Genetics E1- Chromosomal Disorders
1/40
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What is polyploidy?
Cells have more than 2 complete sets of chromosomes
How many chromosomes are there with triploidy (3n)?
69 chromosomes
How many chromosomes are there with tetraploidy (4n)?
92 chromosomes
What is the loss of a singe chromosome?
Monosomy
What is the gain of 1 homologous chromosome (results in 3 copies of that particular chromosome)?
Trisomy
What is the gain of 2 homologous chromosomes (results in 4 copies of that particular chromosome)?
Tetrasomy
What is aneuploidy?
Loss or gain of 1 or more chromosomes
What accounts for the spontaneous loss of a very high proportion of all human conceptions?
Chromosome anomalies
What are causes of Down syndrome?
Nondisjunction & Robertsonian translocation
What is nondisjunction?
Failure of separation of 1 of the pairs of homologous chromosomes during anaphase of meiosis I or II (less common) → gamete receives 2 homologous chromosomes (disomy; results in trisomy if fertilized)
What trisomy is Down syndrome?
Trisomy 21
What is the MC structural chromosome abnormality in humans?
Robertsonian translocation
What are the acrocentric chromosomes?
13, 14, 15, 21, 22
What is Robertsonian translocation?
2 long arms of acrocentric chromosomes, usually 14 & 21, are joined & short arms are lost → results in 45 chromosomes
Why do carriers of Robertsonian translocation often have no phenotypical features?
Short arms contain minimal genetic material, so phenotype is usually unaffected; however, there is a higher risk of having a child with down syndrome
Which has a higher recurrence risk for Down syndrome: carrier of Robertsonian translocation or nondisjunction?
Robertsonian translocation carrier
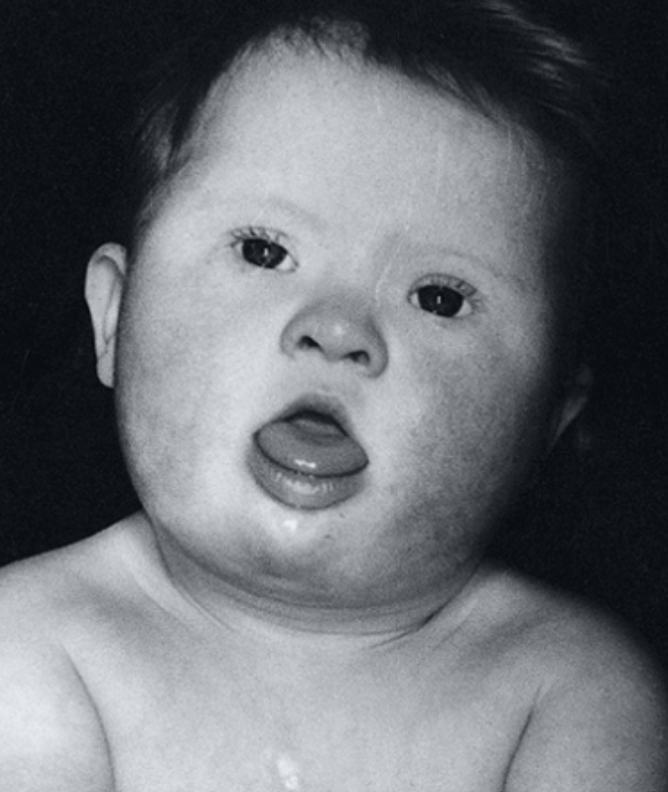
The following clinical features are seen in what condition?
brachycephaly, epicanthic folds, protruding tongue, small ears, upward sloping palpebral fissures
single palmar crease, small middle phalanx of 5th finger (clinodactyly), wide gap bt 1st & 2nd toes
ASD/VSDs, common AV canal, PDA
anal atresia, duodenal atresia, Hirschsprung disease, short stature, strabismus
Trisomy 21
What trisomy is Edwards syndrome?
Trisomy 18
What trisomy is patau syndrome?
Trisomy 13
With what trisomies do most infants die in first days or weeks life, or result in severe physical & mental disabilities?
