human herpes viruses
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
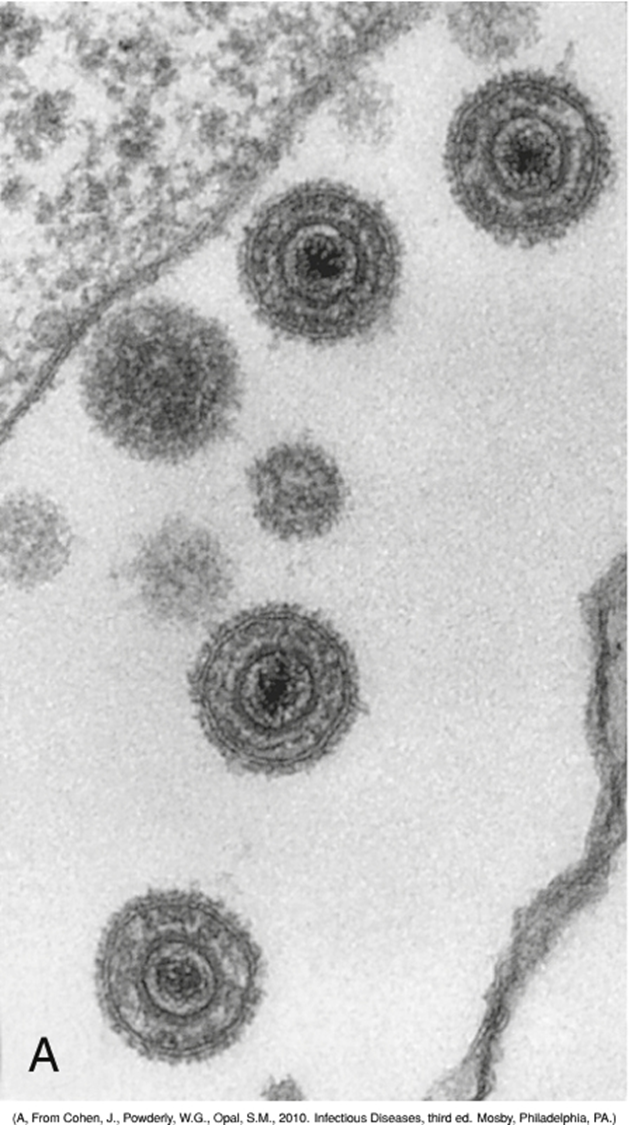
What is this?
HPV
Pardon Papa as He Has Pox
mnemonic to help remember the DNA enveloped viruses
Herpes, Hepadna, POX
All human herpes viruses
lrg genome
linear double stranded DNA
enveloped viruses
hallmark of HSV
Latent infection
HSV 1
painful vesicles on face
HSV 2
painful vesicles on genitals
VZV
varicella (chicken pox)
zoster (shingles) when it recurs
EBV
infectious mononucleosis
CMV
congenital infections
immunocompetent adults: asymptomatic infections
mononucleosis
HHV 6 & 7
roseola
HHV 8
Kaposi sarcoma (KSHV)
Herpesvirus family structure
Linear, dsDNA
Icosahedral capsid
Tegument “matrix”
Enveloped
What is special about the tegument matrix?
space between nucleocapsid & envelope, contains proteins & enzymes for viral DNA replication after infection
active herpes infection targets
one cell type.
budding & cell lysis of infected cells & Cell mediated immunity (CD8+ & NK cells) to infected cells are responsible for symptoms & host mediated destruction
Herpes latent infection targets
a different cell type & is associated w asymptomatic carriage
herpes virion assembly occurs in
nucleus, ER, GOLGI
virus is release by exocytosis or cell lysis
herpes cell-cell release enables
infections without virus exposure to extracellular environment – EVASION OF IMMUNE SYSTEM
Herpes replication steps simplified
attachment
penetration
uncoating
synthesis
assembly
release
each herpes virus has
a number designation & are divided by host cell targets
HHV genome encodes
viral DNA polymerase that are often drug-able targets
HHV replication occurs in
nucleus
herpes voirus packaging occurs in
nucleus, ER, and Golgi apparatus
herpes virus is release through
exocytosis or lysis
herpes viruses establishes
lytic, persistent & latent infections
what herpes virus are associted w cancer development?
