THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD & RESEARCH STRATEGIES
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
THEORY
an explanation using an integrated set of principles that organizes observations and predicts behaviors or events (researched and tested)
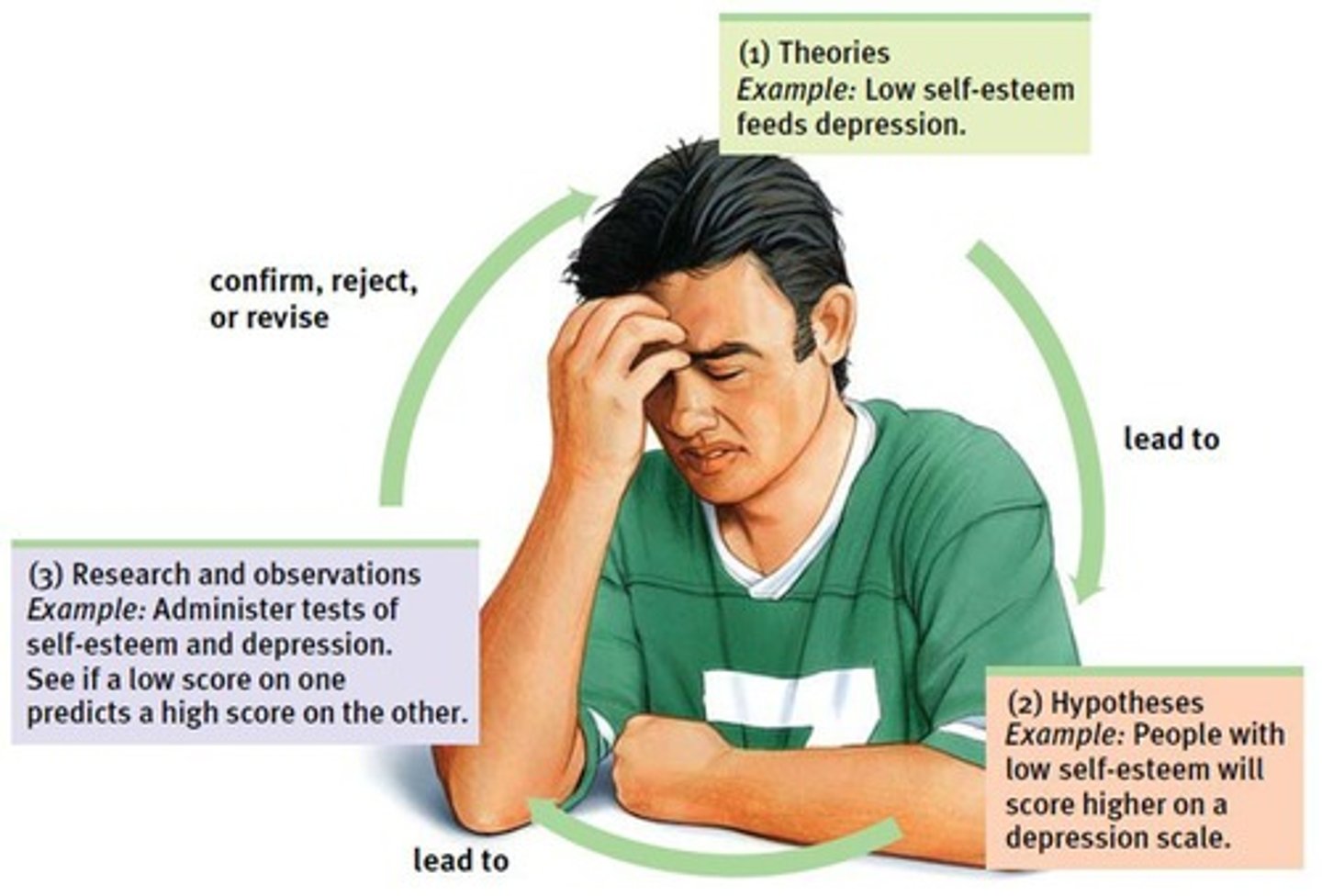
HYPOTHESIS
a testable prediction, often implied by a theory (educated guess)
OPERATIONAL DEFINITION
a statement of the procedures (operations) used to define research variables (needs to be measurable, manageable and clear)
REPLICATION
Main goal of research. Allows for testing of hypotheses with other populations so results can be generalized.
Descriptive Research
Describes characteristics of a population.
Correlational Research
Indicates there might be a relationship between 2 variables.
Experimentation
Shows cause and effect relationship.
Case Study
One person or a small group of people are studied in depth in the hope of revealing universal principles.
Survey
A technique for ascertaining the self-reported attitudes or behaviors of a particular group, usually by questioning a representative, random sample of the group.
