Immunology Exam 1
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Protection and Repair
2 functions of immune system
Innate
Define
Adaptive
Define
Specificity (clonal expansion of specific cells only when that antigen detected, otherwise removed and only memory cells remain)
Diversity (have antibodies for stuff we never encountered)
Memory (can re-incounter same pathogen and have faster immune response)
3 key features of adaptive immunity
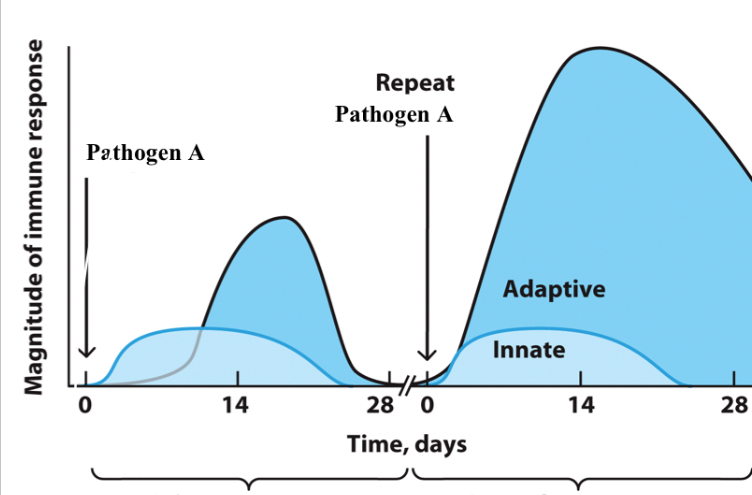
Primary response
Imitated upon first exposure to an antigen
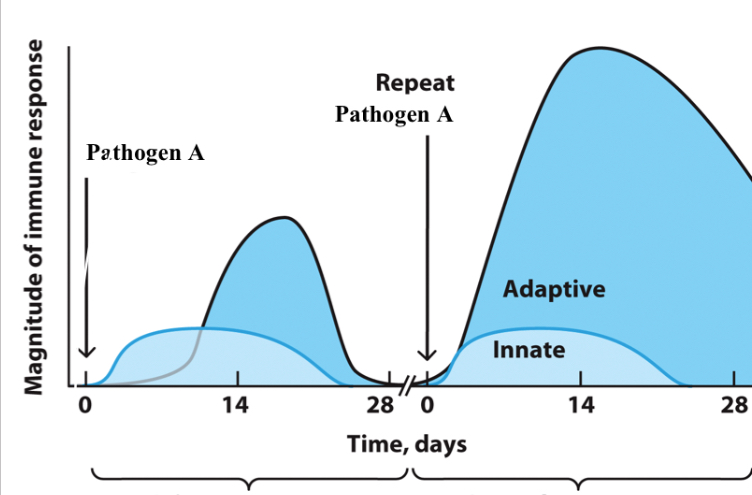
Secondary response
Initiated upon second exposure to the same antigen that stimulates memory lymphocytes
Overly active (allergies/asthma, autoimmune diseases, autoinflammatory diseases)
Immunodeficiency (AIDS, oral thrush, primary/genetic loss of immune function, secondary/acquired loss of immune function)
Dysfunctions of immunity (broadly) and examples
cancer
a situation where the dangerous cells we want to target are our own self-cells , generally tolerated and hard to generate immunity against
innate
adaptive
adaptive
adaptive
Label a-d
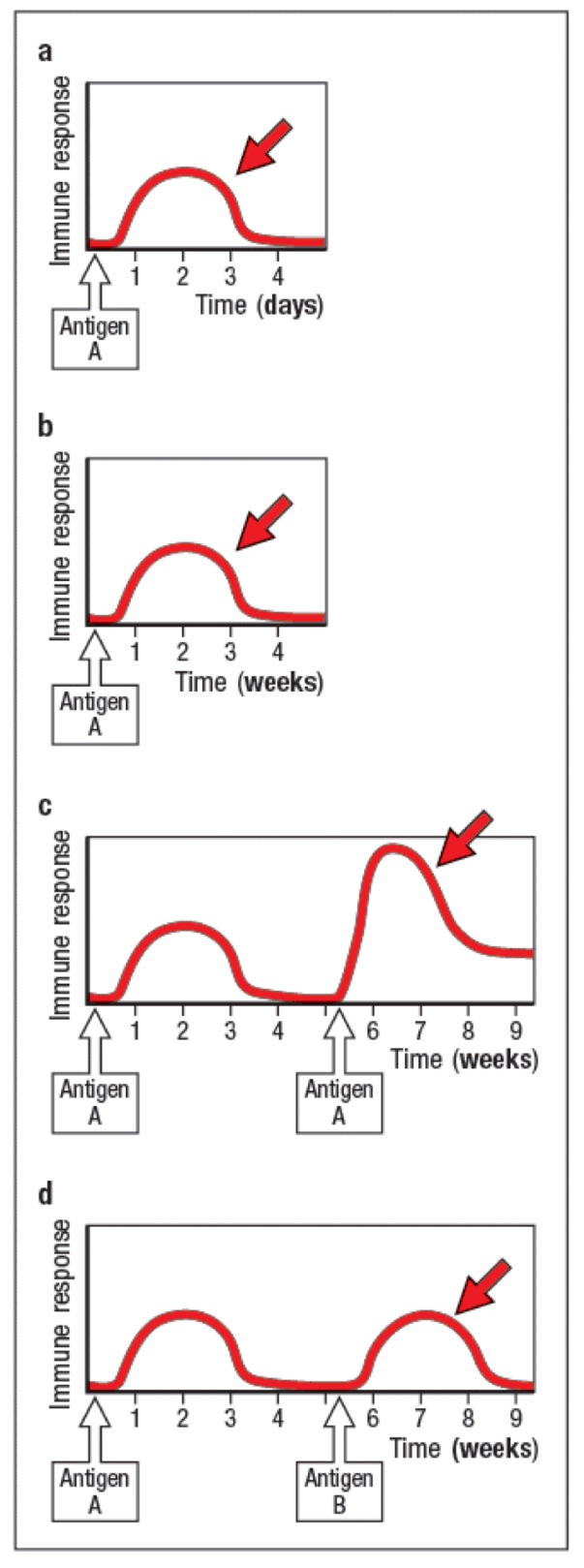
innate
adaptive
How is recognition mediated in immunity?
_
_
innate
_ immunity
germ-line encoded (Pattern Recognition Receptors - PRRs)
bind to Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns (PAMPs)
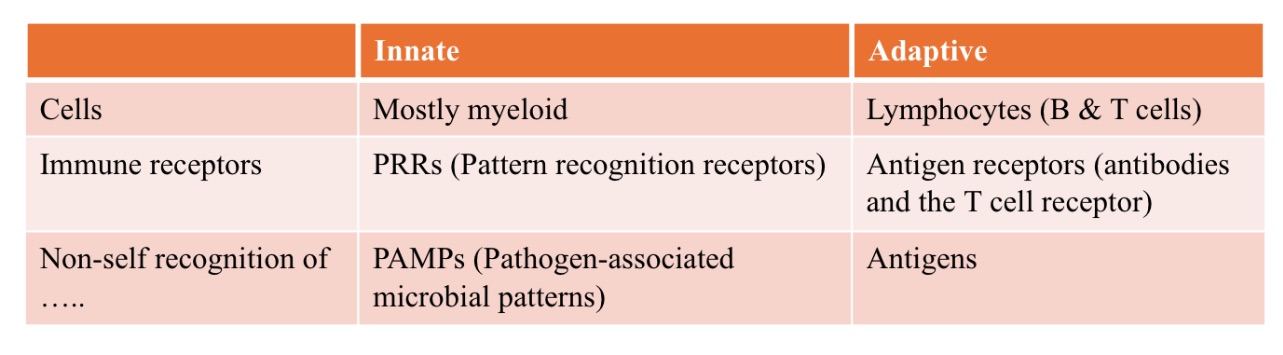
PAMPs
commonly shared structures found on many different types of pathogens (ex., peptidoglycan)
adaptive
_ immunity
Randomly generated (B- and T-cell receptors)
Bind to very specific antigens
(rather than shared molecules found on many pathogens)
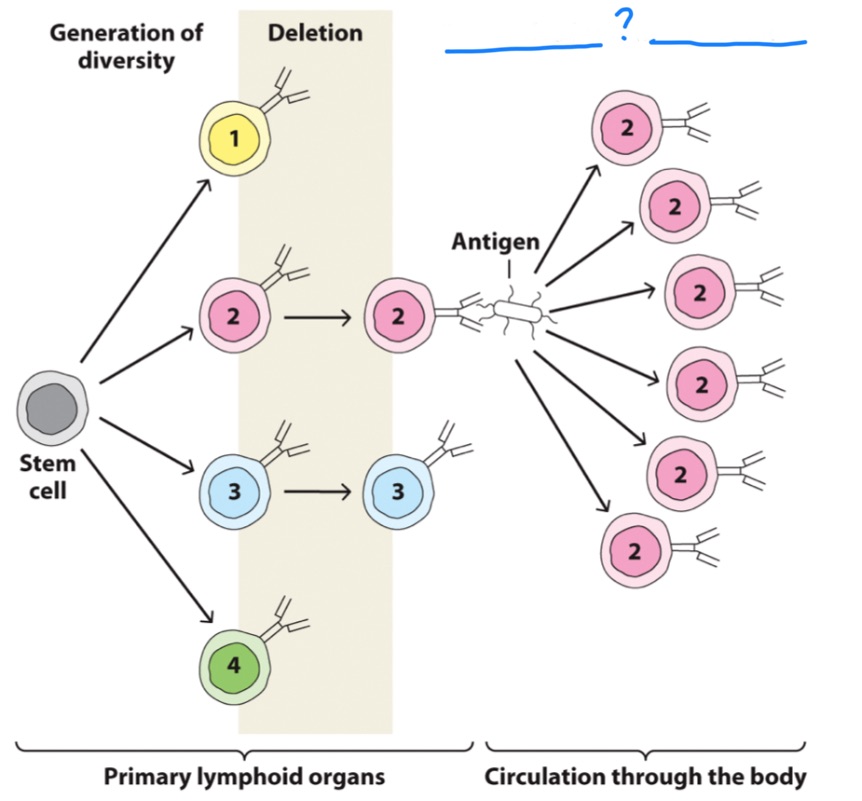
Clonal selection and expansion
Name of process
microflora
Commensal organisms that live in and on us that cause no harm
Function in metabolic and immune balance (homeostasis)
Imbalance or dysbiosis —> immune stimulation —> inflammation
by dietary changes or environmental stress factors
flora = bugs themselves
biome = genome of ^
microflora vs microbiome
Neutrophils,
Lymphocytes,
Monocytes,
Eosinophils,
Basophils
five main types of white blood cells (leukocytes):
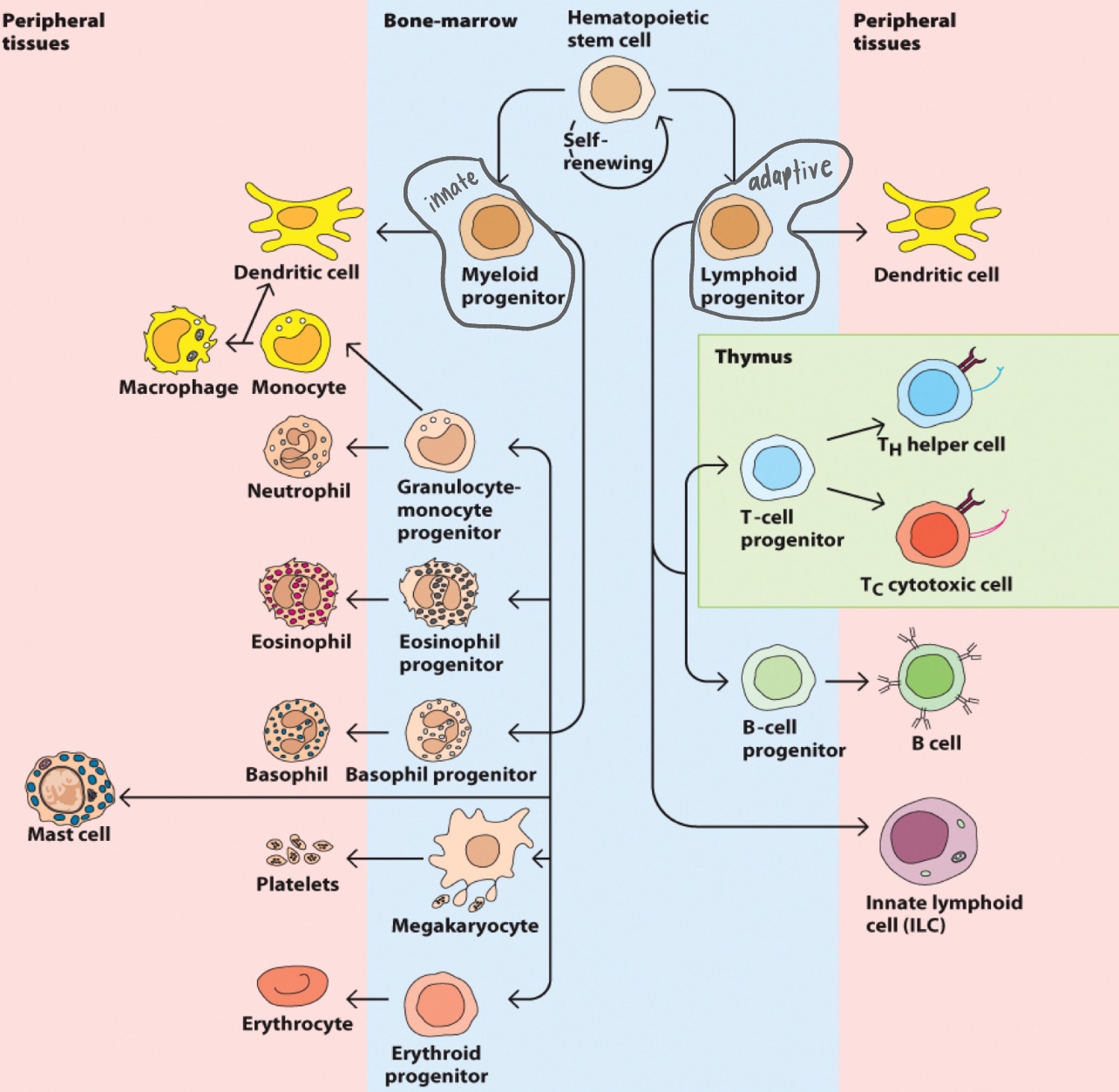
hematopoesis
formation of blood cellular components
RBCs
Monocytes
Granulocytes
neutrophils
basophils + mast cells
eosinophils
Megakaryocytes
Cells of the innate response
Common myeloid progenitors
(premature monocytes)
+
neutrophils
basophils + mast cells
eosinophils
Granulocytes
direct harm to pathogens, don’t need to be “activated,” first on site
inflammation/allergies
antiviral activity, antiparasitic activity
Monocytes
Migrate into tissues and differentiate into macrophages (function to repair/remodel, destroy pathogens, present antigens)
dendritic
Monocytes differentiate into _ cells, which function as presenters of antigens to naïve T lymphocytes for a primary response
phagocytosis ; present antigens
Macrophages are specialized for _, and can _ _ to T cells
antigen ;
APCs
Immature dendritic cells capture _, then mature and migrate out to present antigen to T cells.
They are the most effective _ for activating naïve T cells
DRAINING lymph nodes ;
APCs
Injury in big toe:
Immune cells are in _.
_ in toe migrate to ^, “calling and describing” injury to (CD4+) T cells
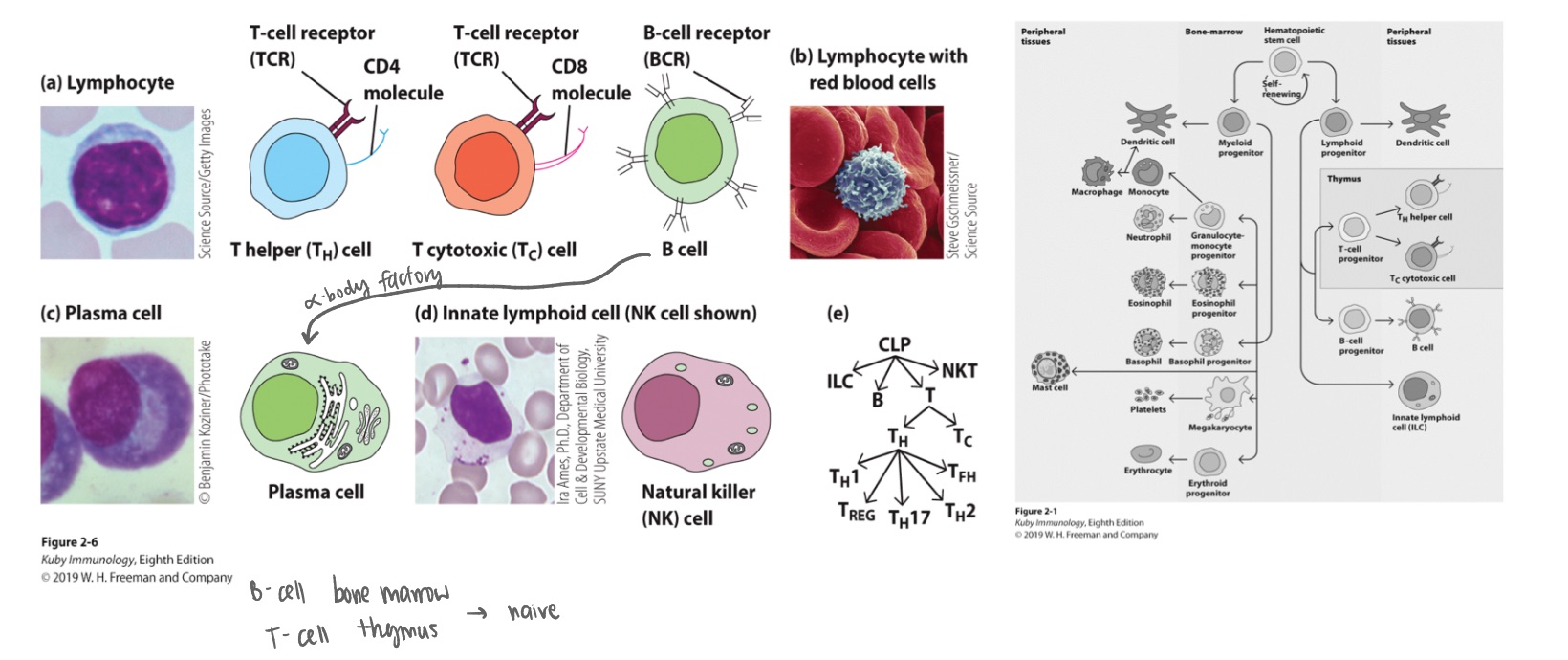
B lymphocytes (expressing diff antibodies)
T lymphocytes (like CD4+ and CD8+)
NK cells (innate lowkey)
Adaptive Immune System:
Common lymphoid progenitors:
Helper ; activating ; II
Cytotoxic ; I
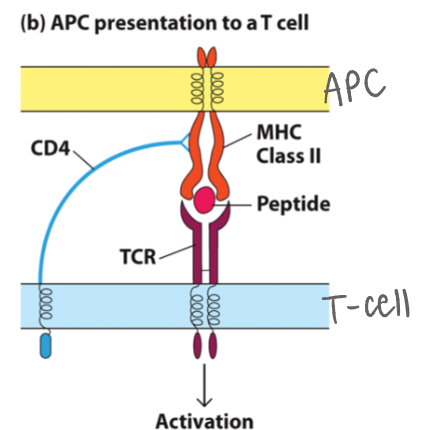
CD4+ vs CD8+ T cells:
CD4+ _ T cells coordinate immune responses by _ other cells (B cells, macrophages, CD8s) and recognize antigens on MHC Class _ molecules. - first (adaptive) responders
CD8+ _ T cells directly kill infected or cancerous cells by recognizing antigens on MHC Class _ molecules, acting as direct killers
CD3
_
Universal marker for all T cells.
Signal transduction element of T-cell receptor.
