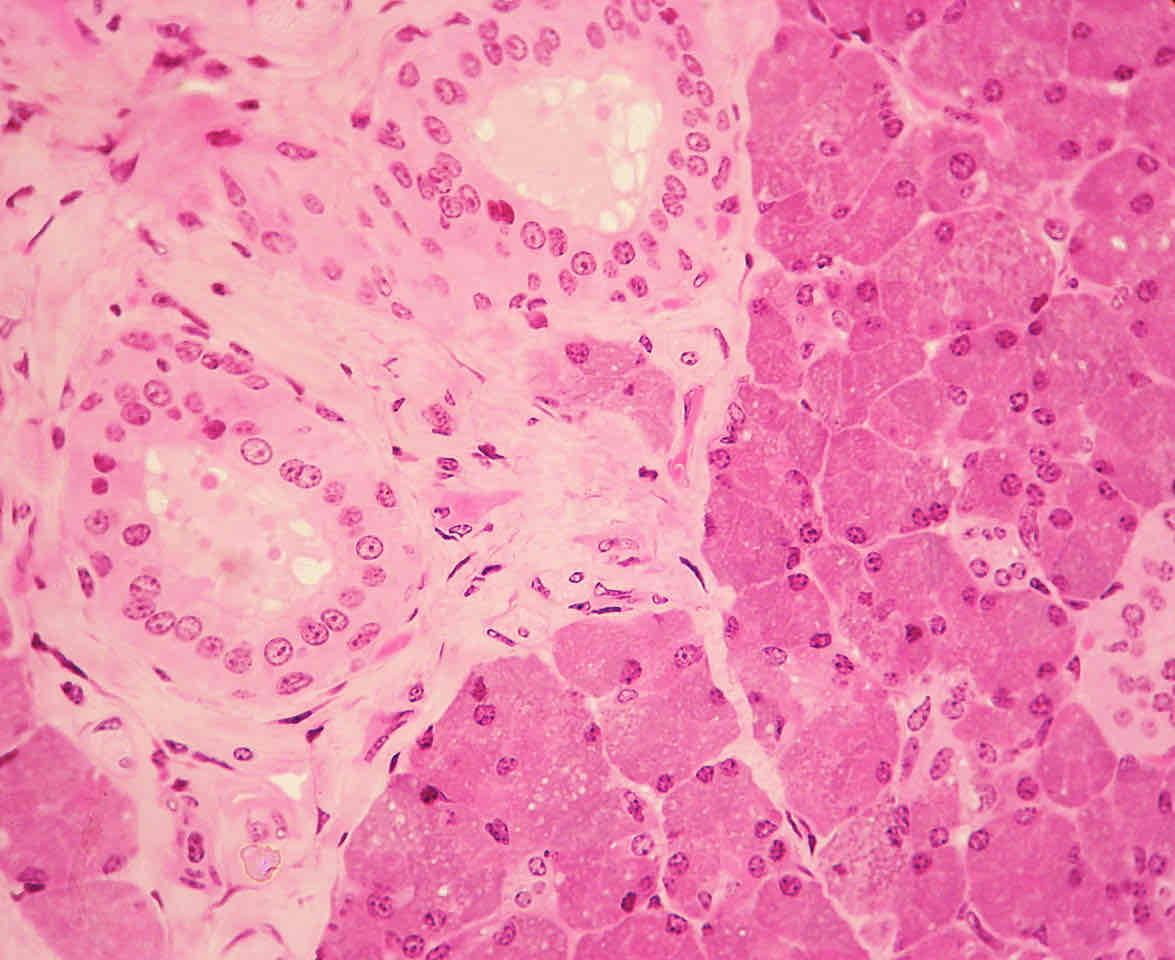
simple cubiodal epithelium structure
equal height and width
simple cubiodal epithelium location
secretory portions if glands, kidney tubules, ducts of glands, and tissue covering of ovary
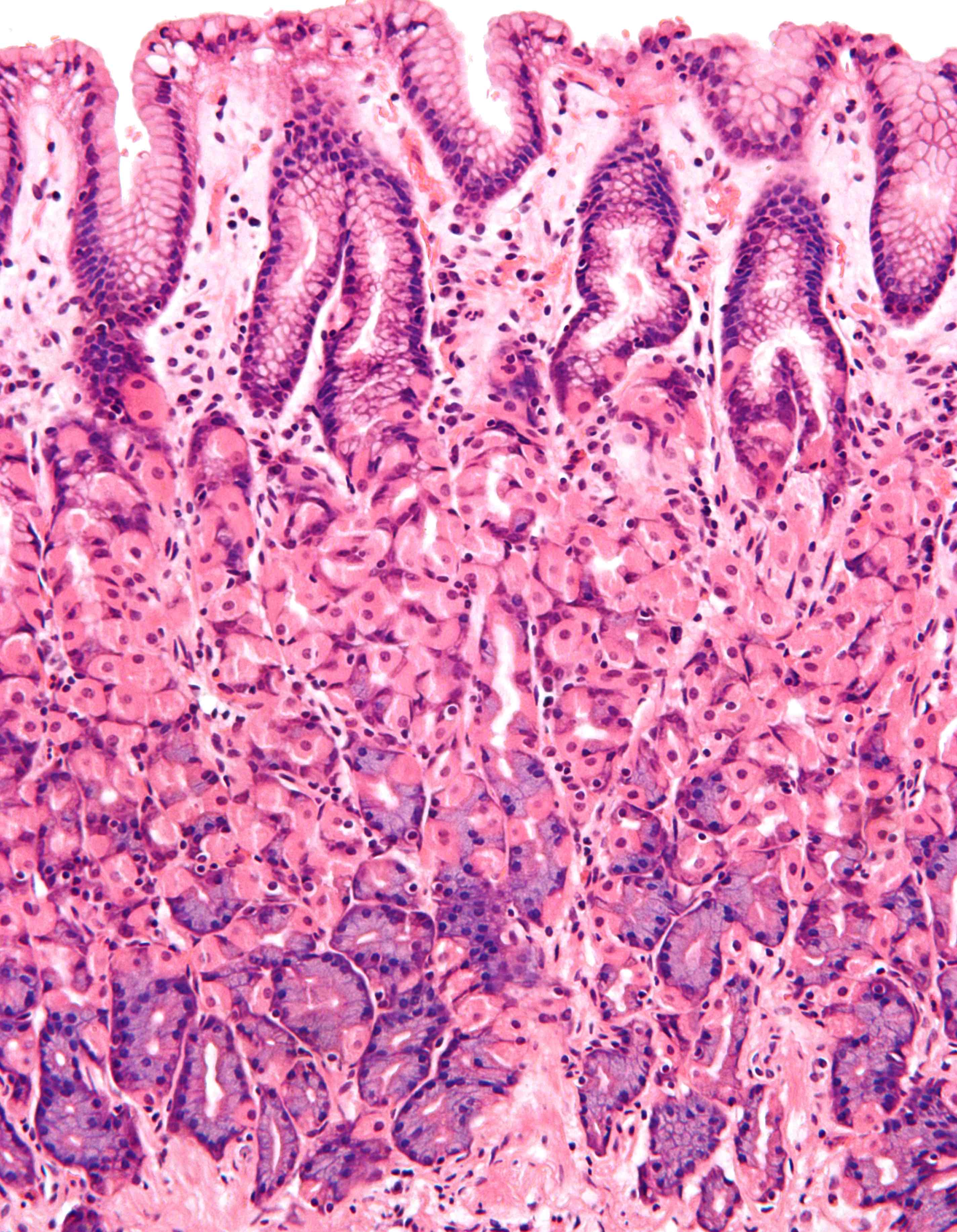
simple columnar epithelium structure
tall, closely packed together cells
simple columnar epithelium function
protects organs
goblet cells
secretes mucus and enzymes found in the lining of digestive tract
ciliated epithelium structure
modified columnar with cilia covered cell
ciliated epithelium function
movement if particles
dust and debries up the trachea
eggs move from ovary into oviduct
sperm from testes through seminal tubules
psudeostratified columnar structure
single layer, nuclei are uneven which gives it a layered appearance and can have goblet cells and cilia