EBV KSV
Herpes is
ubiquitous
HSV 1 & 2
“Mixing and matching of mucous membranes” or via direct contact of infected fluid from vesicles
VSV
Aerosol or direct contact of infected fluid from vesicles
CMV
Aerosol (saliva), sexual, vertical or parental transmission
EBV
saliva aka kissing disease
HHV 6 7 8
unknown relating to ubiquitous
Herpes simplex Type 1 HHV1 primary target cell
mucoepithelial cells
Herpes simplex Type 1 HHV1 site of latency
neuron- trigemial ganglia
Herpes simplex Type 1 HHV1 means of spread
close contact (sexuallry transmitted)
alpha herpes virinae
HHV 1: herpes simplex type 1
HHV 2: HSV type 2
HHV 3: varicella-zoster virus (VZV)
Betaherpes viriniae
HHV5: cytomegalovirus (CMV)
HHV6a, 6b, 7: genus roseolovirus
gammaherpesvirinae
HHV 4: EBV epstein-barr virus
HHV8: kaposi sarcoma-related virus
HHV 2: HSV type 2 targets
mucoepithelial cells
HHV 2: HSV type 2 site of latency
neuron- lumbar or sacral ganglia
HHV 2: HSV type 2 means of spread
close contact (sexually transmitted)
HHV 3: varicella-zoster virus (VZV) targets
mucoepithelial & T cells
HHV 3: varicella-zoster virus (VZV) site of latency
neuron: cranial or thoracic ganglia
HHV 3: varicella-zoster virus (VZV) means of spread
respiratory & close contact
HHV5: cytomegalovirus CMV targets
monocytes, grnaulocytes, lymphocytes, epithelial cells
HHV5: cytomegalovirus CMV site of latency
monocyte, myeloid stem cell & T cells
HHV5: cytomegalovirus CMV means of spread
close contact, transfusions, tissue transplant, congenital
HHV 6a, 6b, 7: genus roseolovirus targets
lymphocytes
HHV 6a, 6b, 7: genus roseolovirus site of latency
T cells
HHV 6a, 6b, 7: genus roseolovirus means of spread
saliva
HHV 4: Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) targets
B cells & epithelial cells
HHV 4: Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) site of latency
B cell
HHV 4: Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) means of spread
saliva (kissing disease)
HHV 8: Kaposi sarcoma-related virus target cell
lymphocytes
HHV 8: Kaposi sarcoma-related virus site of latency
B cell
HHV 8: Kaposi sarcoma-related virus means of spread
close contact
sexual
saliva
HSV 1 clinical presentation/ primary infection
Gingivostomatitis, keratoconjunctivitis, pharyngitis
HSV 1 clinical presenation recurrent infection
cold sores
HSV 2 clinical presentation/ primary infection
Genital herpes, neonatal herpes
HSV 2 clinical presentation recurrent infection
genital herpes
VZV clinical presentation/ primary infection
chickenpox
VZV clinical presentation recurrent infection
shingles (zoster)
EBV clinical presentation/ primary infection
Mononucleosis (heterophile-positive)
EBV clinical presentation recurrent infection
Asymptomatic shedding of virus
CMV clinical presentation/ primary infection
Mononucleosis (heterophile-negative), cytomegalic inclusion disease
CMV clinical presentation recurrent infection
Asymptomatic shedding of virus
HSV 6 & 7 clinical presentation/ primary infection
Roseola infantum/exanthem subitum/6th disease
HSV 6 & 7 clinical presentation recurrent infection
Asymptomatic shedding of virus
HSV 8 clinical presentation/ primary infection
Kaposi sarcoma, primary effusion lymphoma (rare B cell), multicentric Castleman disease (lymphoma?)
herpes family sites of latency
neurotropic or lymphotropic
neurotropic latency
HSV 1 & 2, VZV
lymphotropic latency: EBV
B cells
Lymphotropic latency: CMV
T cells, monocytes
Lymphotropic latency: HHV 6 & 7
T cells
lymphotropic latency: HHV 8
probably B cells
HHV (HSV, VZV, CMV and EBV) can
cause recurrent lytic infection
HHVs remain silent in latency until
stress signal AND lower T cell activity trigger activation.
HHV reactivation is often associated w
depressed T cell response
Herpes Family are responsible for TORCH congenital infections
Toxoplasmosis
Other (VZV, Parvo, Syphillus)
Rubella
Cytomegalovirus
Herpes (type 2)
HSV-1, HSV-2, and VSV target
Mucoepithelial cells for lytic primary infection and
Nerve cells for latent infection
HSV pathogenesis
Direct contact- sexual, other intimate
Enter in the mucous membranes or through skin breaks
Virus replicates in cells at base of lesion
infects the innervating neuron and travels to the ganglion
Trigeminal ganglia for HSV-1 (face)
Sacral for HSV-2 (genitalia)
Virus then returns to the initial site of infection
HSV clinical syndrome
Herpatic vesicular lesion
“dew drop on a rose petal”
Usually clustered
Painful, fluid-filled blisters
Preceded by tingling
Accompanied by fever
Symptoms last 3-7 days
HSV 1 & 2 is highly labile
most primary infections are acquired through direct contact with a lesion or contaminated secretions.
HSV 1 vs HSV 2
1 above the belt
2 below the belt lesions not always true
HSV-1 is often acquired early in life, while HSV-2 often appears after the onset of sexual activity.