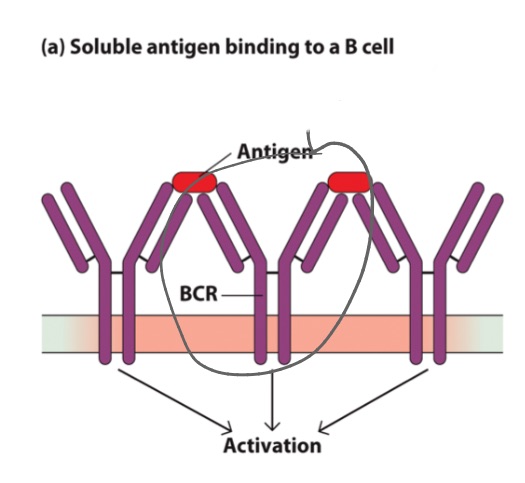
BCR
in _s, antibody is retained on surface
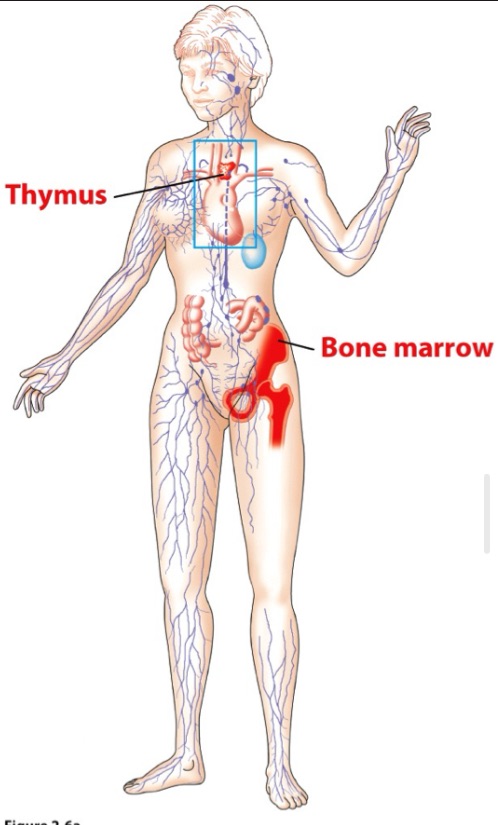
Bone marrow and Thymus
2 primary lymphoid organs are
_
_
leukocytes
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) are self-renewing and differentiate into mature _
Stromal cells facilitate HSC proliferation, direct migration, and stimulate differentiation
bone marrow ; thymus
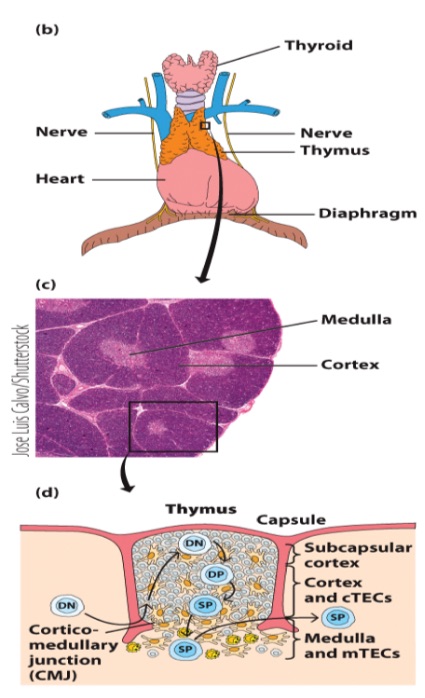
T cells develop initially in the _ but then migrate to the _ to achieve full maturity.
the microenvironment of the thymic cortex and medulla directs stepwise changes in thymocytes
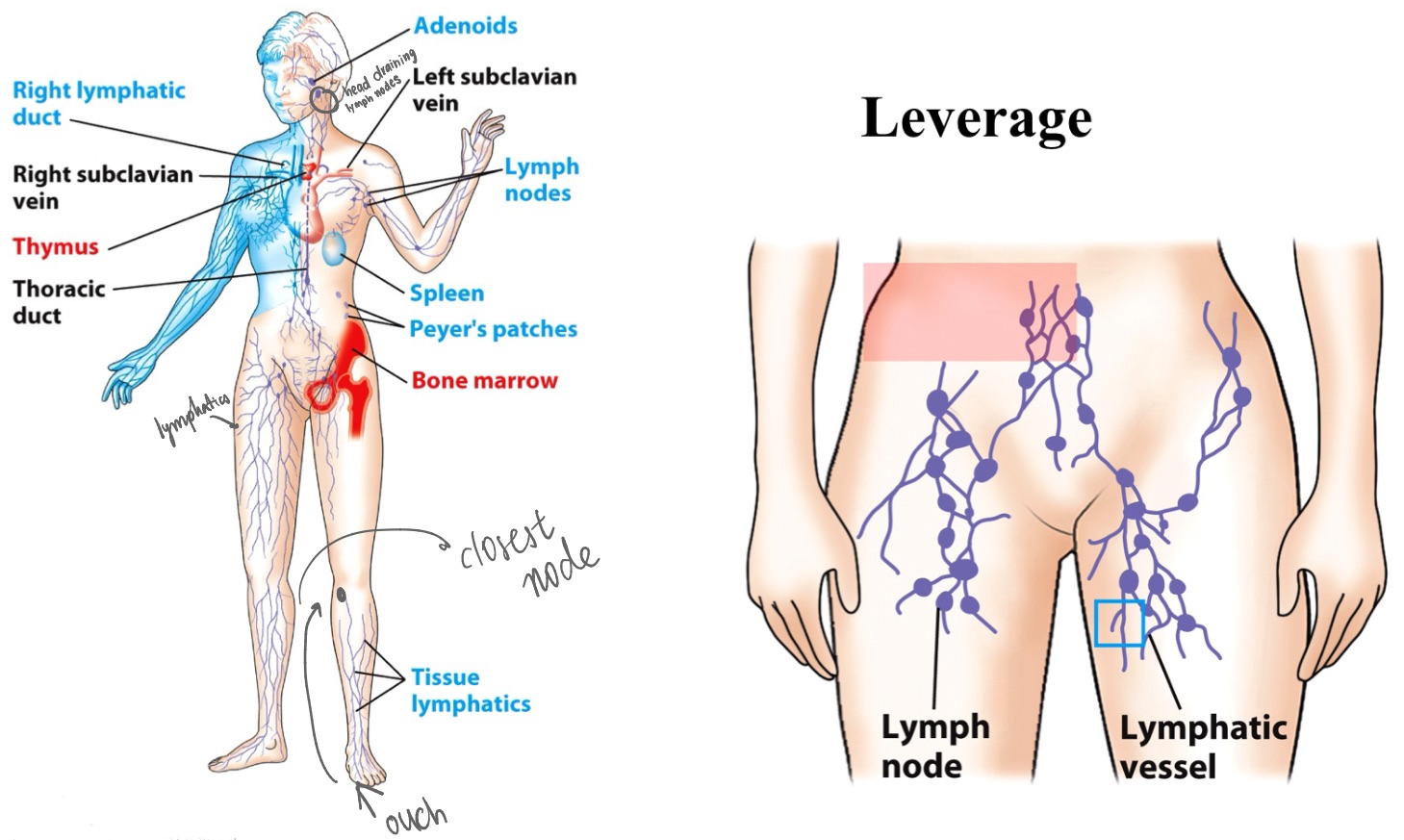
MALT
(mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue, lymph nodes, spleen)
Secondary lymphoid organs - where immune cells respond:
Connected to each other via blood & lymphatic circulatory systems
Lymphocytes
_ (cell type)
encounter antigens
activated
clonal expansion
specialize into effector cells
lymph nodes
_ are bean-shaped areas of tissue that filter fluid in your body (lymph) for harmful substances or cells.
Immune cells here remove germs, damaged cells and cancer cells. Lymph moves from lymph vessels to here for filtering before the fluid goes back into your blood.
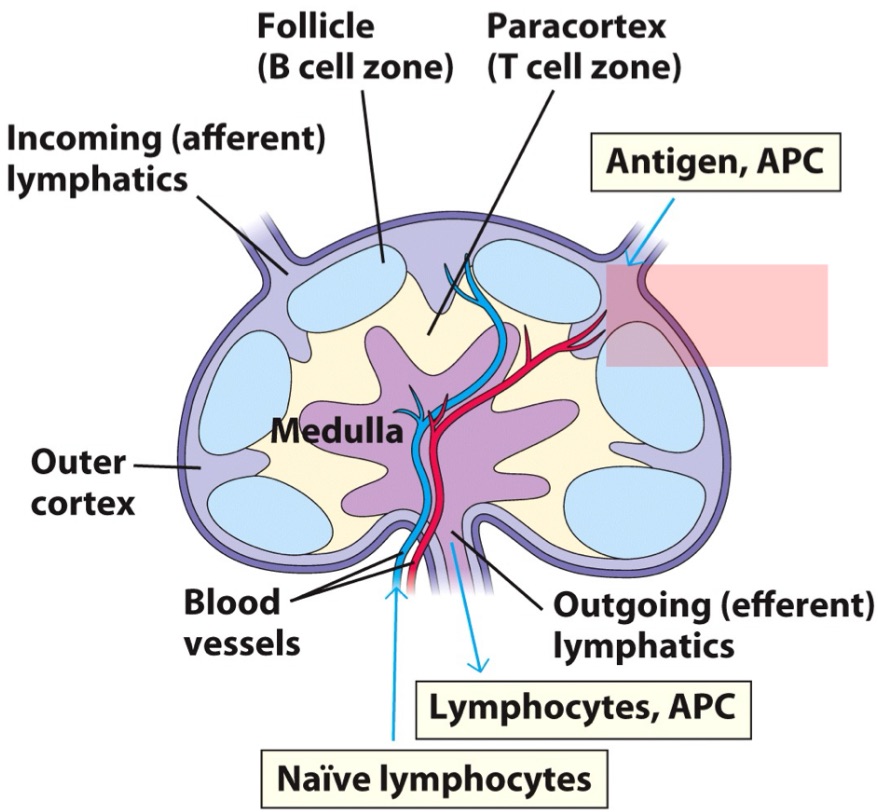
T cells ; APCs
Fibroblastic reticular cells (FRCC) guides _ and _ migration
Specialization occurs in follicles
B cells: clonal expansion in germinal centers.
CD4+ T cells: Specialize into distinct helper T cells that orchestrate the response.
CD8+ T cells: Specialize into cytotoxic T cells.
Spleen
Marginal Zone
_ (organ)
draining “lymph node” for blood
first line of defense against bloodborne pathogens
RBCs are compartmentalized in RED pulp
WBCs are compartmentalized in WHITE pulp
Specialized region for macrophages and B cells is the _, bordering the white pulp
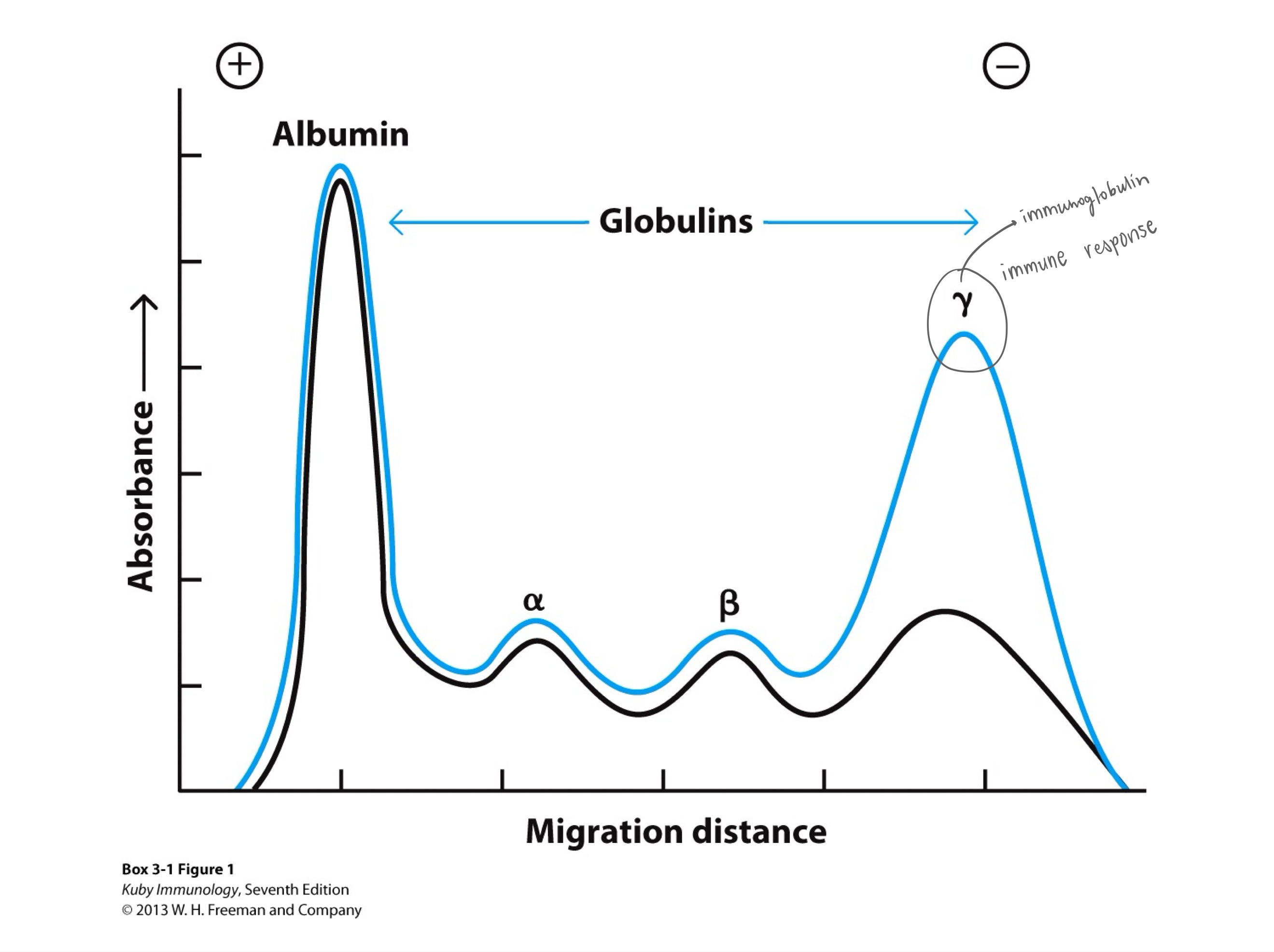
albumin
An albumin/globulin graph from protein electrophoresis shows blood proteins separated by size/charge,
with a large _ peak (transport/oncotic pressure) followed by smaller peaks:
alpha-1 (AAT), alpha-2 (haptoglobin),
beta (transferrin/lipoproteins),
and a broad gamma (antibodies/immunoglobulins) region,
indicating inflammation (broad gamma/alpha-2) or specific disorders (narrow M-spike for myeloma), with shapes revealing health status.