psudeostratified columnar location
lining air passages and tubes of the reproductive system, most of the upper respiratory tract, parts of the male urethra, ducts of large glands
transitional epithelium function
stretchable, blocks diffusion (no leaking)
transitional epithelium location
lining of the urinary bladder, ureters and parts of the urethrea
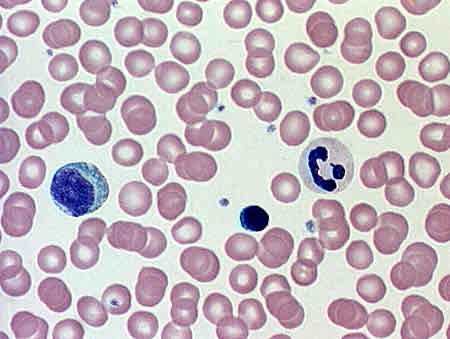
blood (connective tissue)
consists of various types of cell with fluid ground substance
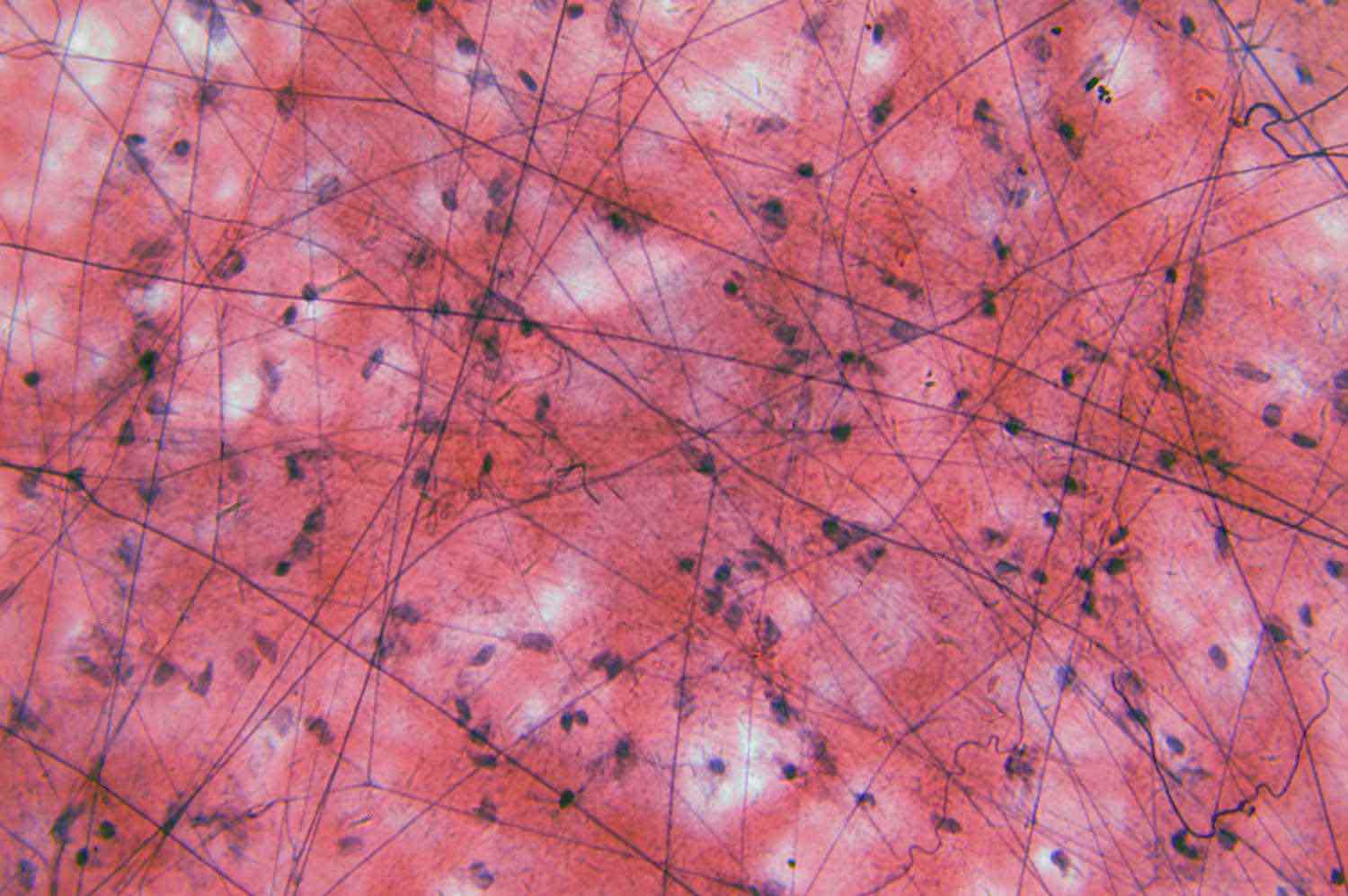
connective (connective tissue)
cells in a fibrous matrix with a jellylike material
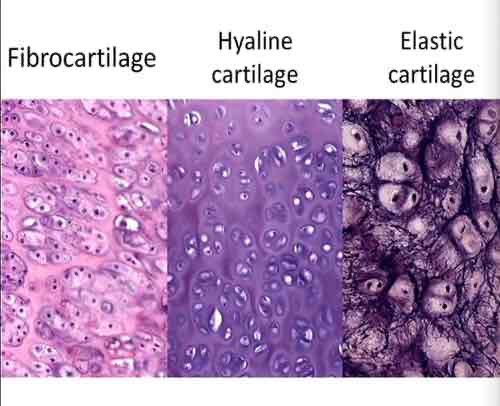
cartilage (connective tissue)
cells in a fibrous matrix with semisolid ground

bone (connective tissue)
cells in a fibrous matrix with a solid, mineralized ground substances
mast cells (type of cell in connective tissue)
