lab practical 1
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
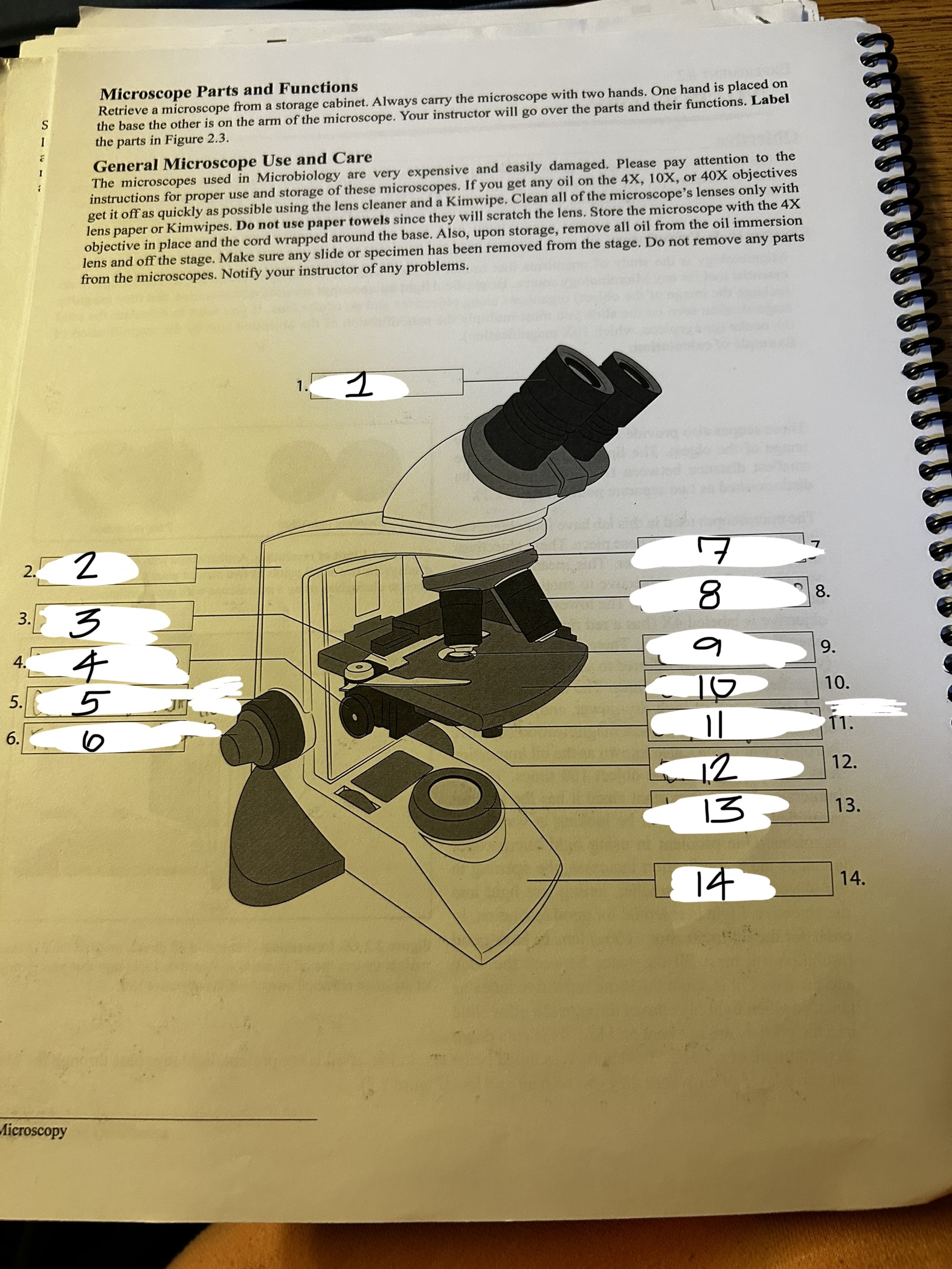
microscope 1
ocular
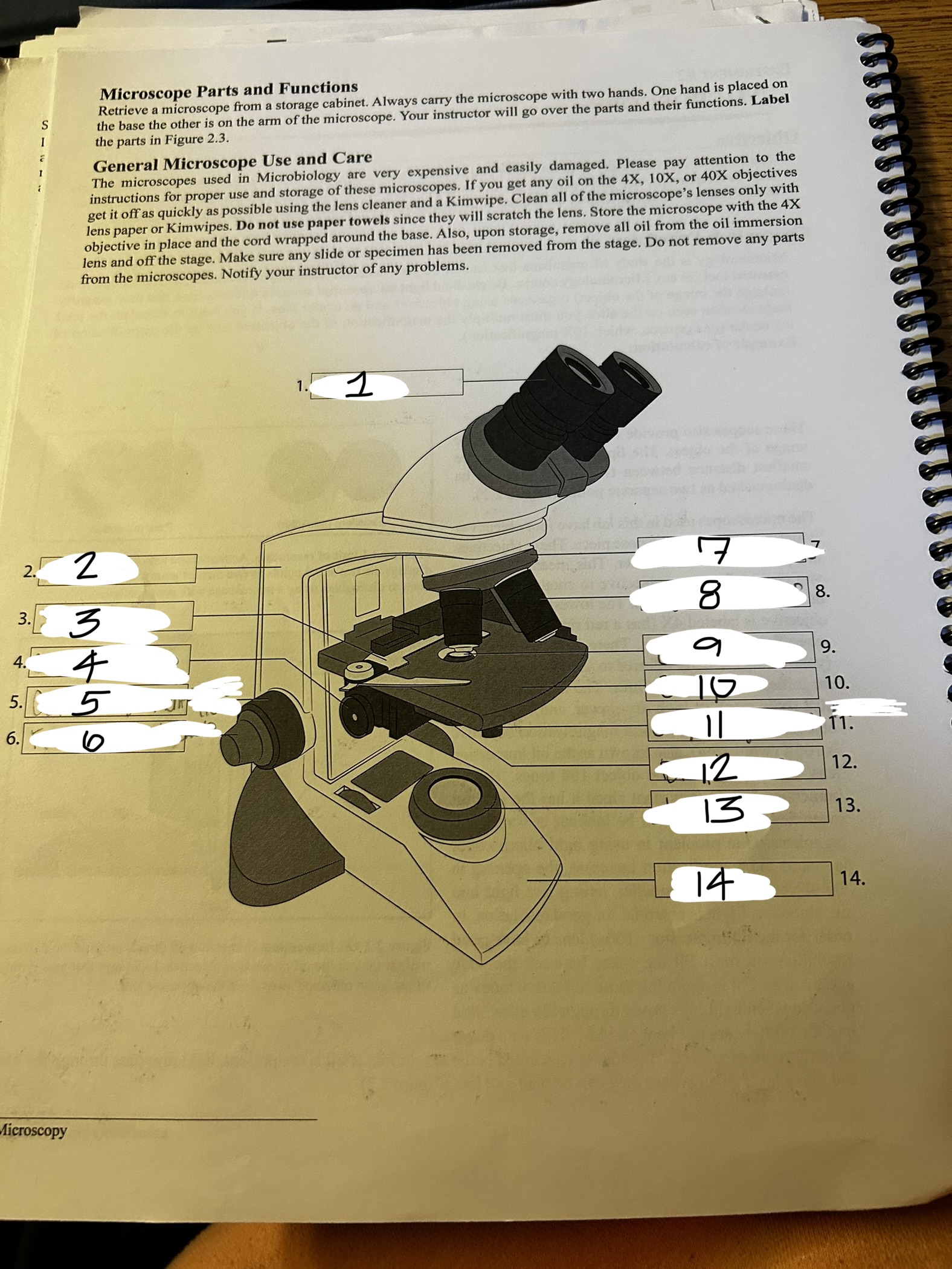
microscope 2
arm
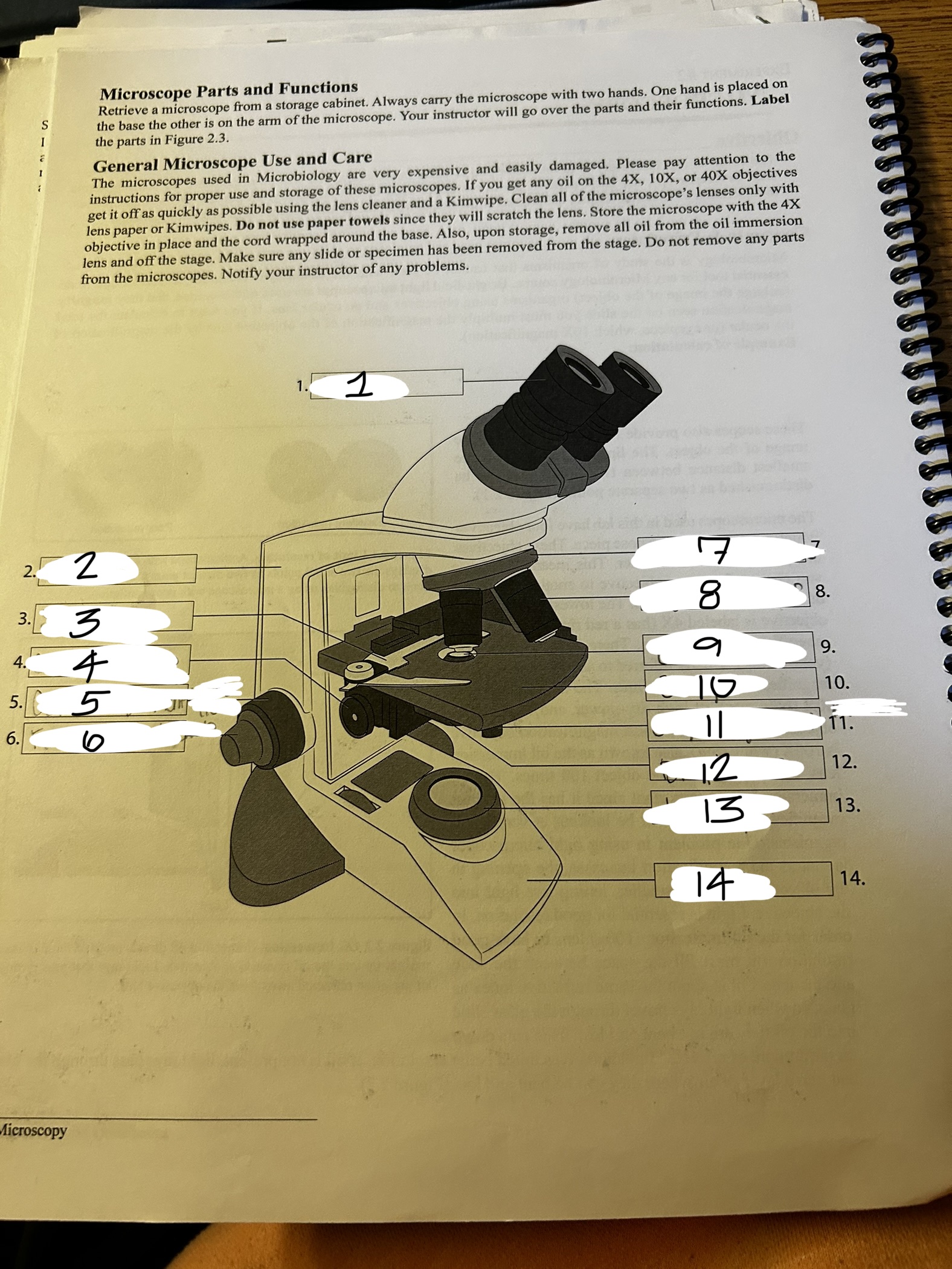
microscope 3
stage clip