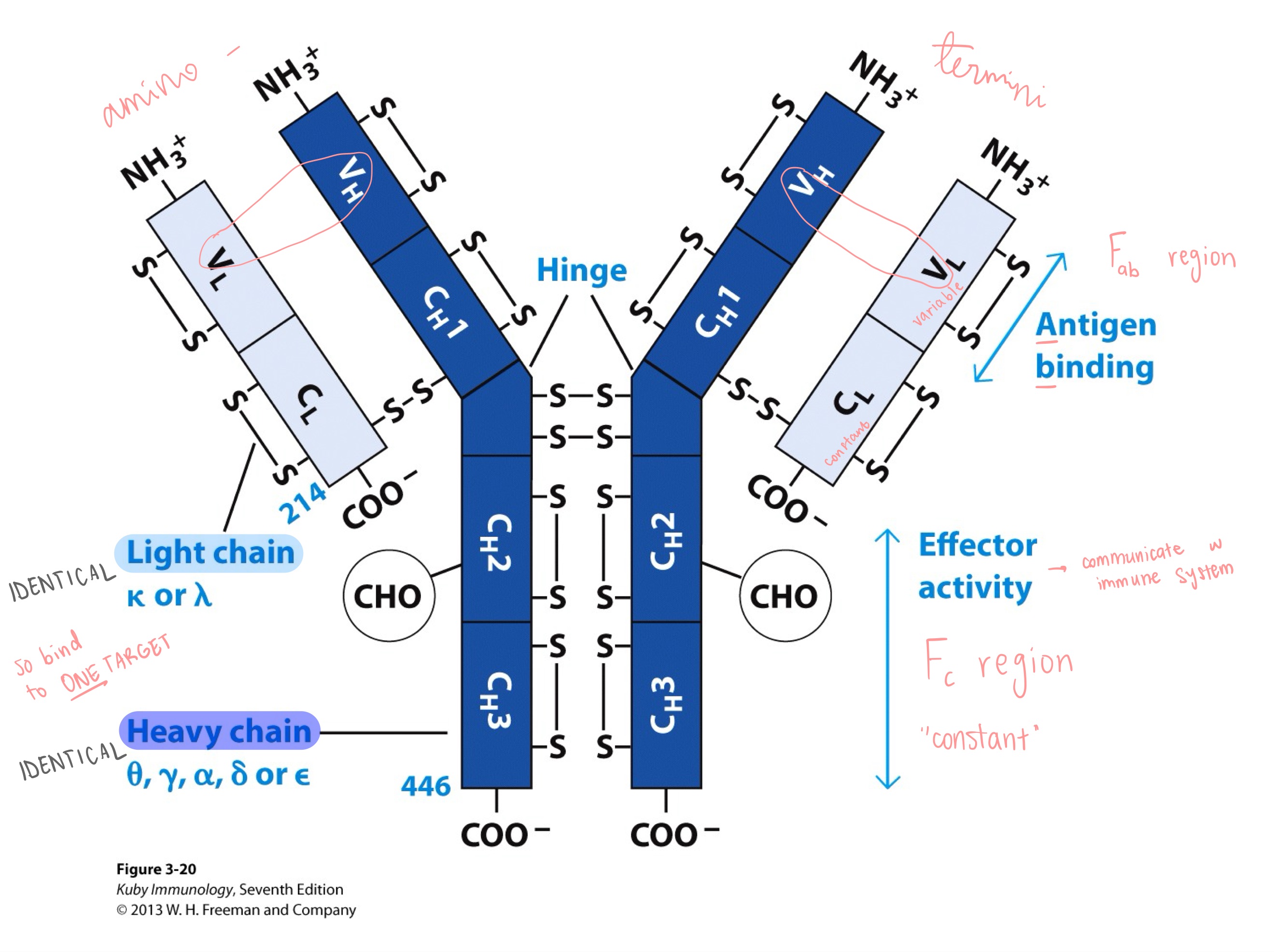
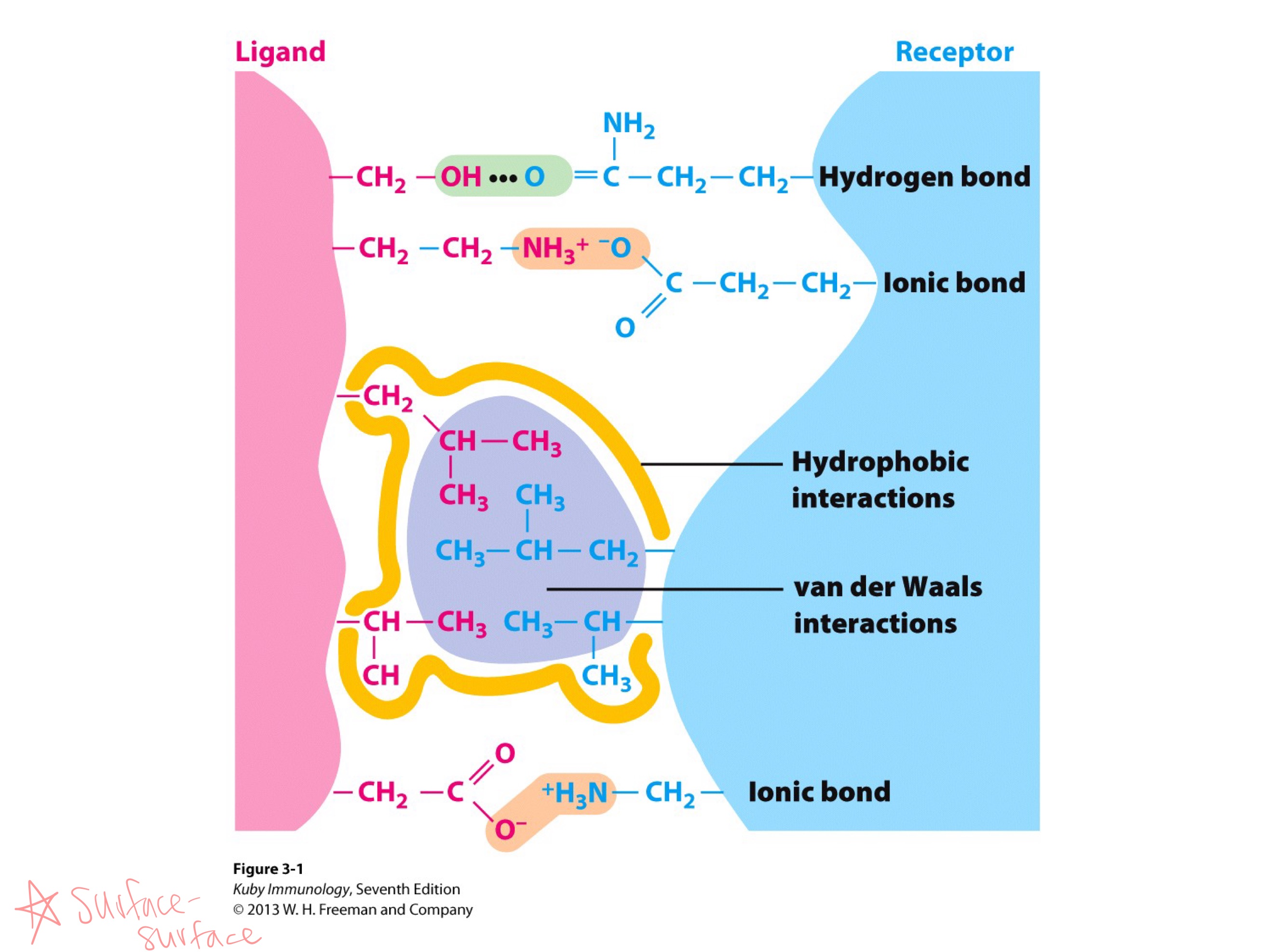
both variable and constant regions
constant region (only)
Fab region has _
Fc region _
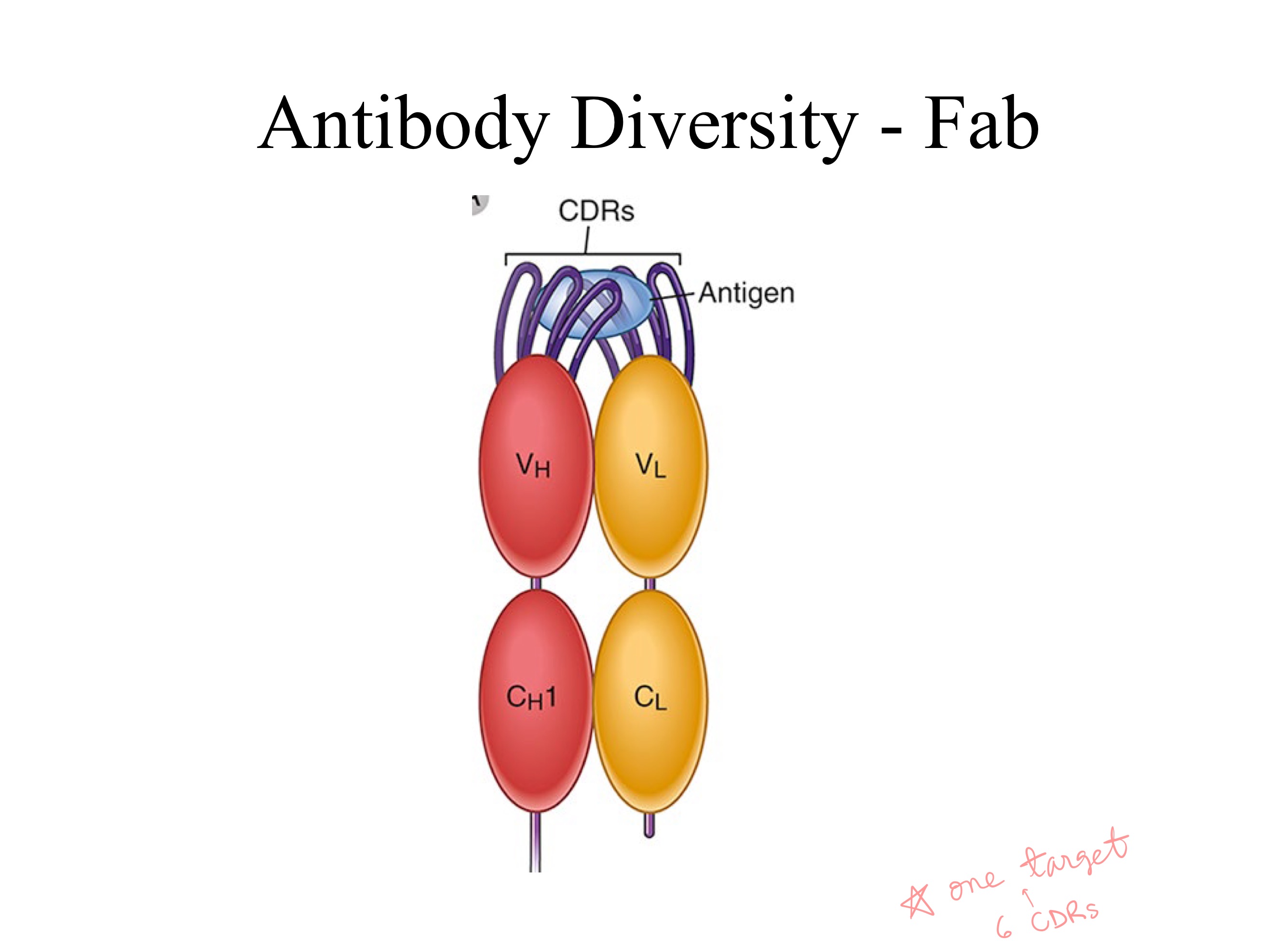
CDRs ; 6 (3 light , 3 heavy)
On an antibody, which regions have highest variablility?
How many total ^ regions?
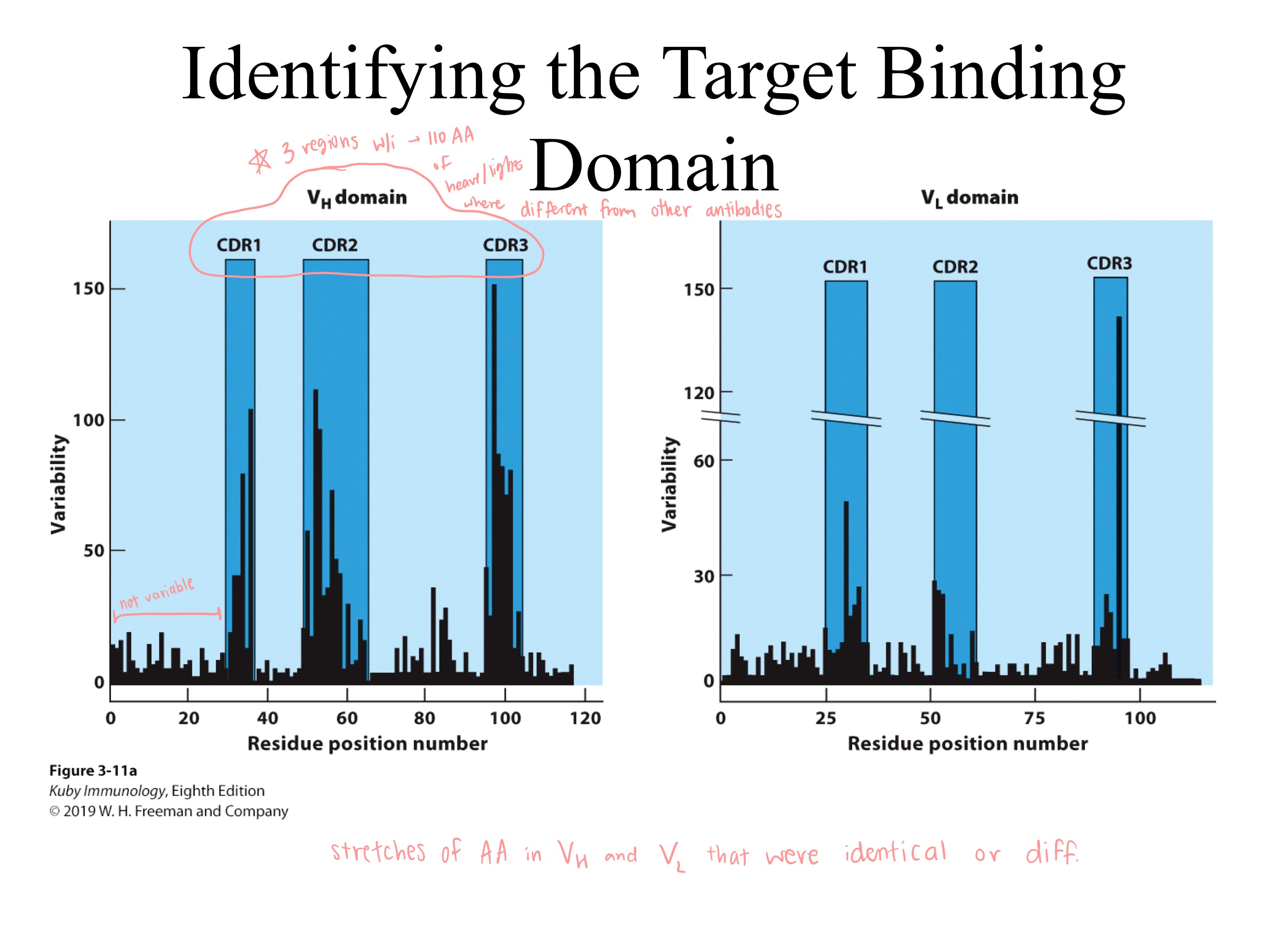
CDRs ; immunoglobulin
_ are all close to each other, and _ are in loops
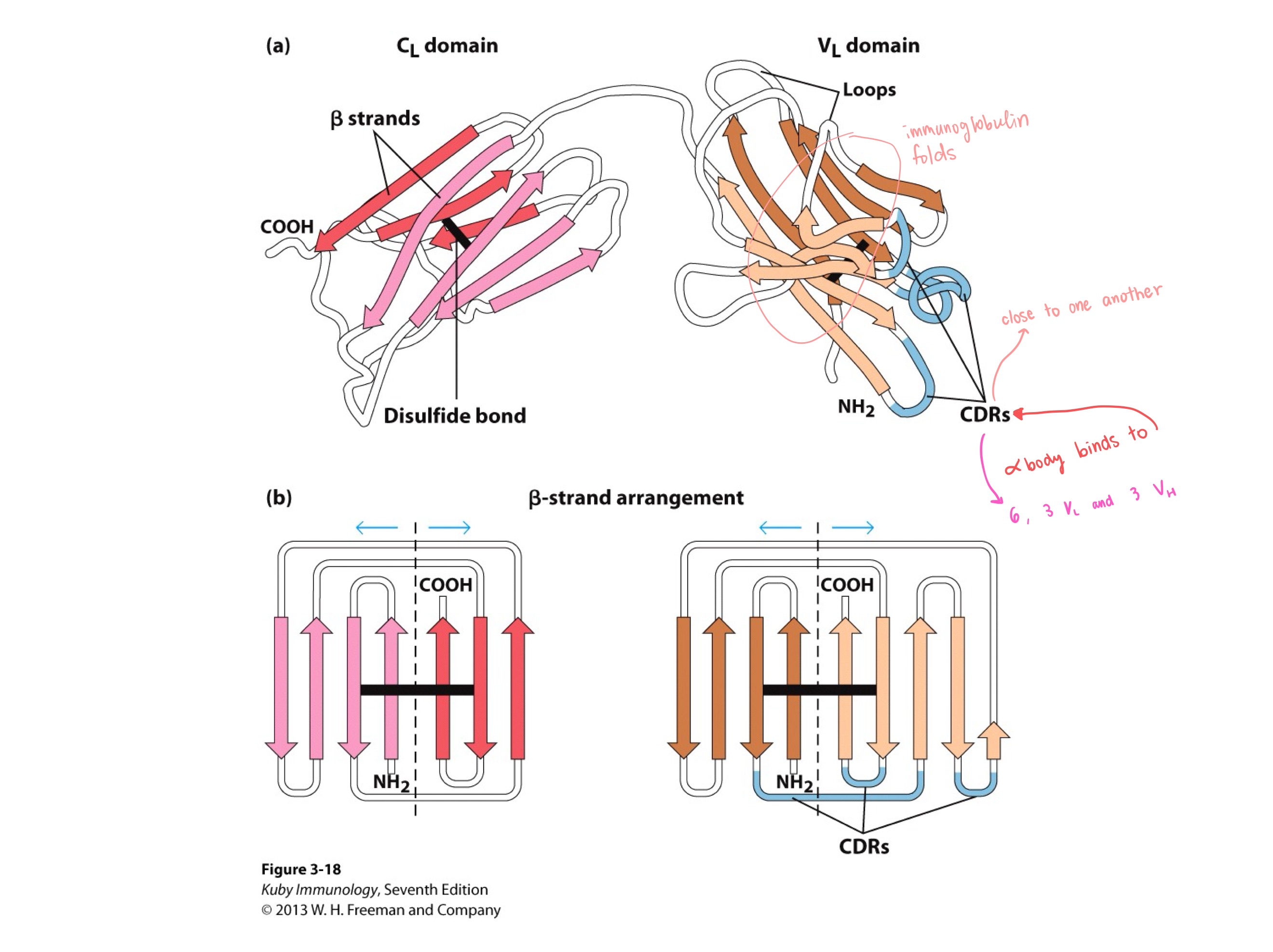
all 6
_ CDRs bind to ONE antigen
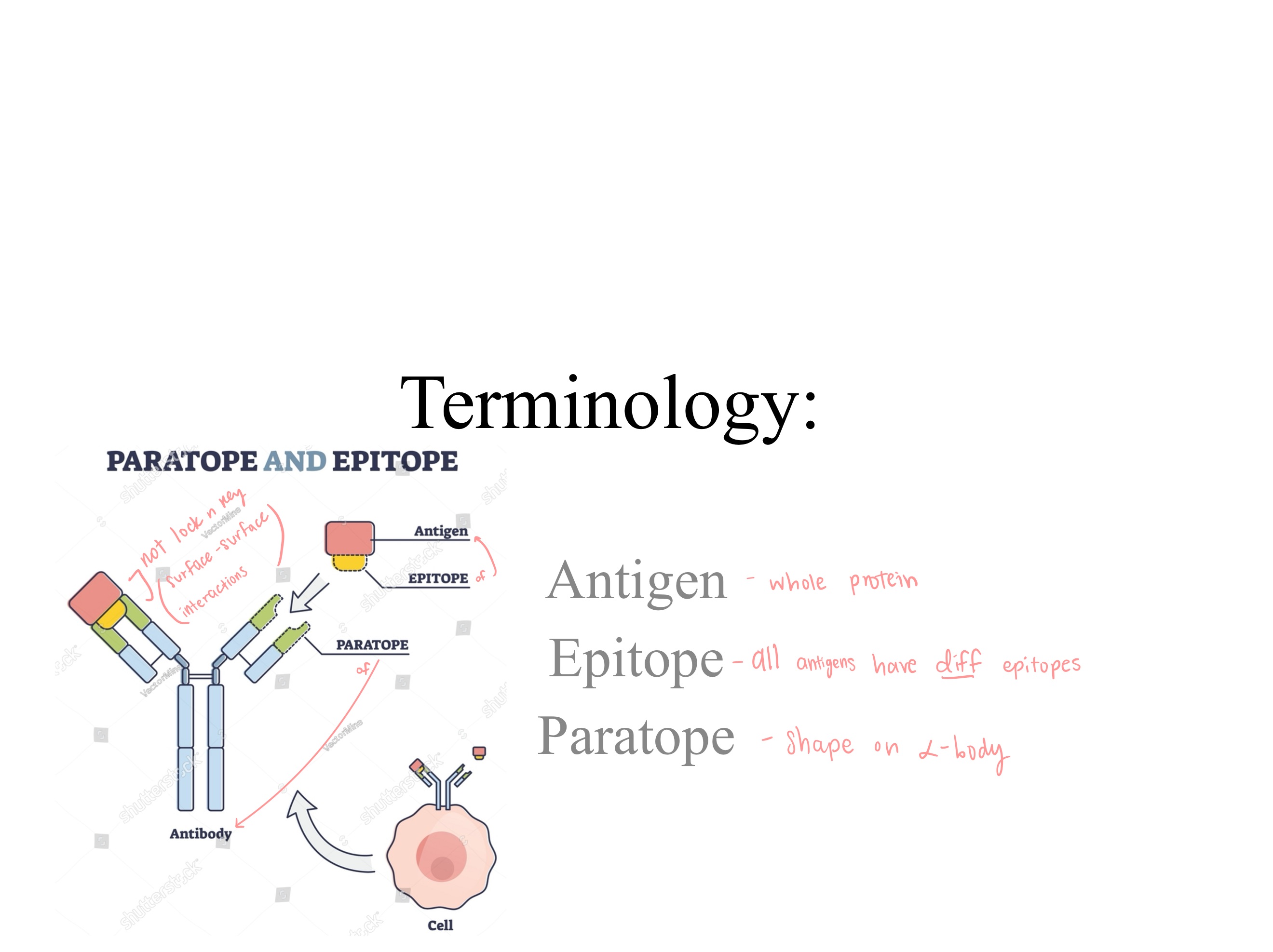
epitope ; paratype
The _ on the antigen binds to the _ on the antibody
antibody ; antigen
right side is _
left side is _
2
lock and key
orsurface-surface interaction
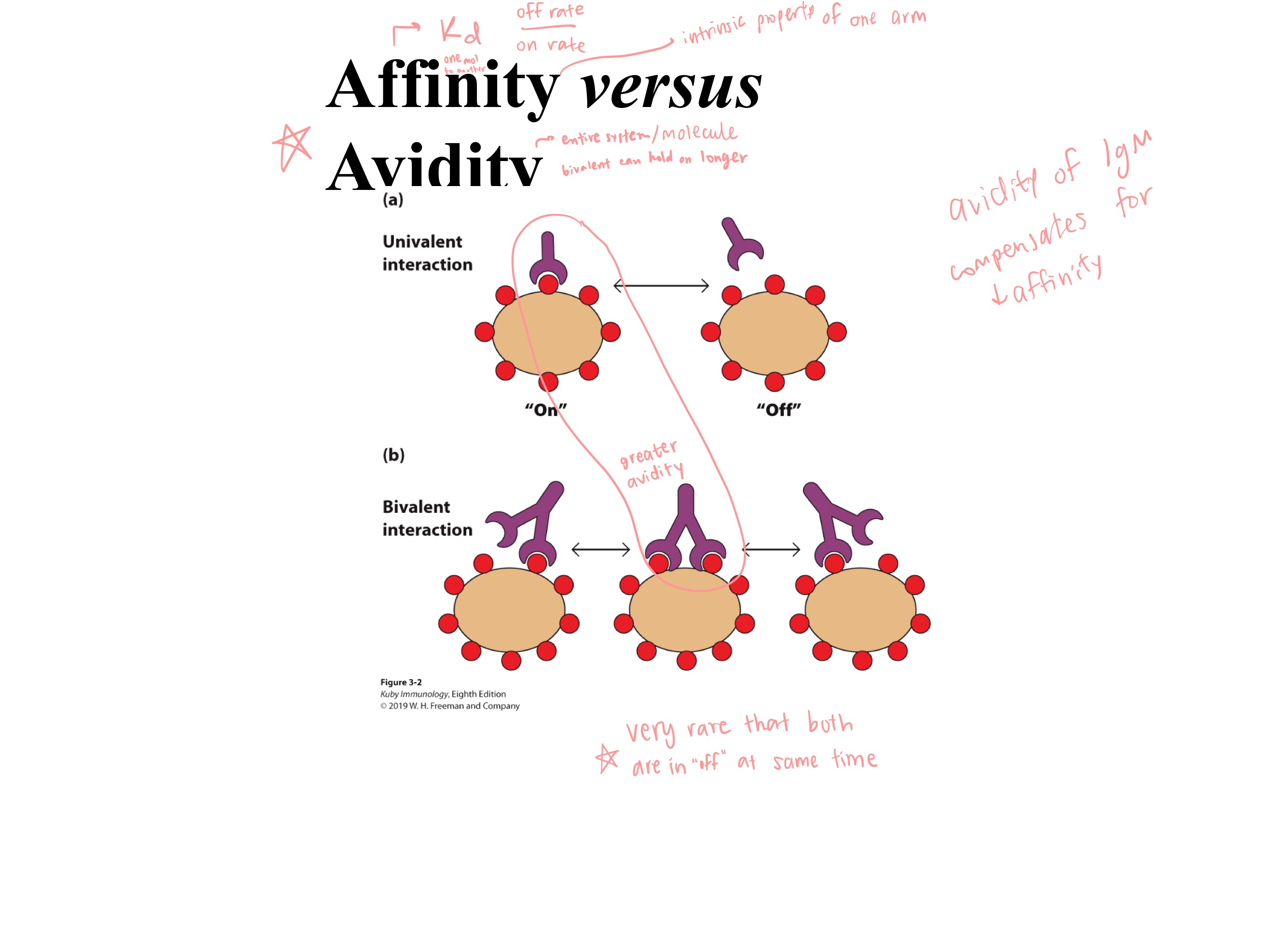
affinity
avidity
_ is an intrinsic property of “one arm” of antibody
_ is of the entire system/molecule
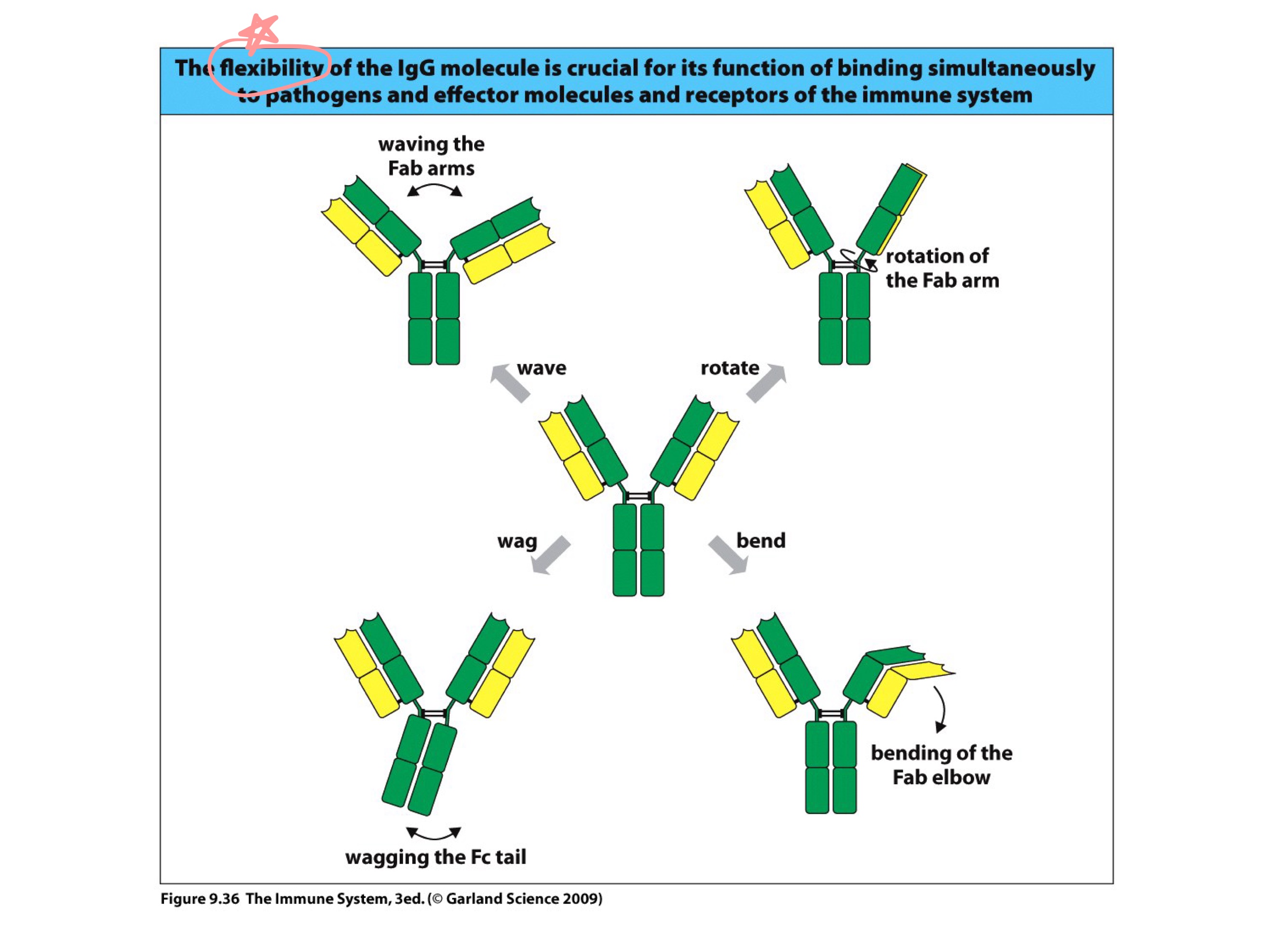
