Exam Tips/Tricks Pt. 2 - Focus Topics & Exam Strategies
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Rapid Questions
• Uncompensated Forefoot valgus: Rearfoot
• Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS): Main symptom
• White color finger while applying cryotherapy:
•Ultrasound Frequency: Deep muscles
Uncompensated Forefoot valgus: Rearfoot
big toe is on the ground, little toes in the air
Neutral rearfoot - does not compensate and stays where it is at
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS): Main symptom
Impaired sensation
White color finger while applying cryotherapy:
Raynaud’s Phenomenon
Ultrasound Frequency: Deep muscles
1 MHz
when deeper, you touch it once then come back in one second
when superficial, 3 MHz you can do 3 in one second
Trust your gut!!!

Practice Question 5
A patient with leukemia is being treated in the acute care unit. The most recent complete blood count reveals a platelet count of 15,000 cells/cu.mm3, a hemoglobin level of 9 g/dL, and a white blood cell count of 6,000 cells/cu.mm3. The patient is afebrile (not feverish) and medically stable. Which of the following activities is MOST APPROPRIATE for the physical therapist to include in today’s treatment session?
A. Ambulation and stationary cycling with light resistance
B. Range of motion exercises and walking without resistance
C. Therapeutic exercises including resistance training
D. Withhold therapy due to low platelet count
B. Range of motion exercises and walking without resistance
RATIONALE: Based on the patient’s platelet of 10,000- 20,000. ROM, walking and ADL activities without resistance are appropriate.
<10,000 and/or temperature >100.5° F: No therapeutic exercise/hold therapy
>20,000: Therapeutic exercise/bike with or without resistance
WBC (6,000) —> exercise permitted, no restrictions
Hemoglobin (9 g/dL) —> light aerobic exercise and ADLs allowed
Exercises Guidelines based on Lab Values:
Normal range of platelets is 150,000-450,000 cells/cu.mm3
What are the 3 abnormal ranges?
When can they exercise with/without resistance, ROM/ADLs, or hold therapy?
>20,000
therapeutic exercise/bike with or without resistance
20,000-10,000
ROM, ADLs, walking or bike without resistance
<10,000 and/or temp 100.5ºF
therapy on hold
Exercises Guidelines based on Lab Values:
Normal WBC is 4,800-10,800 cells/cu.mm3
What are the 2 abnormal values?
When would you do light exercise or no exercise?
>5,000
light exercise with progression to resistive exercise
<5,000 with fever
no exercise, protective mask required
Exercises Guidelines based on Lab Values:
What are normal hemoglobin values for males and females?
What are 3 abnormal values?
Could you do resistance and aerobic exercise, or when should you do ADLs or light exercise?
normal women
12-16 g/dL
normal men
13-18 g/dL
> 10
resistance and aerobic exercise, ambulation and self-care as tolerated
8-10
ADLs, assistance as needed for safety, light aerobic exercise, light weights (1-2 lbs.)
<8
ADLs
Exercises Guidelines based on Lab Values:
Normal hematocrit values for women and men - 3,6,4,9
What are 3 abnormal values?
Exercise recommendations are similar to hemoglobin levels.
normal women
36-46%
normal men
37-49%
>35%
resistance and aerobic exercise, ambulation and self-care as tolerated
25-35%
ADLs, assistance as needed for safety, light aerobic exercise, light weights (1-2 lbs.)
<25%
ADLs, assistance as needed for safety
Recall some scales and outcome measures. Found in BONUS MATERIAL reading folder 10:
ASIA scale
Modified Ashworth Scale
Practice Question 6
A 67-year-old male patient reports of difficulty initiating urination, dribbling after urination, a weak urinary stream, and increased frequency of urination, particularly at night. He reports no pain or hematuria. Considering the patient’s symptoms, which of the following conditions is MOST LIKELY responsible for his urinary difficulties?
A. Urinary tract infection
B. Benign prostatic hyperplasia
C. Kidney stones
D. Bladder cancer
B. Benign prostatic hyperplasia
RATIONALE: BPH is a common condition in older males, characterized by an enlarged prostate gland that compresses the urethra, leading to symptoms such as difficulty initiating urination, weak stream, and increased urinary frequency, especially at night (nocturia). UTIs typically present with burning pain during urination and possibly fever, which this patient does not report. Kidney stones is associated with midback and flank pain. Bladder cancer is usually associated with weight loss, hematuria (blood in the urine), which is absent in this case.
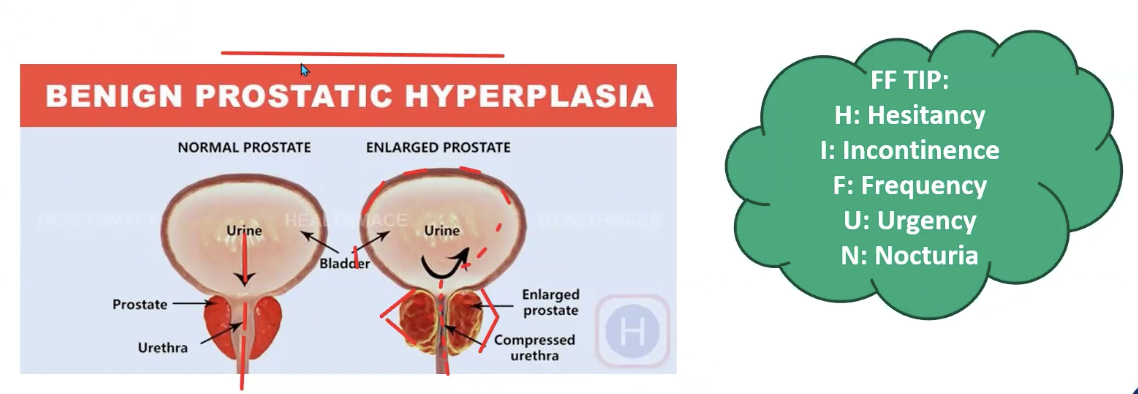
Describe benign prostatic hyperplasia.
How is the urethra affected and how does it affect urination?
Recall HIFUN to remember the symptoms of BPH.
hypertrophy of the prostate glands surrounding the urethra
enlarged prostate gland causes narrowing of the urethra lumen which increases urinary retention and dilation of urinary bladder
Practice Question 7
A patient presents to an outpatient clinic with acute low back pain radiating to bilateral lower extremities. The physical examination reveals significant bilateral weakness in the lower extremities, as well as saddle anesthesia. What is the MOST APPROPRIATE action for the physical therapist to take in managing this patient?
A. Call emergency medical services
B. Initiate flexion-biased exercises
C. Provide TENS to manage the pain and ask the patient to see a physician if pain worsens
D. Recommend bed rest and follow up in a week
A. Call emergency medical services
RATIONALE: Cauda Equina Syndrome (CES): The combination of acute low back pain, bilateral weakness, and saddle anesthesia strongly suggests cauda equina syndrome, which is a medical emergency. The physical therapist must act quickly to ensure the patient receives urgent medical evaluation and treatment to prevent permanent neurological damage.
Keep it safe and functional - be gold, identify red flags.
What are the 10 red flag/911 emergencies?
AAAMCADHPR
recall the symptoms
aortic abdominal aneurysm (AAA)
appendicitis
acute compartment syndrome
myocardial ischemia / cardiac arrest
cauda equina sundrome
anaphylaxis (allergic reaction)
diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)
head trauma associated with unconsciousness
preeclampsia
rhabdomyolosis

