AP REVIEW: Scientific foundations of psychology
1/97
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
Wilhelm Wundt
German psychologist known as the father of experimental psychology, established the first psychology laboratory in 1879. Founder of structuralism.
Max Wertheimer
A psychologist who co-founded Gestalt psychology, emphasizing how people perceive the world as unified wholes rather than the sum of its parts. Disagreed with structuralism.
Psychoanalysis/Psychodymanic theory
A psychological approach that emphasizes unconscious processes and childhood experiences influencing behavior and mental health. Founded by Sigmund Freud
Applied research
Practical study aimed at solving specific problems or improving existing processes, often conducted in real-world settings. “How can I use this”
Hindsight bias
The tendency to believe that an event was predictable after it has already occurred, leading to overestimating one's ability to have foreseen the outcome.
Range
The difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution. → 100-10=90 ←90 is the answer.
Biopsychosocial perspective
Focuses on how biological, psychological, and social factors influence human behavior and mental health.
Empirical evidence
Information gathered using direct observation or experience, often through scientific methods, to support or refute a hypothesis or theory.
Descriptive methods
Involve observing and recording behaviors, characteristics, or phenomena as they naturally occur, without manipulating variables.
Naturalistic observation
Case study’s
Surveys
Experimental methods
Research techniques used in psychology to manipulate variables and measure their effects on behavior, allowing for cause-and-effect conclusions.
Hawthorne effect
When subjects of an experiment change or improve their behavior because it is being evaluated or studied.
Wording effect
When the wording of a question or statement influences the response given. It highlights the impact of language on decision-making.
Standard deviation
The spread of scores, its a computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean.
Z-score
A statistical measure that shows how many standard deviations a data point is from the mean of a dataset. It helps analyze and compare data in a standardized way.
Negative z-score
Indicates a data point below the mean in a standard normal distribution. It represents values lower than the average.
Positive z-score
A statistical measure indicating the number of standard deviations a data point is above the mean in a normal distribution.
P-value
The probability of results of the experiment being attributed to chance. p=probability
Philosophy
Study of fundamental questions about existence, knowledge, values, reason, mind, and language, often through critical analysis and rational argument.
Phsiology
Study of functions and processes within living organisms, including how organs and systems work together to maintain life.
Introspection
The process of examining one's thoughts and feelings. It involves reflecting on internal experiences to gain insight and self-awareness. - Founded by Wilhelm Wundt
Structuralism
The idea that the mind operates by combining subjective emotions and objective sensations. Believe that the mind could be dissected into its individual parts. - Developed by Wilhelm Wundt & Edward Titchner
In-ward looking
Refers to a focus on internal thoughts, feelings, and experiences rather than external factors. Examining ones own thoughts, emotions, judgements, and perceptions. - Related to structuralism.
William James
American psychologist and philosopher known for his contributions to functionalism and pragmatism. He wrote "The Principles of Psychology" and emphasized the importance of studying consciousness and the mind.
Functionalism
Psychological perspective that focuses on how mental processes help individuals adapt to their environment and function effectively in society. Describes the mind as a functional tool that allows us to adapt to our environment.
Mind-body dualism
Philosophical belief that the mind and body are distinct entities with separate functions and existences.
Mary Whiton Calkins
Was the first woman to become the president of the American Psychological Association in 1905. She was also a student of William James. - Denided a PHD even after finishing all the coursework in Harvard.
Outliers
Data points that lie far from other observations in a dataset. They can skew results and impact statistical analyses.
