Chapter 13 - Factor Markets and their Functions
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Physical Capital
Often referred to simply as "capital" -consists of manufactured productive resources such as equipment, buildings, tools, and machines.
Human Capital
Human capital is the improvement in labor created by education and knowledge that is embodied in the workforce.
Derived Demand
The demand for a factor is a derived demand. It results from (that is, it is derived from the demand for the output being produced.
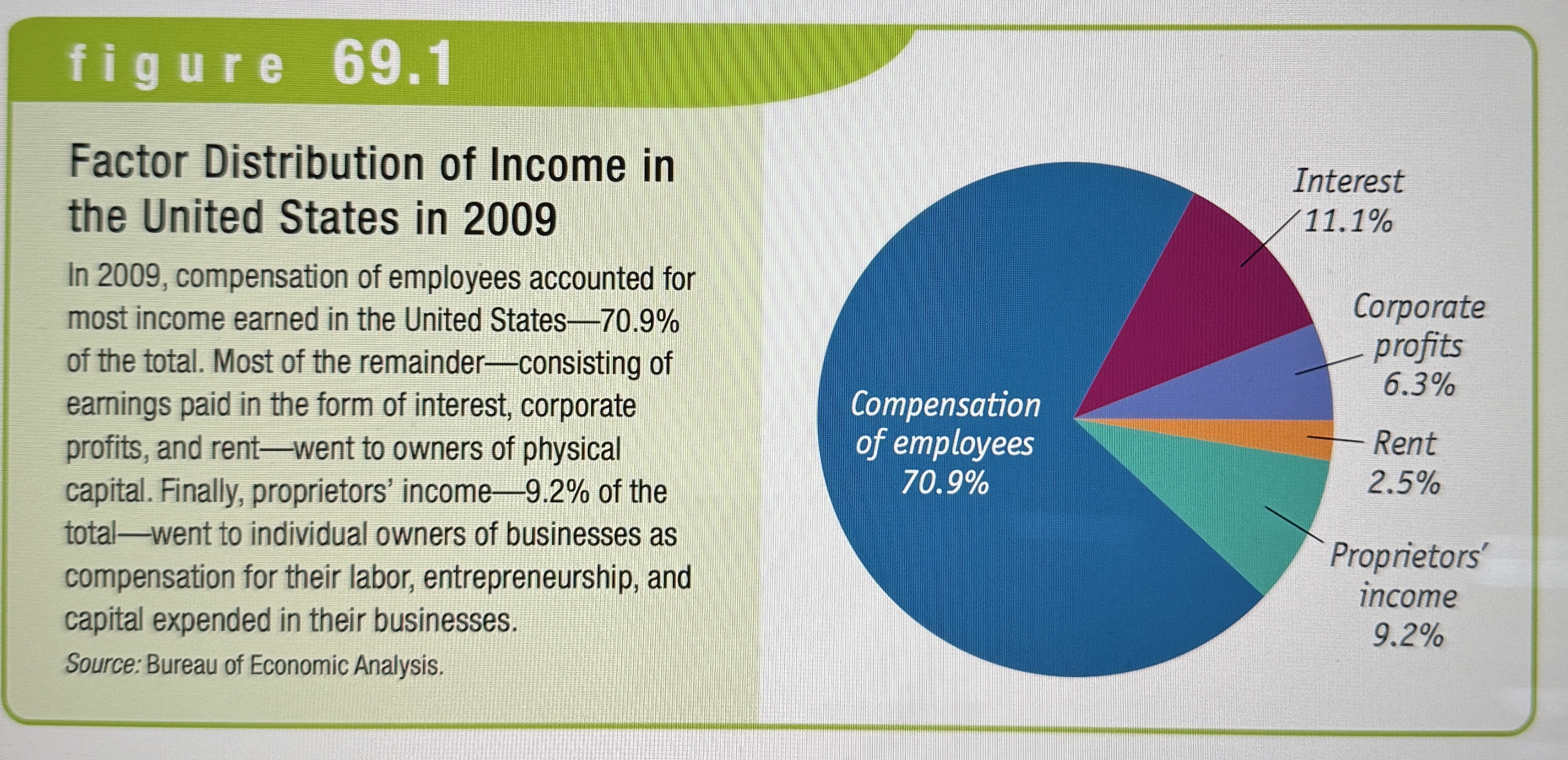
The Factor Distribution of Income
The division of total income among land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship.
Factor Distribution of Income in the United States in 2009
Ex.
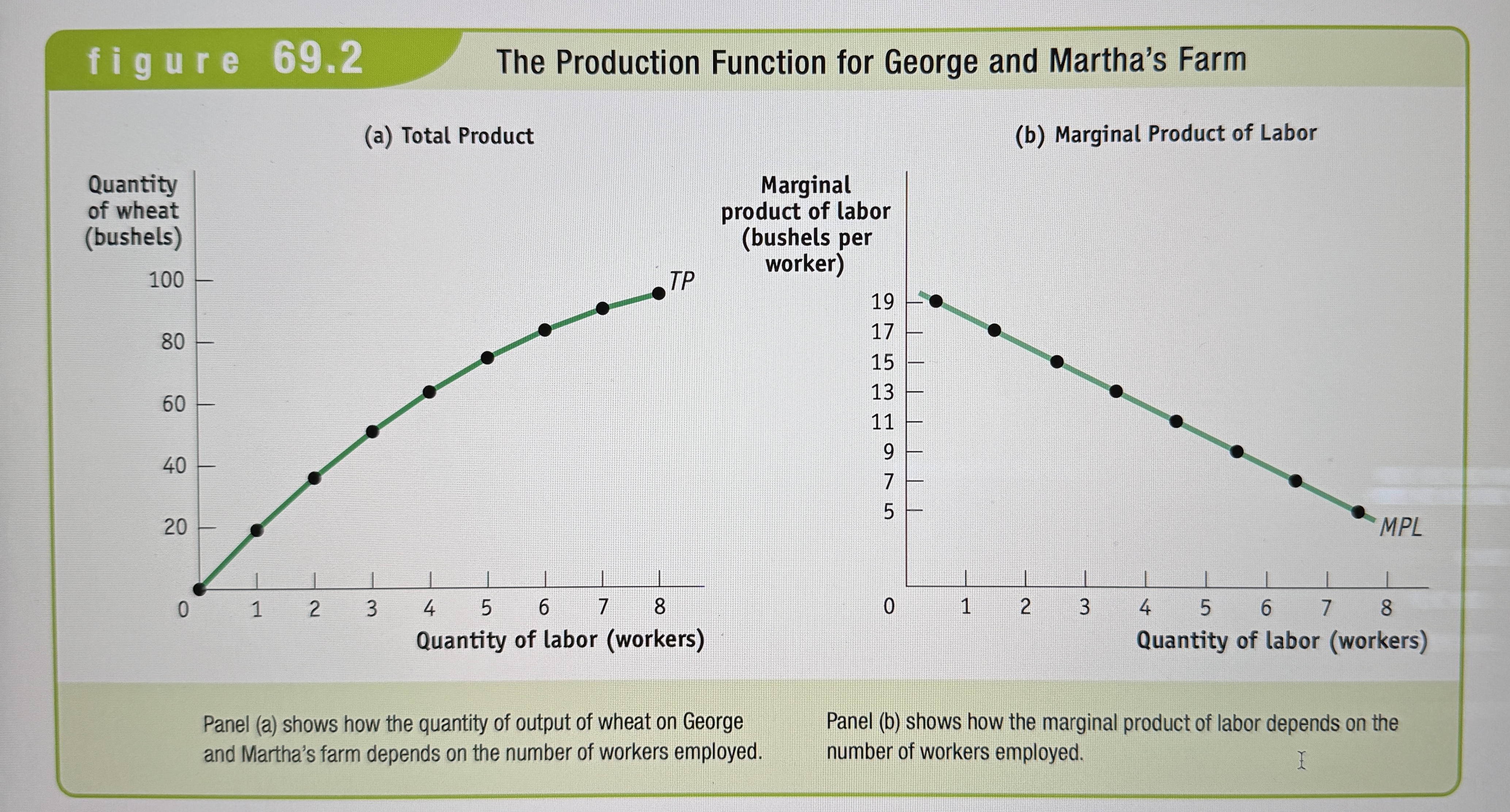
The Production Function for George and Martha's Farm
Ex.