flexible
antibodies are _
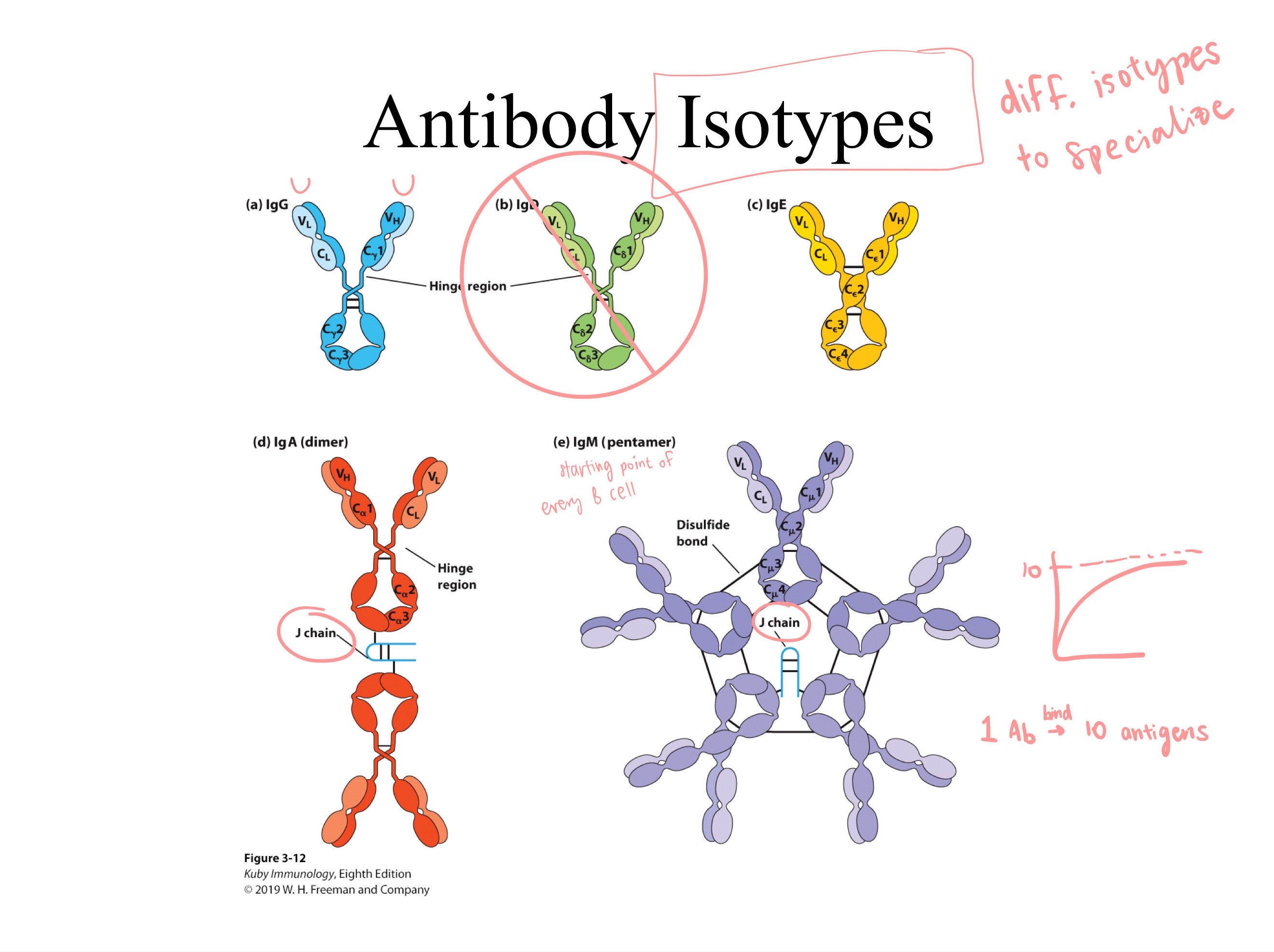
G, D, E, A, and M
A and M (can pass epithelial)
Antibody isotypes:
Which 2 have J chains?
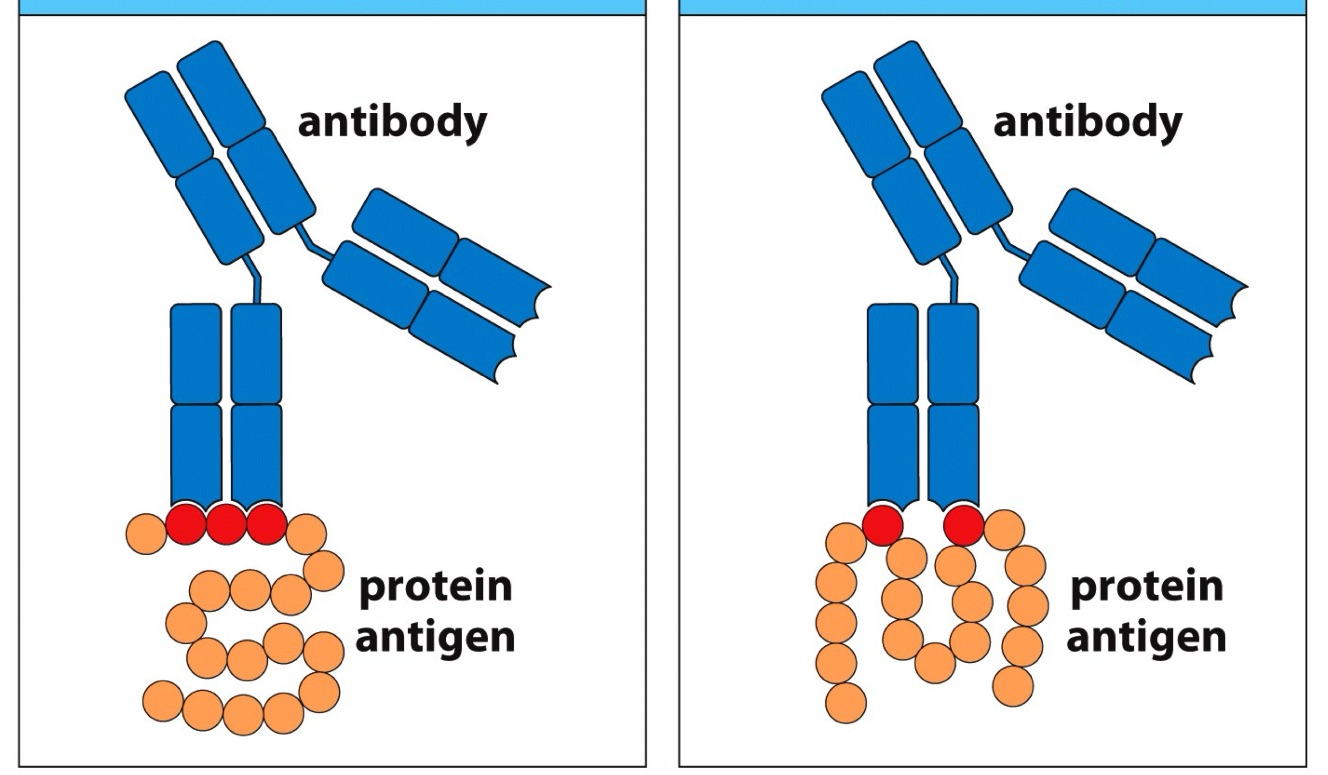
Linear v Conformational Epitope
Name L —> R
antigen
immunogen
_ and _
(in order)

NO
(need to be with carrier - large protein!!)
Can haptens alone cause immune response?
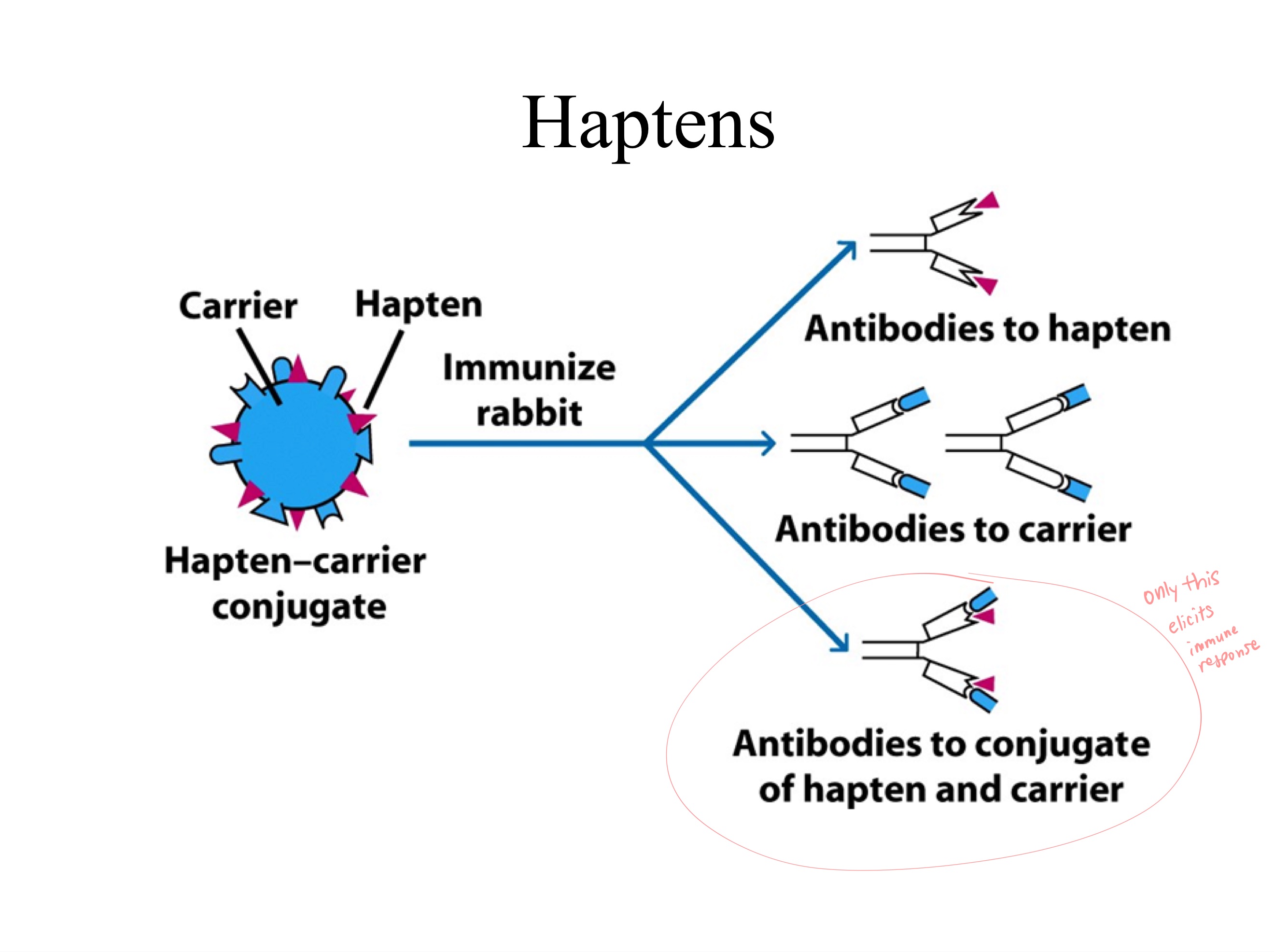
albumin (protein)
example of carrier
surface
BCRs have receptors on _
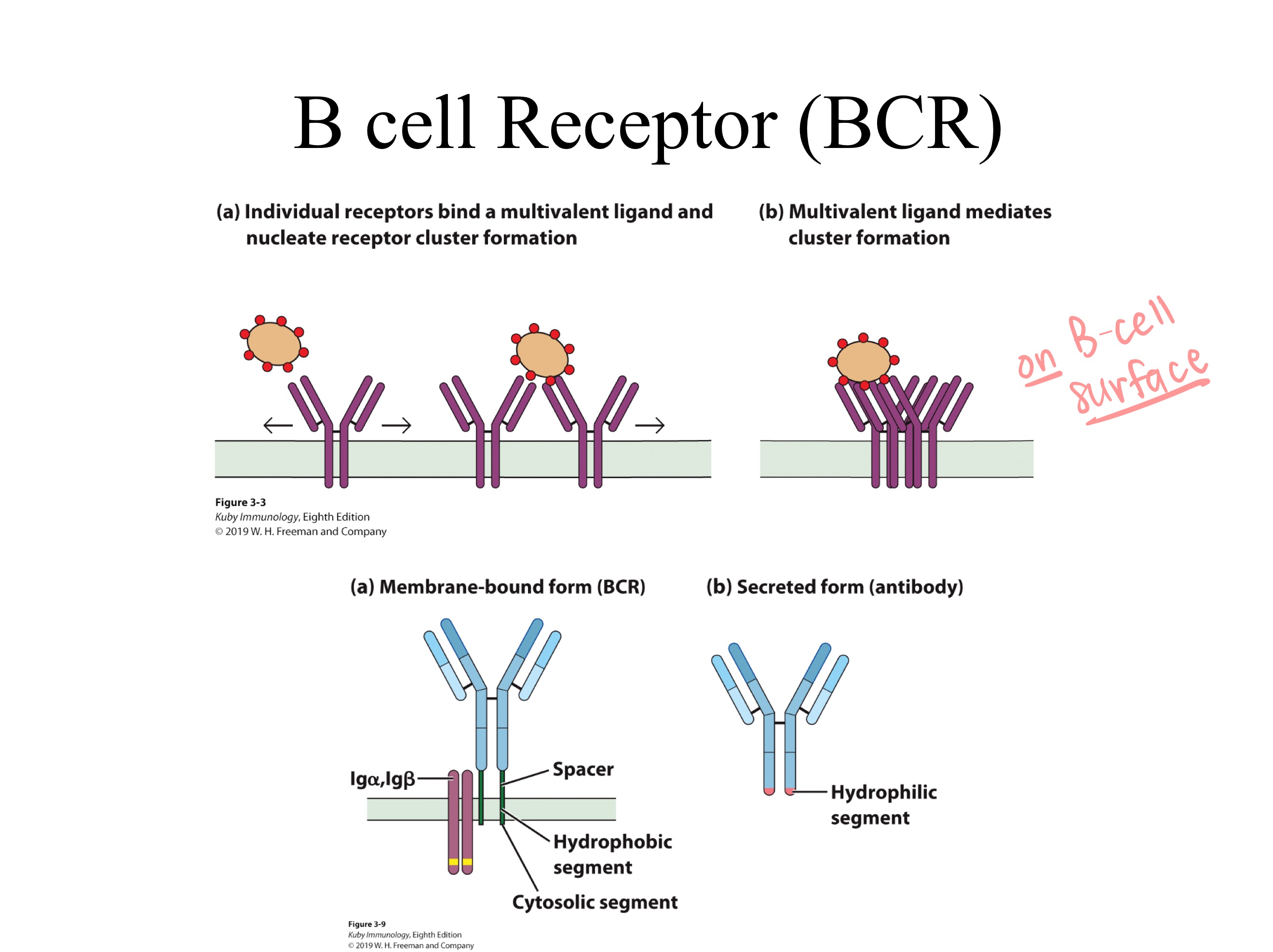
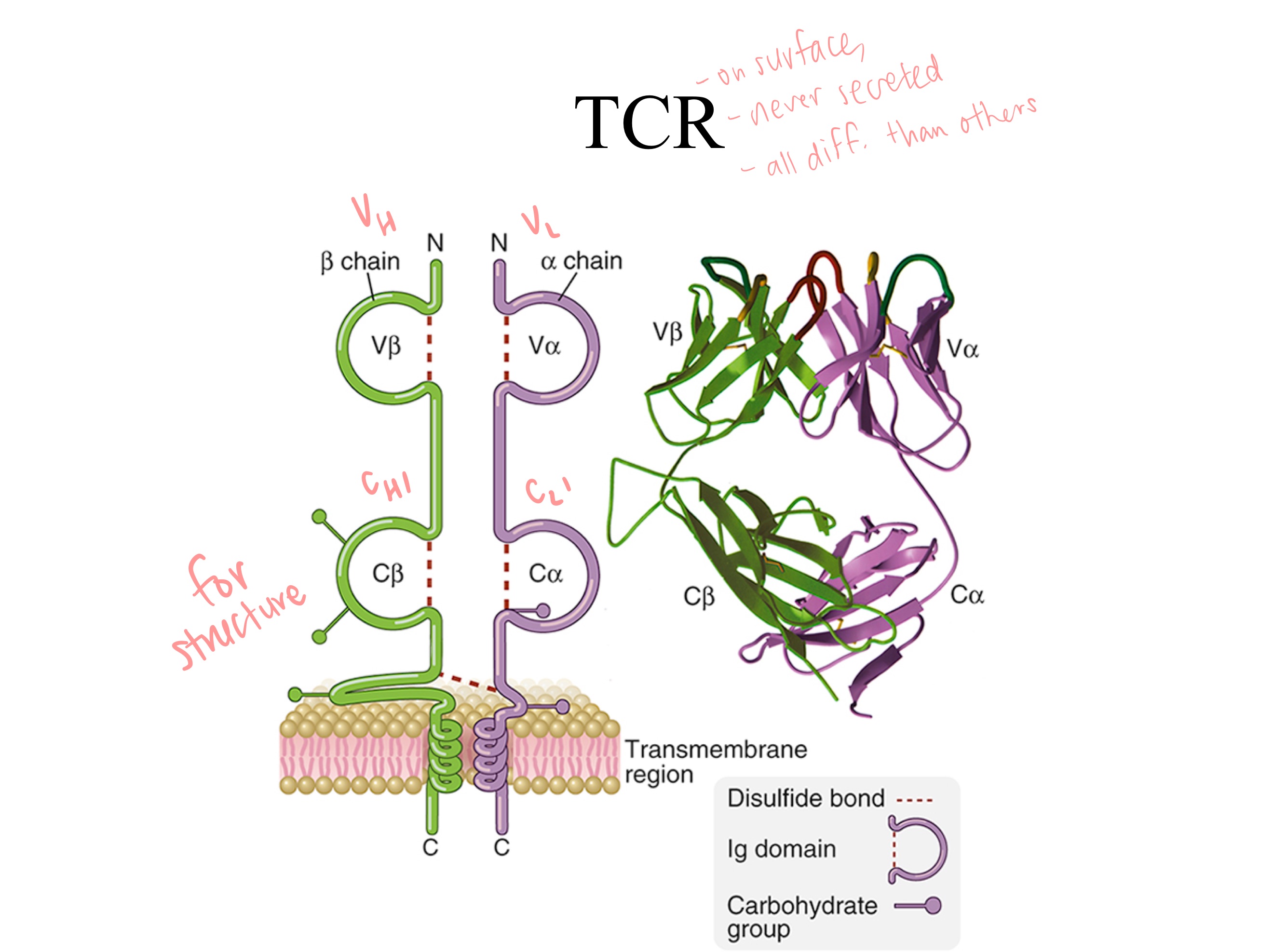
Remove Fc ; add transmembrane region
(KEEP Fab = VL , VH , CL , CH1)
(Fc is what communicates w immune sys., not needed bc TCR is on T cell surface)
If you were to use an antibody as a template for a molecule with high diversity and specificity, how might you model the TCR from the antibody structure?
