Biochem Sept. 17th
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
(Topic 4)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Whats a Ligand?
A molecule that binds to a protein. Can be a small molecule, a peptide, or another protein
Explain the Dissociation constant
PL ⇌ L + P in equilibrium
Kd = [P][L]/[PL]
The higher the affinity for the ligand, the lower the dissociation constant (Kd).
What are the common units?
Millimolar - m 10^-3 M
Micromolar - µ 10^-6 M
Nanomolar - n 10^-9 M
(many protein-protein interactions lie in the micromolar to nanomolar range)
What is myoglobin?
oxygen binding protein in muscle cells
Consists of 8 alpha helices
Contains a heme prosthetic group, which is essential for binding oxygen
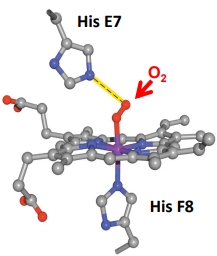
How does O2 bind to myoglobin?
the central Fe II is coordinated by 4 N atoms of the ring and 1 N atom from one side chain of Histidine
O2 can bind reversibly to form the 6th coordination bond
His E7 forms a H bond to the bound O2
What is the Fractional Saturation of Binding formula?
Y = Concentration of protein with ligand bound / total protein concentration
or [PL] / [P] + [L]
Can also express as Y = [L] / Kd + [L]
What is the formula for when asked “How much of O2 is bound to myoglobin?”
YO2 = pO2 / K + pO2
O2 is a gas, therefore its concentration can be expresses as its partial pressure, pO2
What is the p50?
The p50 is the partial pressure of oxygen at which myoglobin is 50% saturated with oxygen. It is an important measure of oxygen affinity in myoglobin
K = p50
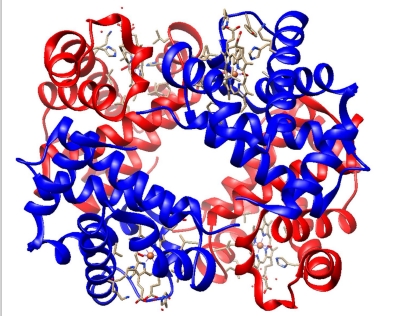
What is Hemoglobin?
Hemoglobin is a oxygen-transport protein in red blood cells
2 alpha subunits (blue)
2 beta subunits (red
With heme groups shown as white
Are Hb and Mb similar? How?
yes, Hb and Mb are similar in their secondary and tertiary structures
But, Hb and Mb are only ~18% identical in primary sequence
Describe the O2 binding differences between Hb and Mb
Hemoglobin:
O2 binding affinity of Hemoglobin is lower than that of Myoglobin because it needs to release O2 to tissues
At low pO2, Hemoglobin exhibits low oxygen affinity but as the pO2 increases, the affinity increases; binding of first O2 increases the affinity of the remaining binding sites
Sigmoidal = affinity lower at tissues (to release it) and higher at lungs
Myoglobin:
has a higher O2 binding affinity, which makes it ideal for holding oxygen until muscle cells need it
Hyperbolic = affinity always high
What happens when O2 binds to Hb?
Hb undergoes a conformational change when O2 binds (T-state —> R-state)
It changes for T to R to increase the affinity for the next O2
T-state = tense = low affinity (Deoxy)
R-state = relaxed = higher affinity (Oxy)
What is the Bohr Effect?
Describes the phenomenon where if the pH decreases, (acidity increases) the oxygen-binding affinity of hemoglobin decreases, promoting oxygen release in tissues
This occurs due to certain ionizable groups in Hb become acidic and release protons (H+) upon binding O2
This means increasing pH favours O2 binding
How does BPG effect Hb and O2 affinity?
BPG (2,3-bisphosphoglycerate) reduces the O2 affinity of hemoglobin by stabilizing the T-state, facilitating oxygen release in tissues.
BPG is an allosteric effector that decreases Hb O2 affinity
Increased BPG levels promote the release of O2, particularly under conditions of high altitude or exercise.
What is Collagen?
A structural protein found in connective tissues, providing strength and support to skin, bones, tendons, and ligaments.
Collagen is essential for maintaining the integrity of various tissues in the body.
Every 3rd residue is a glycine
Contains many repeating triplets Gly-Pro-Hyp (hydroxyproline)
Quite hydrophobic
Why is collagen so strong?
Due to its cross-linking between chemically modified lysine residues in collagen
Its triple helix structure
Many proline and glycine residues contributing to stability and strength
because proline is has a rigid ring structure that can force chains into a fixed angle
and glycine is the smallest so it packs tightly
What are some collagen related diseases?
Scurvy
lack of vitamin c in diet (needed for enzyme that hydroxylates proline)
Osteogenesis imperfecta
due to the replacement of glycine with another amino acids