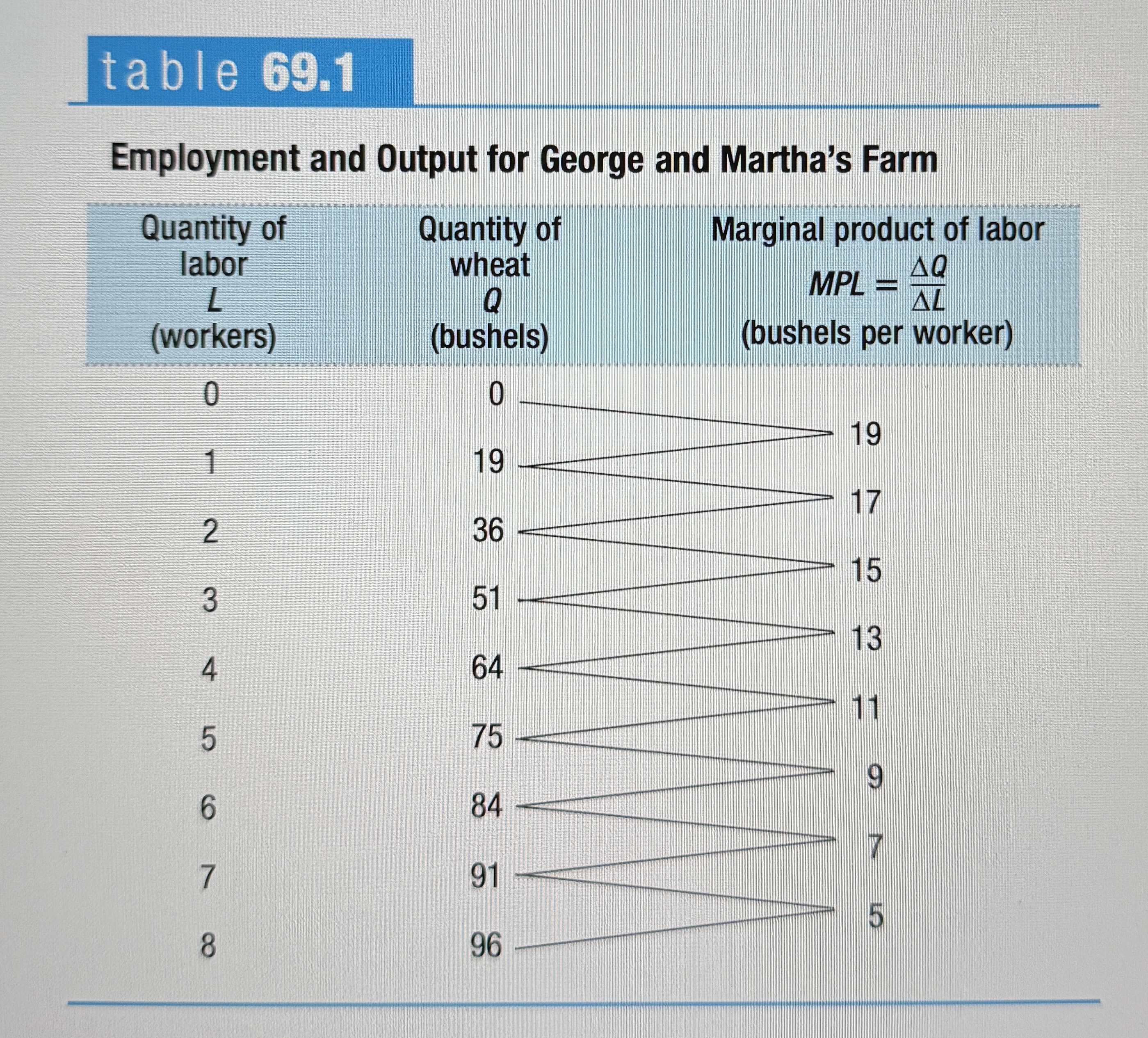
Employment and Output for George and Martha's Farm
Ex.
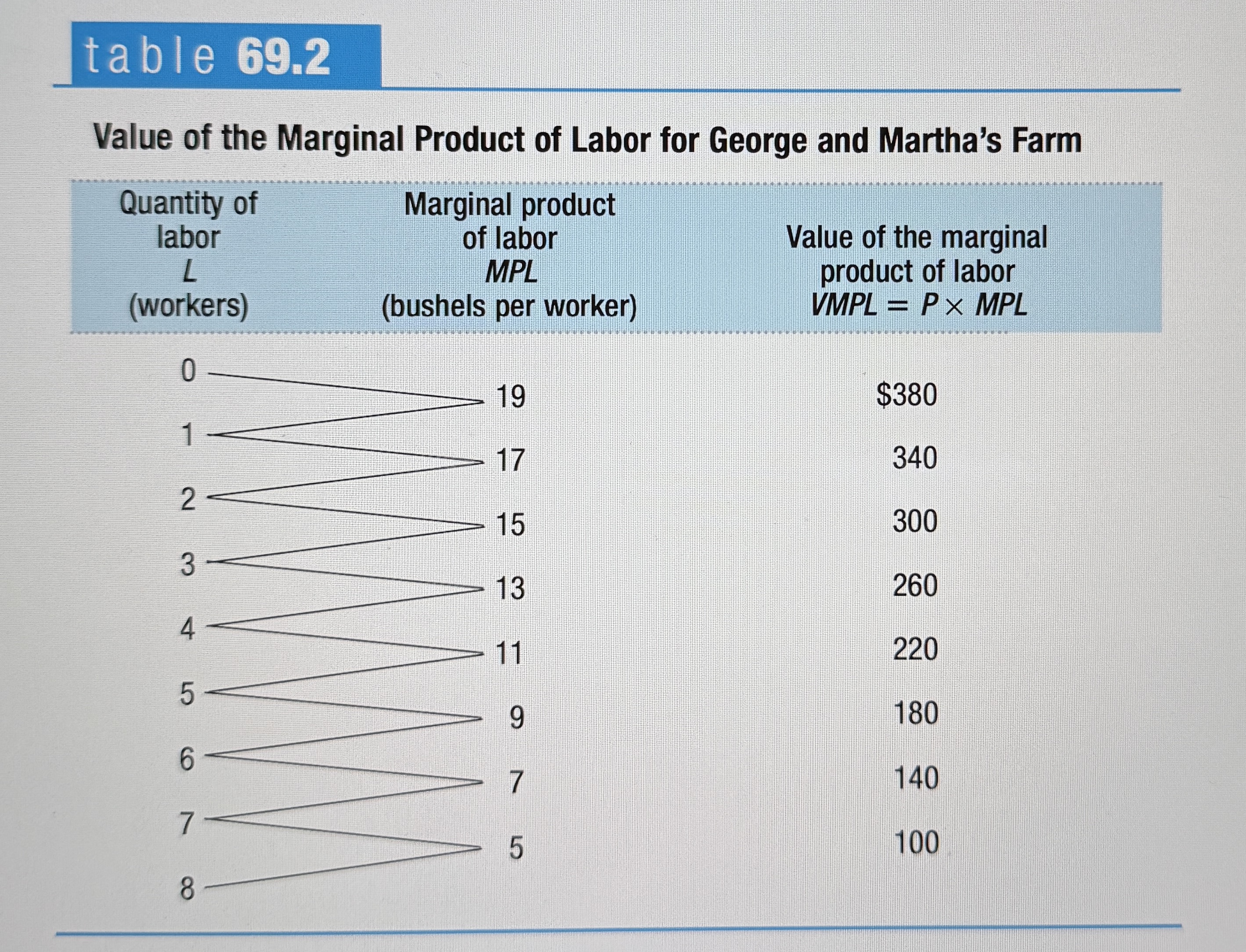
The Value of the Marginal Product
The value of the marginal product of a factor is the value of the additional output generated by employing one more unit of that factor.