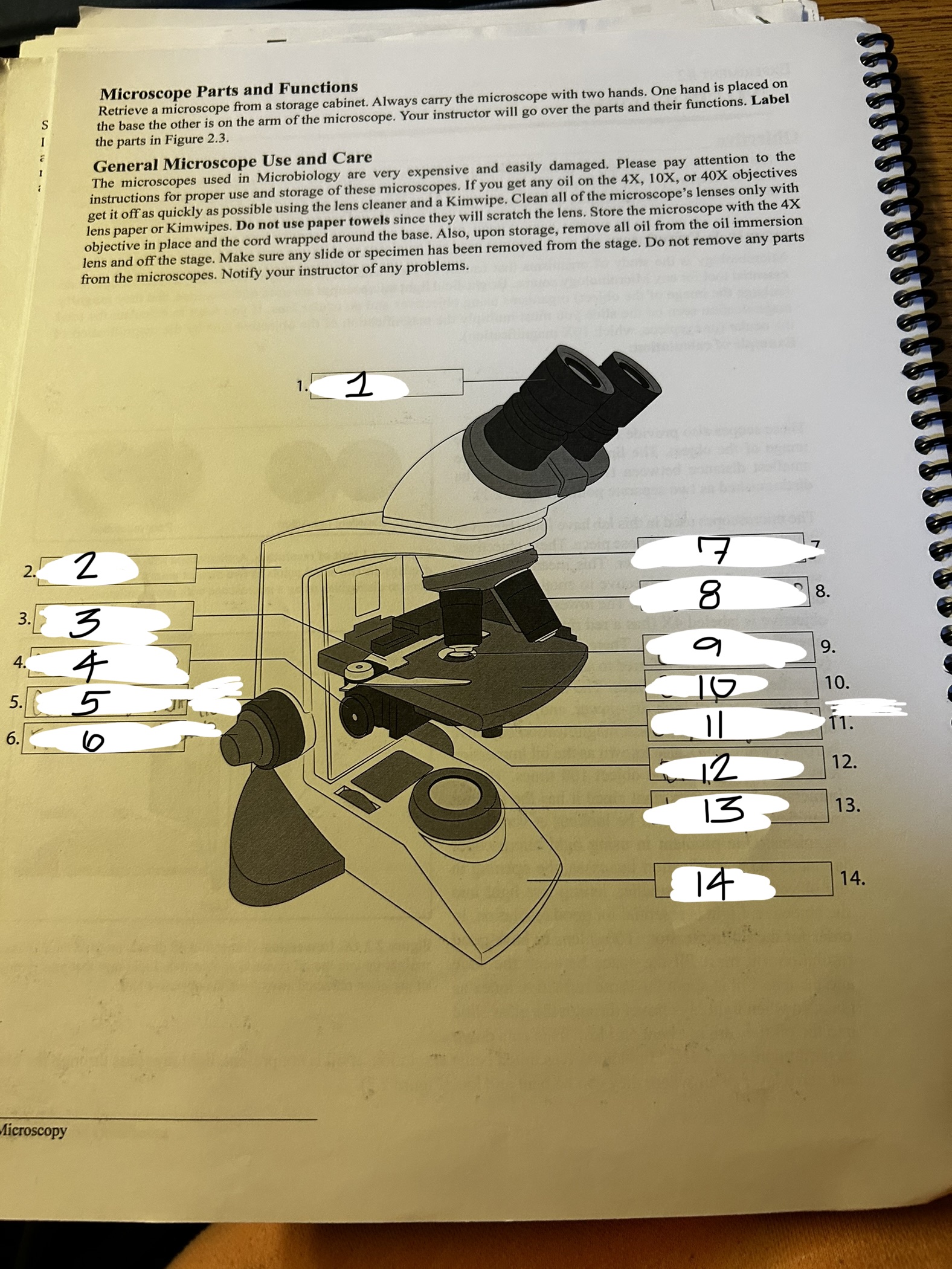
microscope 4
condenser knob
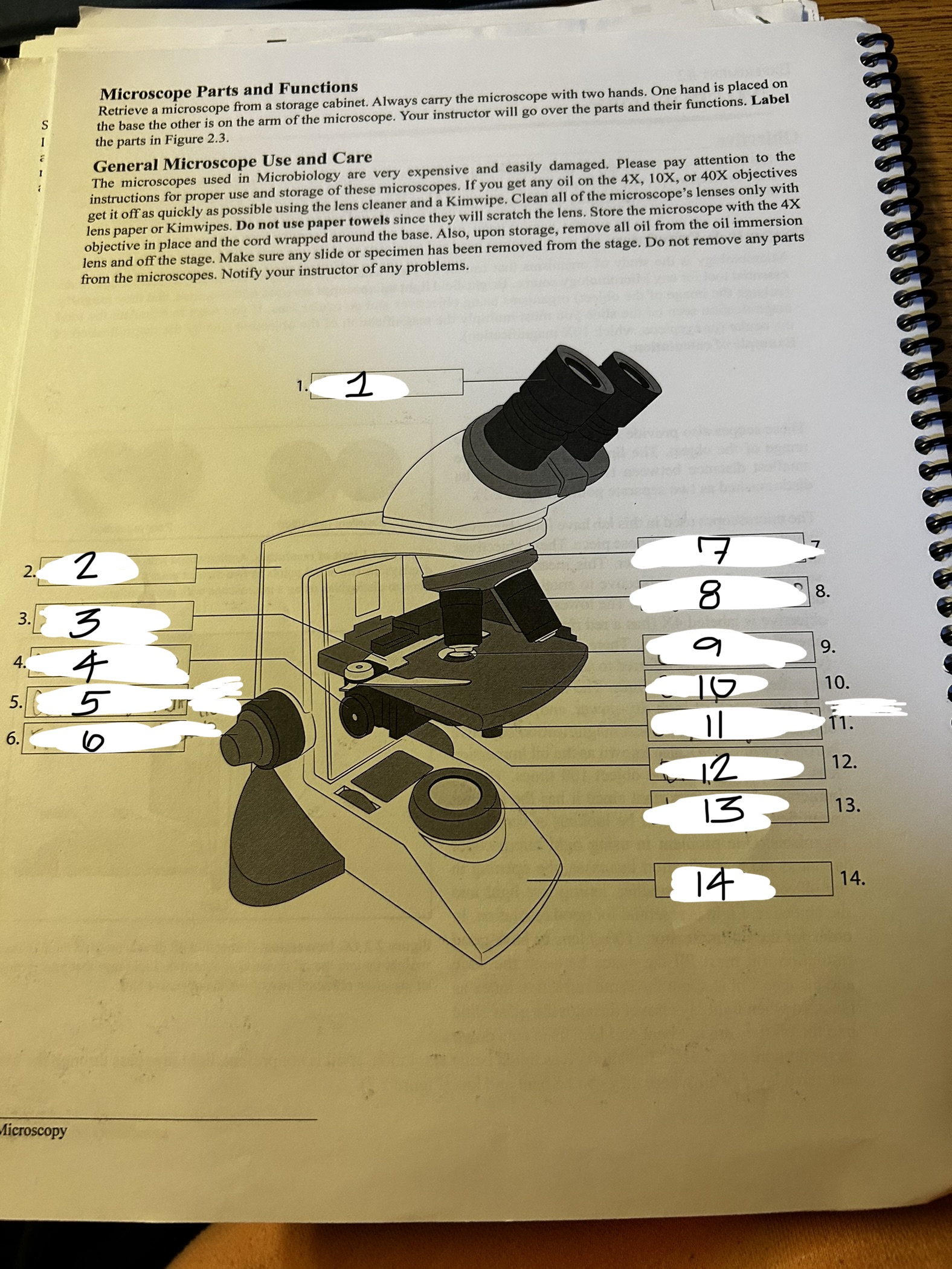
microscope 5
course adjustment knob (10x)
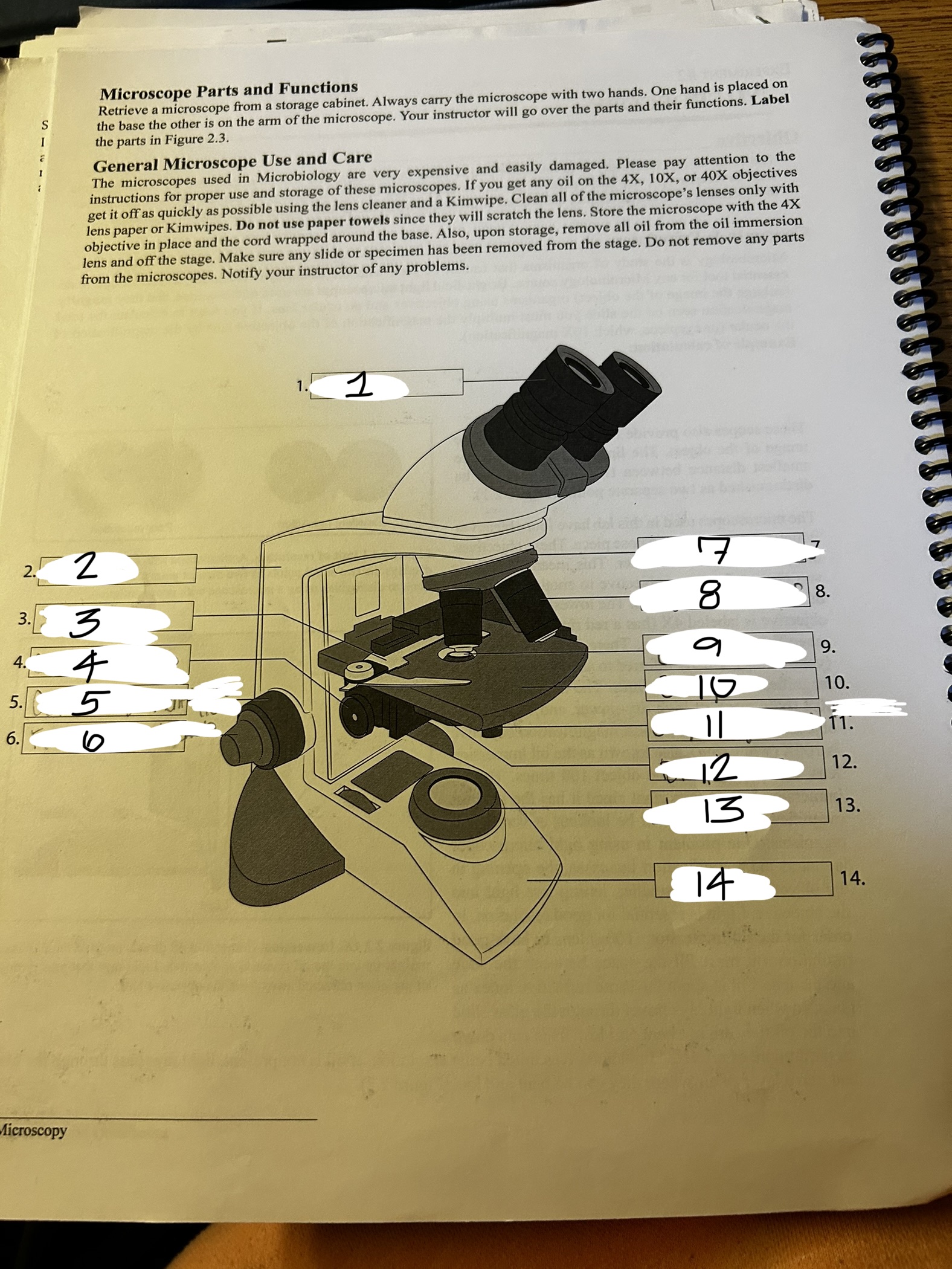
microscope 6
fine adjustment knob
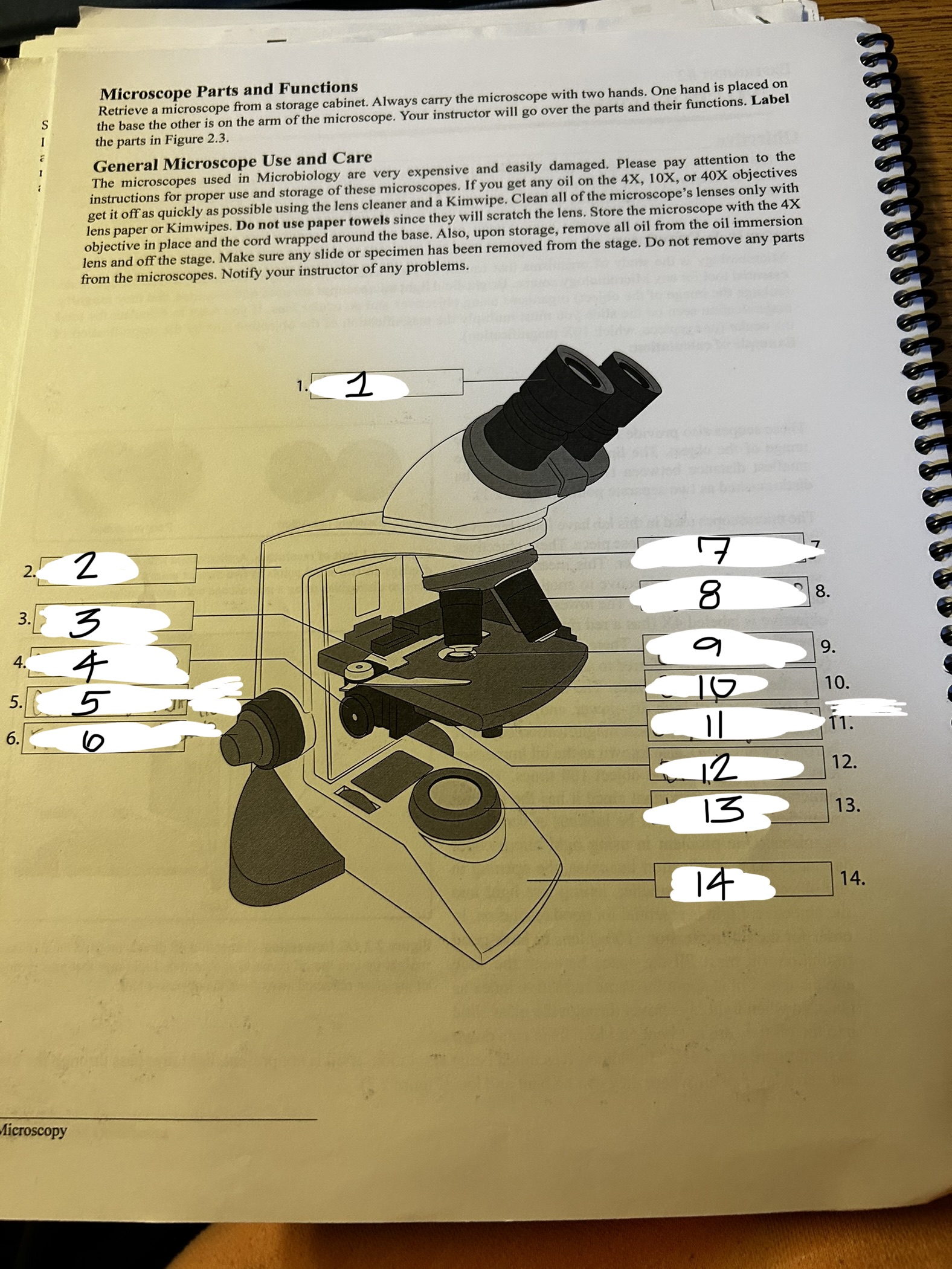