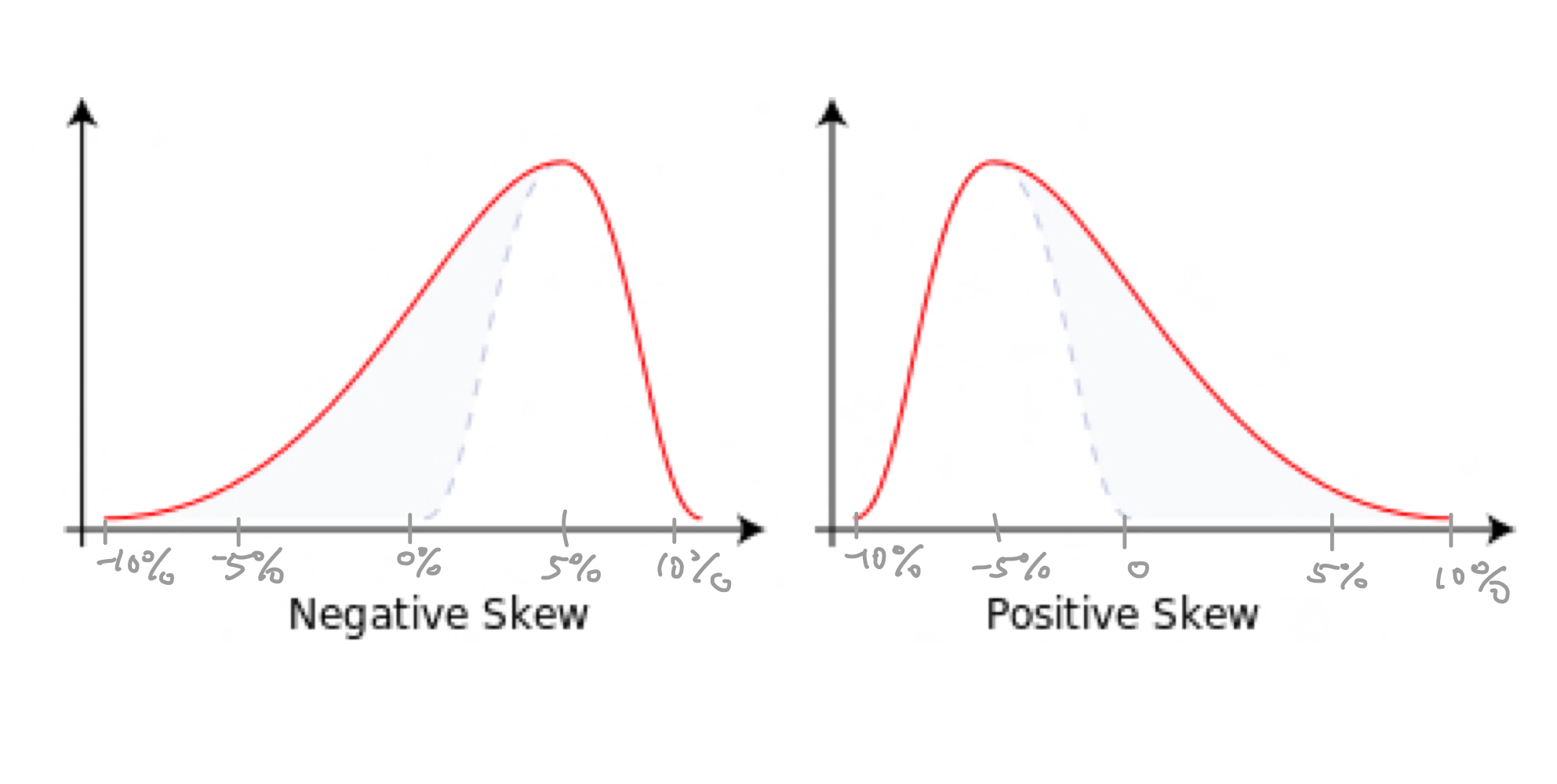
Negative Skew
A distribution where the tail is on the left side and the majority of the data is concentrated on the right side.
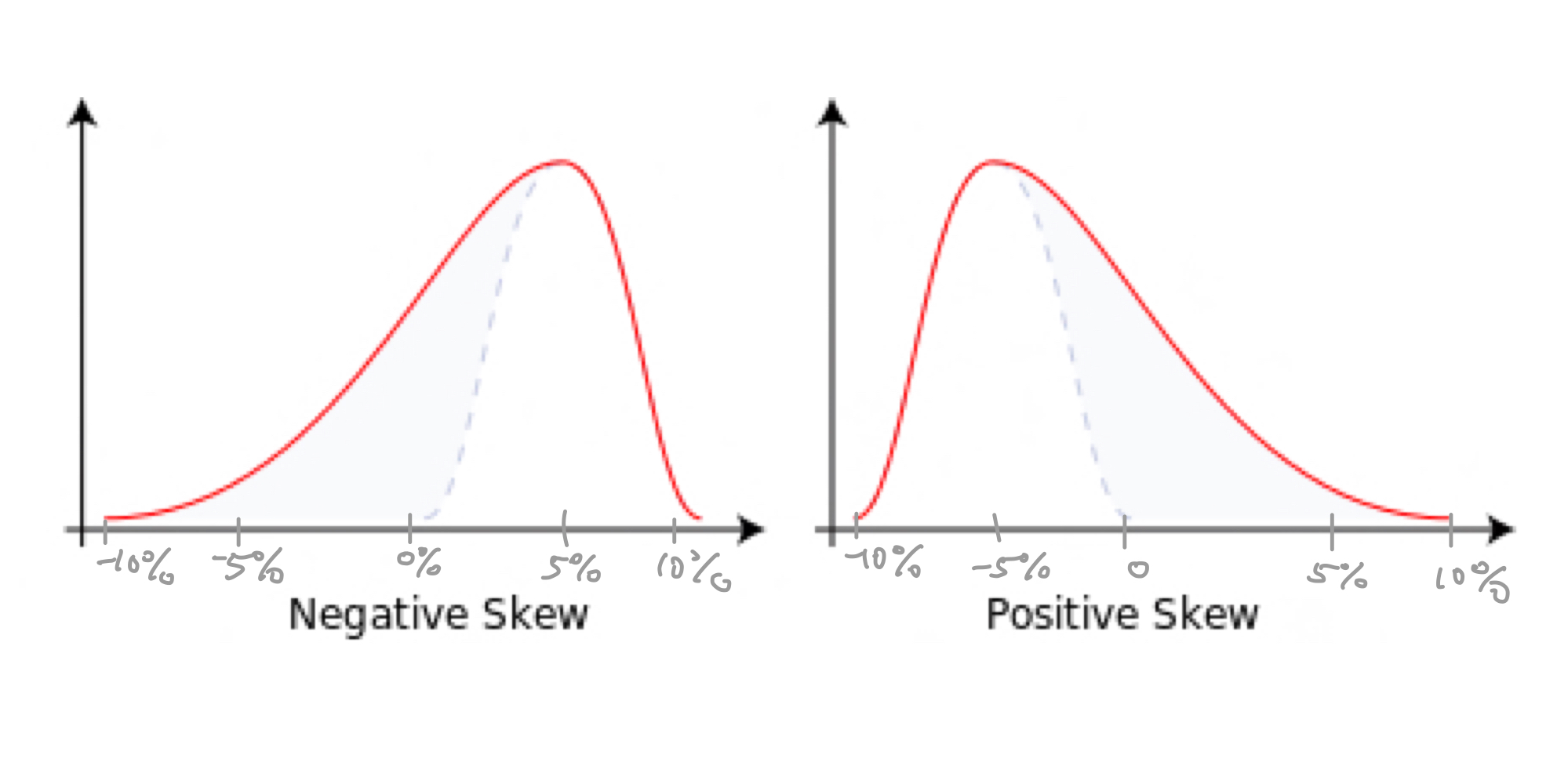
Positive Skew
A distribution where the tail is on the right side and the majority of the data is concentrated on the left side.
Frequency
A numerical count of how often something occurs within a specific period, often used in research and statistics to analyze patterns and trends. - How often a number appears in a distribution.

Bar Graph
A visual representation of data using bars of different heights to show comparisons between categories. The length of each bar corresponds to the value it represents. - Categorical values only.