Value of the Marginal Product of Labor for George and Martha's Farm
Ex.
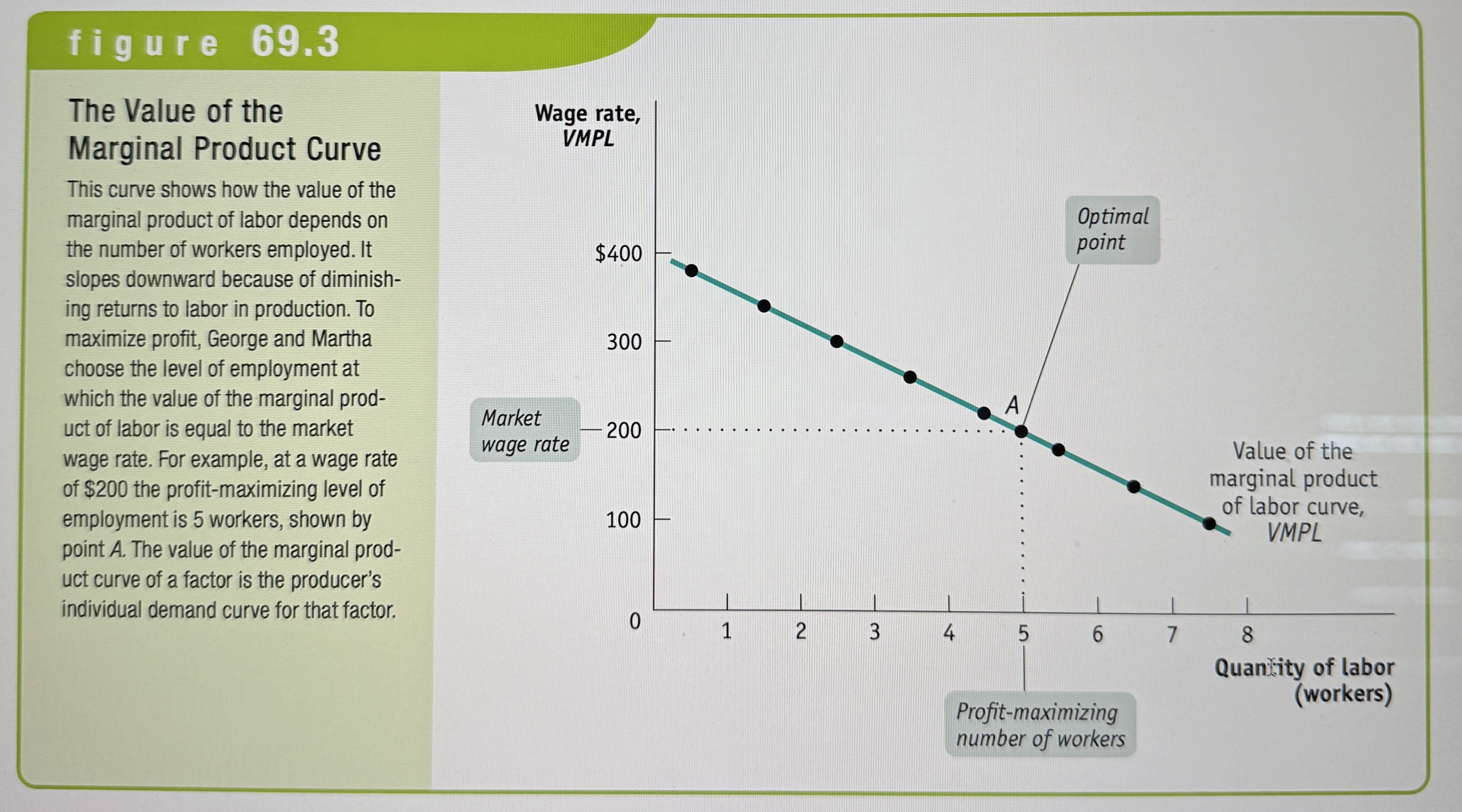
The Value of the Marginal Product Curve
The value of the marginal product curve of a factor shows how the value of the marginal product of that factor depends on the quantity of the factor employed.
Shifts of the Factor Demand Curve
Changes in the prices of goods
Changes in the supply of other factors
Changes in Technology
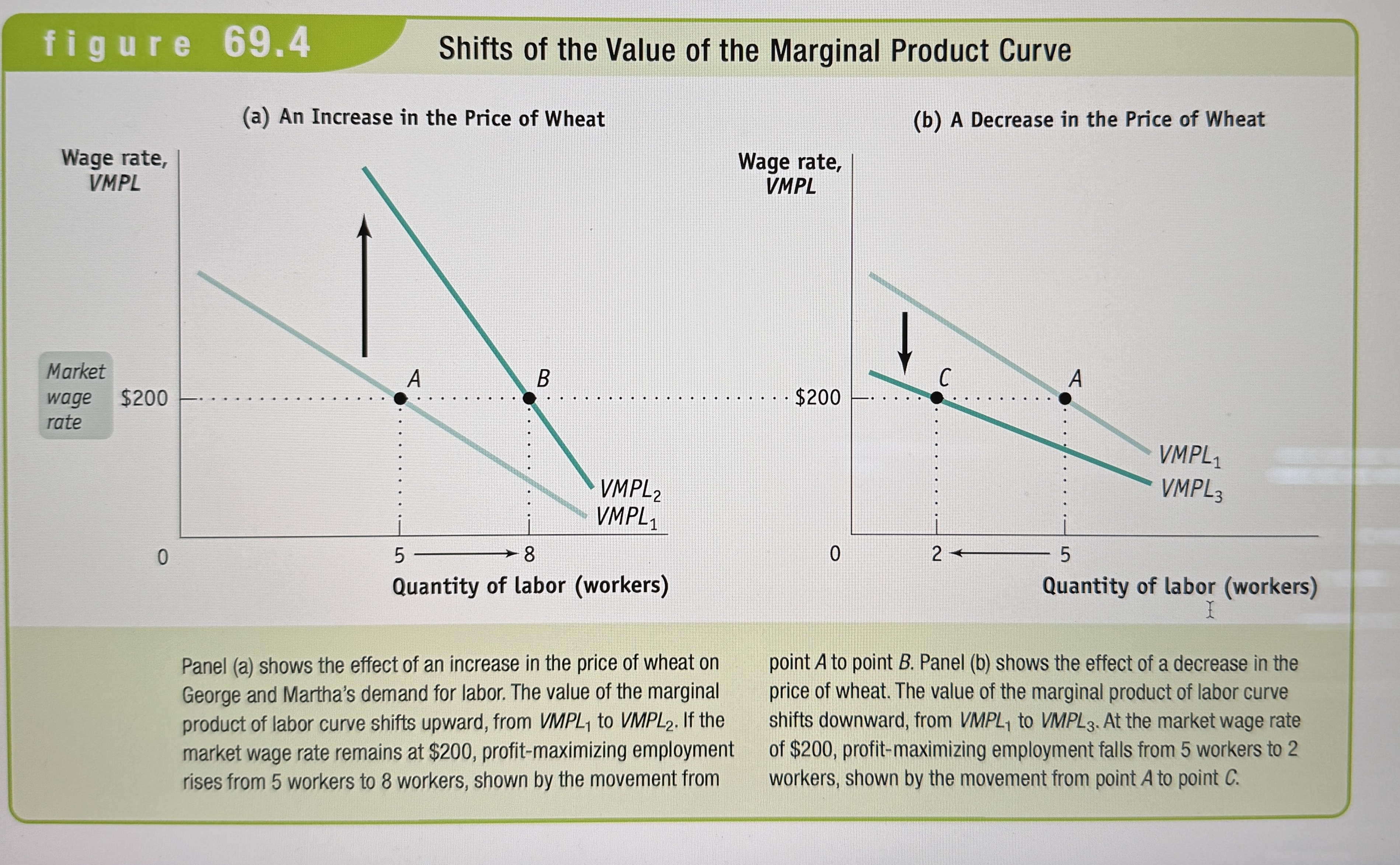
Shifts of the Value of the Marginal Product Curve
Ex.