microscope 7
revolving nose piece
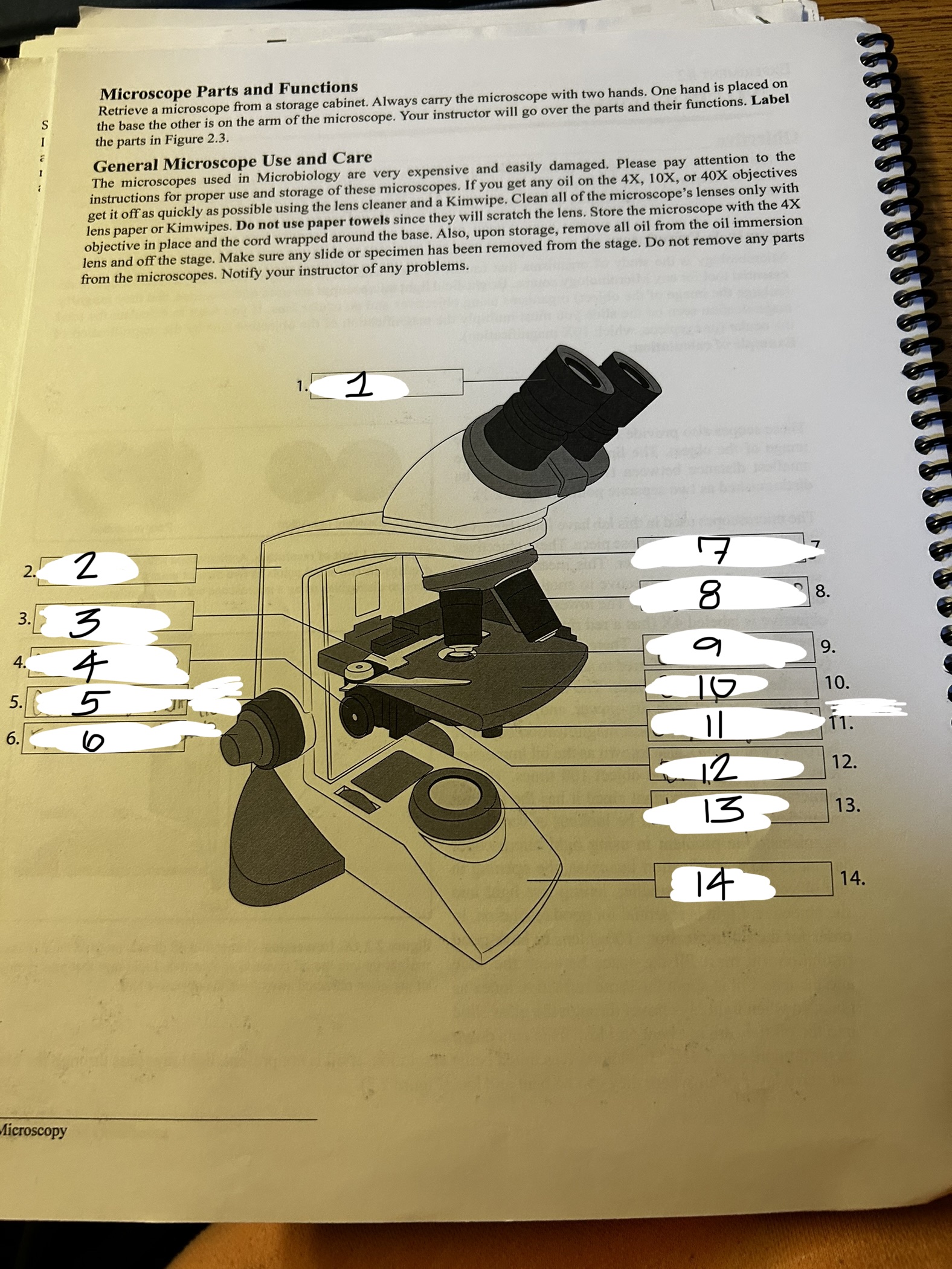
microscope 8
objective lens
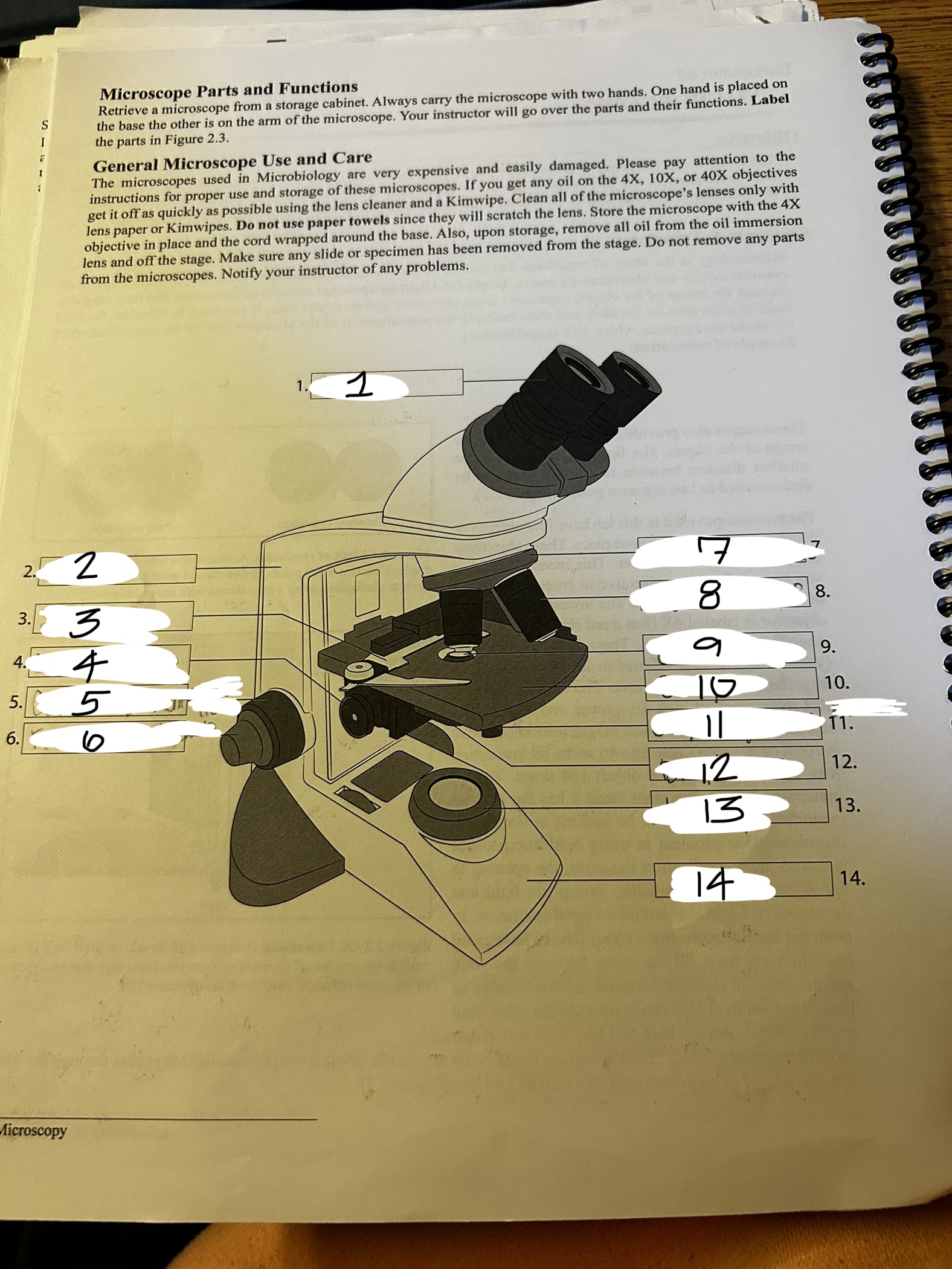
microscope 9
condenser
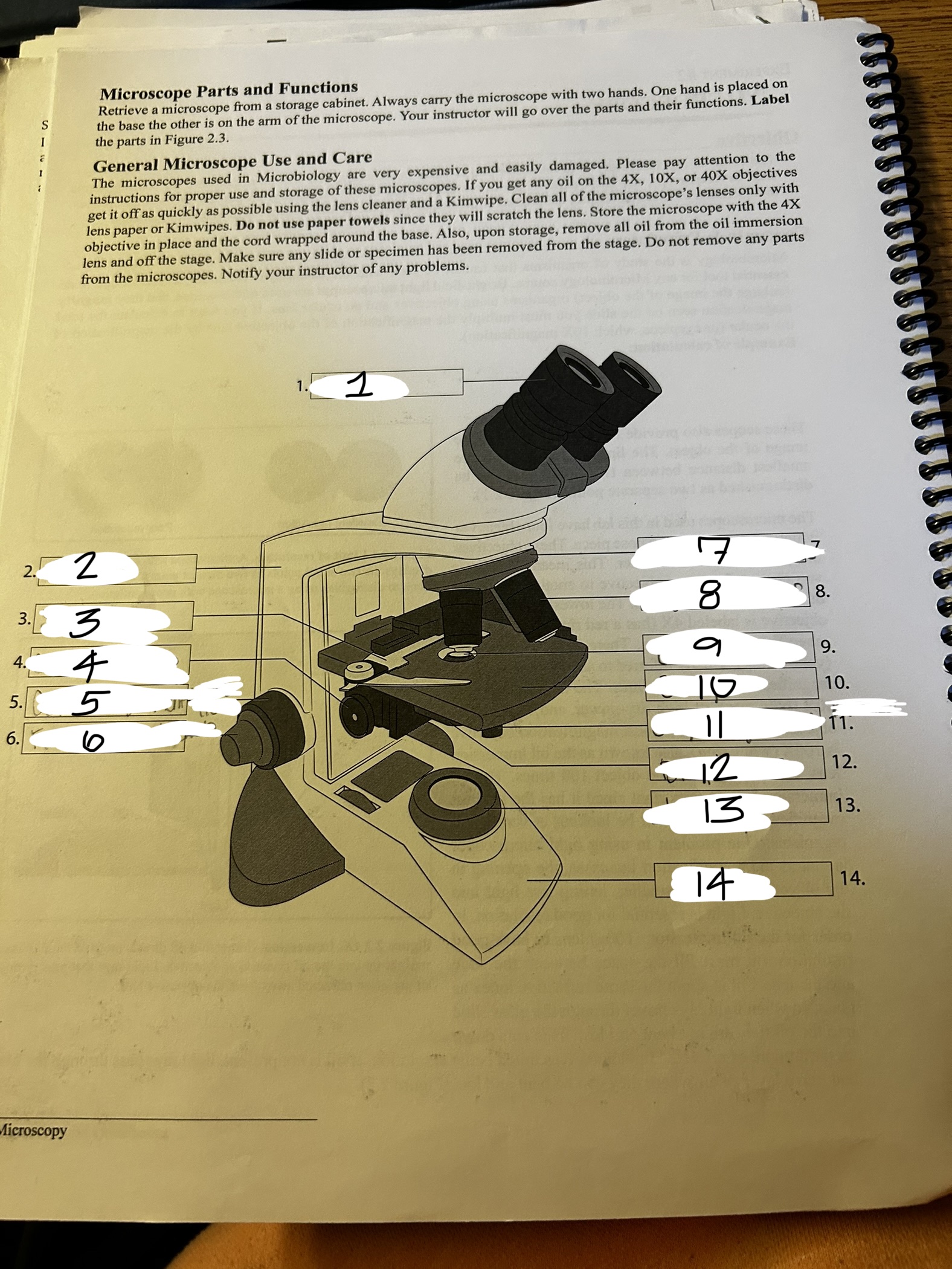
microscope 10
stage
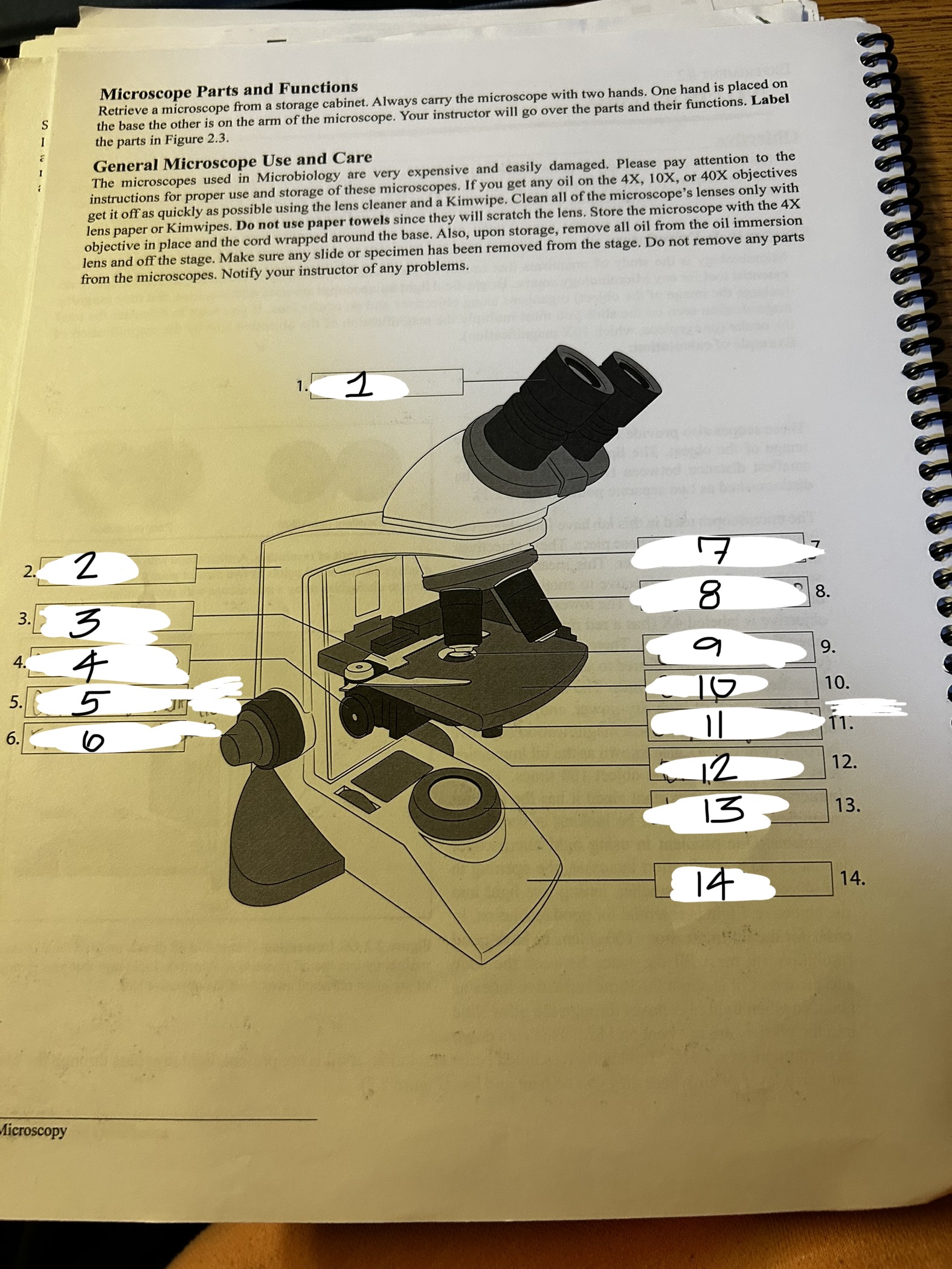