Practice Question 8
Which of the following patients will be an absolute CONTRAINDICATION for an aquatic therapy session?
A. A 22-old-year patient athlete with an open wound covered with occlusive dressing
B. A 40-old-year patient with lymphedema post mastectomy with no prior experience in water
C. A 55-old-year patient post stroke with a gastrostomy tube
D. A 50-old-year patient with respiratory disorder and vital capacity <1 liter
D. A 50-old-year patient with respiratory disorder and vital capacity <1 liter
RATIONALE: Special precautions may be required for patients with open wounds with occlusive dressing, fear of water and for patients with G-tube. These patients need to be closely monitored and may be relatively contraindicated at times.
However, Water immersion may adversely affect the breathing of the patient with a respiratory disorder. Lung expansion tends to be inhibited due to hydrostatic pressure against the chest wall. Additionally, increased circulation in the chest cavity may further inhibit lung expansion due to increased circulation to the center of the body. Hence, a patient with vital capacity <1L is absolutely contraindicated for aquatic therapy.
Aquatic therapy Contraindications:
___ failure and unstable ___
__ dysfunction, vital capacity less than __
Severe peripheral __ disease
Danger of __ or hemorrhage
Severe __ disease
Open wounds without ___ ___, colostomy and ___ infections
Uncontrolled ___ during last year
Cardiac failure and unstable angina
Respiratory dysfunction, vital capacity less than 1 liter
Severe peripheral vascular disease
Danger of bleeding or hemorrhage
Severe kidney disease
Open wounds without occlusive dressings, colostomy and skin infections
Uncontrolled seizures during last year
Rapid questions:
osteopenia intervention
lipitor: side effects
posterior canalithiasis treatment
ankylosis spondylitis antigen
osteopenia intervention
weight-bearing exercises
avoid flexion and rotation exercises
lipitor: side effects
is a cholesterol lowering drug
too many —> rhabdomyolysis
muscle breakdown, tea-colored urine
911
posterior canalithiasis treatment
Epley’s/Canalith repositioning maneuver
ankylosis spondylitis antigen
HLA B27
differentiate between similar sounding special tests:
Thompson vs. Thomas
Epley vs. Ely’s
Homan’s vs. Hoffman
Adson vs. Allen’s
tibiofibular vs. talofibular

review your rationales

final tips