Rental Rate
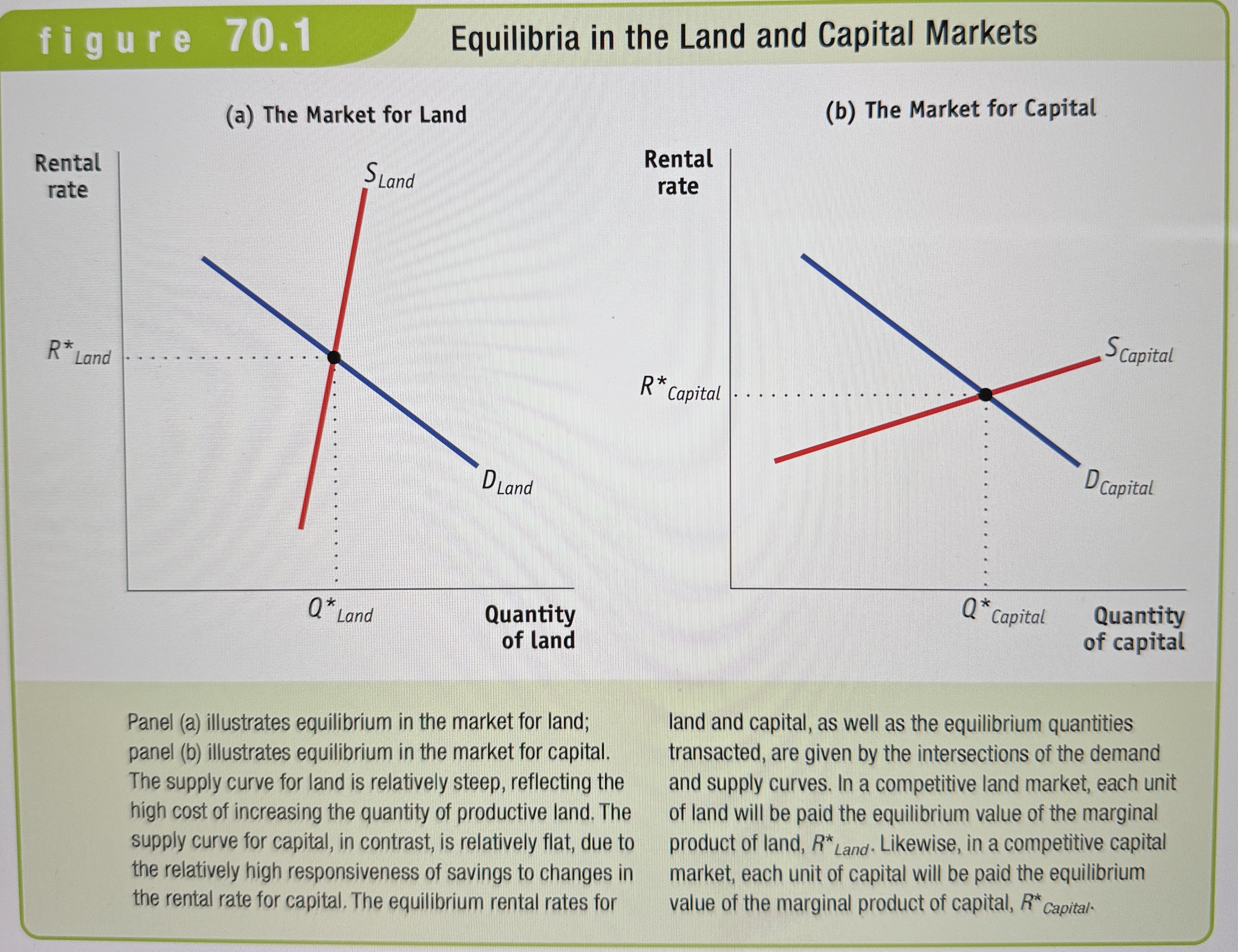
The rental rate of either land or capital is the cost, explicit or implicit, of using a unit of that asset for a given period of time.
Equilibria in the Land and Capital Markets
Ex.
The marginal productivity theory of income distribution
According to the marginal productivity theory of income distribution, every factor of production is paid the equilibrium value of its marginal product.
Time Allocation
Decisions about labor supply result from decisions about time allocation: how many hours to spend on different activities.
Leisure
Leisure is time available for purposes other than earning money to buy marketed goods.
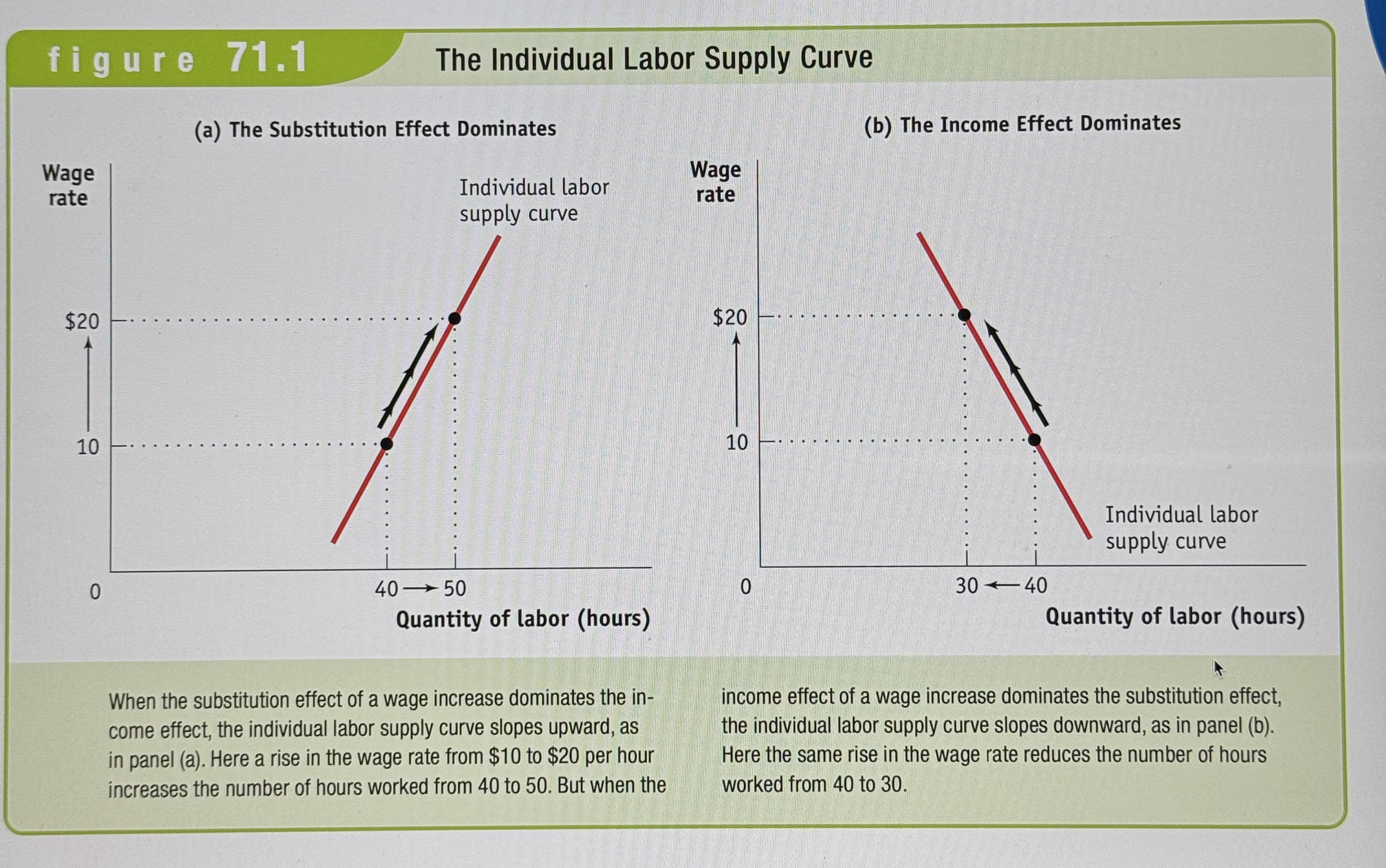
The Individual Labor Supply Curve
The individual labor supply curve shows how the quantity of labor supplied by an individual depends on that individual's wage rate.