prevents clots
macrophages (type of cell in connective tissue)
consumers
fibroblasts (type of cell in connective tissue)
produce fibers
collagenous (type of cell in connective tissue)
bones, ligaments, tendons
elastic (type of cell in connective tissue)
respiratory
loose connective tissue
modified columnar in a semifluid matrix
loose connective tissue location
epidermis and subcutaneous, surround nerve cells, blood vessels
loose connective tissue function
wraps and cushions organs, its phagocytes engulfs bacteria
adipose tissue (connective tissue) structure
cells have a central vacuole with a fat droplet
adipose tissue (connective tissue) function
insulates, protects, reserve supple of energy
adipose tissue (connective tissue) location
under skin, behind eyeball, around kidneys, within abdomen
blood (liquid connective tissue) structure
plasma(fluid) / solid(corpuscles)
red corpuscles = erythrocytes (red blood cells)
white corpuscles = leukocytes (white blood cells)
platelets = thrombocytes
blood (liquid connective tissue) function
transports materials
fibrous connective tissue structure
closely packed while collagen ; fibers are flexible but not elastic
fibrous connective tissue function
ligaments holds bone to bone in place tendons attaches muscle to bone
hyaline cartilage (connective tissue) function
allows flexibility between bones
hyaline cartilage (connective tissue) location
ends of bones, nose, trachea, larynx, costal cartilage
matrix
cells in groups surrounded by a capsule of transparent membrane
bone (osseous tissue) (connective tissue) structure
osteoblast - bony material
osteoclast - reabsorbs bony material
bone (osseous tissue) (connective tissue) function
supportive framework