Trisomy 13 & 18
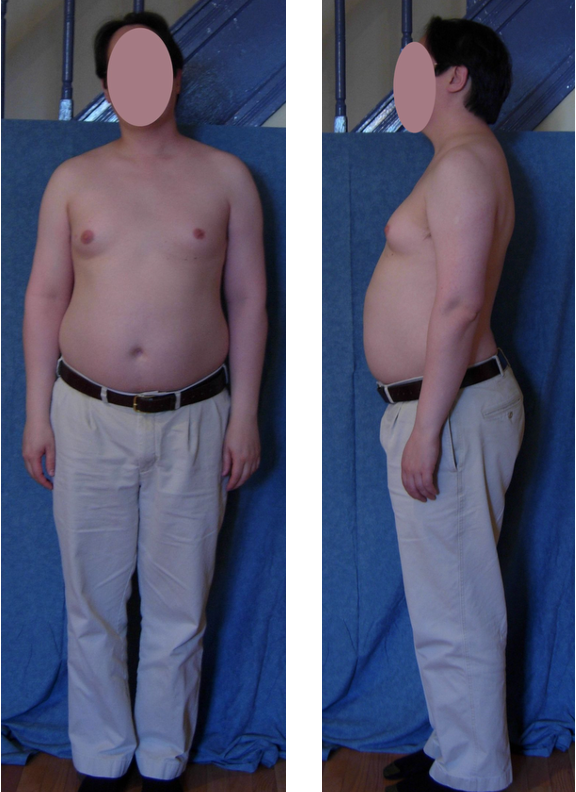
The following clinical features are associated with what condition?
affects males only
“pear shaped mama’s boy”
long limbs, tall height
gynecomastia, hypogonadism, azoospermia
Klinefelter syndrome (47,XXY)
What is the treatment for Klinefelter syndrome (47,XXY)?
Exogenous testosterone
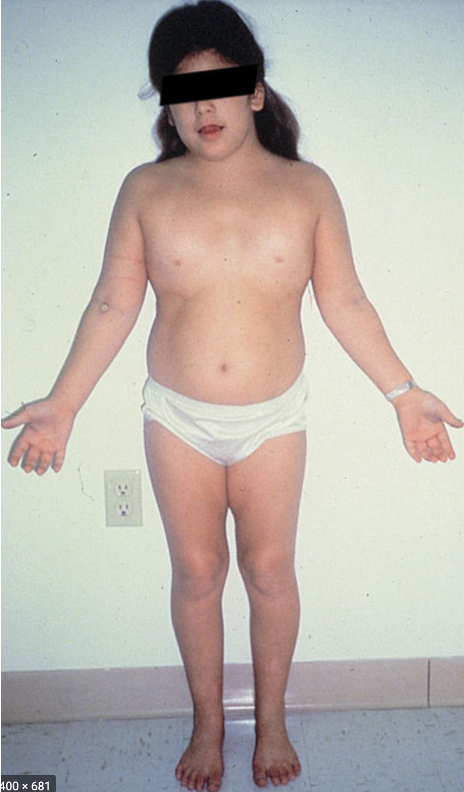
The following clinical features are associated with what condition?
females
short stature, webbed neck, wide spaced nipples
premature ovarian failure
CoA
normal intelligence
high rate of spontaneous miscarriage, but child is high functioning if they make it to term
Turner syndrome (45,X0)
What is the treatment for Turner Syndrome (45,X0)?
Exogenous estrogen-progestin & cardio referral for serial echos
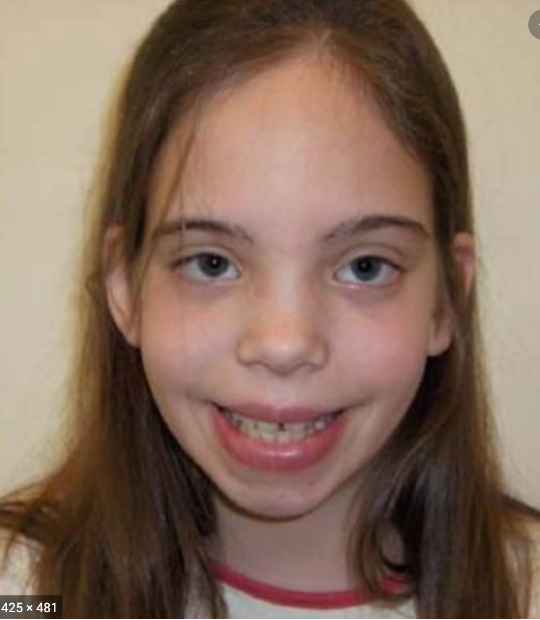

The following clinical features are associated with what condition?