Shifts of the labor supply market
Changes in preferences and social norms
Changes in Population
Changes in Wealth
Changes in Opportunities
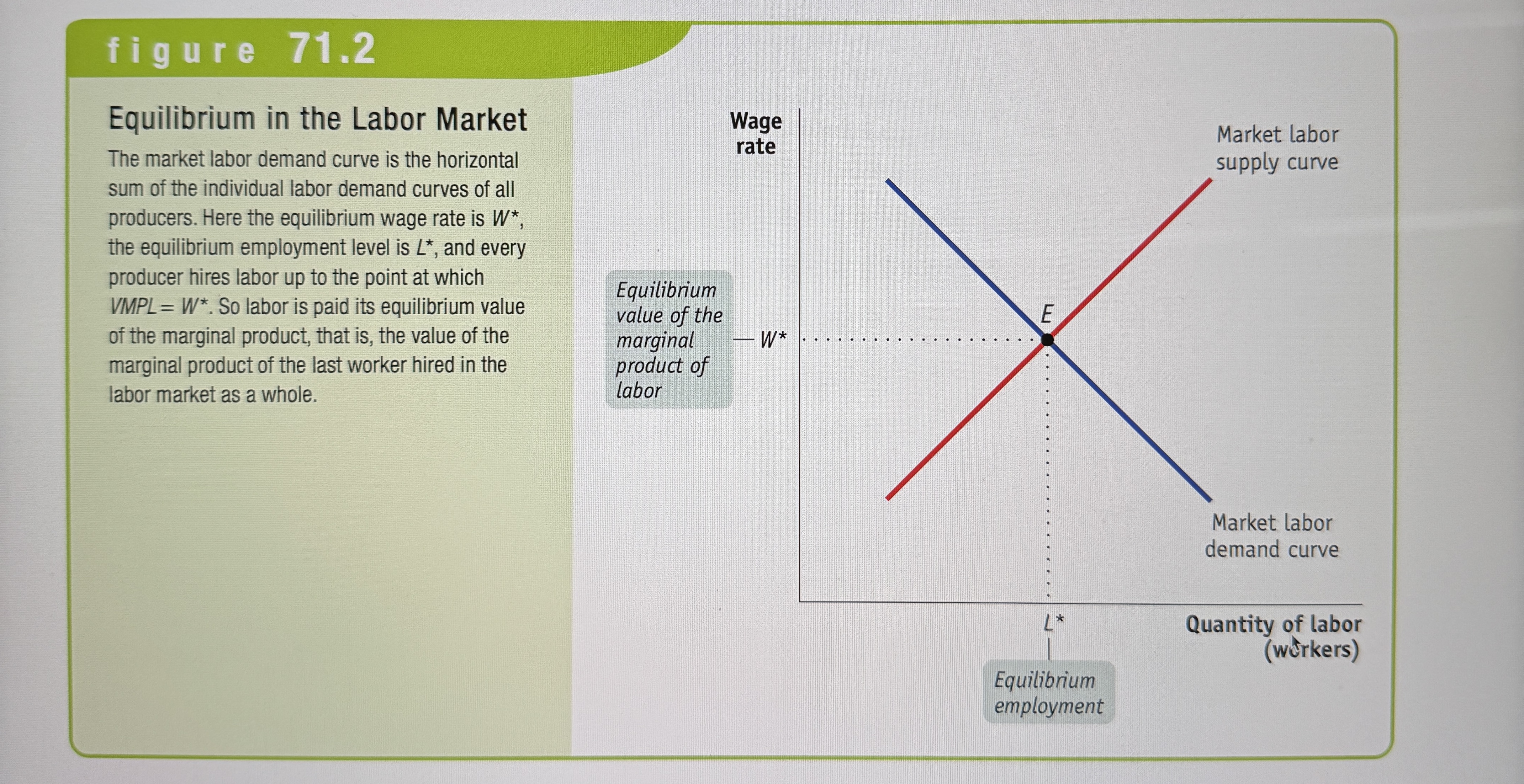
Equilibrium in the Labor Market
Ex.
The marginal revenue product of labor (MRPL)
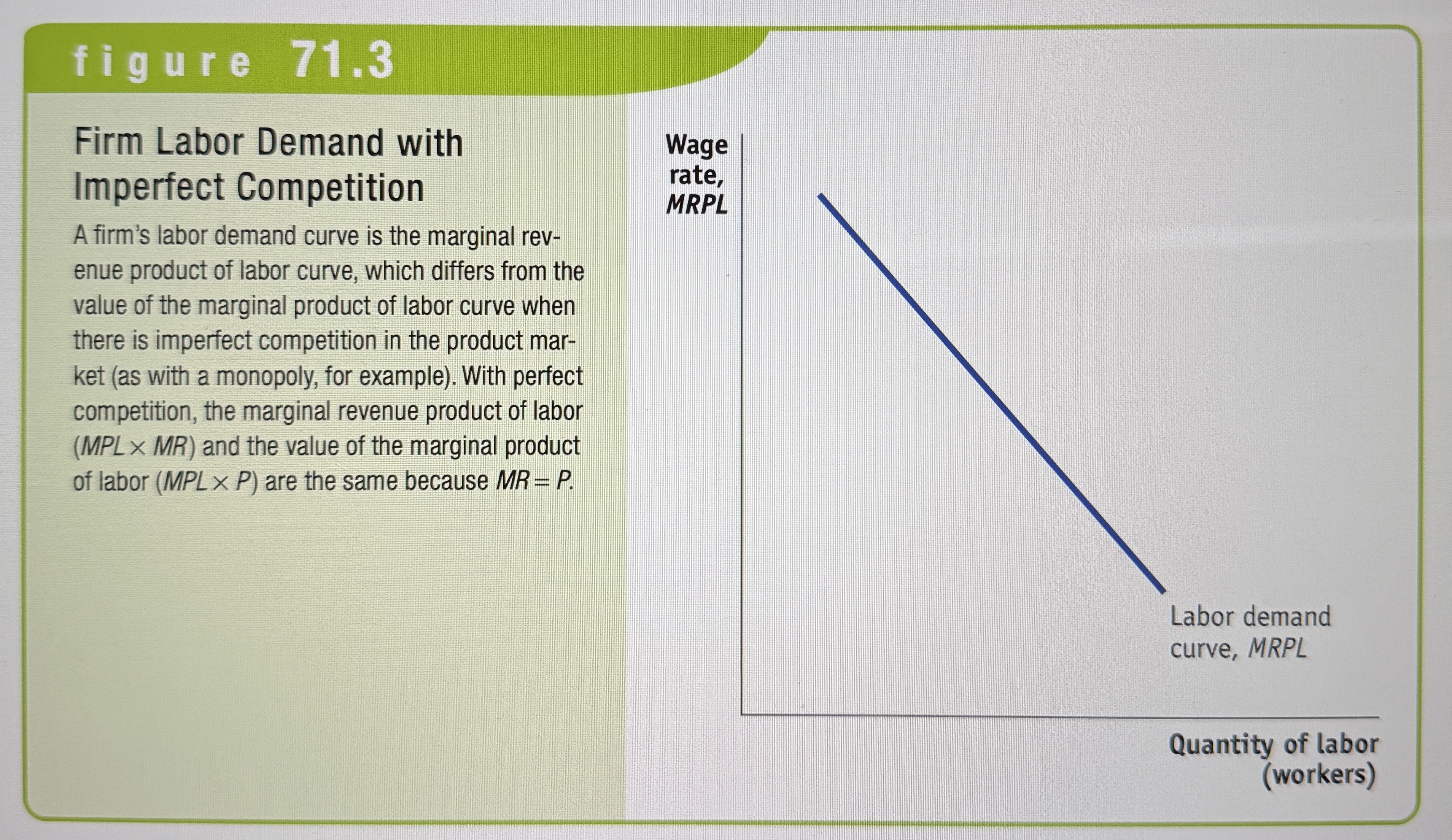
The demand curve for labor for a firm operating in an imperfectly competitive product market is the marginal revenue product of labor curve. The marginal revenue product of labor (MRPL) is equal to the marginal product of labor times the marginal revenue received from selling the additional output. The marginal revenue product of land and the marginal revenue product of capital are equivalent concepts.