If 10 epitopes, but only 1 binds to pathogen, then other 9 might bind to self
(If one cell recognized multiple epitopes (e.g., self and foreign), it would be much harder for the immune system to regulate and prevent self-reactive, harmful cells.)
Why only 1 B-cell with 1 epitope, not multiple, like 10 epitopes on a single B-cell?
Subtractive hybdrization
How might you use the similarity btwn a B cell and T cell to isolate genes for TCR?
20,000 ; 4,000
There are about _ genes on a chromosome, and _ are ON in a cell
CDRs ; paratope
(Complementary-determining regions)
_ are short, hypervariable amino acid loops within the variable domains of antibodies and T-cell receptors that directly bind to antigens.
As the key determinants of antigen specificity, the six (three on heavy, three on light chains) form a _.
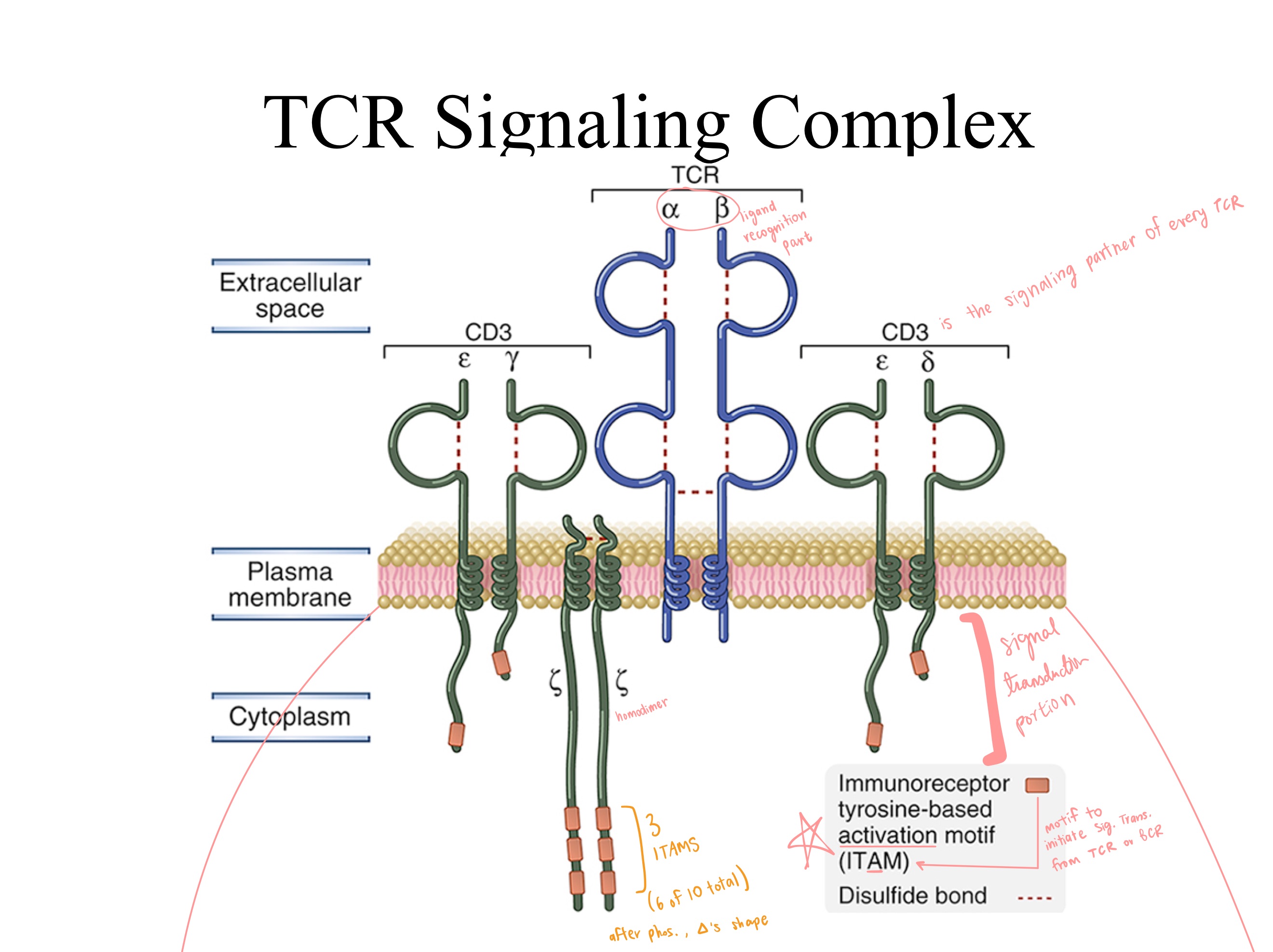
alpha ; beta
ITAMs
homodimer ; 3 ; 6
ITAM
CD3
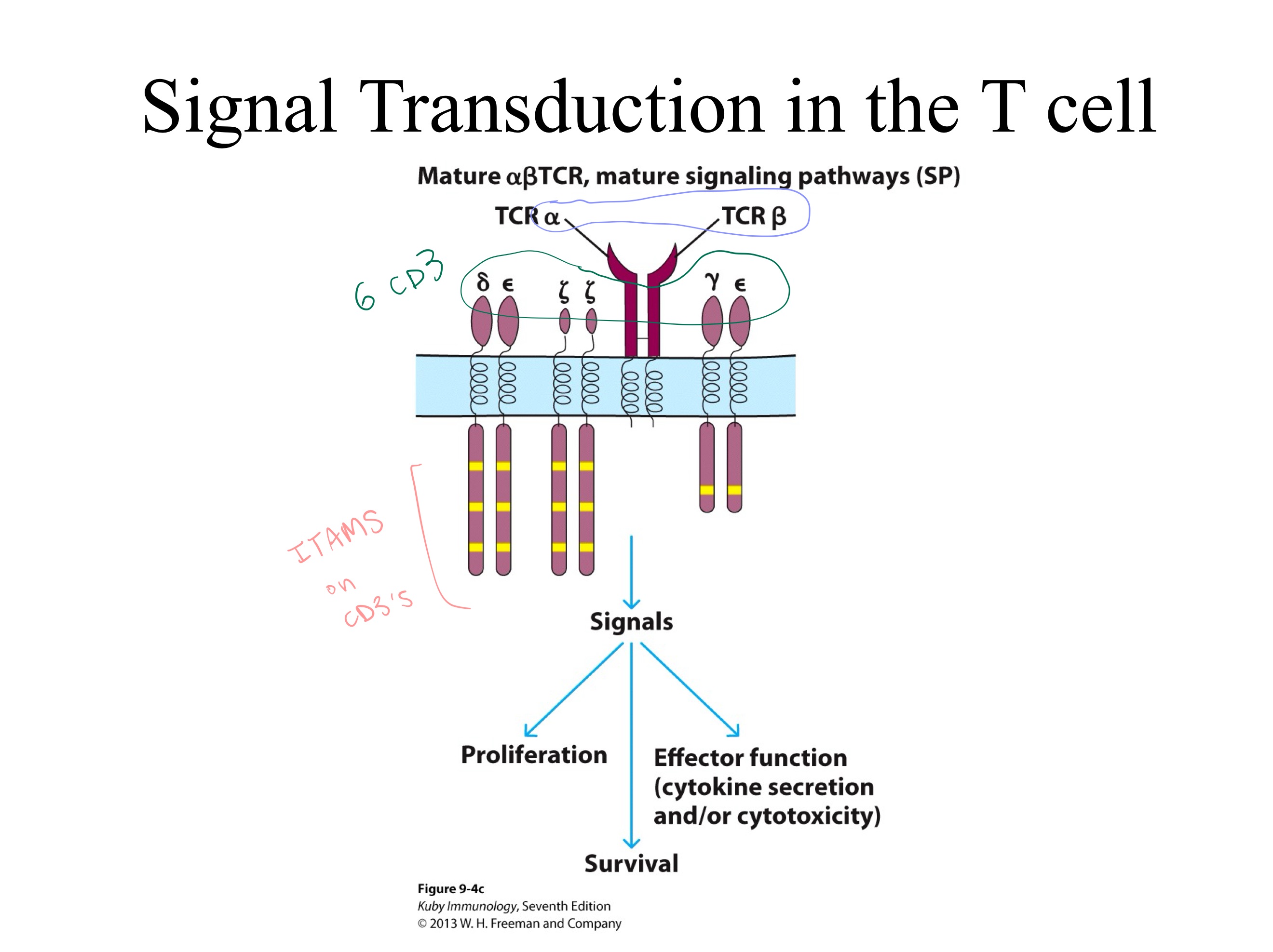
TCR Signaling Complex:
TCRs have _ and _ regions = ligand recognition portion.
CD3s have _ regions = signal transduction portion.
The TCR zeta chain exists as a _.
Each individual zeta chain contains _ Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-based Activation Motifs (ITAMs), meaning a single TCR complex contains a total of _ ITAMs from the two zeta chains.What is the motif to initiate signal transduction in TCRs and BCRs?
What is the primary signaling partner of every TCR?
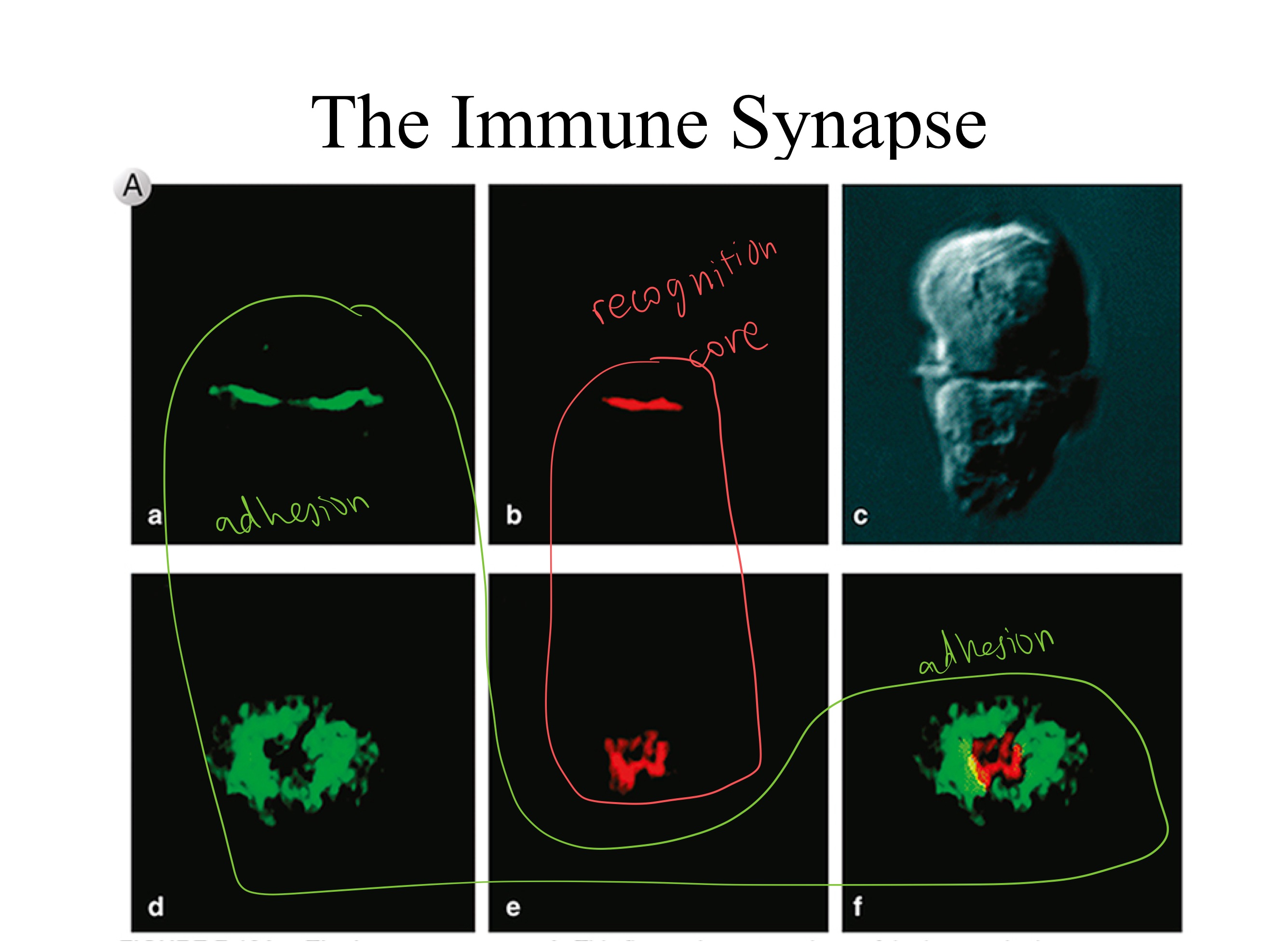
APC ; TCR
recognition
adhesion
The dendritic cell (type of _) presents ligand to _.
cSMAC mainly _.
pSMAC mainly _.
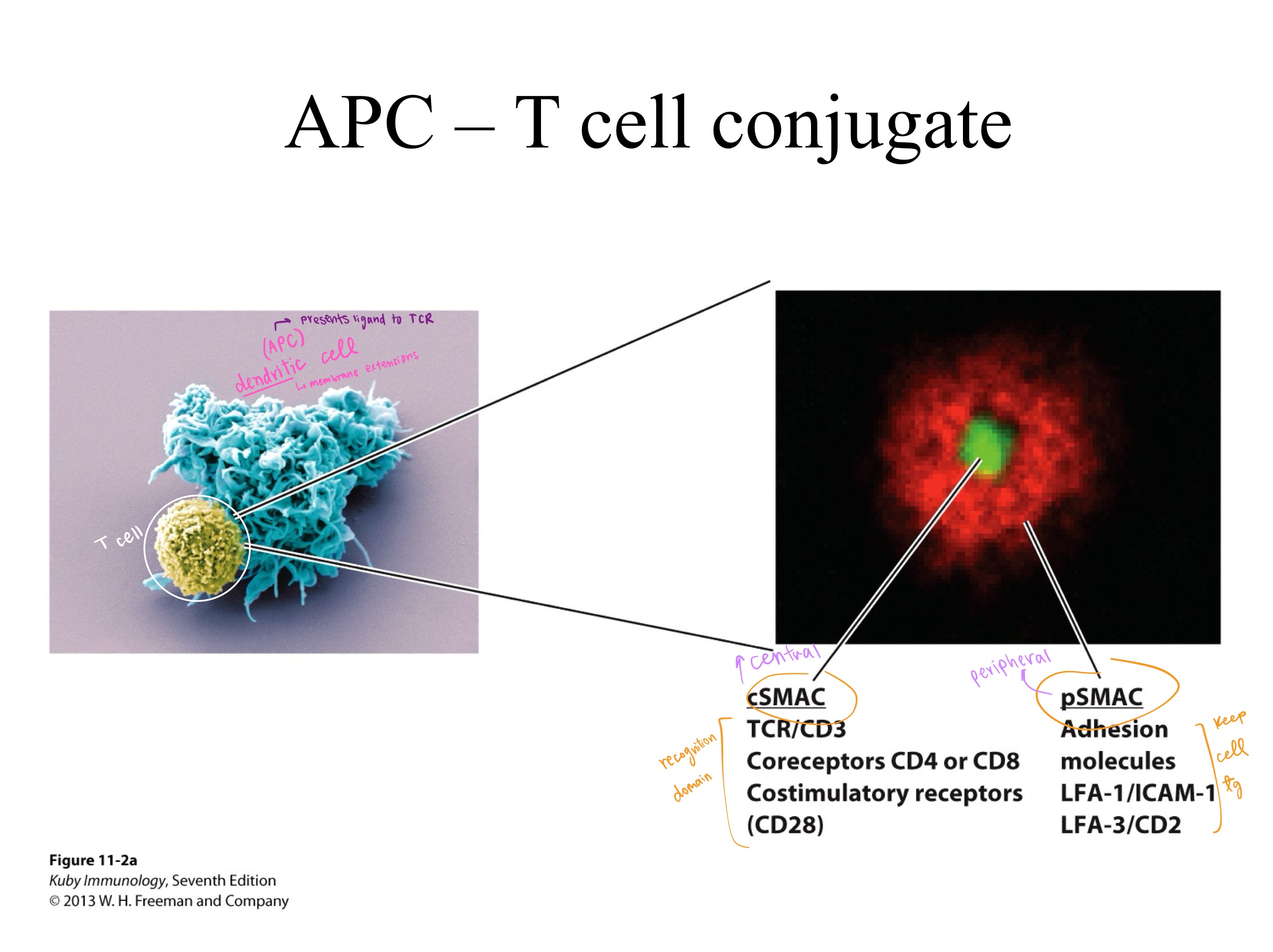
CD3
The _ signaling complex is composed of three dimers:
one heterodimer, CD3ϵγ
one heterodimer, 𝐶𝐷3𝜖𝛿
and one zeta-zeta homodimer (𝐶𝐷3𝜁𝜁)
which associate with the T-cell receptor (TCR).