Females
Tall height & relatively small head circumference
Intelligence 15-20 pts lower than siblings
Most diagnosed incidentally / never
XXX / Triple X syndrome
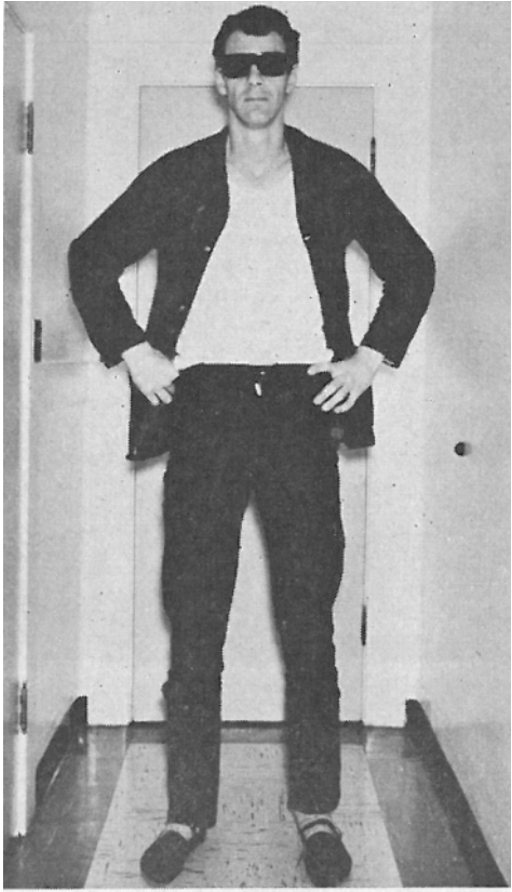
The following clinical features are associated with what condition?
Males
Tall stature
IQ mildly impaired; higher rates of ADHD & Autism
Do not have increased aggression
XYY syndrome
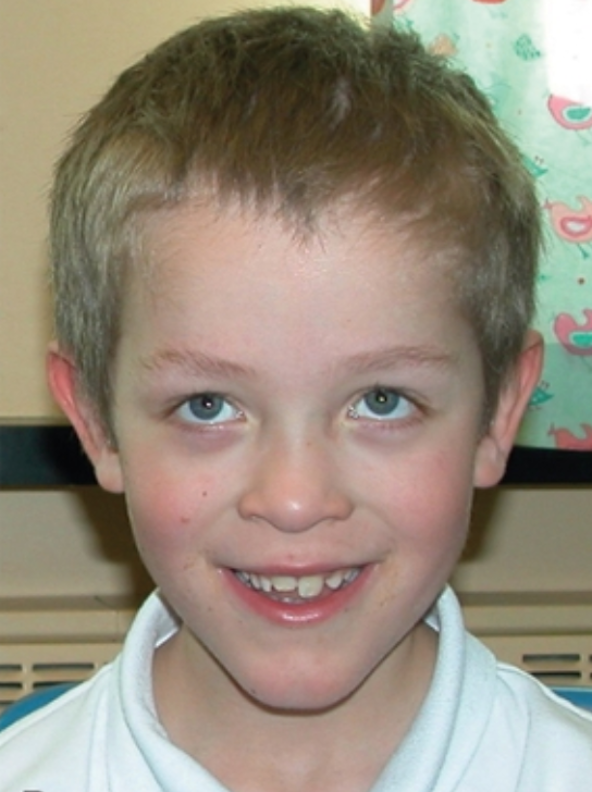

The following clinical features are associated with what condition?
High forehead, large ears, long face, prominent jaw
Macro-orchidism
Connective tissue weakness → hyper mobile joints, MVP
Intellectual disability
Fragile-X syndrome
What is the MC inherited cause of intellectual disability?
Fragile-X syndrome
What do individuals with either deletion of 4p or 5p present with?