microscope 11
stage adjustment knobs
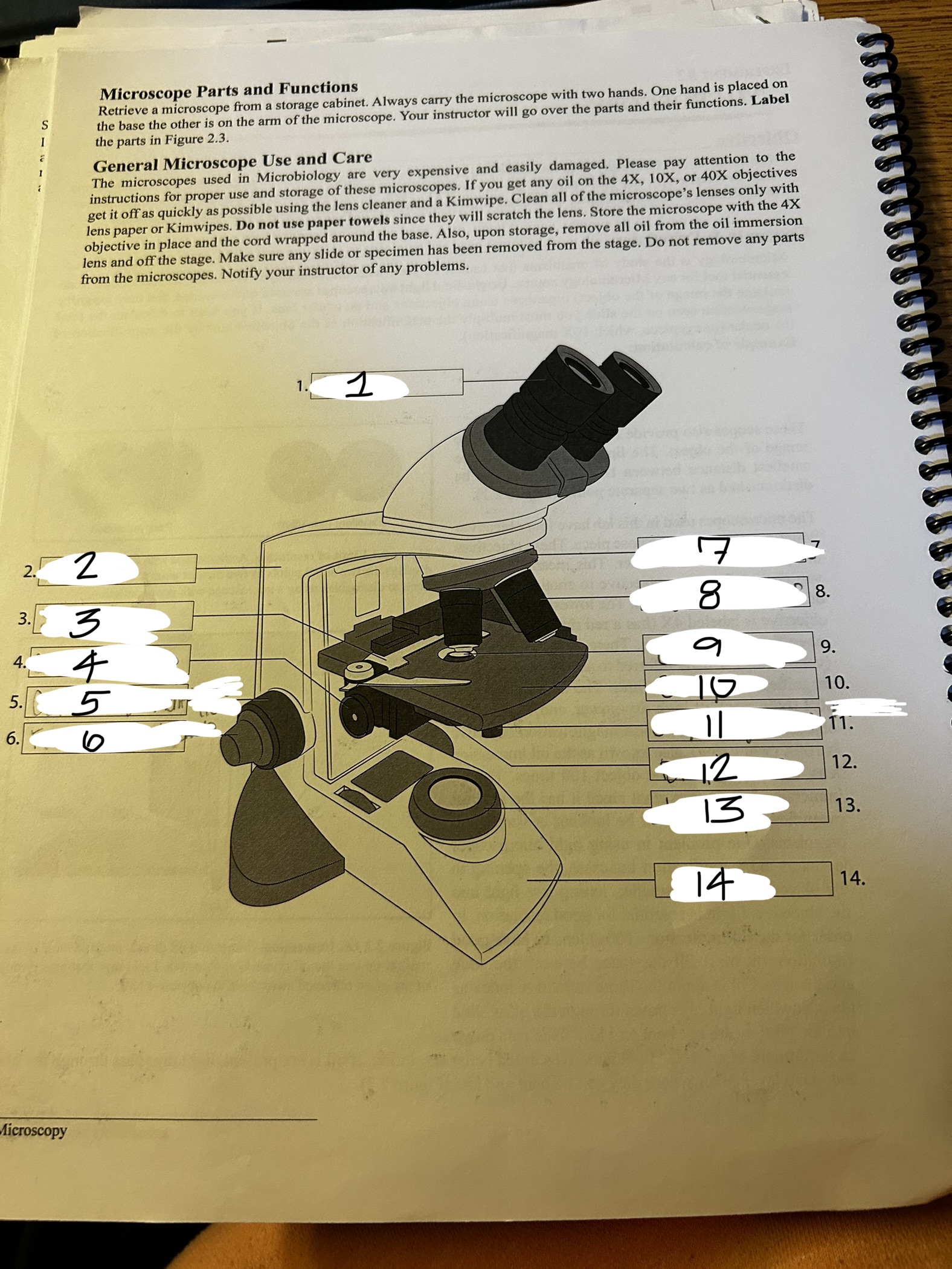
microscope 12
diaphram
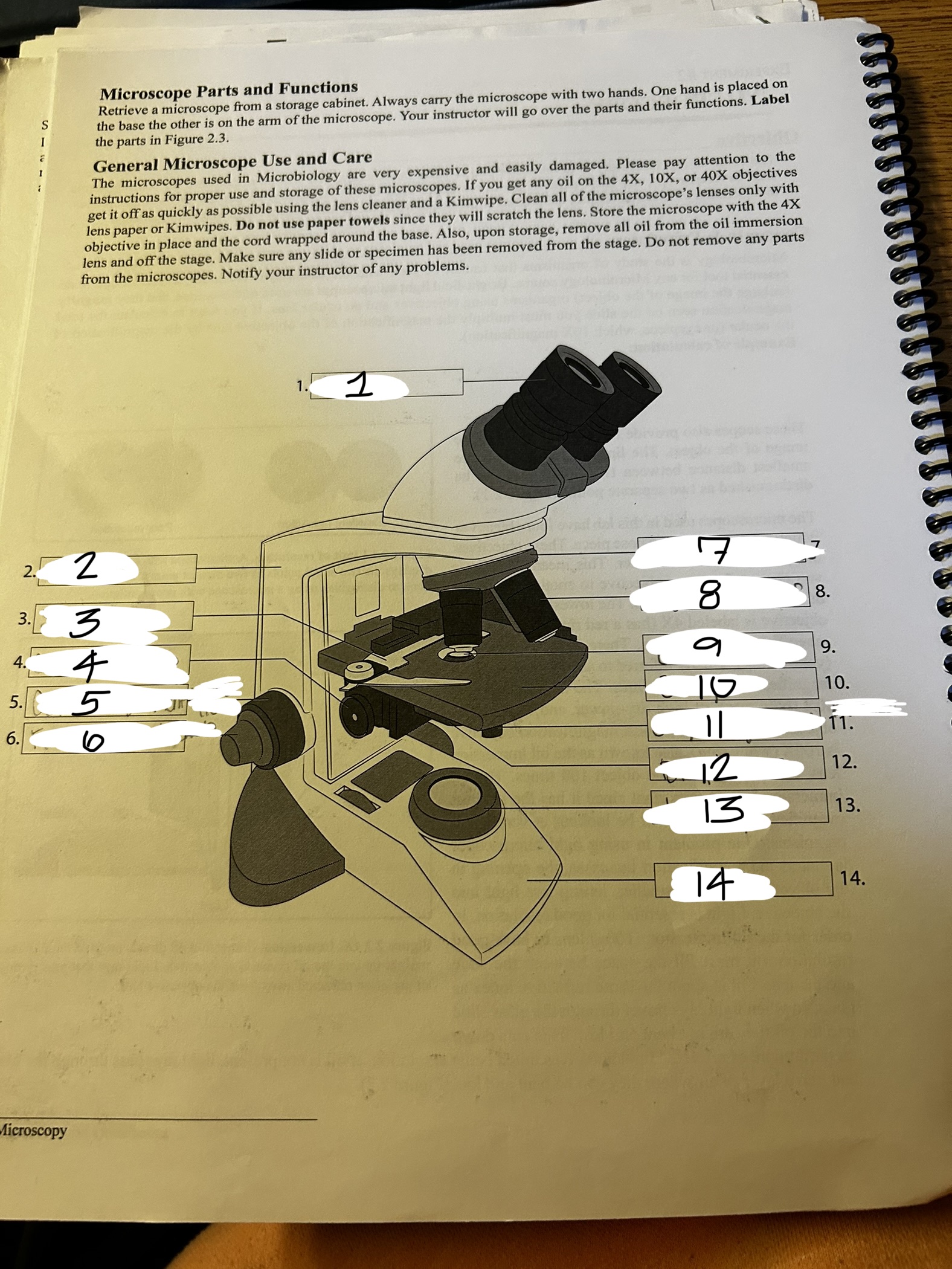
microscope 13
lamp
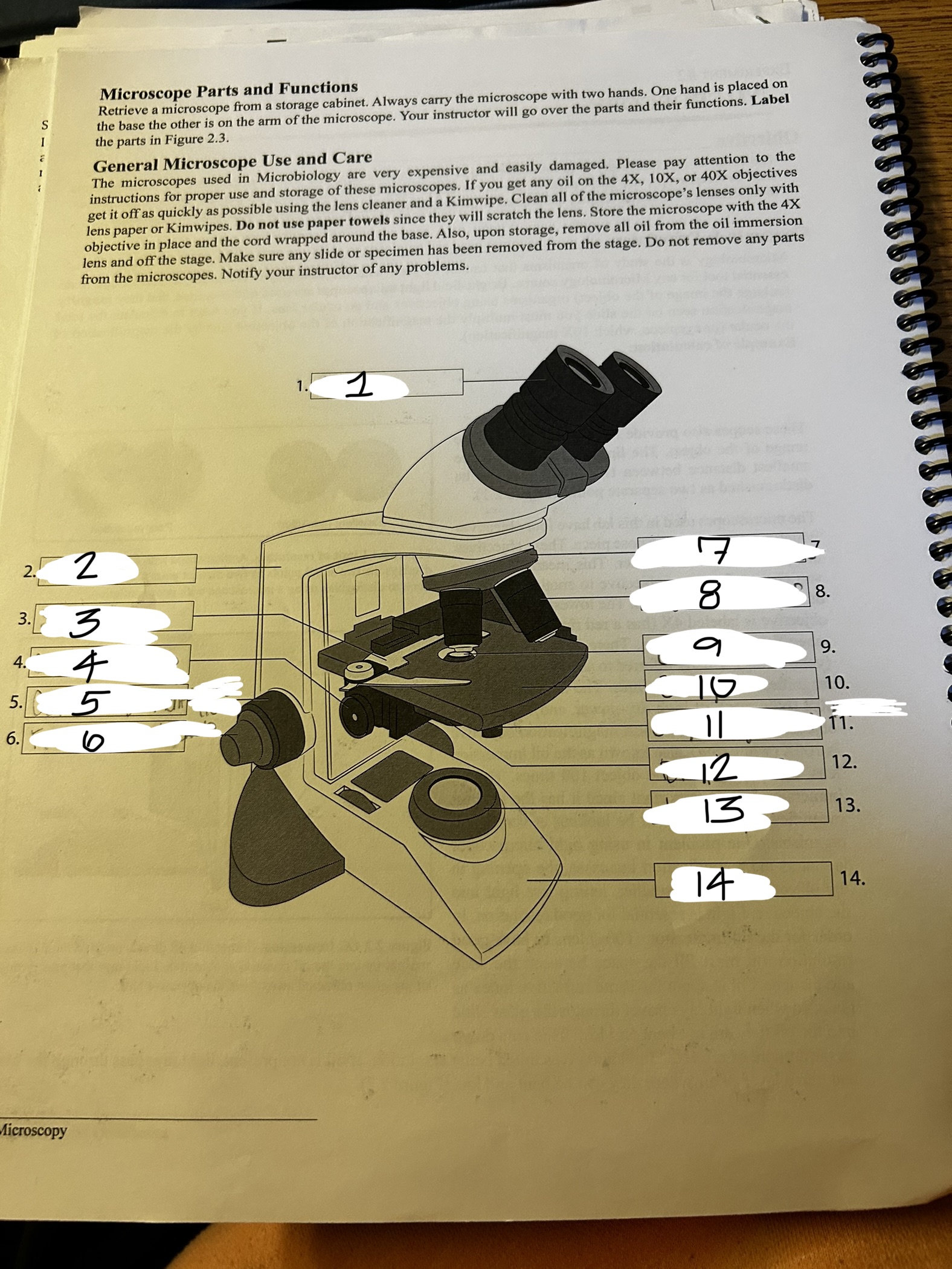
microscope 14
base
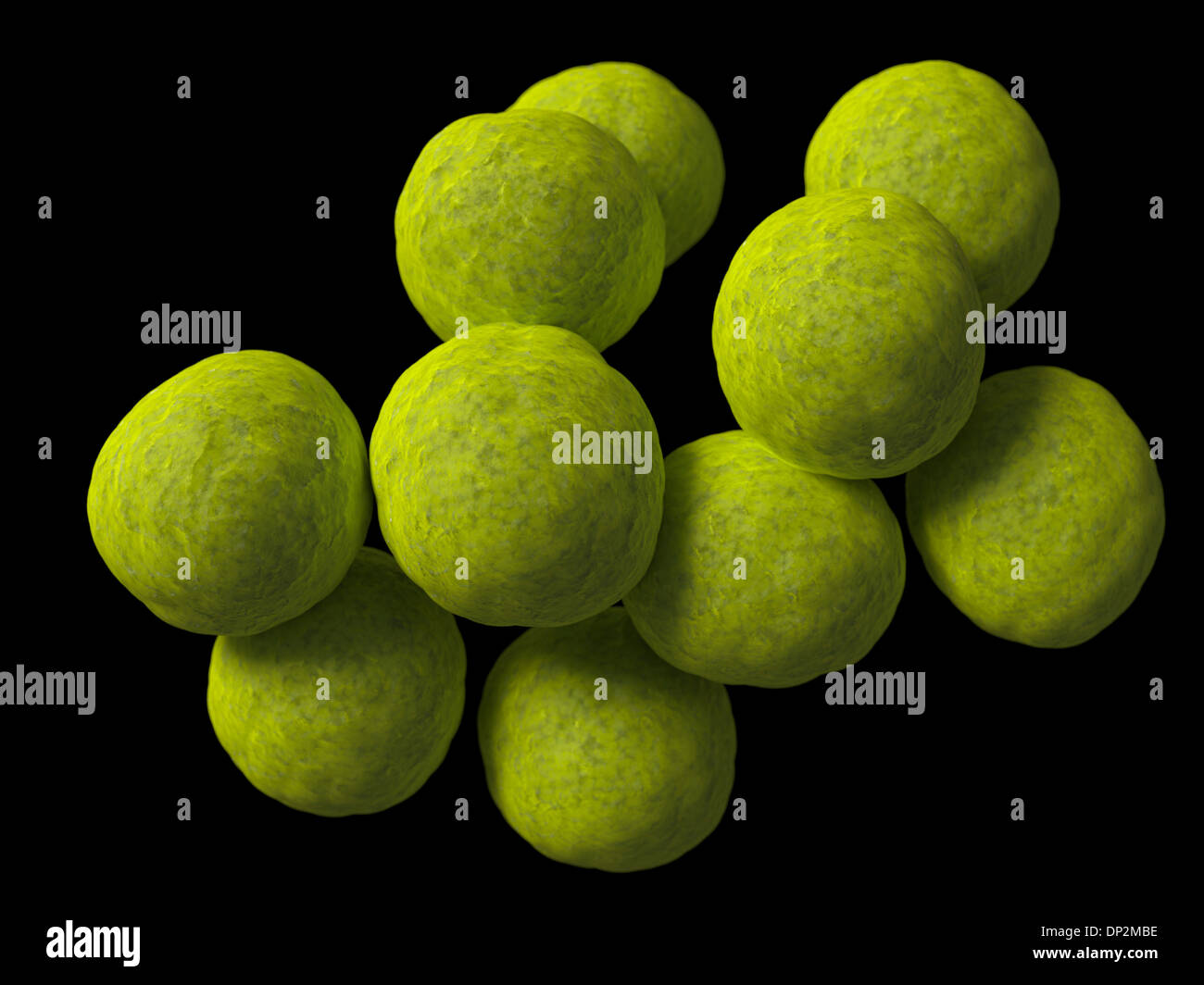