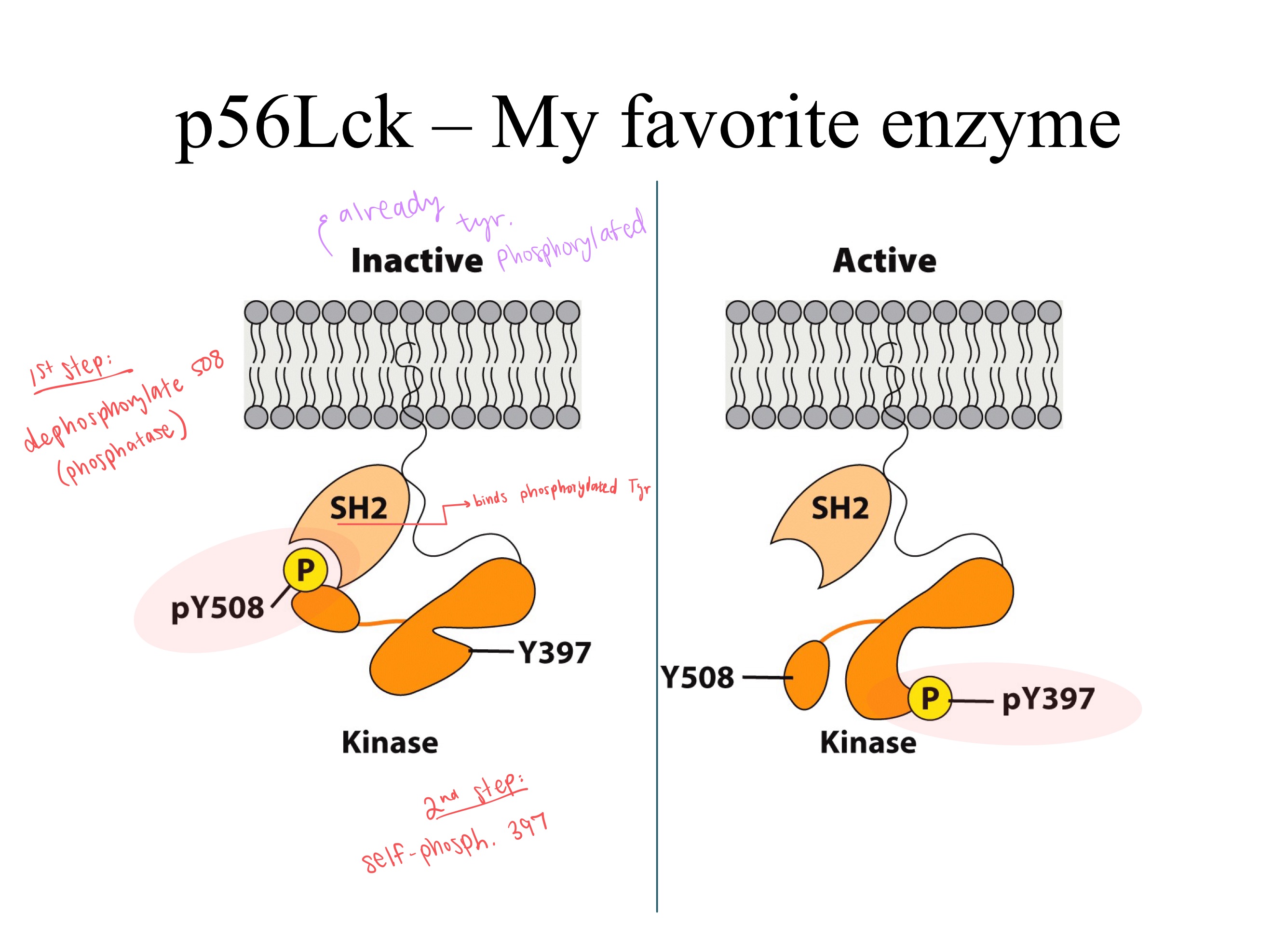
dephosphorylates ; phosphatase
(self) phosphorylates ; kinase
ZAP-70 ; kinase ; LAT
LAT
TCR Signal Transduction:
To tyrosines on ITAMs, (p56)Lck ___ Y508 using a _, and ___ Y397 making it a _ (enzyme), turning it from INactive to active.
Then the zeta region changes shape after phosphorylation, ___ binds to it.
LAT is now an active _, which phosphorylates _.
That final structural change to _ leads to secondary messaging pathways (Ras, MAPK, GEFs).
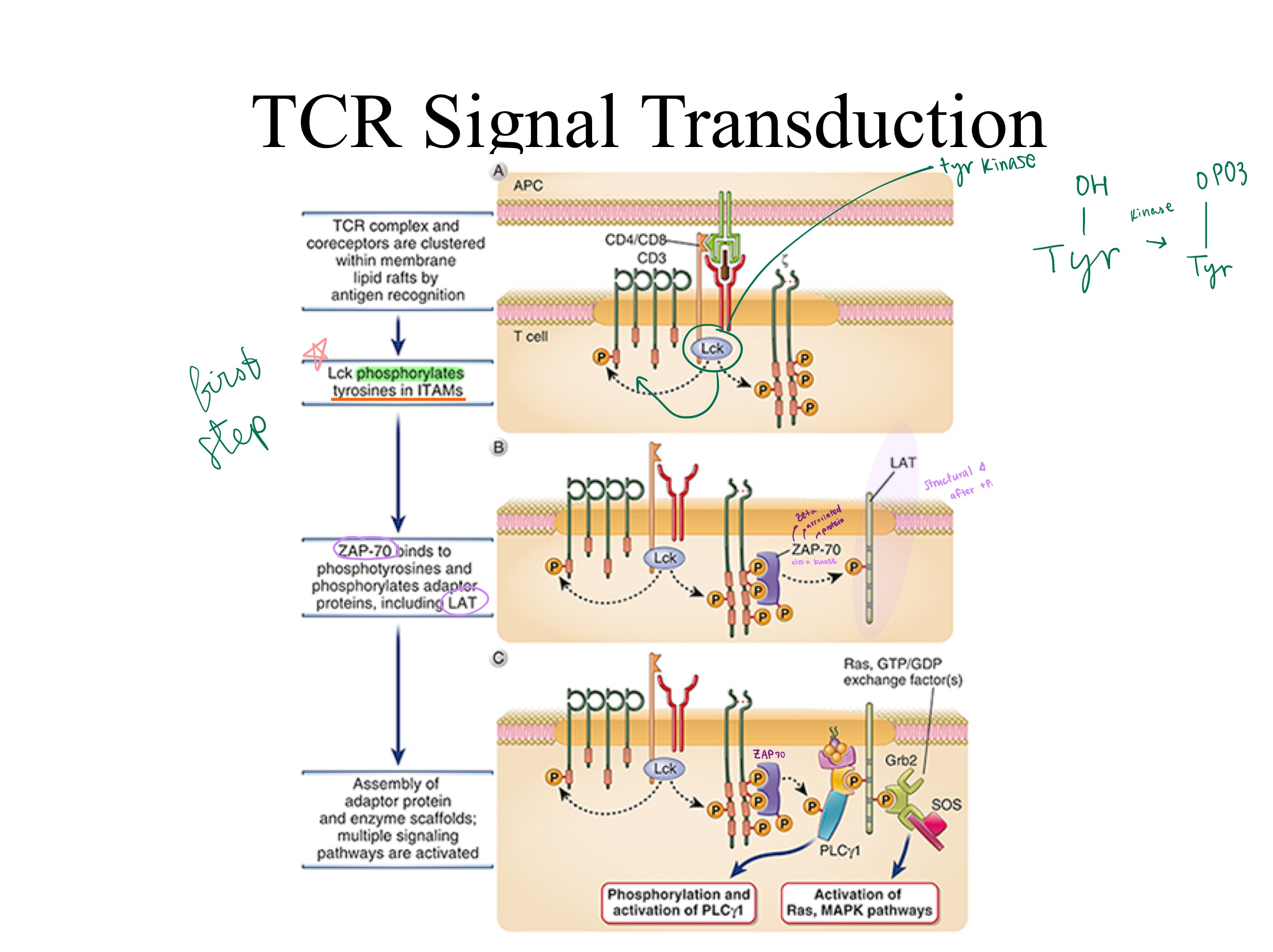
ITAMs ; ZAP-70
LAT
TCR signaling:
Upon activation, Lck phosphorylates CD3 _, creating binding sites for _, which Lck then activates.
Active ZAP-70 phosphorylates the adaptor protein _, triggering downstream T-cell activation.
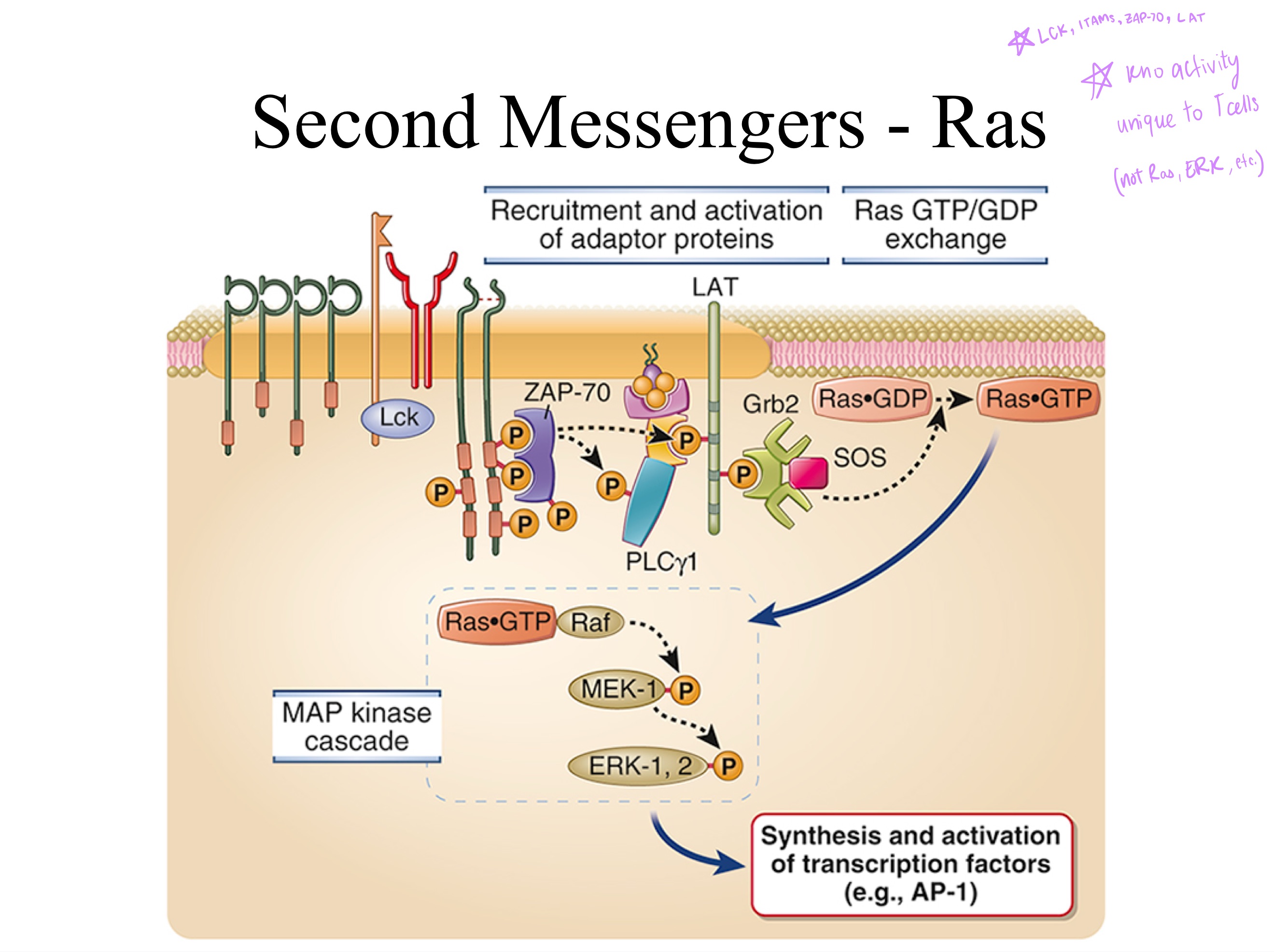
Lyn
(also Blk and Fyn (Src family kinases) used to initiate BCR signaling)
B-cells don’t use Lck. They use _
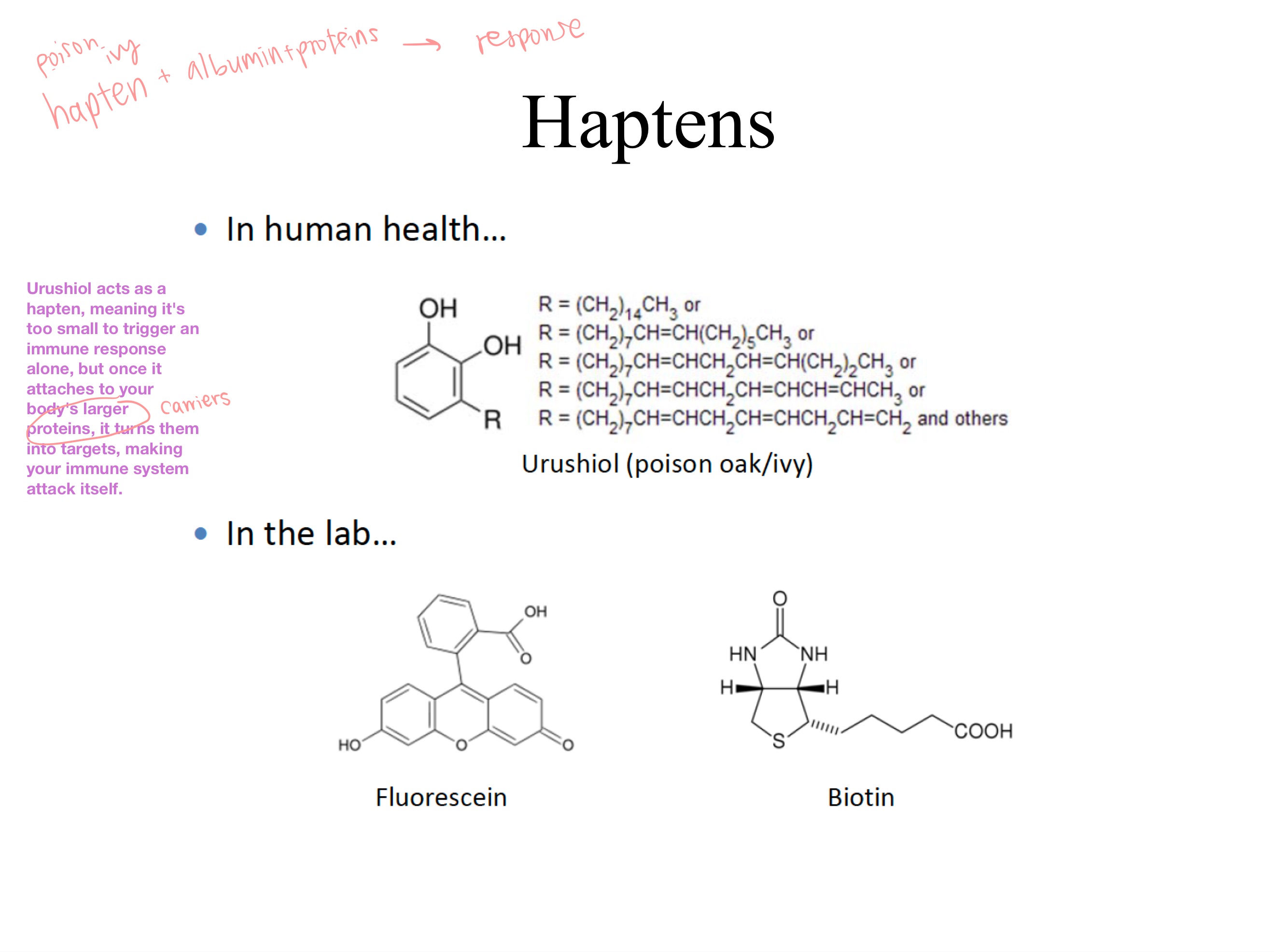
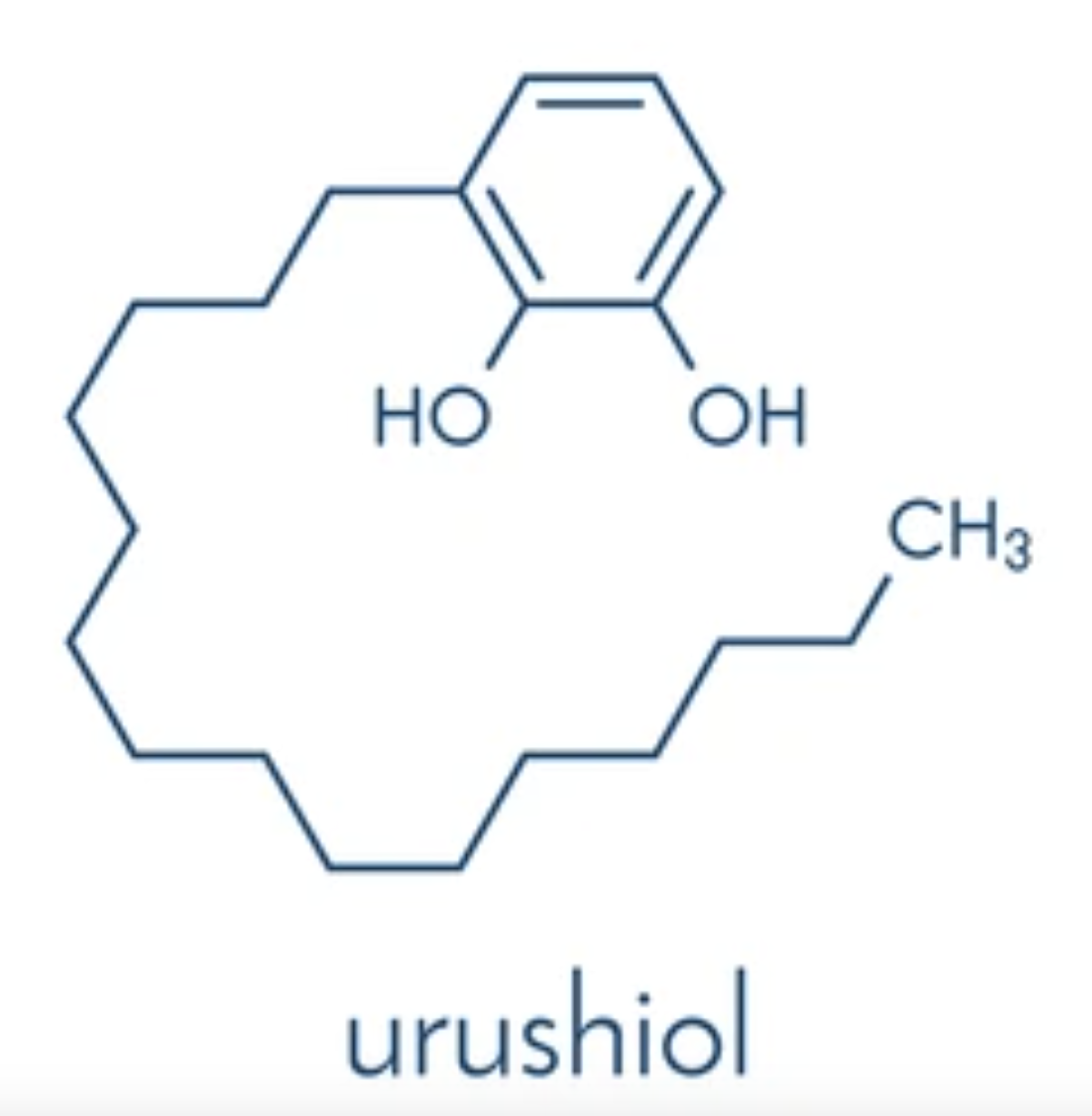
hapten
Urushiol acts as a _, meaning it’s too small to trigger an immune response alone, but once it attaches to your body’s larger proteins (ex. albumin), it turns them into targets, making your immune system attack itself.