Severe intellectual disability
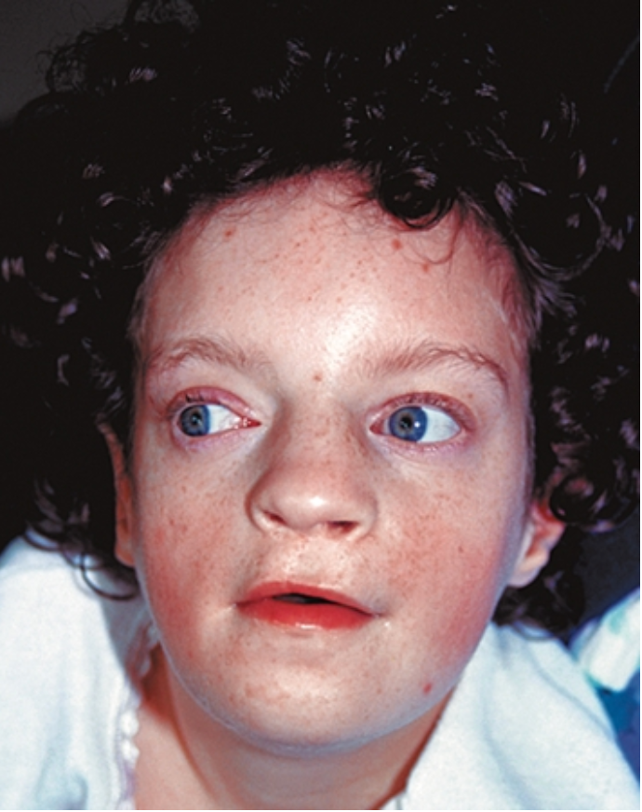
What condition is deletion of 4p?
Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome
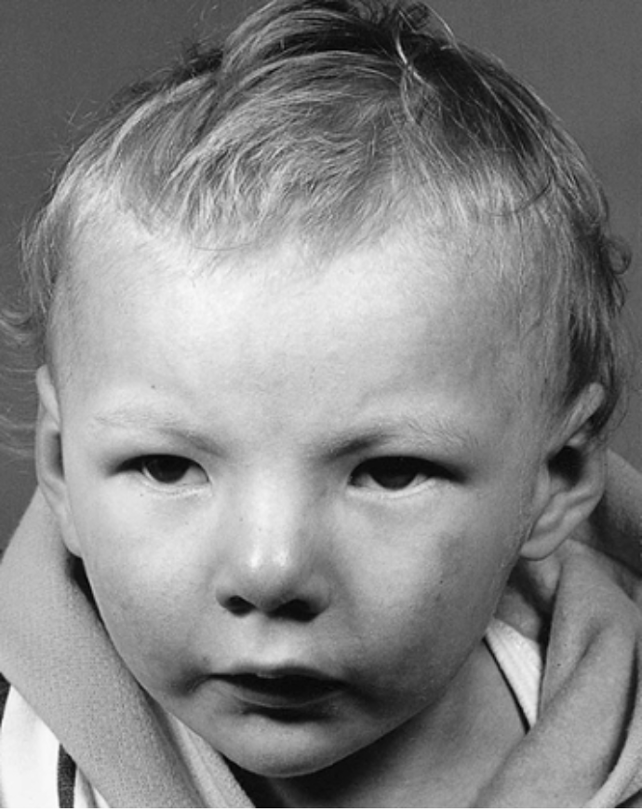
What condition is deletion of 5p?
Cri-du-chat syndrome
The following features are seen in what condition?
Wilms tumor (rare renal embryonal neoplasm)
Aniridia (absence of iris)
GU abnormalities
Retardation of growth & development
*deletion of 11p13
WAGR syndrome
What condition is a maternally derived 15q11.2-q13 deletion?
Angelman syndrome
What condition is a paternally derived 15q11.2-q13 deletion?
Prader-Willi syndrome
What features are seen in angelman syndrome?
Inappropriate laughter, convulsions, ataxia, severe learning difficulties
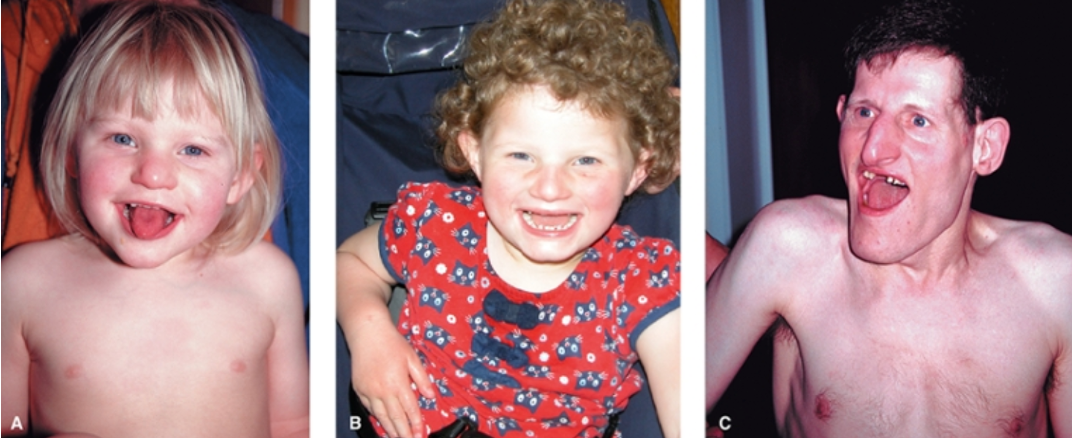

What features are seen in Prader-Willi syndrome?