coccus

bacillus
spirillum
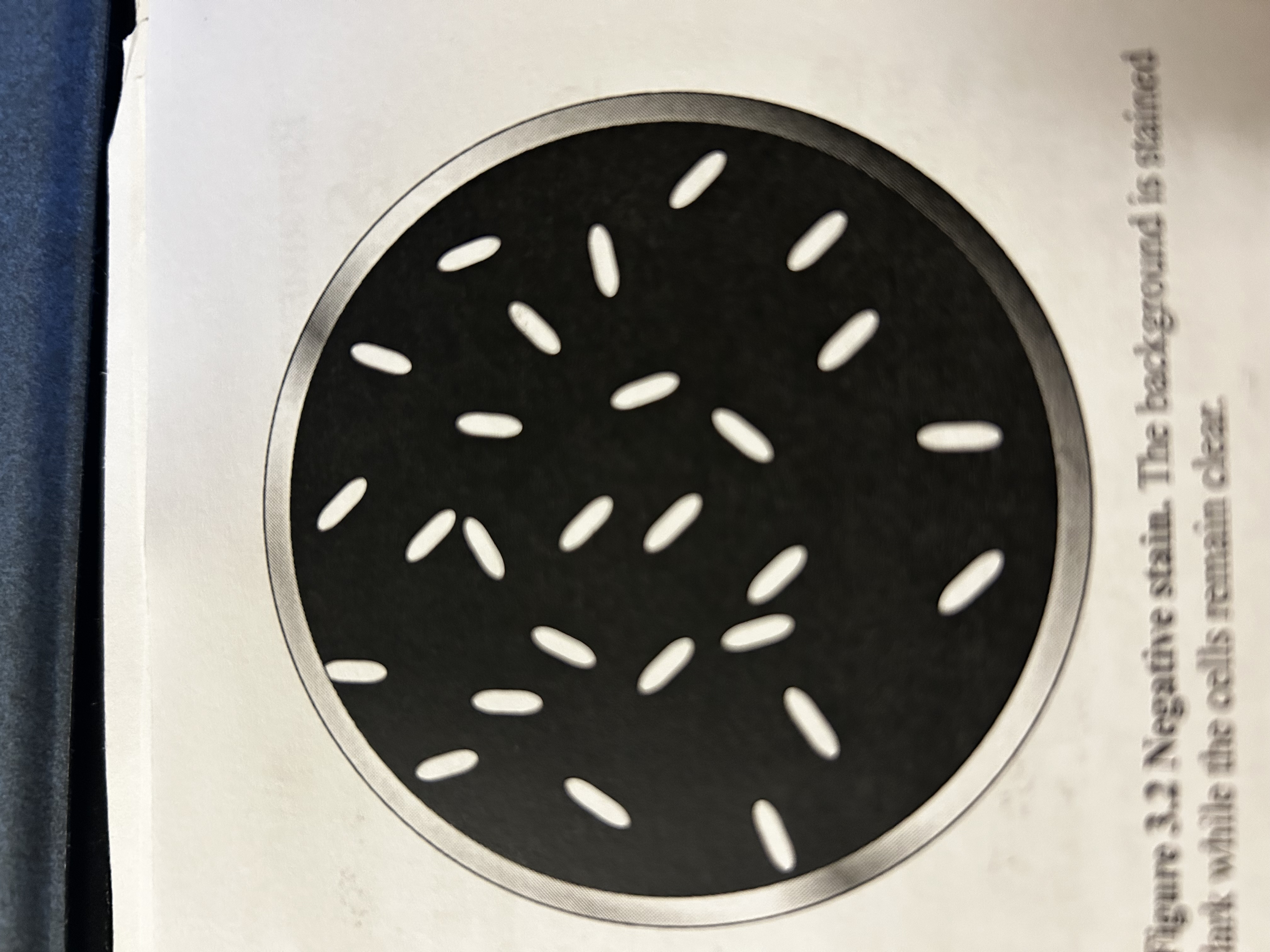
Why negative staining
When bacteria do not stain well with other methods. Quick not heat fixing. Bacteria negative and so is stain so repel and satin background
What does a negative stain look like?