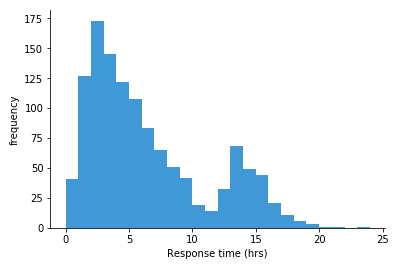
Histogram
A visual representation of data distribution that uses bars to display the frequency of numerical data within specific intervals. - Numerical values only
Confounding variable
A variable that distorts the true relationship between the independent and dependent variables in a study, leading to inaccurate conclusions. - Throws off your study. You can avoid it by using randomization, restriction, and matching.
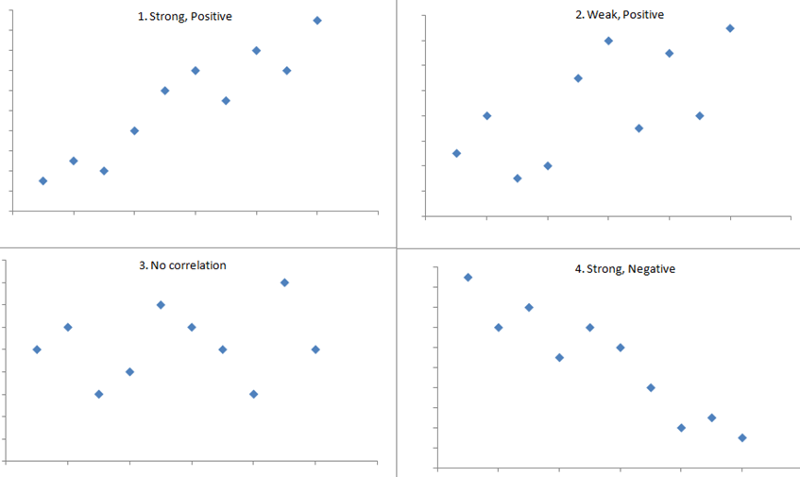
Weak correlation
Refers to a relationship between two variables that is not very strong or consistent. - Less than .5
Correlation coefficient (r )
Measures the strength and direction of a linear relationship between two variables, ranging from -1 to 1.