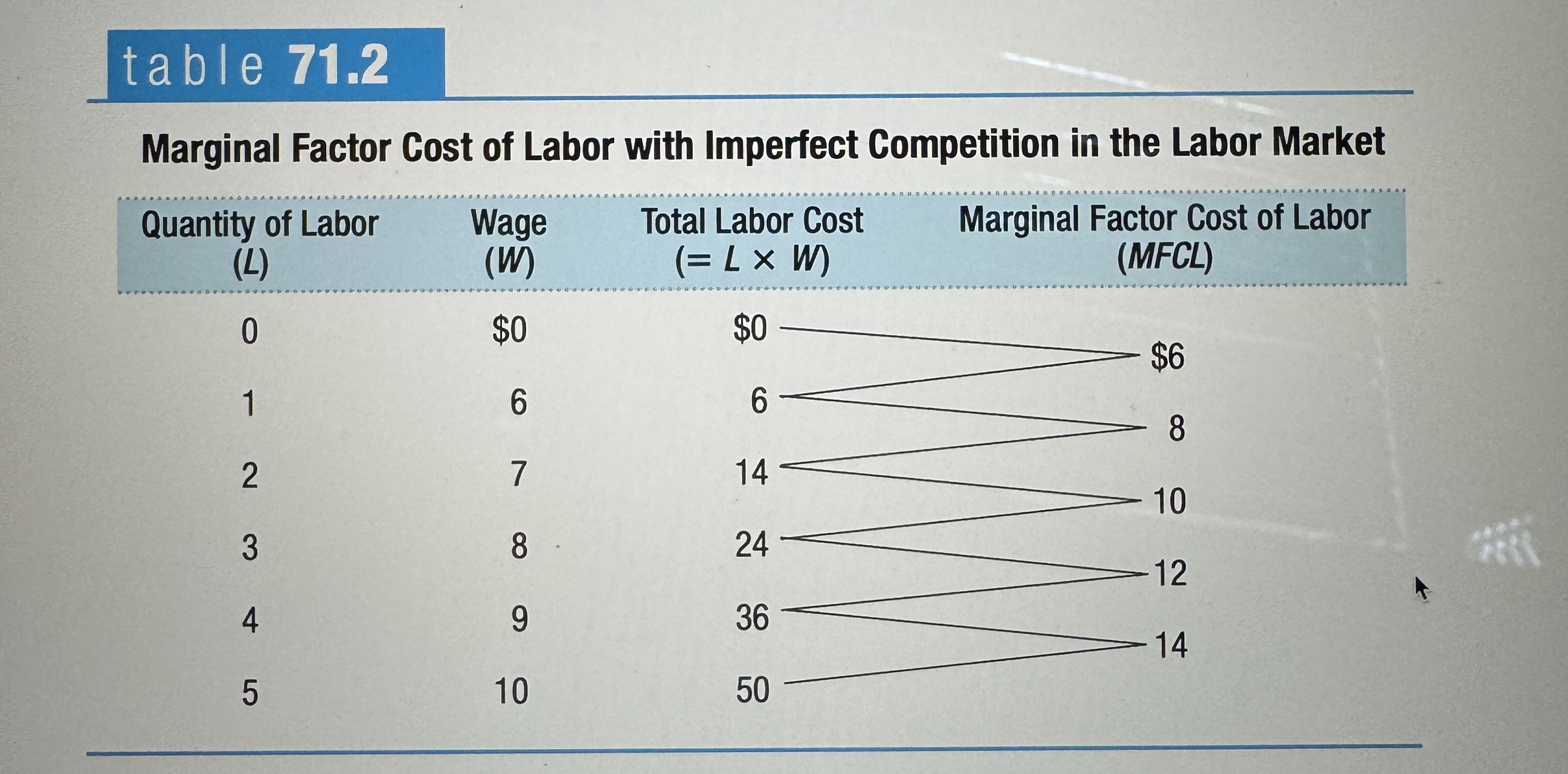
The marginal factor cost of labor (MFCL)
The marginal factor cost of labor (MFCL) is the additional cost of hiring an additional worker. The marginal factor cost of land and the marginal factor cost of capital are equivalent concepts.
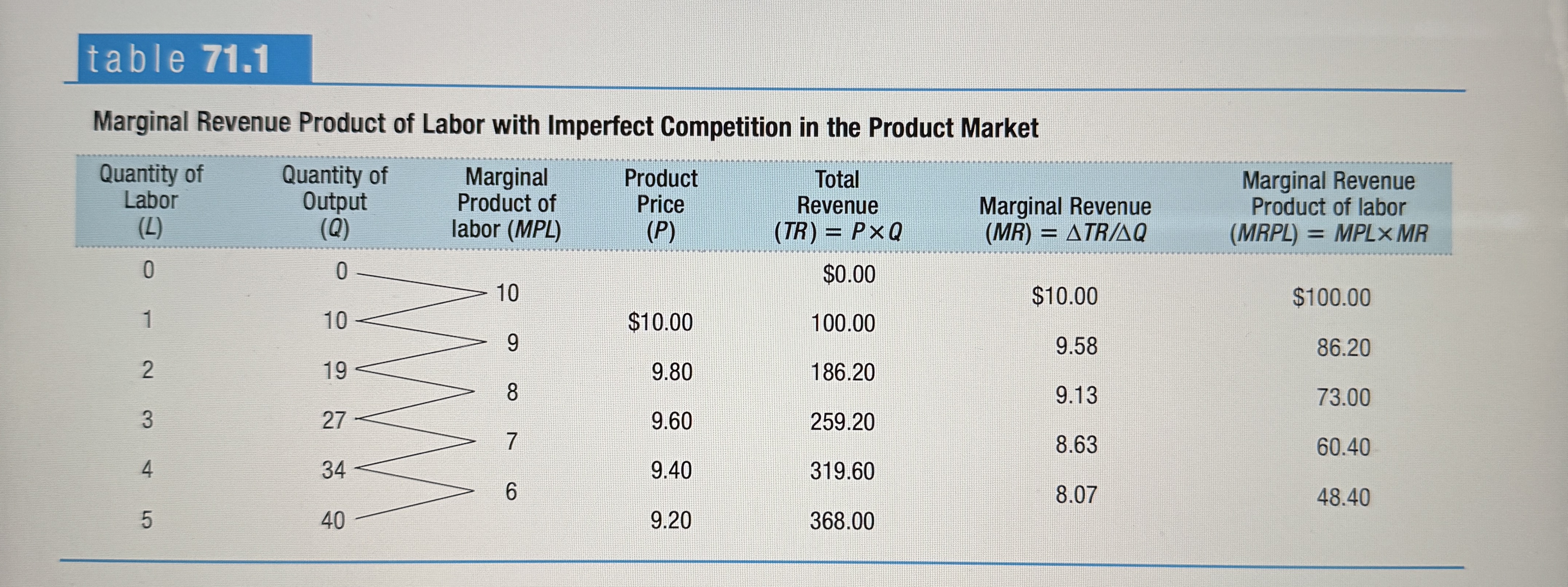
Marginal Revenue Product of Labor with Imperfect Competition in the Product Market
Ex.
Firm Labor Demand with Imperfect Competition
Ex.
Monopsony
A monopsonist is a single buyer in a factor market. A market in which there is a monopsonist is a monopsony.