HSV 1 transmitted in
in vesicle fluid, saliva, and vaginal secretions
“Mixing and matching of mucous membranes”
HSV 1 latency
in trigeminal ganglia
Herpes pharyngitis and gingivostomatitis
Swollen gums or throat
Lesions in mouth
Fever
Painful eating/drinking
Differentials
HPV (no pain)
Canker sores (no fever)
Foot and mouth disease
Herpes Labialis “Cold sores”
was in romeo & juliet
Lesions occur at the corners of the mouth or next to the lips.
Benign and self-resolving
Recurrent episode
less severe and shorter
more localized
herpetic whitlow
finger
establishes infection through cuts
Common in health care workers
thumb-sucking children
Herpes gladiatorum
body
establishes infection through cuts or abrasions in the skin
acquired during wrestling or rugby.
Herpetic keratitis HSV-1
most common cause of corneal blindness in USA
Typically limited to one eye
Pain
Photophobia
Blurred vision
Tearing
Redness
Recurrent disease
permanent scarring
corneal damage
Blindness
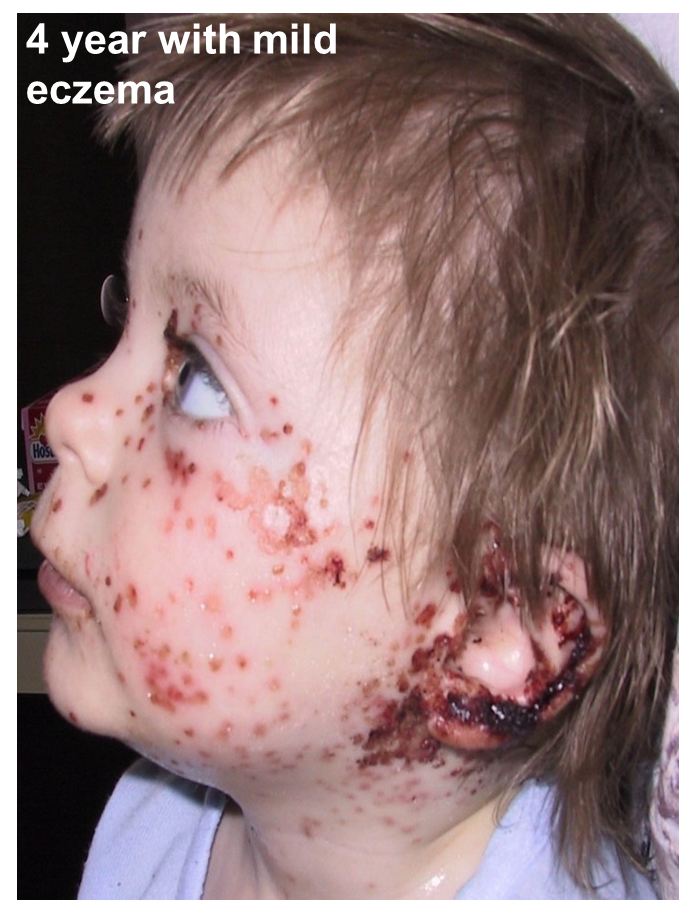
Eczema herpeticum
Acquired by children with active eczema
Underlying disease promotes the spread of the infection
Skin
adrenal glands
Liver
other organs
Herpes encephalitis typically HSV-1
Immunocompromised patients
Viral pathology and immunopathology (CMI) cause
Personality alterations
Fever and headache
Destruction of the temporal lobe
Erythrocytes in the cerebrospinal fluid
Seizure
Focal neurologic abnormalities
Genital herpes – typically HSV-2
Vesicular lesions (blisters) last for 10-15 days
1-2% individuals transmit virus though asymptomatic
HSV-2 and host interactions in nerve root ganglia
DRG are clusters of sensory neuron cell bodies located in the dorsal roots of the spinal column
neonatal herpes HSV-2
Often fatal or chance of chronic carriage
Contract from HSV+ mother
Most commonly contracted during passage through vaginal canal
Baby initially appears septic
Vesicular lesions may/may not be present
UNDERDEVELOPED CMI leads to Virus disseminates to the liver, lung, etc., and CNS
High risk of developmental complications
immunity to HSV
Th1, CTL and NK cells are critical for controlling active infection. ~80% infections are asymptomatic.
IFN and CD8+ cells are important for limiting herpesviruses.
Suppression of immunity triggers reactivation, spread, and severe disease.
Establishment of memory CTL reduces the severity of flare-ups
antiviral response for HSV
Th1 lead to CTL activation
(IFN-a, -b, and TNFa) are important players in CMI response
Entry of herpes viral DNA results in :
Active infection targets one cell type. Lysis of infected cells and CMI to infected cells are responsible for symptoms.
Latent infection targets another cell type and is associated with asymptomatic carriage.
herpes virion assembly occurs in
nucleus, ER, GOLGI
cell-cell release for herpes ensures
infections without virus exposure to extracellular environment – EVASION OF IMMUNE SYSTEM