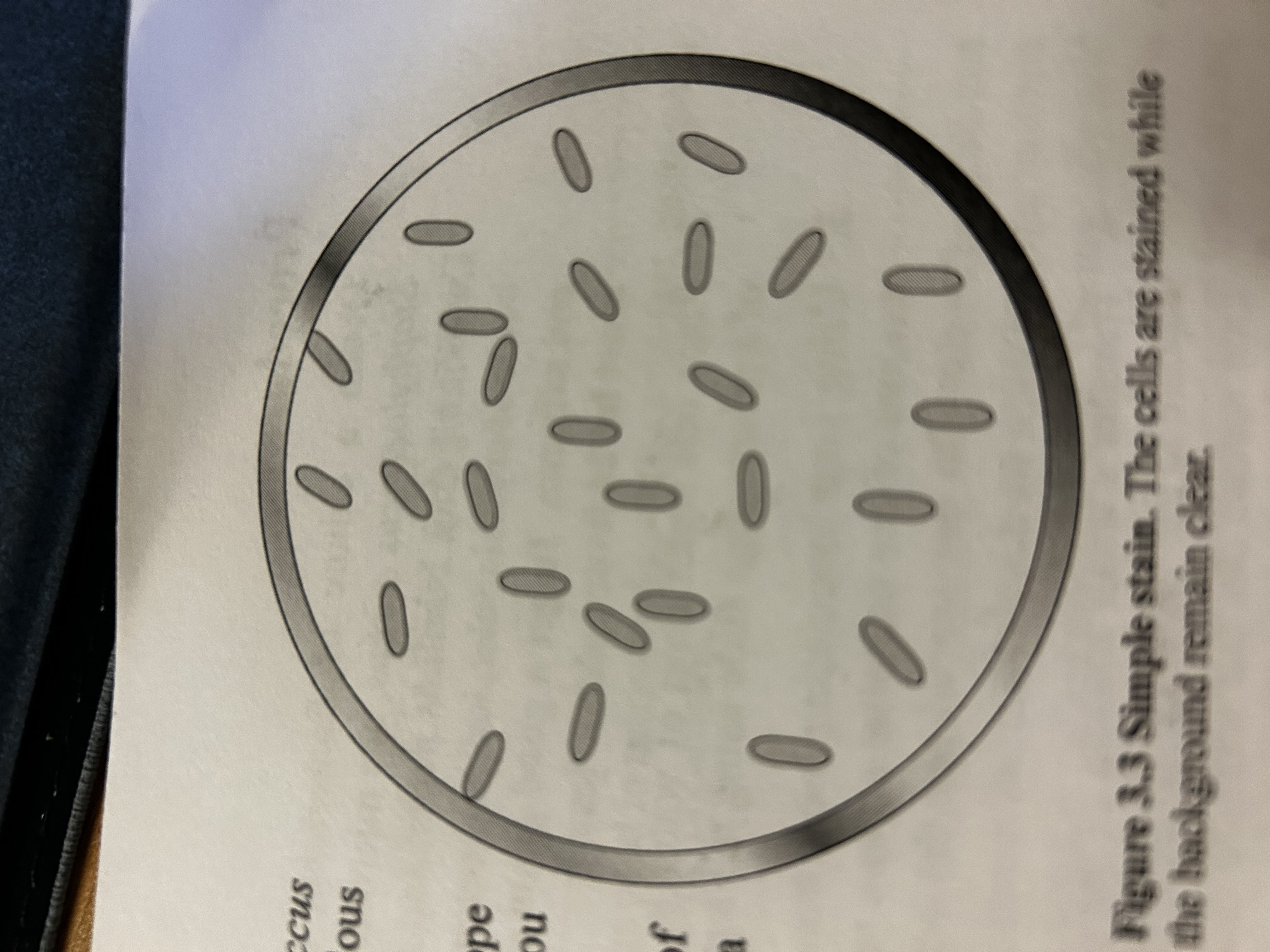
Why simple stain
View bacterial size, shape, or arrangement. Bacteria are negative, stain positive attract and stain bacteria. Must be heat-fixed to kill bacteria and adhere them to the slide.
What does simple stain look like
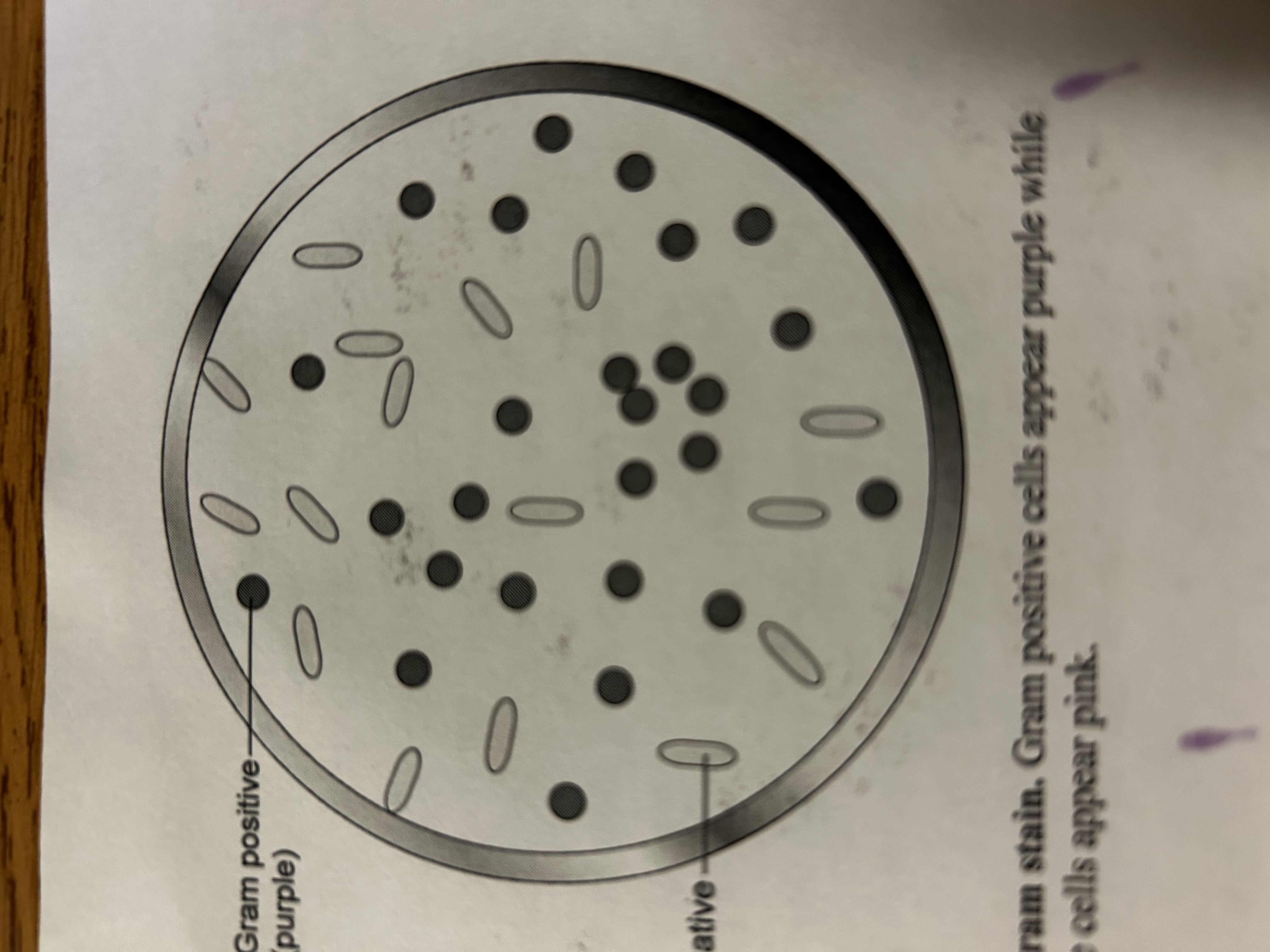
why gram stain
differential stain because two groups of bacteria with different cell walls. Gram +: purple. Gram -: pink.
What does gram stain look like
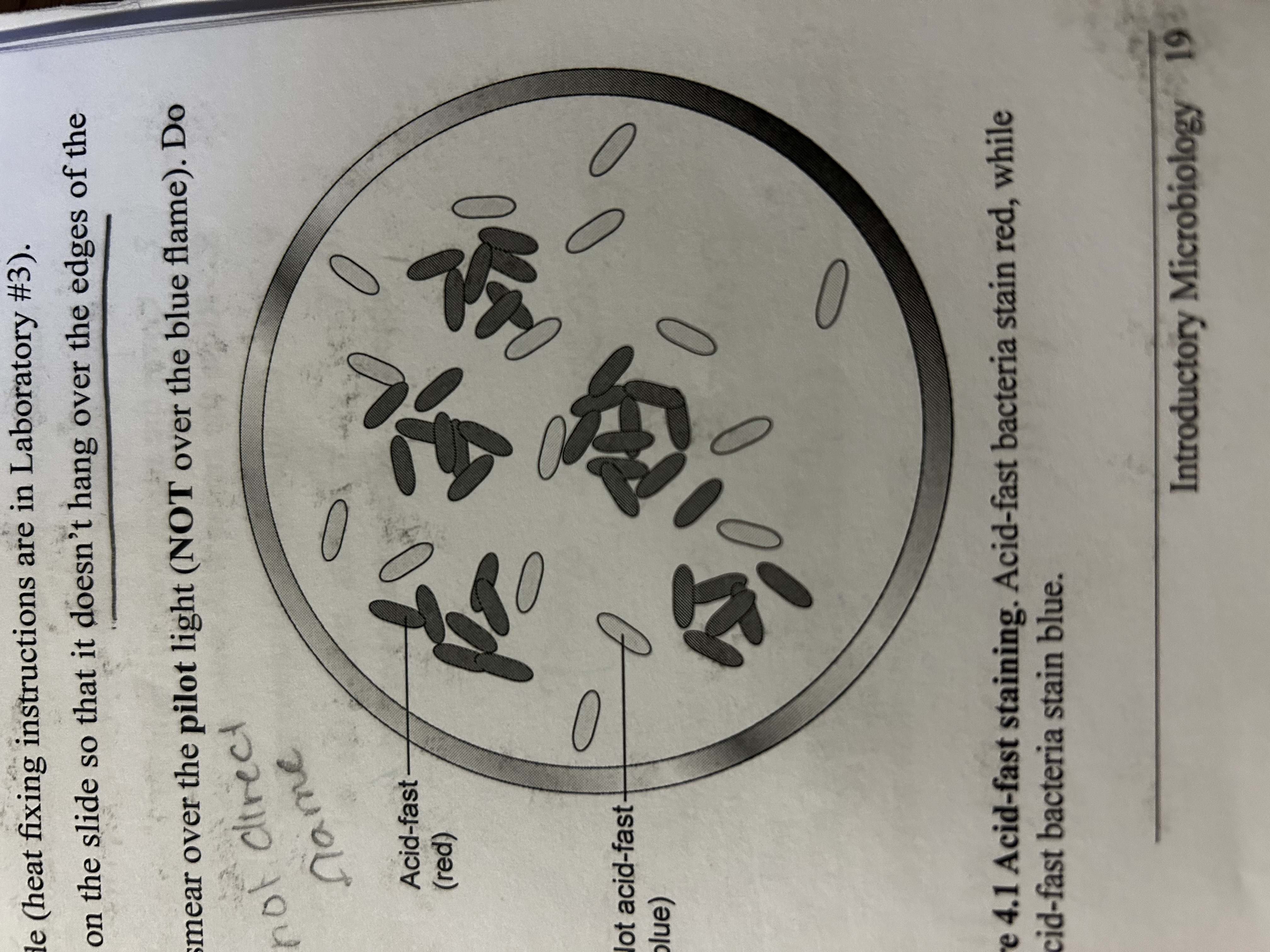
why acid fast stain
some bacteria don’t stain well with typical stain techniques. Uses heat. Drives stain into bacteria through the thick waxy lipid present in cell wall. Acid fast: red. Not acid fast: blue
what does acid fast look like
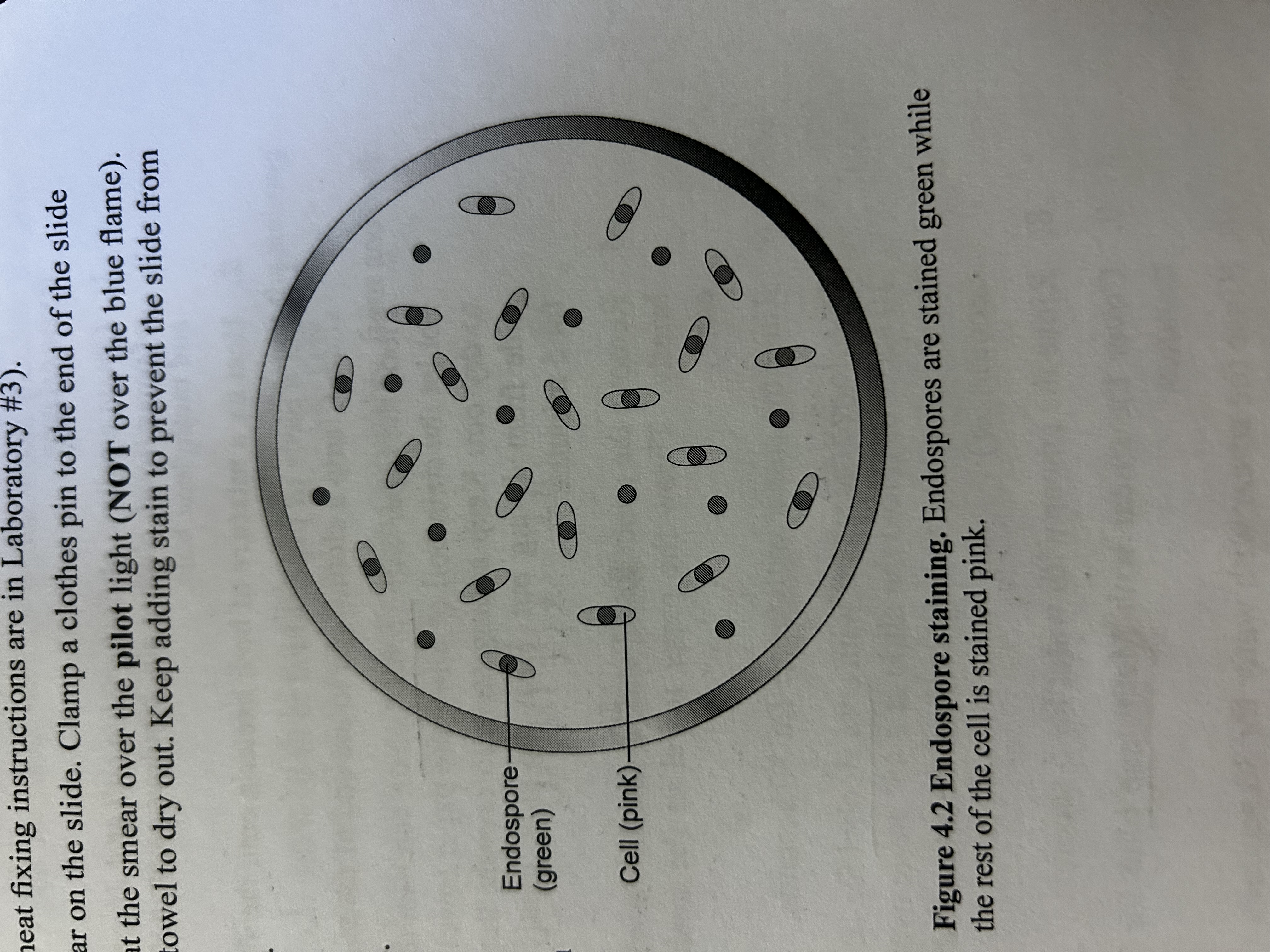
why endospore staining
some bacteria produce resistant dormant structures. Endospores are difficult to stain by ordinary methods. The location of endospores in cells can help identify bacterial species. Endospores green. Pink normal cell. Pink with green: vegetative cell with endospore
What do endospores look like
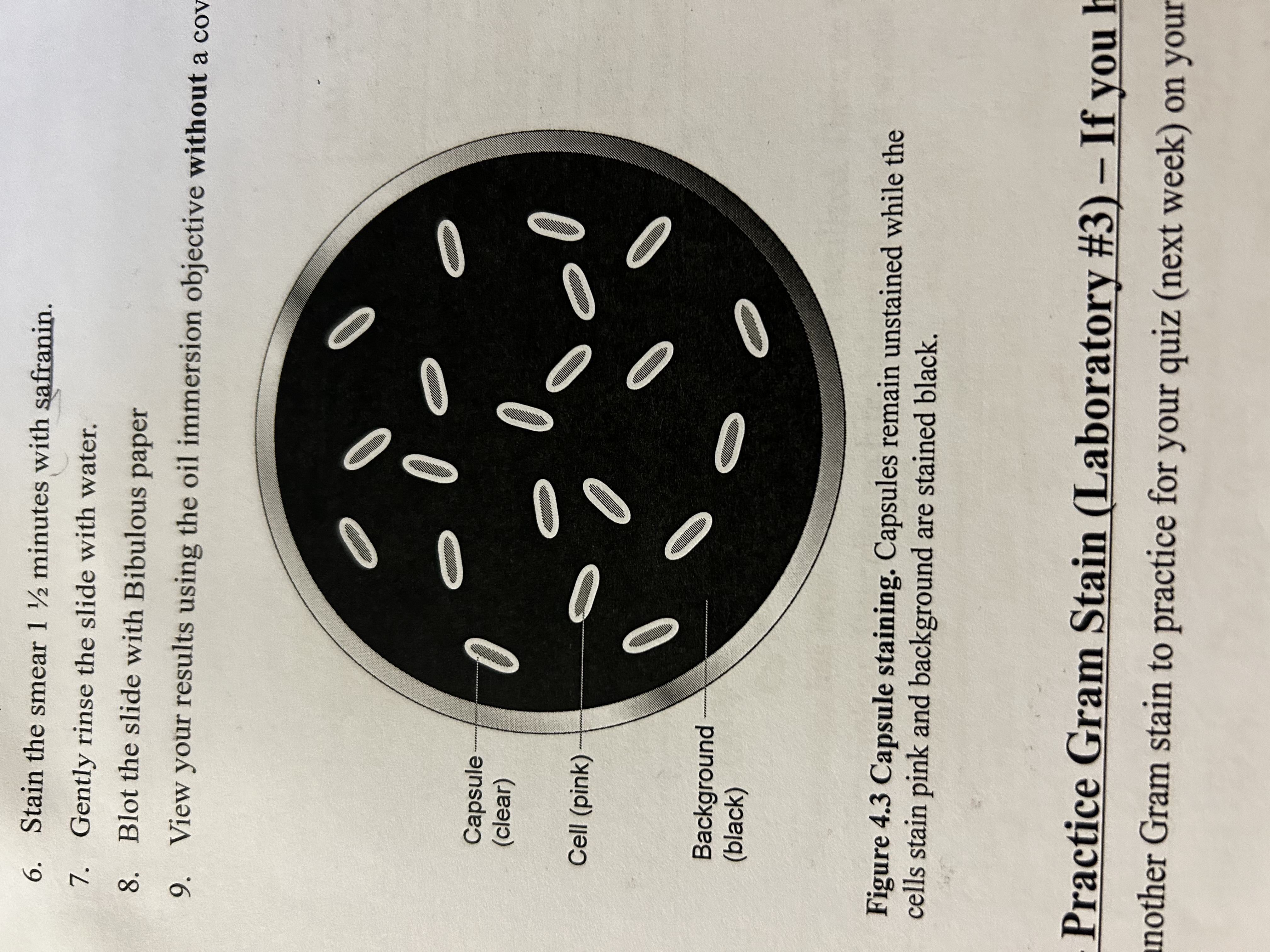
Why Capsule staining
Bacteria with sticky sugary layer around. Combination of negative stain and simple stain. Capsule clear, cell pink, background black
What do capsule stain look like
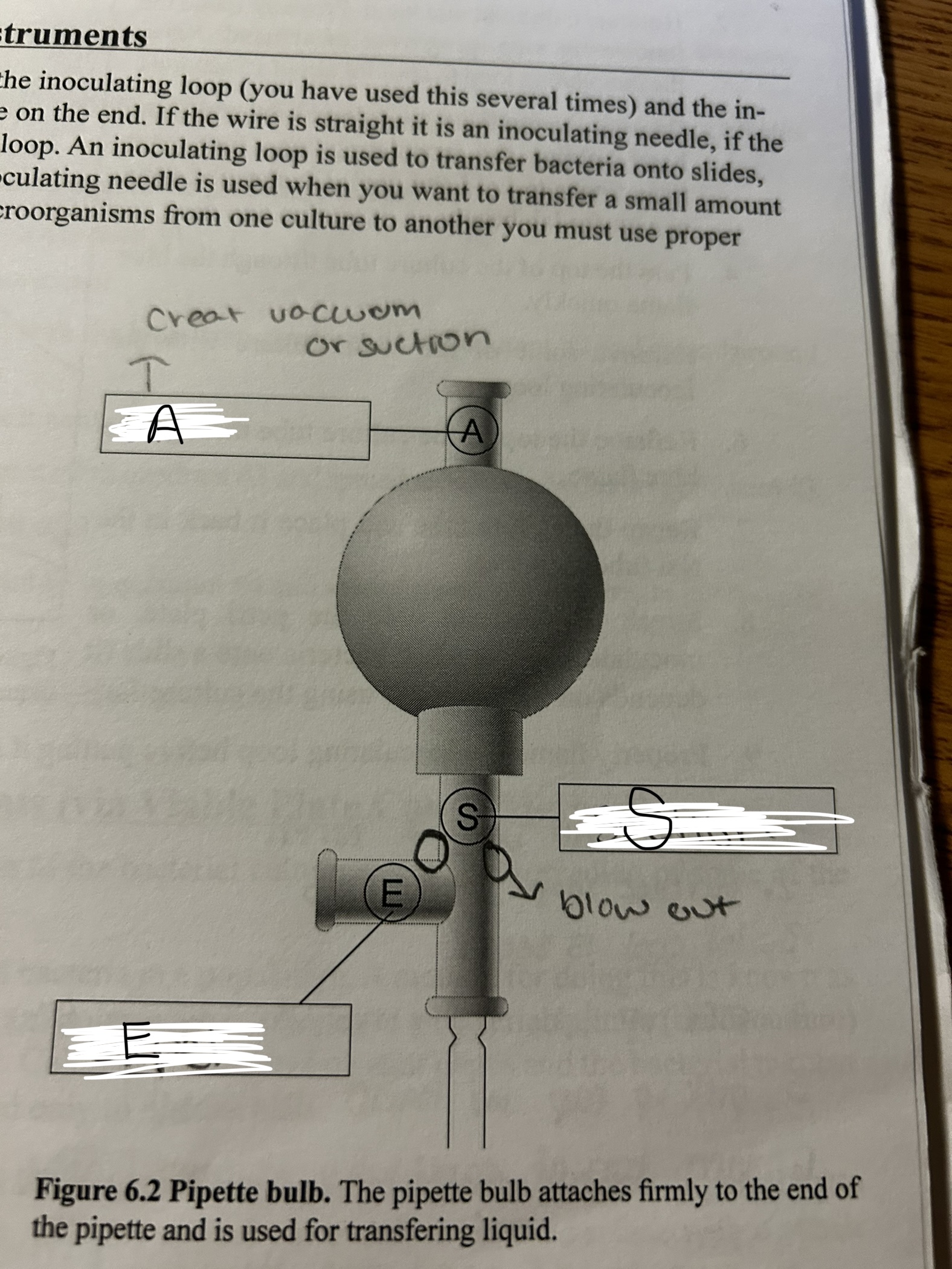
pipette a
air
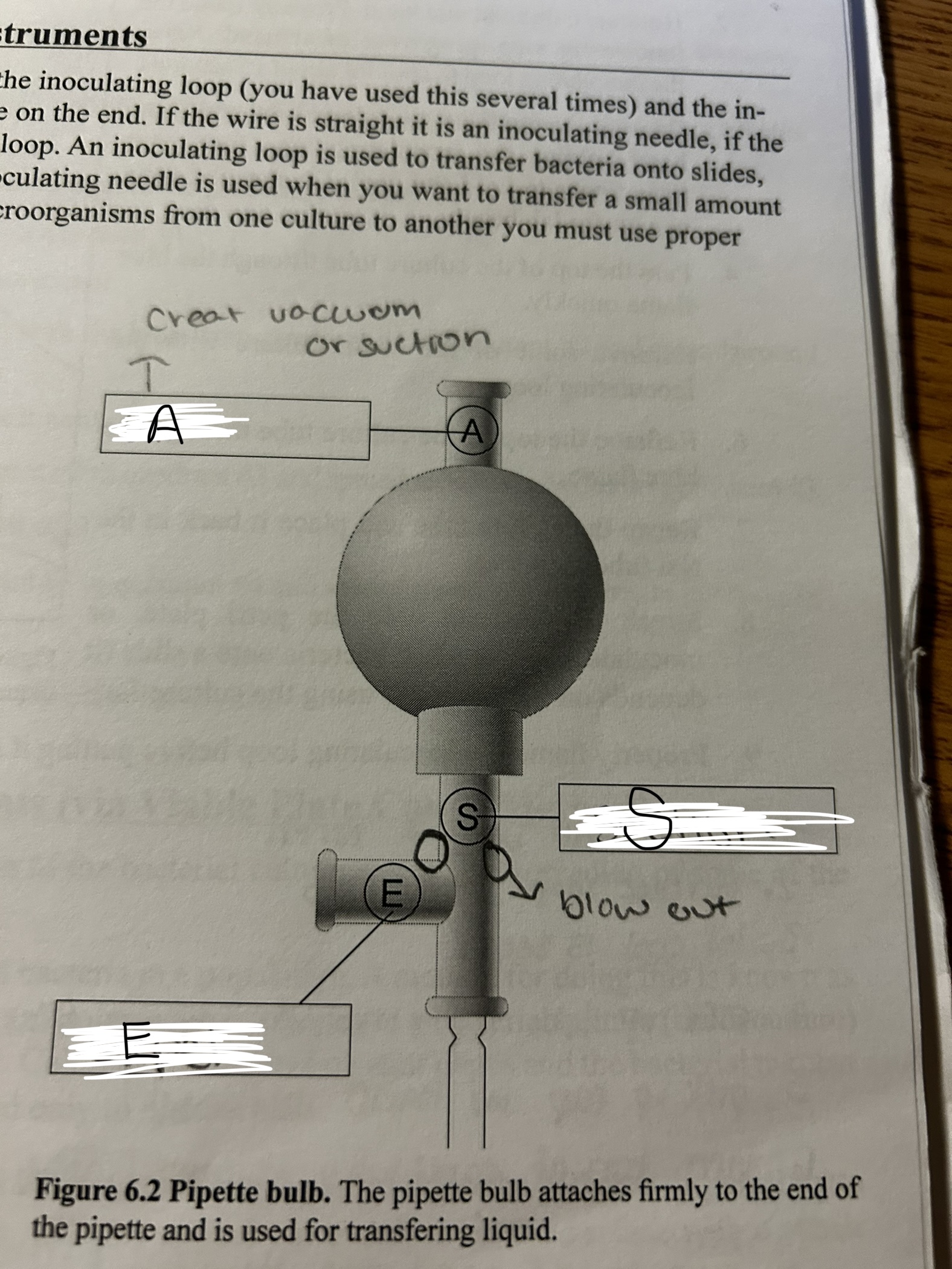
pipette e
expel
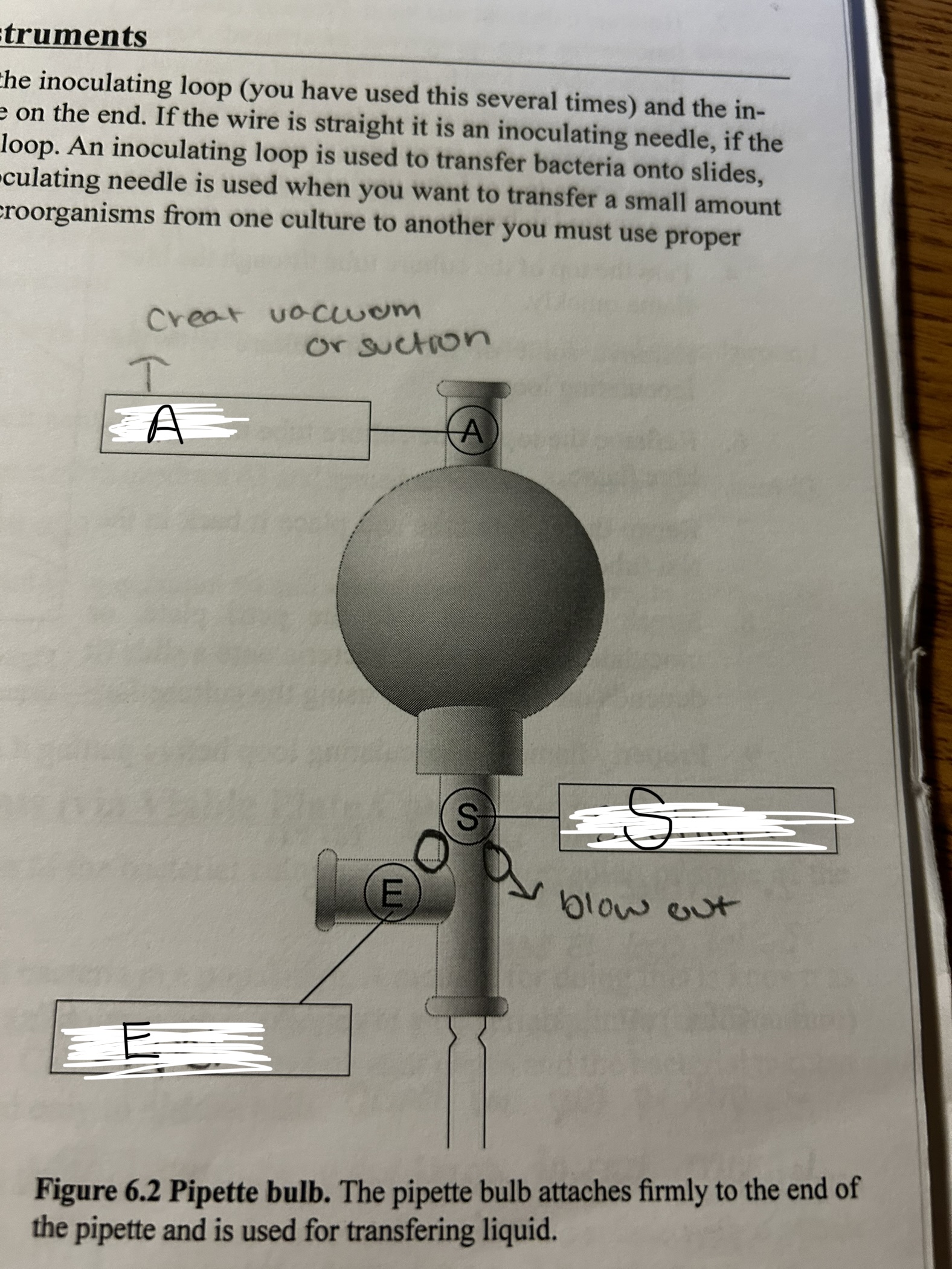
pipette s
suction
temperature what is being affected
the enzymes or proteins denature with too low, also membrane fluidity
membrane becomes too fluid if temp is too low
thermoduric bacteria survive why
form endospores
what is thermoduric
bacteria that do not grow at elevated temperatures.
Psychrophiles
0-20 degrees Celsius
Mesophiles
20-45 degrees Celsius
Thermophiles
55+ degrees Celsius
Why do bacteria have minimum and maximum growth pH
The proteins and enzymes denature and hydrogen bonding is effected
Acidophiles
0-5.5 pH
Neutrophiles
5.5-8.0 pH
Alkalophiles
8.0-11.5 pH
Hypotonic
Water move into cell
Hypertonic
Water move out of cell
Isotonic
No net gain or loss of water
Facultative halophile
0-10% NaCl
Obligate halophile
15+% NaCl
Obligate aerobe
Grow only in presence of O2
Facultative anaerobe
Organisms grow with or without presence of O2, but prefer it
Obligate anaerobe
Killed by O2
Aerotolerant anaerobes
Don’t use O2 for growth and not harmed either
Microaerophiles
Less than atmospheric concentrations of O2

oxygen growth 1
obligate aerobe

oxygen growth 2
facultative anaerobe

oxygen growth 3
obligate anaerobe

oxygen growth 4
aerotolerant

oxygen growth 5
microaerophile
Bacteriostatic
Antibiotics inhibit bacterial growth
Blurred line
Bacteriocidal
Antibiotic kills bacteria
Solid line
Some people do not wash their hands correctly and don’t remove all the transient microorganisms present. What could be some problems with their techniques? b
Missing spots, not enough time, not using soap
What is a healthcare associated infection (nosocomial infection)? How are they usually spread (be specific)?
It is an infection that is acquired in a clinical/healthcare setting that is most commonly spread by healthcare workers who don’t properly wash their hands.
Are hand sanitizers a safe alternative to washing hands with soap and water (explain)?