Poor feeding in infancy, later develops hyperphagia / obesity, mild-moderate intellectual disability
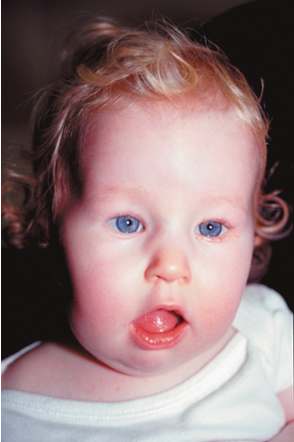
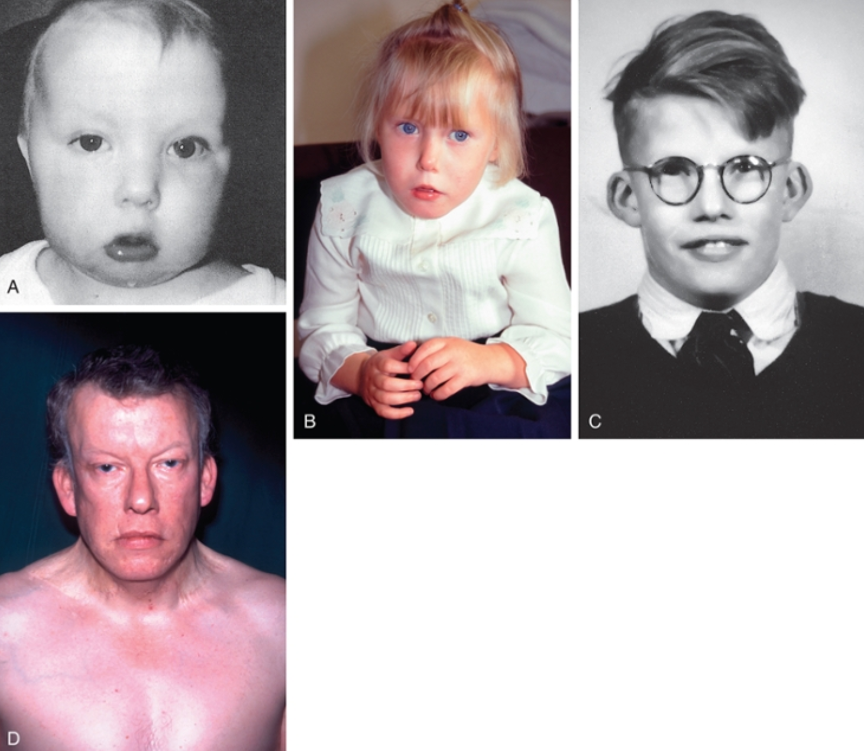
What condition is a microdeletion of 22q11.2?
DiGeorge Syndrome
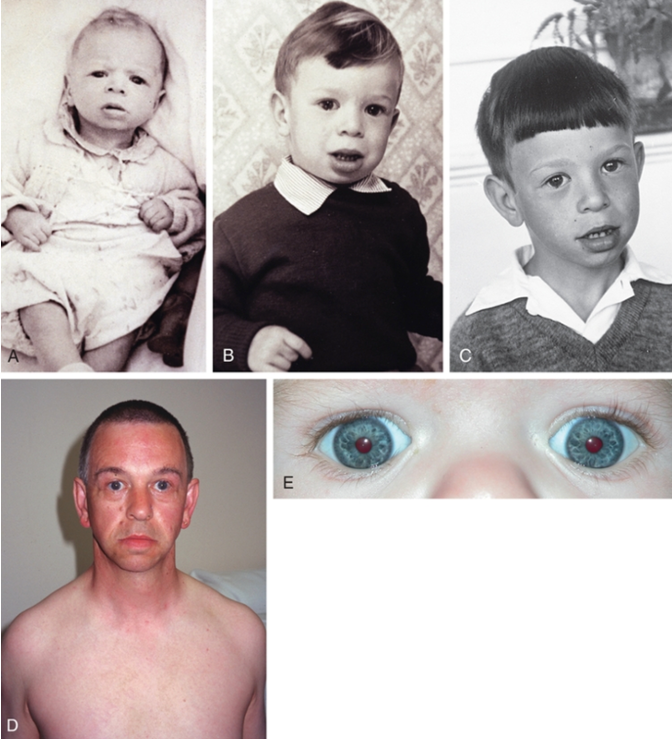
What condition?