Naturalistic Observation
Observing and recording behavior in naturally occurring situations without trying to manipulate and control the situation.
Cross Sectional Research
A descriptive research method that analyzes data collected from a population, or a representative subset, at a specific point in time.
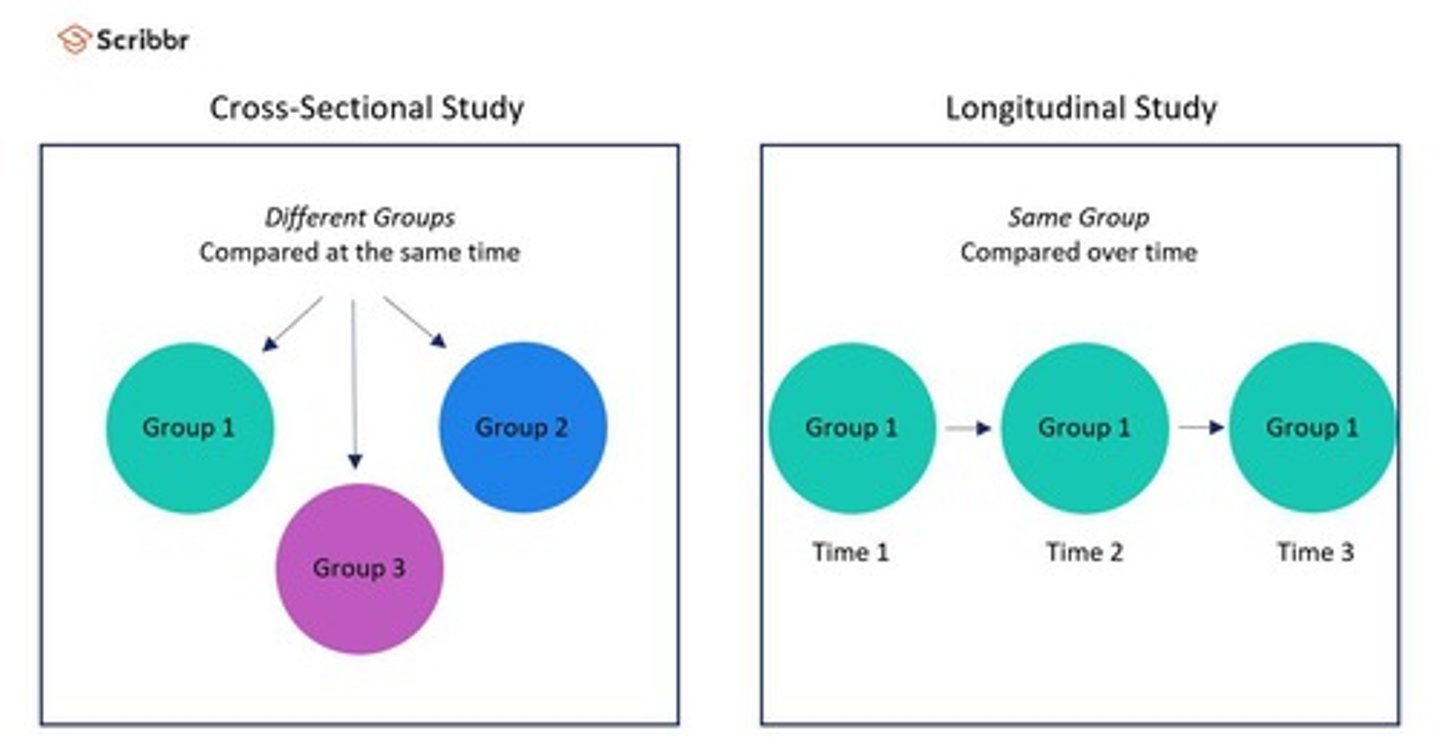
Longitudinal Research
A descriptive research method in which data is gathered for the same subjects repeatedly over a period of time.
Positive Correlation
Two factors increase or decrease together.
Negative Correlation
One factor increases while another decreases and vice versa.
Correlation Coefficient
Reveals how closely 2 things vary together and thus how well either one predicts the other (direction and strength of relationship) (-1 to +1).
Illusory Correlation
The perception of a relationship where none exists.
Correlation Does Not Mean Causation
Indicates only a possibility of a cause-effect relationship.
False Consensus Effect
The tendency to overestimate others' agreement with us.
Sigmund Freud
Studied his patients in the context of psychoanalysis.
John Watson and Rosalie Rayner
Conducted the Little Albert experiment, teaching fear of white lab rats.
Jean Piaget
Studied cognitive development in his children.
Paul Broca
Studied a man with damage to a particular area of the brain in the context of neuroscience.
Ex: Violence on TV and Aggressive Behavior
An example of a positive correlation.