Yes but it doesn’t work completely depending on how dirty your hands are and if there is organic matter present. It also kills your normal flora.
What is the different between cleaning and disinfecting?
Cleaning removes dirt and some of the bacteria while disinfecting destroys vegetative (non-endospore forming) pathogens
What physical or environmental factors can influence the activity of a disinfectant?
Organic Matter, Surface Type, and time
What is the difference between a disinfectant and an antiseptic? What is an example of each?
A disinfectant kills bacteria on a nonliving surface. Examples include Lysol and bleach. An antiseptic kills bacteria on a living surface and includes hydrogen peroxide and alcohol.
What is a hot zone in your home that requires disinfection? Why is it considered a hot zone?
The kitchen and bathroom are considered hot zones because there is a significantly higher amount of bacteria there
When doctors wash their hands for surgery, they must scrub their hands with a brush. What category of bacteria are surgeons trying to remove by using a brush?
They are trying to remove their normal flora
What is the difference between resolution and magnification?
Magnification makes the image or cell appear larger while resolution provides more detail of the image
The 40X lens is called the ‘high dry’ lens. Why do we call it that?
It is the highest objective our microscopes have without adding oil
Define parfocal. How does this characteristic affect the way you would view a slide?
When you switch from one objective to another, the object stays in the same plane of view so all you have to do is adjust the fine adjustment knob.
What is the function of the condenser? The iris diaphragm knob?
The condenser concentrates the light and the iris diaphragm controls light intensity
What are the two functions of the ocular (eyepiece) lens?
The functions are to magnify and measure
In this course, which objective lens will be used the most? Why?
White will be used to look at shape and color which is the oil immersion lens
If you are using the oil immersion lens to view your bacteria, what is the total magnification? What does this measurement mean?
1000X, the cell will appear 1000X larger
Why must we use immersion oil to get good resolution with the 100X lens?
To get more light into the objective lens and to trap the light
If 50 ocular micrometer divisions = 5 stage micrometer divisions and if one division of the stage micrometer = 0.1 mm. The cells you measure are 42 ocular micrometer divisions long. Therefore the cells are _____ mm long.
.42 mm
Before the microscope is put away, name 2 things you must do.
You must wipe off any oil, wrap up the cord, and put it on the lowest objective lens
Why don’t acidic or background dyes stain the bacteria?
Both bacteria and dye are negative so it is repelled
Why do basic dyes stain the bacteria?
The dye is positively charged and bacteria is negative so they are attracted
When using a basic stain, the cells must be heat fixed. What are the 2 benefits of heat fixing?
It is used to kill the bacteria and adhere the bacteria to the slide
What are the benefits of using a simple stain?
The stain highlights the entire microorganism to show shape and size. It is also simple and fast
What are the benefits of using a negative stain? Why/when would you want to do a negative stain instead of a simple stain?