microdeletion at 7q11.23
outgoing in childhood (“cocktail party manner”) but become withdrawn and sensitive as adults
Williams syndrome
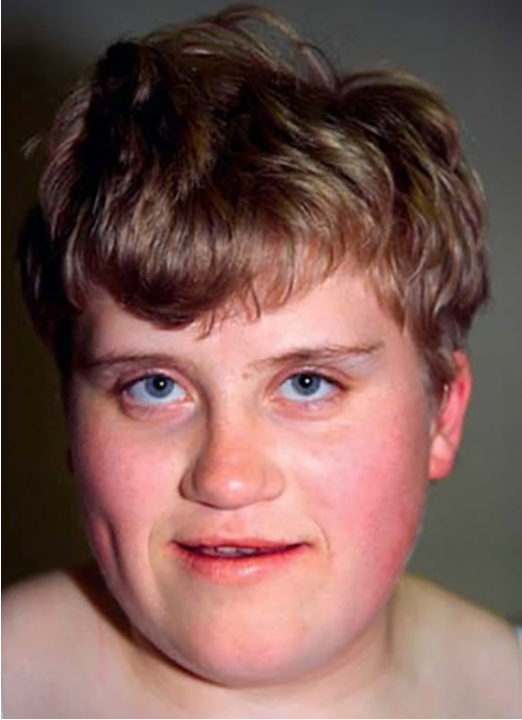

What condition?
microdeletion at 17p11.2
behavioral characteristics: self harming, persistently disturbed sleep pattern, characteristic “self-hugging”
Smith-Magenis syndrome
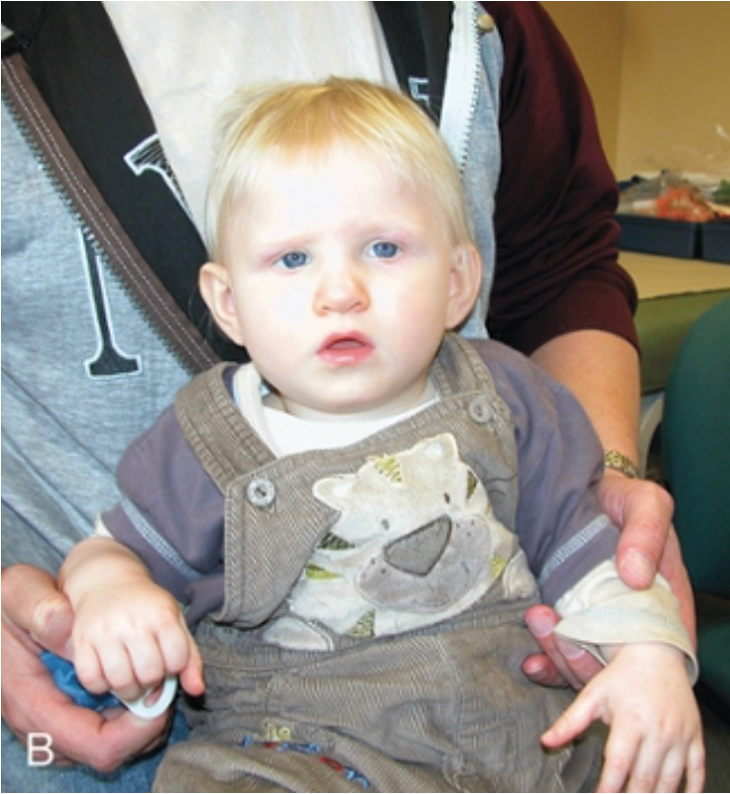

Why is genetic counseling highly problematic for deletion 1q21.1 syndrome?
Variable penetrance & lack of highly distinctive features
What are indications for chromosome microarray analysis?
Multiple congenital abnormalities, dysmorphic features, unexplained intellectual disability & neurodevelopmental disorders, disorder of sexual development/ ambiguity, infertility, recurrent miscarriages, & unexplained stillbirth