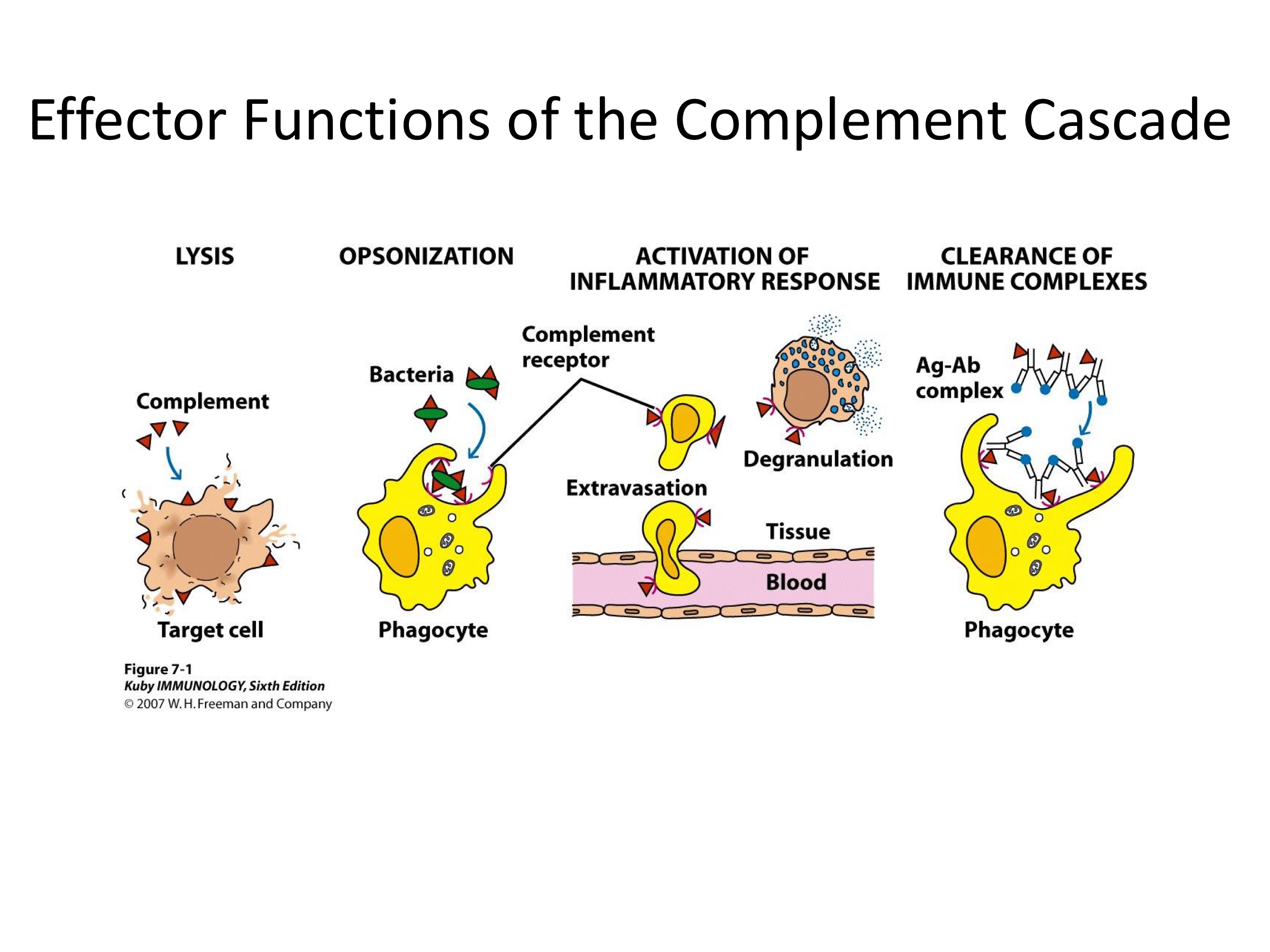
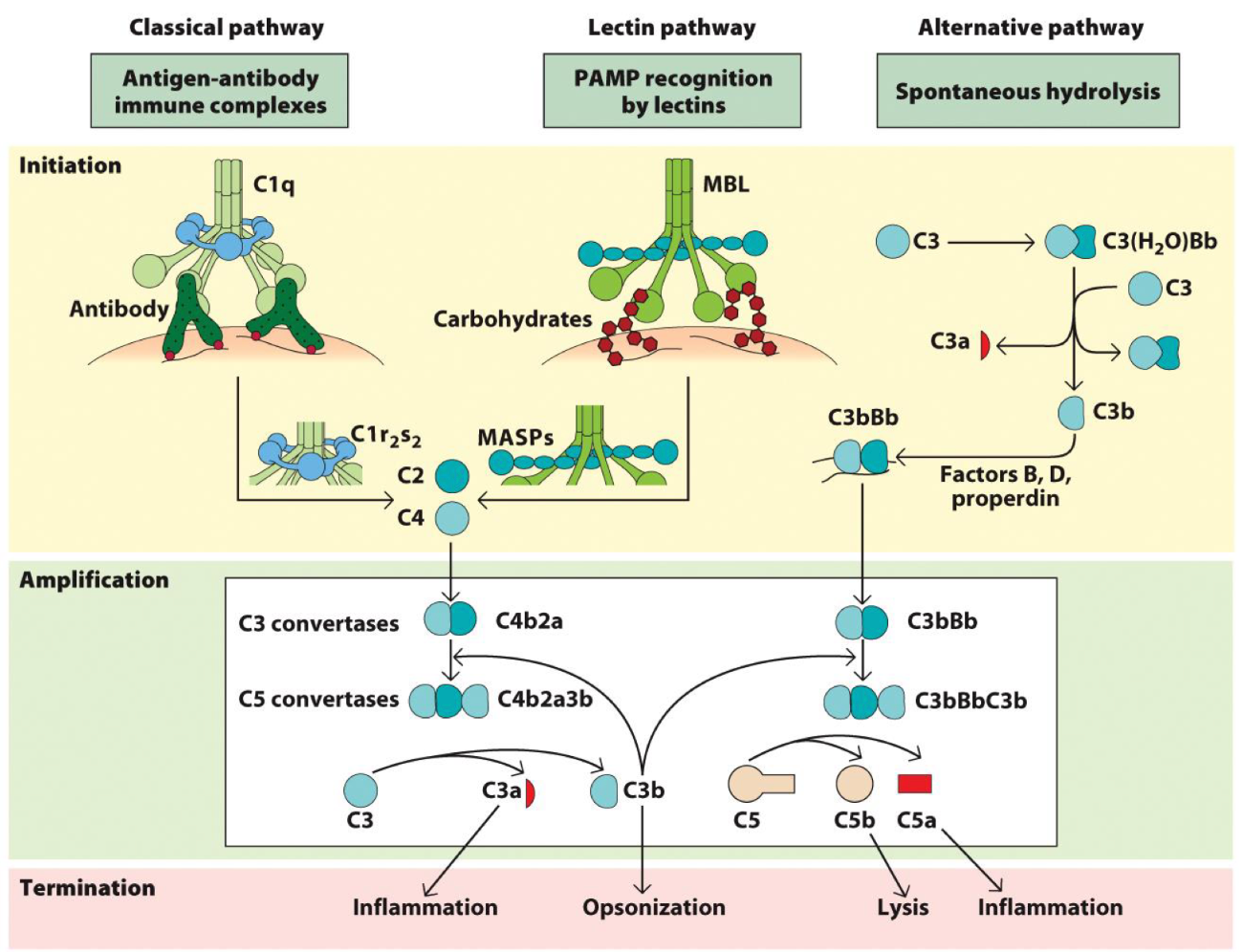
Complement
A proteolytic cascade!
System of plasma proteins that can be activated directly by pathogens or indirectly by pathogen-bound antibody —> reactions that occur on the surface of pathogens & generates active components with various effector functions
COMPLEMENTED
How was the complement system discovered?
Antibody killing of bacteria in vitro was _ by serum proteins.
classical
lectin
alternative
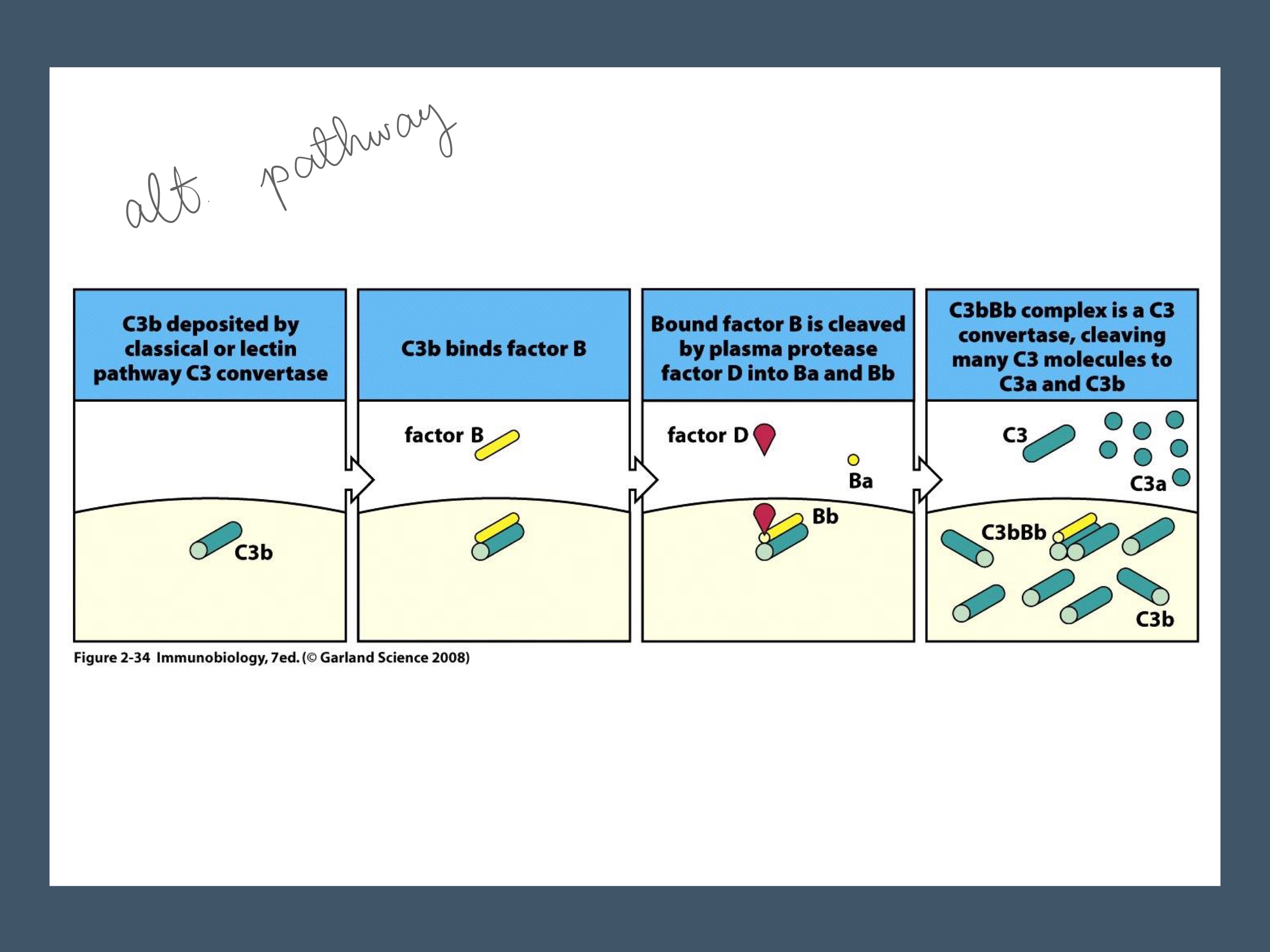
C3b
3 activation pathways of the complement system are…?
All generate _, an important, multifunctional complement protein.
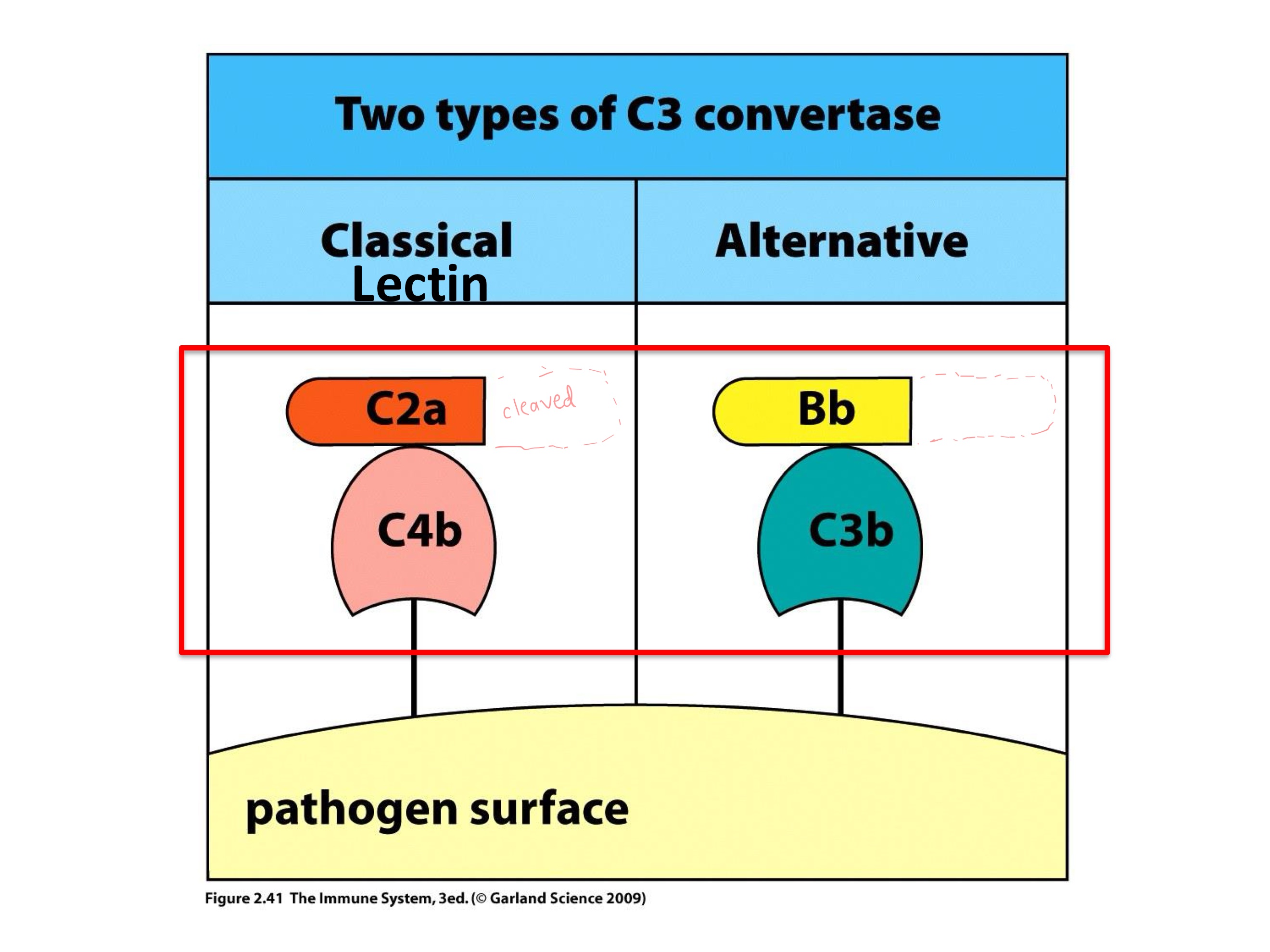
C3 Convertase
protease that cleaves C3 into C3a and C3b
C3a recruits phagocytes, C3b tags bacterium for destruction
Functions of PRODUCTS of C3 convertase?
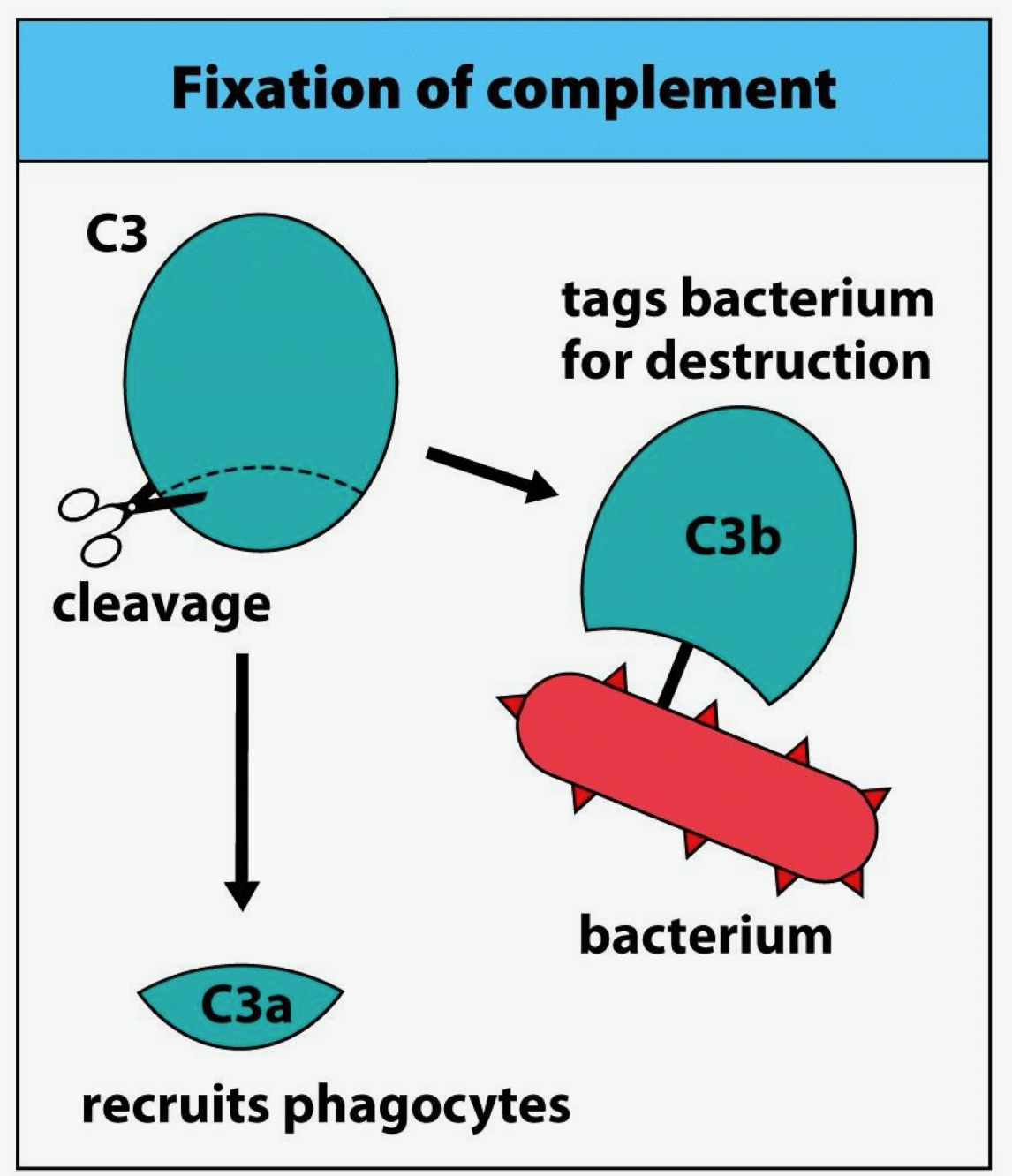
C3b
The C3 convertase cleaves C3, and _ is just a scaffold piece of that enzyme.