No heat is used so it keeps the shape and size
For the Gram stain, name the reagent used for each and its purpose. Also identify the color after each step.
Primary stain-crystal violet stains everything purple so both + and – are purple
Mordant-iodine shrinks the pores in the cell wall of + to trap dye but both + and – are purple
Decolorizer-acetone alcohol removes excess crystal violet so + is purple and – is clear
Counterstain-safranin stains anything that is not already stained pink so + is purple and – is pink
Why must cultures between 18-24 hours old be used for the Gram stain?
When the cells are older the pores in + cells are more likely to be weak and leak which makes them unable to hold the dye. This would create false negatives
What is the step that is the most likely to cause poor Gram stain results. Describe,
Decolorizer as it is easy to be left on too long and then pull dye out of the gram + cells
What cell structure is the most important for a Gram stain? Why (be specific)?
Cell wall because of the thickness; the + have a think wall while – has a thin cell wall and outer membrane
What is the difference between virulence and a virulence factor?
Virulence is the severity of disease (how harmful it is) and virulence factor is the component of bacteria that gives it the ability to cause disease
What makes a bacterium acid fast?
There is a waxy lipid layer of mycolic acid which allows it to resist drying and certain disinfectants
Why must the bacteria be heated with the stain in the acid fast procedure?
To drive/force the stain into the mycolic acid lipid layer
What are 2 diseases that can be diagnosed using the acid fast stain?
leprosy and TB
What is an endospore? Why does bacteria produce endospores?
Resistant, dormant (non-living) that has a durable coat around the DNA that is created in unfavorable conditions
How can an endospore be a virulence factor?
it can survive harsh conditions and preserves the bacteria’s genetic material. It lives in unfavorable conditions such as high heat, household disinfectants and can live 100s of years in dormant state
What are 2 diseases can be diagnosed using an endospore stain?
Anthrax, Botulism, and Tetanus
Of what value is the capsule to a bacterium?
Sugary/sticky layer that help it stick to the host. The body does not recognize it as foreign because of the sugar so the bacteria can hide from the white blood cells. The capsule is also a back-up food source for a bacteria.
Why does the capsule stain require both a negative stain and a basic stain?
The negative stain makes the background black, the basic stain makes the cell purple/pink, ad the capsule remains clear
What type of infections are generally caused by bacteria that have a capsule?
Respiratory
What causes the difference between nutrient media broth, nutrient media semi-solid and nutrient media solid?
The amount of agar
Lauria Bertain Agar (LBA) is used in lab for most experiments. The recipe is: 10g Tryptone, 5g Yeast Extract, 10g NaCl, 15g agar, 1L distilled water. Is this complex or chemically defined? How do you know?
Complex; there is yeast extract and extract or digest are not specific so it is not chemically defined
If you wanted to sterilize 3L of LBA how would you do it?
Autoclave at 121 degrees C with 15 PSI for 20 min
If you wanted to sterilize a liquid sample of heat labile antibiotic, how would you do it?
Bacteriologic filter