Myers Psychology for AP Unit 11 - Intelligence (copy)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/44
Earn XP
Last updated 5:04 AM on 3/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
1
New cards
intelligence
mental quality consisting of the ability to learn from experience, solve problems, and use knowledge to adapt to new situations
2
New cards
intelligence test
a method for assessing an individual’s mental aptitudes and comparing them with those of others using numerical scores
3
New cards
general intelligence
a general intelligence factor that underlies specific mental abilities and is therefore measured by every task on an intelligence test
4
New cards
factor analysis
a statistical procedure that identifies clusters of related items (called factors) on a test; used to identify different dimensions of performance that underlie a person’s total score
5
New cards
savant syndrome
a condition in which a person otherwise limited in mental ability has an exceptional specific skill, such as computation or drawing
6
New cards
grit
in psychology, grit is passion and perseverance in the pursuit of long term goals
7
New cards
emotional intelligence
the ability to perceive, understand, manage, and use emotions
8
New cards
mental age
a measure of intelligence test performance devised by Binet, the chronological age that most typically corresponds to a given level of performance
9
New cards
Stanford-Binet
the widely used American revision (by Terman at Stanford University) of Binet’s original intelligence test
10
New cards
intelligence quotient (iq)
defined originally as the ratio of mental age (ma) to chronological age (ca), multiplied by 100 (ma/ca x 100).
On contemporary intelligence tests, the average performance for a given age is assigned to a score of 100, with scores assigned to a relative performance above or below average
On contemporary intelligence tests, the average performance for a given age is assigned to a score of 100, with scores assigned to a relative performance above or below average
11
New cards
achievement test
a test designed to assess what a person has learned
12
New cards
aptitude test
a test designed to predict a person’s future performance; the capacity to learn
13
New cards
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale
the most widely used intelligence test; contains verbal and performance (nonverbal) subtests
14
New cards
standardization
defining uniform testing procedures and meaningful scores by comparison with the performance of the pretested group
15
New cards
normal curve
the symmetrical, bell-shaped curve that describes the distribution of many physical and psychological attributes. Most scores fall near the average, and fewer and fewer scores lie near the extreme
16
New cards
reliability
the extent to which a test yields consistent results, as assessed by the consistency of scores on two halves of the test, on alternate forms of the test, or on retesting
17
New cards
validity
the extent to which a test measures or predicts what it is supposed to
18
New cards
content validity
the extent to which a test samples the behavior that is of interest
19
New cards
predictive validity
the success with which a test predicts the behavior it is designed to predict; it is assessed by computing the correlation between test scores and the criterion behavior (also called criterion-related validity)
20
New cards
cohort
a group people form over a period of time
21
New cards
crystalized intelligence
our accumulated knowledge and verbal skills; tends to increase with age
22
New cards
fluid intelligence
our ability to reason speedily and abstractly; tends to decrease during late adulthood
23
New cards
intellectual disability
a condition of limited mental activity, indicated by an intelligence score of 70 or below, and difficulty in adapting to the demands of life (formerly known as mental retardation)
24
New cards
down syndrome
a condition of mild to severe intellectual disability and associated physical disorders, caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21
25
New cards
heritability
the proportion of variation among individuals that we can attribute to genes. May vary depending on the range of populations and environments studies
26
New cards
stereotype threat
a self-confirming concern that one will be evaluated based on a negative stereotype
27
New cards
Charles Spearman
We have one general intelligence “g”
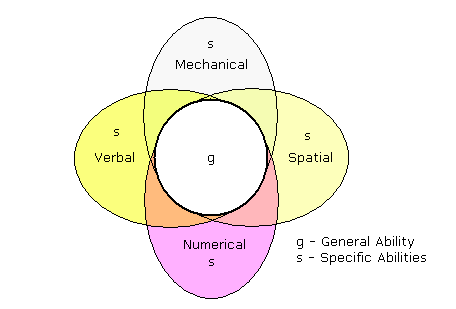
28
New cards
l.l thurstone
Identified seven clusters of primary mental abilities and those who did well in one category did well in the others supporting Spearmans theory
\
verbal comprehension, word fluency, number facility, spatial visualization, associative memory, perceptual speed and reasoning
\
verbal comprehension, word fluency, number facility, spatial visualization, associative memory, perceptual speed and reasoning
29
New cards
Howard Gardner
Proposes 8 relatively independent intelligence’s
\
Visual Spatial-ability to perceive, analyze
\
Linguistic-ability to learn languages
\
Interpersonal-capacity to understand the intentions
\
Intrapersonal-capacity to understand oneself
\
Logical-ability to solve problems
\
Musical-ability to produce and appreciate rhythm
\
Bodily kinesthetic-ability to solve problems or create products using the body or parts
\
Natualistic-ability to identify, classify and manipulate elements of the environment
\
Visual Spatial-ability to perceive, analyze
\
Linguistic-ability to learn languages
\
Interpersonal-capacity to understand the intentions
\
Intrapersonal-capacity to understand oneself
\
Logical-ability to solve problems
\
Musical-ability to produce and appreciate rhythm
\
Bodily kinesthetic-ability to solve problems or create products using the body or parts
\
Natualistic-ability to identify, classify and manipulate elements of the environment
30
New cards
Robert Sternberg
Proclaims the triarchic theoryof intelligence’s
Analytical-solve well defined problems
Creative-come up with new ideas
Practical-everyday tasks that have multiple solutions
Analytical-solve well defined problems
Creative-come up with new ideas
Practical-everyday tasks that have multiple solutions
31
New cards
William Stern
Creator of IQ and IQ test. Was also a racist and believed whites were more intelligent than others
32
New cards
David Wechsler
Creator of the Wechsler intelligence scale
33
New cards
Heritability of intelligence
Twins share intelligence levels
5% attributing factors
5% attributing factors
34
New cards
Environmental on intelligence
\-Extreme neglect reduces intelligence
\-After children are adopted their intelligence levels increase
\-After children are adopted their intelligence levels increase
35
New cards
Woman are better at
Better at verbal fluency, detecting emotion and locating objects
36
New cards
Men are better at
Spatial ability like math
37
New cards
Schools and culture
what influences intelligence more race or schools and culture
38
New cards
Classical Bias
Test failing to predict future behavior accurately across all groups
39
New cards
Innate Bias
Produced to to cultural differences from the test writer and test taker
40
New cards
Sir Frances Galtan
proponent of social Darwinism, eugenics, and scientific racism
\-believed that intelligence and most other physical and mental characteristics of humans were inherited and **biologically based**
\-eugenics
\-invented the **word-association test**
\-believed that intelligence and most other physical and mental characteristics of humans were inherited and **biologically based**
\-eugenics
\-invented the **word-association test**
41
New cards
longitudinal study
research design that involves repeated observations of the same variables over short or long periods of time.
42
New cards
James Flynn
Discovered the **Flynn Effect**
\-Increase in both fluid and crystallized intelligence test scores over time
\-Increase in both fluid and crystallized intelligence test scores over time
43
New cards
WAIS
The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale
\-The most advanced adult measure of cognitive ability
\-Designed to measure adults
\-The most advanced adult measure of cognitive ability
\-Designed to measure adults
44
New cards
WISC
**Measures intellectual ability of children from 6 to 16 years.** It was developed to provide an overall measure of general cognitive ability, Verbal Comprehension, Perceptual Reasoning, Working Memory and Processing Speed
45
New cards
Cross Sectional Study
the investigator measures the outcome and the exposures in the study participants at the same time.