thioester ; H2O ; R-OH/R-NH2
Cleavage of C3 to C3b reveals a _, which is attacked by either _ (if healthy), or _ (if sick) from bacteria
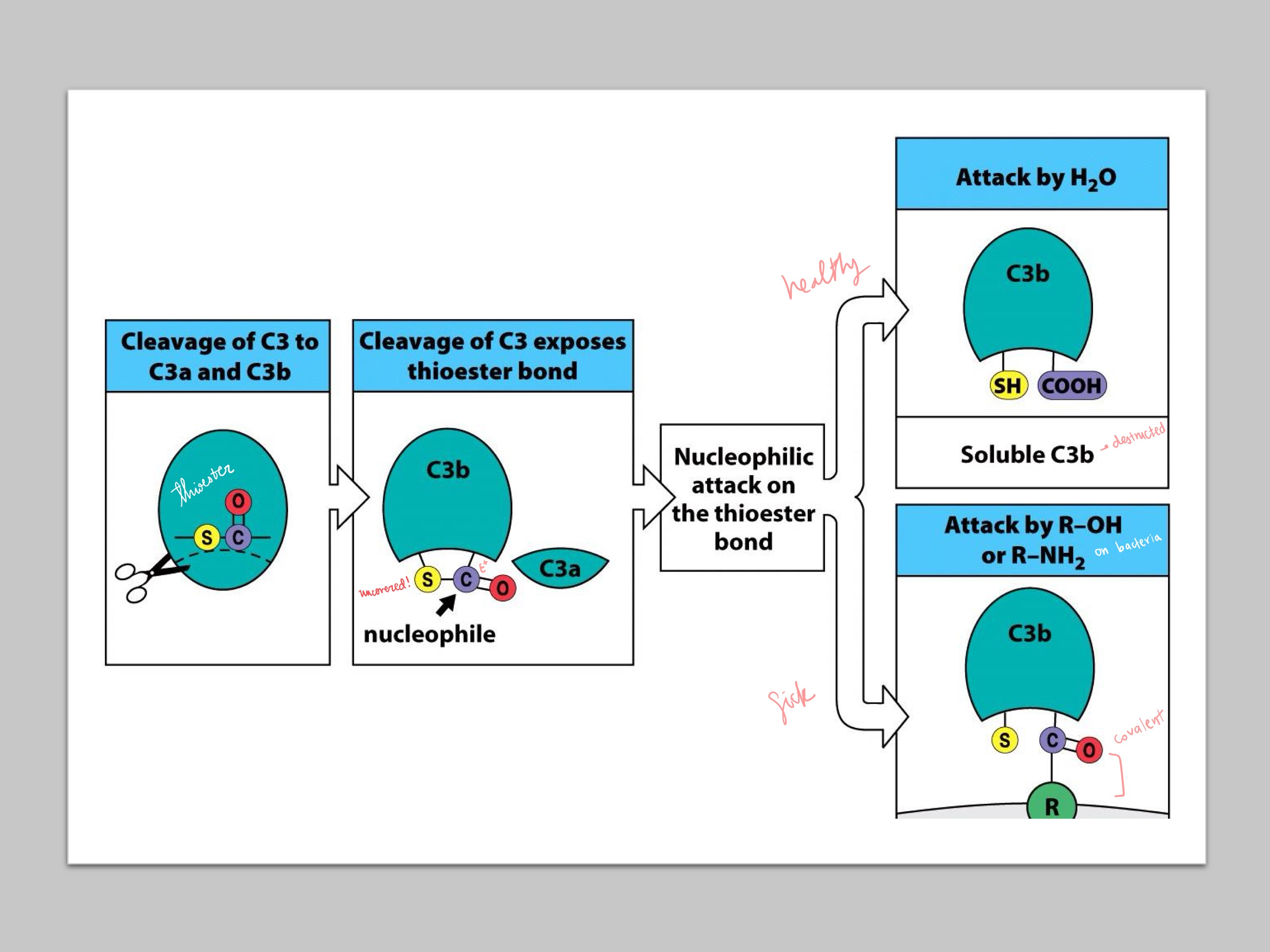
C3*
B ; D
C3a and C3b
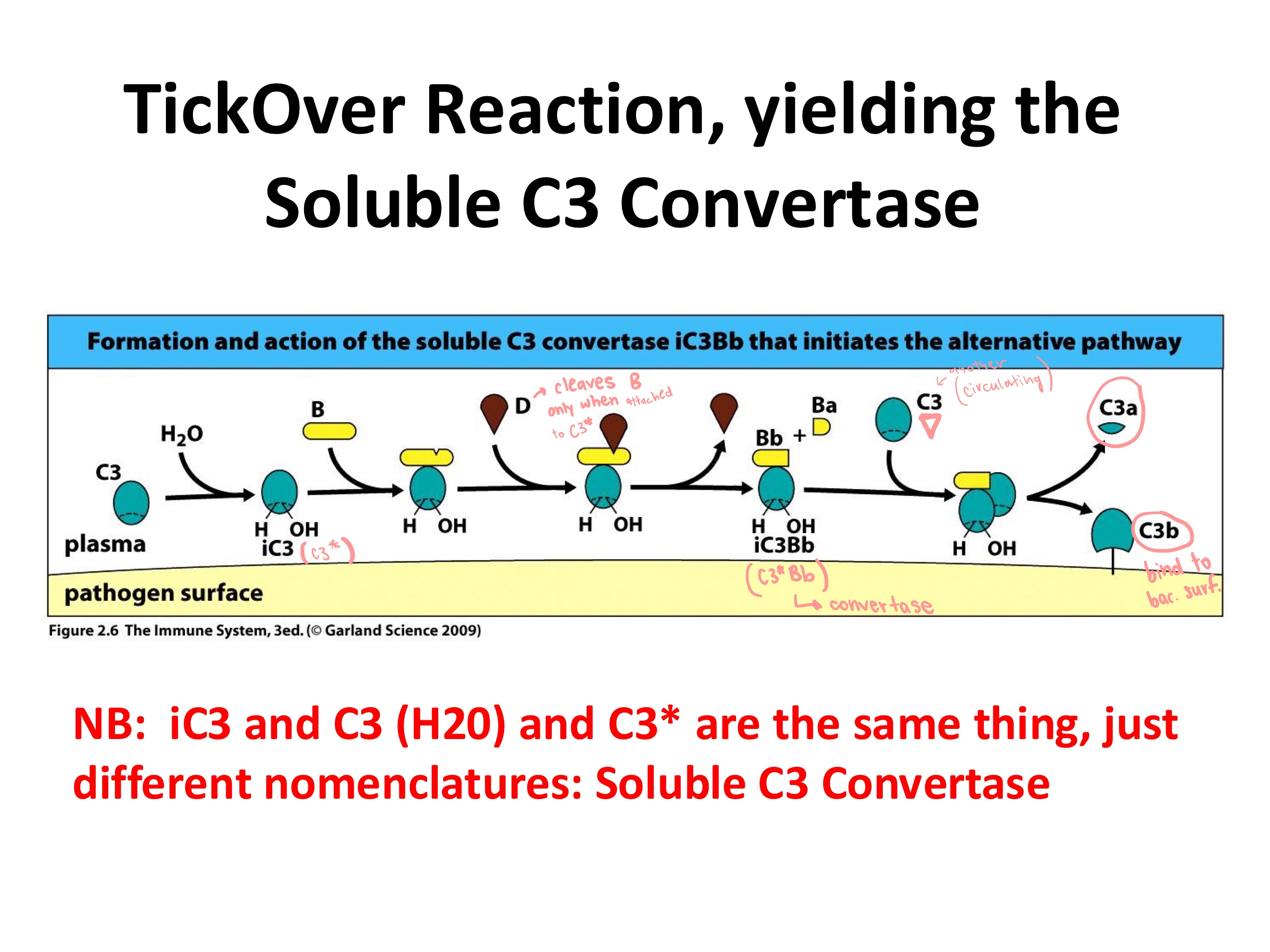
TickOver Reaction: allows for some active C3 convertase to be available all the time (C3*Bb)
Water slowly attacks C3, forming _
Now _ can bind, and is cleaved by _, forming Bb and thus C3*Bb
Plasma C3 gets cleaved by C3*bb to _ and _
D ; C3bBb
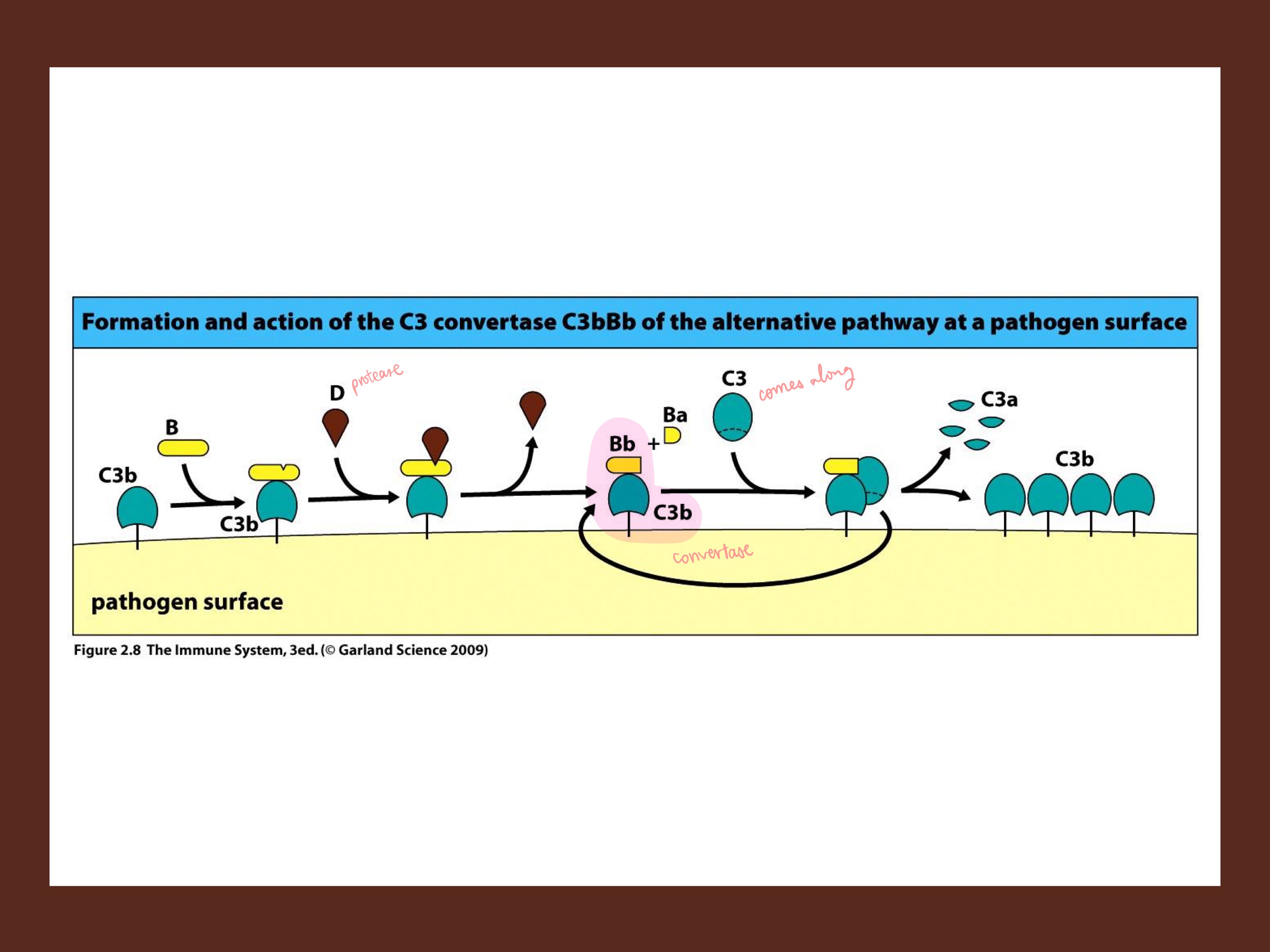
C3b
C3b, once on the pathogen surface…
B binds, and is cleaved by _, forming _ complex (releasing Ba). This is the alternate convertase! (as compared to C3*Bb, the weaker convertase)
This complex then cleaves more free C3’s into C3a and _ on the pathogen surface
Fc
C1q
S (C1s)
C4
C2
S (C1S)
LARGE ; small
C4bC2a
C4bC2a3b
C5b-9
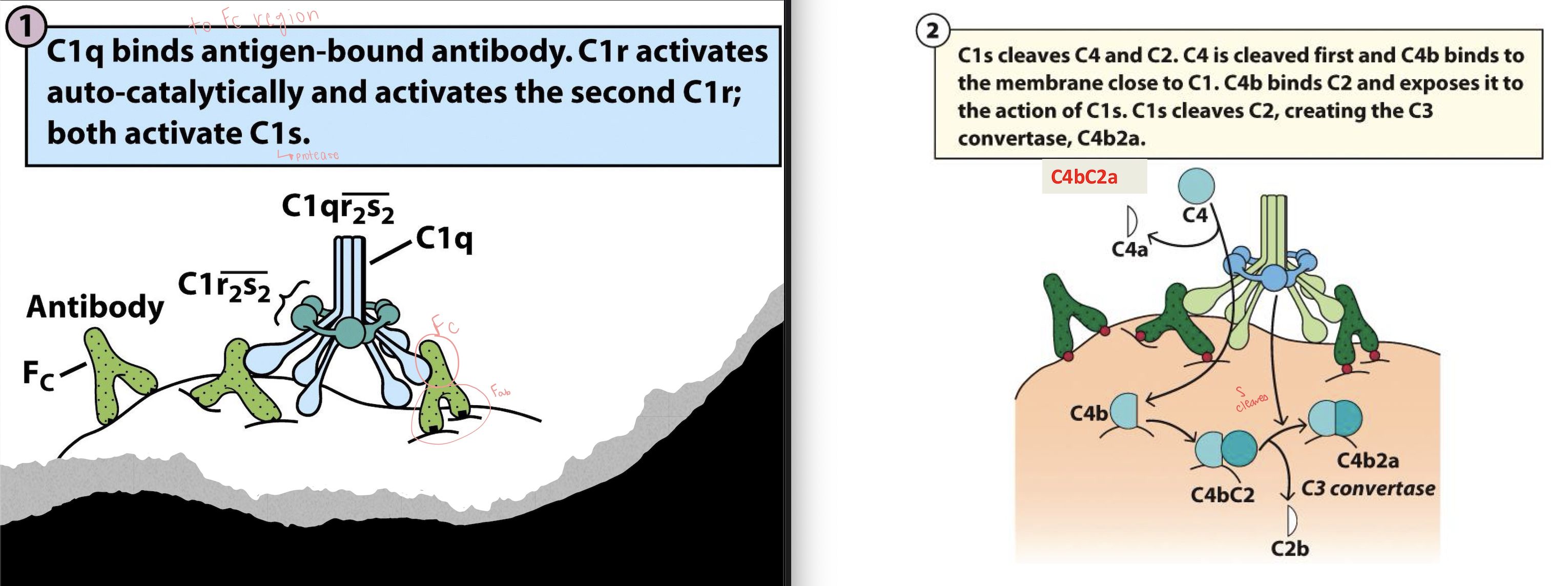
Classical Complement Pathway:
Antibody (IgG or IgM) binds antigen on a pathogen, and _ region becomes exposed
_ binds Fc region of antibody
causes: C1r → activated, C1r activates _ (the protease)
C1s cleaves _
C4 → C4a + C4b
_ binds C4b
_ cleaves C2
C2 → C2a + C2b
But this time
C2a = _ fragment, and C2b = _ fragment
Result is _, a C3 convertase (+ C3 → C3a + C3b)
Then C4b2a + C3b → , the C5 convertase
C5 → C5a + C5a
Then MembraneAttackComplex: C5b → C6 → C7 → C8 → C9 (x many)
Final complex: _
Mannose
MASP-1 and MASP-2
S
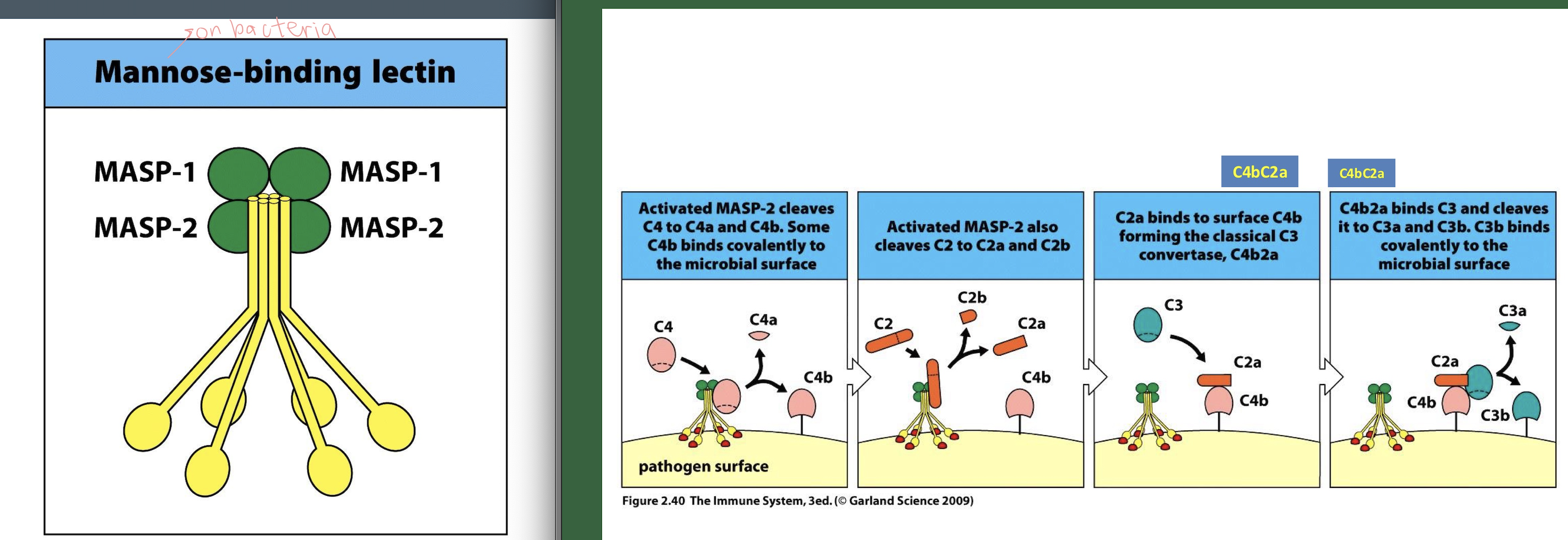
Lectin Complement Pathway:
_-binding lectin (MBL) or ficolins Bind mannose / N-acetylglucosamine on microbial surfaces.
MBL circulates with: _ and _
Once MBL binds the pathogen: MASPs become enzymatically active.MASP-2 is the key protease (functionally equivalent to _)
MASP-2 cleaves C4 → C4a + C4b
(Same as classical from here)
C4b + C2 → C4bC2
MASP-2 cleaves C2
C2 → C2a (large) + C2b —> C4b2a = C3 convertase complex
C4b2a + C3 → C3a + C3b
C4b2a + C3b → C4b2a3b
C5 → C5a + C5b
C5b → C6 → C7 → C8 → C9 (× many) —> C5b-9
Antibodies
Alternative
Alternative vs Classical pathway:
Classical pathway needs _
_ pathway: no antibodies. Trigger: spontaneous C3 hydrolysis
C3BbC2aC3b and C4bC2aC3b
What are the two active C5 convertases?