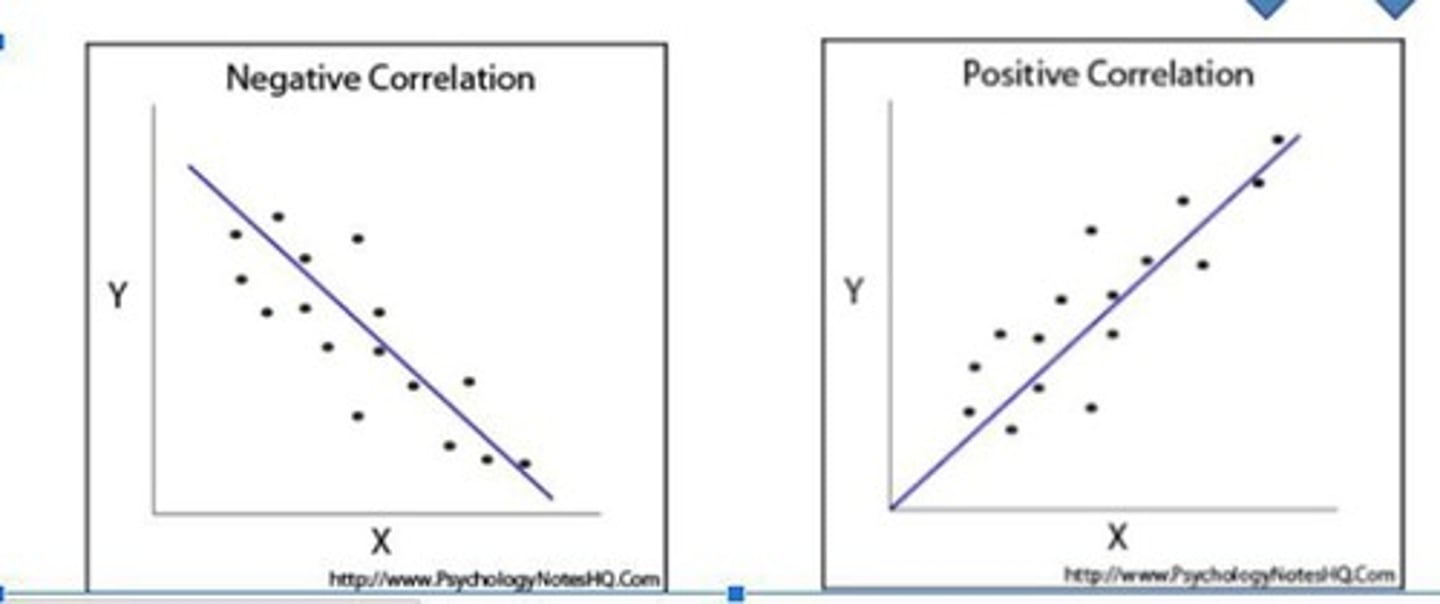
Ex: Lack of Sleep and Bad Grades
Another example of a positive correlation.
Ex: Low Self-Esteem and High Levels of Depression
An example of a negative correlation.
Ex: r = -0.93
An example of a correlation coefficient indicating a strong negative correlation.
Ex: r = 0.23
An example of a correlation coefficient indicating a weak positive correlation.
Ex: r = -0.14
An example of a correlation coefficient indicating a weak negative correlation.
Ex: r = -0.45
An example of a correlation coefficient indicating a moderate negative correlation.
Intervening Variables
Factors that may explain the correlation between low self-esteem and depression.
Mnemonic Device
A technique for identifying correlation on a graph.
Hypothesis
A proposed explanation for a phenomenon, such as 'If children watch violent cartoons then they will become violent themselves.'
Independent Variable
The experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied.

Dependent Variable
The outcome factor; the variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable.
Confounding Variable
A factor other than the independent variable that might produce an effect in an experiment.
Experimental Group
The group in an experiment that is exposed to the treatment, or one version of the independent variable.
Control Group
The group in an experiment that is NOT exposed to the treatment; serves as a comparison for evaluating the effect of treatment.
Random Assignment
Assigning participants to experimental and control groups by chance, ensuring each participant has the same opportunity to be assigned to any group.
Sampling
The process of selecting a subset of individuals from a population to participate in a study.
Between-Subjects Design
An experiment that has two or more groups of subjects each tested by a different testing factor simultaneously.
Within-Subjects Design
An experimental design where the same subjects are used in both conditions.
Single-Blind Experiment
An experiment in which the participants are unaware of which participants receive the treatment.
Double-Blind Experiment
An experimental procedure in which both the research participants and the research staff are ignorant about whether the participants have received the treatment or the placebo.
Placebo Effect
Experimental results caused by expectation alone; any effect on behavior caused by the administration of an inert substance or condition, which the recipient assumes is an active agent.
