Carbohydrates
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:27 AM on 3/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
1
New cards
Example of high carb foods
Pasta, bread, potatoes, soft drinks
2
New cards
General functions of carbohydrates in living organisms
Makes energy/fuel for cell; storage
3
New cards
Monosaccharides
Simple sugars; monomers; serve as fuel for cells; energy: ATP; simplest type of carbohydrates
4
New cards
3 elements of simple sugars/ carbs
carbon, hydrogen, & oxygen
5
New cards
General formula of simple sugars
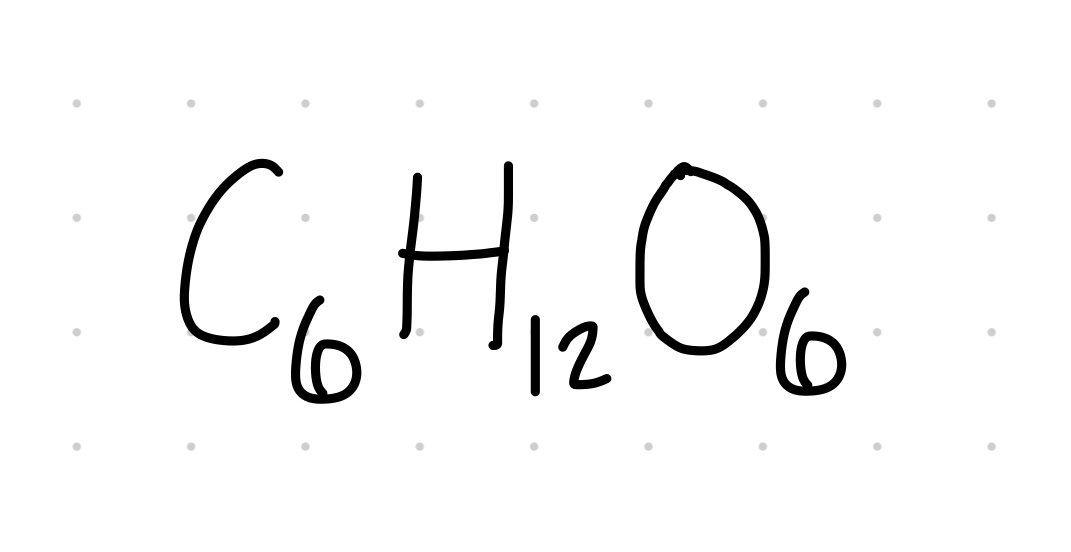
6
New cards
Compare # of C atoms to # of H atoms to # of O atoms
1:2:1
7
New cards
3 monosaccharides
Glucose, fructose, and galactose
8
New cards
Hexose sugars
Refers to monosaccharides with 6 carbons
9
New cards
Pentose sugars
Refers to monosaccharides with 5 carbons
10
New cards
Glucose
The simple sugar sugar (monossacharide) made by plants
11
New cards
Fructose
The simple sugar found in fruits
12
New cards
Galactose
The simple sugar found in milk “milk sugar”
13
New cards
What ending do most sugars have?
\-ose
14
New cards
Isomers
Two compounds that have the same chemical formula but different structures
15
New cards
3 Carbohydrate isomers
Glucose, Fructose, & Galactose
16
New cards
Aqueous
Watery or dissolves in water
17
New cards
Ring Structures
Formed when simple sugars, monosaccharides are put into aqueous solutions inside cells. (Cells have a lot of water in them)
18
New cards
Disaccharide
Double sugar formed by combining 2 monosaccharides through dehydration synthesis
19
New cards
3 common disaccharides
Sucrose, Maltose, & Lactose
20
New cards
Sucrose
Table sugar formed by glucose & fructose
21
New cards
Lactose
Milk sugar formed by galactose & glucose
22
New cards
Malatose
Grain sugar formed by glucose & glucose
23
New cards
Polysaccharides
Complex carbohydrates made of chains of monosaccharides
24
New cards
4 polysaccharides important to living organisms
starch, glycogen, cellulose, chitin
25
New cards
Starch
Carbohydrate energy/stored molecules in plants; found in some foods
26
New cards
Monomer (monosaccharide) for starch
Glucose
27
New cards
Glycogen
Carbohydrate storage/energy molecules in animals (the liver)
(short term energy storage; carb-loading)
(short term energy storage; carb-loading)
28
New cards
Monomer (monosaccharide) for glycogen
Glucose
29
New cards
Cellulose
Makes up structural component in plants and serves as dietary fiber in animals
CAN NOT BE DIGESTED BY HUMANS
CAN NOT BE DIGESTED BY HUMANS
30
New cards
Monomer (monosaccharide) for cellulose
Glucose
31
New cards
Can humans digest cellulose
NO
32
New cards
How can cows digest fiber?
They have bacteria in their digestive tracts that can break down cellulose
33
New cards
Chitin
found in the exoskeleton of insects and found in the cell walls of fungi which cannot be digested by humans
34
New cards
Monomer (monosaccharide) of Chitin
Glucose & nitrogen containing compound
35
New cards
Peptoglycan
Polysaccharide found in bacteria makes up cell wall (gram + thicker & more peptoglycan; gram - thinner & less peptoglycan)
36
New cards
What type of carbohydrate compound isn’t hydrophilic?
Polysaccharides
37
New cards
Hydrophilic
“water loving”
38
New cards
Oligosaccharides
Identifies for the cell, short: 3-10 monosaccharides long, attaches to a protein/lipids outside of the cell mb
39
New cards
What happens if you hydrolyze a starch molecule
Glucose
40
New cards
What happens if you hydrolyze a glycogen molecule
Glucose
41
New cards
What happens if you hydrolyze a sucrose molecule
Glucose & fructose
42
New cards
What happens if you hydrolyze a cellulose molecule?
Glucose
43
New cards
What happens if you hydrolyze a lactose molecule
Glucose & galactose
44
New cards
What happens if you hydrolyze a malatose molecule
glucose & glucose
45
New cards
What molecules cannot be hydrolyzed by the digestive system of most animals?
cellulose & chitin