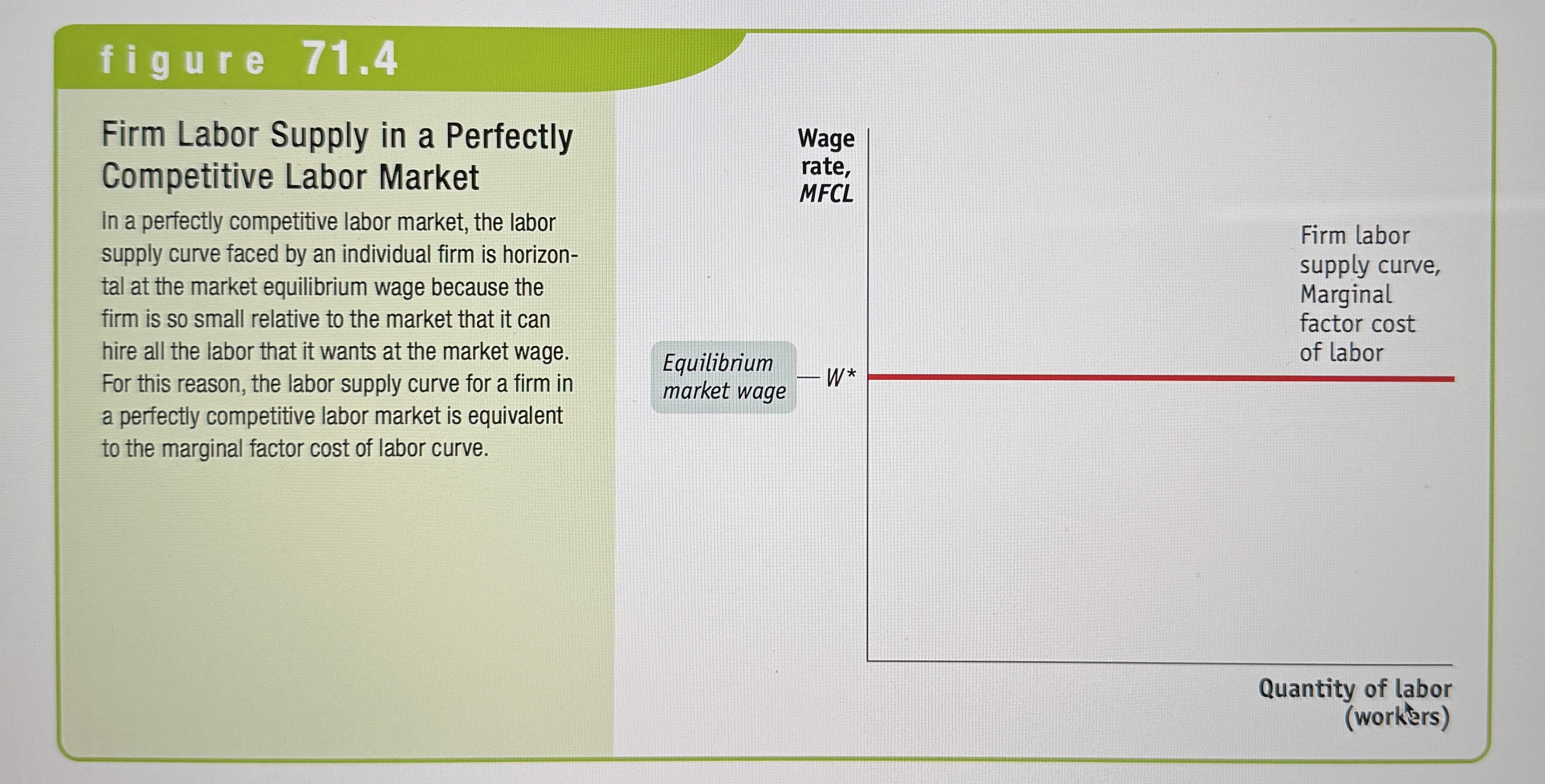
Firm Labor Supply in a Perfectly Competitive Labor Market
Ex.
Marginal Factor Cost of Labor with Imperfect Competition in the Labor Market
Ex.
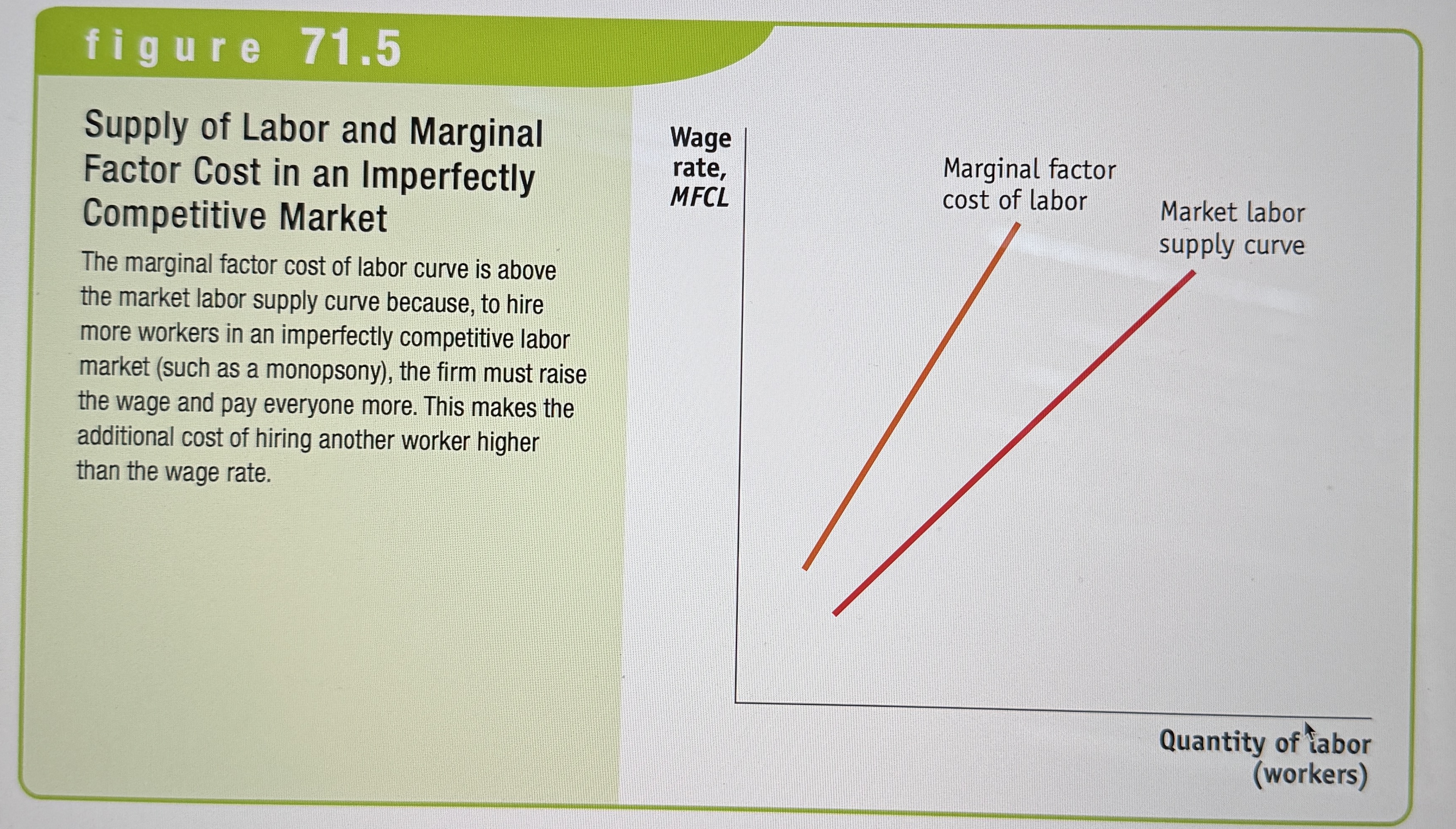
Supply of Labor and Marginal Factor Cost in an Imperfectly Competitive Market
Ex.
Hire Workers until…
MRPL = MFCL
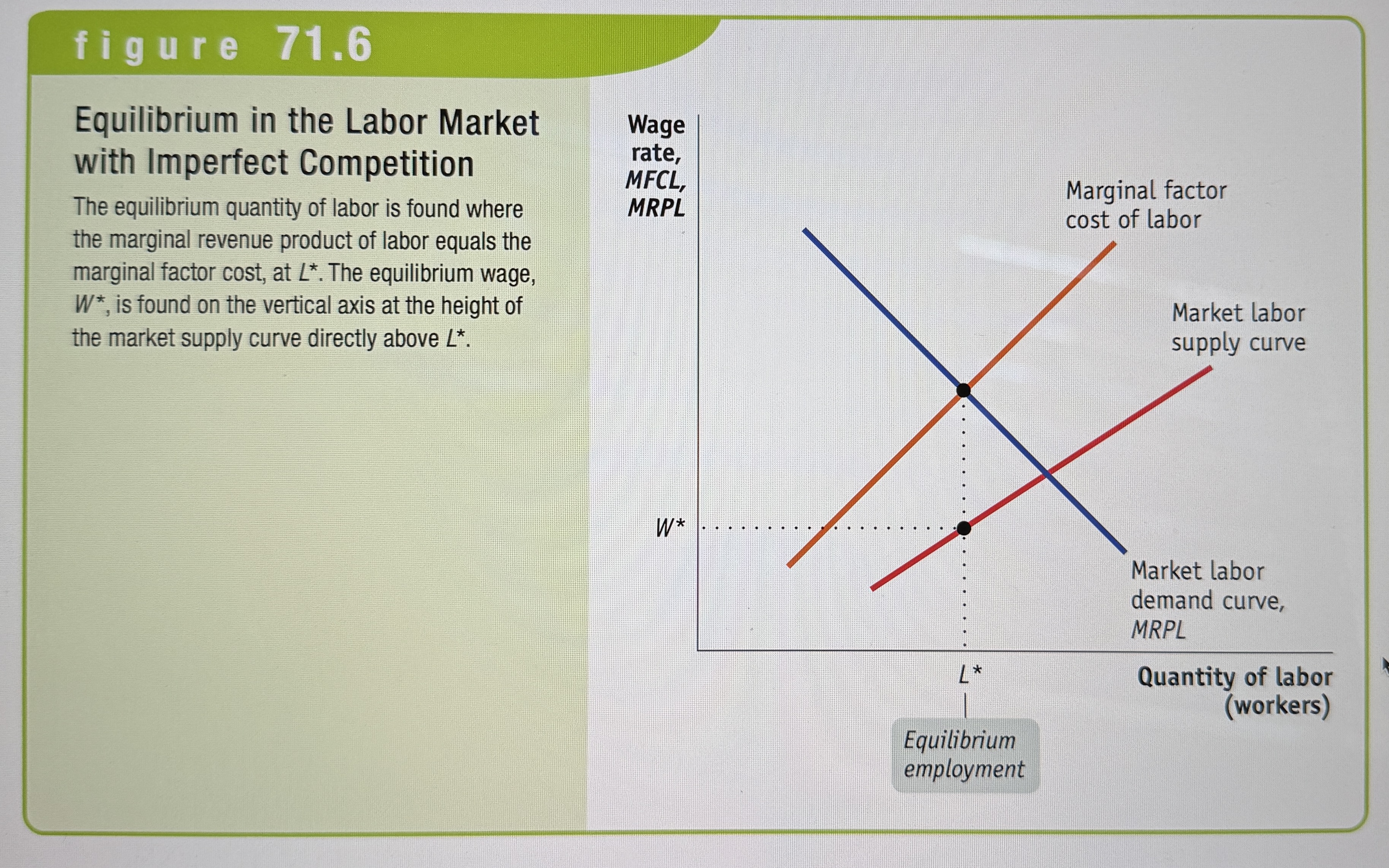
Equilibrium in the Labor Market with Imperfect Competition
Ex.
The Cost-Minimization Rule
A firm determines the cost-minimizing combination of inputs using the cost-minimization rule: hire factors so that the marginal product per dollar spent on each factor is the same.
Cost Minimizing Explained (Long)
Ex.

Compensating Differentials
Compensating differentials are wage differences across jobs that reflect the fact that some jobs are less pleasant or more dangerous than others.
The equilibrium value of the marginal product
The equilibrium value of the marginal product of a factor is the additional value produced by the last unit of that factor employed in the factor market as a whole.
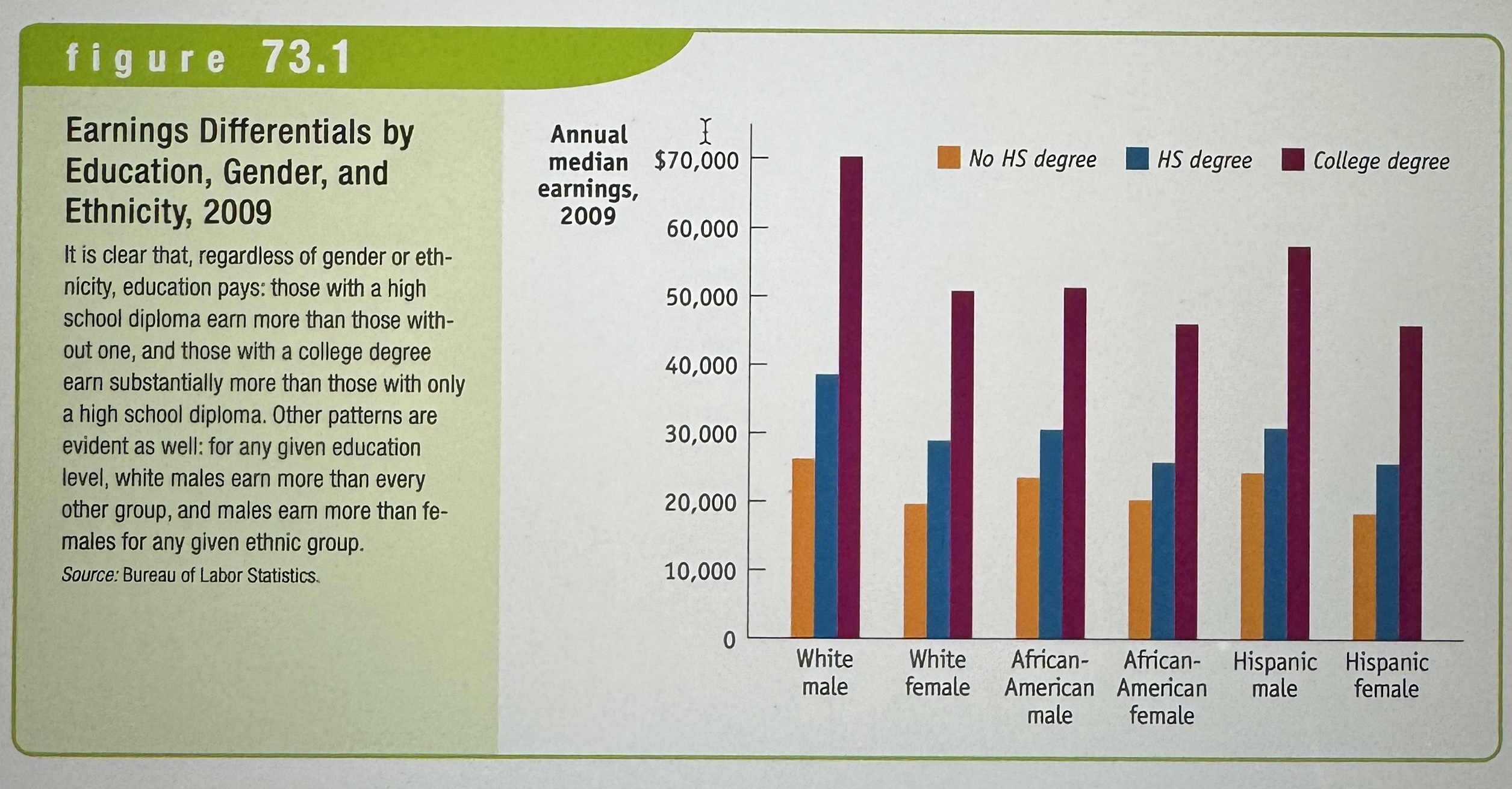
Earnings Differentials by Education, Gender, and Ethnicity, 2009
Ex.
Unions
Organizations of workers that try to raise wages and improve working conditions for their members by bargaining collectively.
The Efficiency-Wage Model
According to the efficiency-wage model, some employers pay an above-equilibrium wage as an incentive for better performance and loyalty.
Median Earnings by Gender and Ethnicity, 2009
Ex.