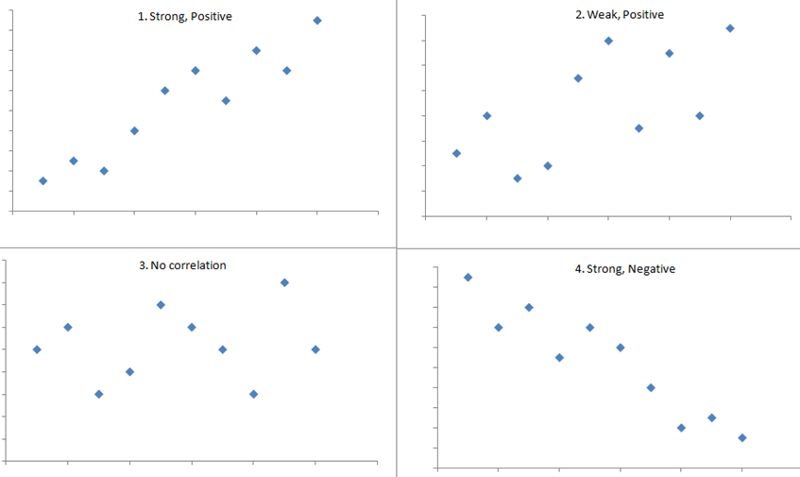
Strong correlation
A statistical measure indicating the extent to which two or more variables change together. It shows a close relationship between the variables.- More than .5

Line of best fit
A straight line that best represents the relationship between two variables in a scatter plot, showing the general trend of the data points. - Also known as line of regression and tread line.
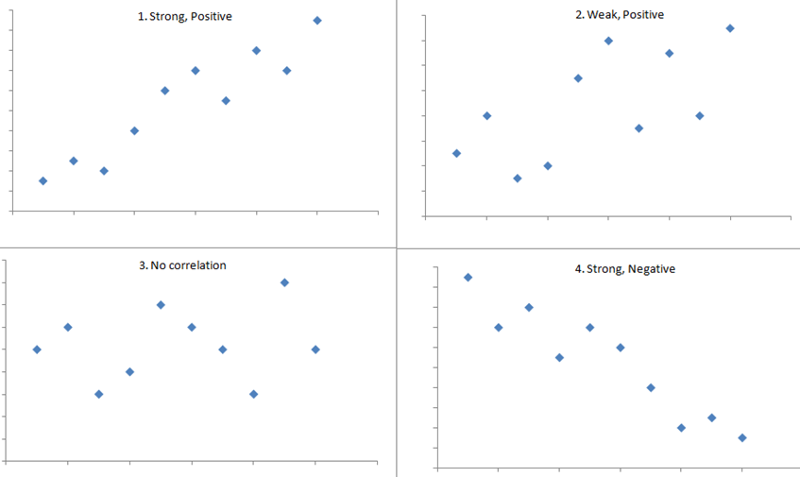
Negative correlation
When two variables move in opposite directions, meaning as one variable increases, the other decreases.
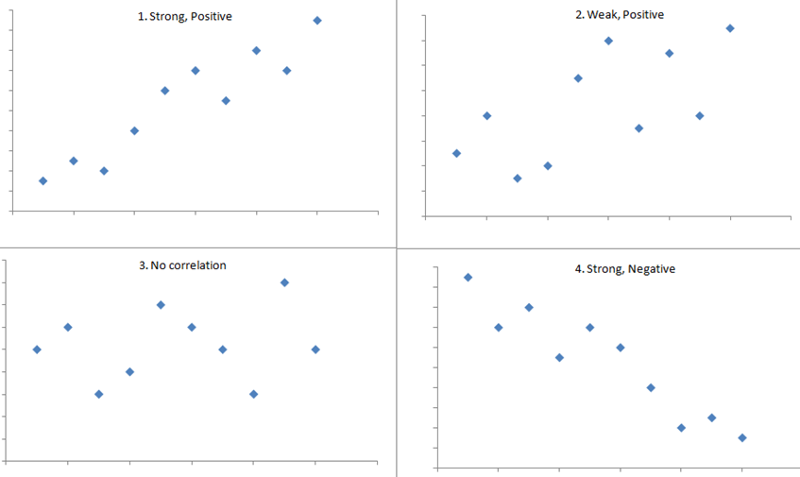
Positive correlation
A relationship where two variables move in the same direction. As one variable increases, the other variable also increases.
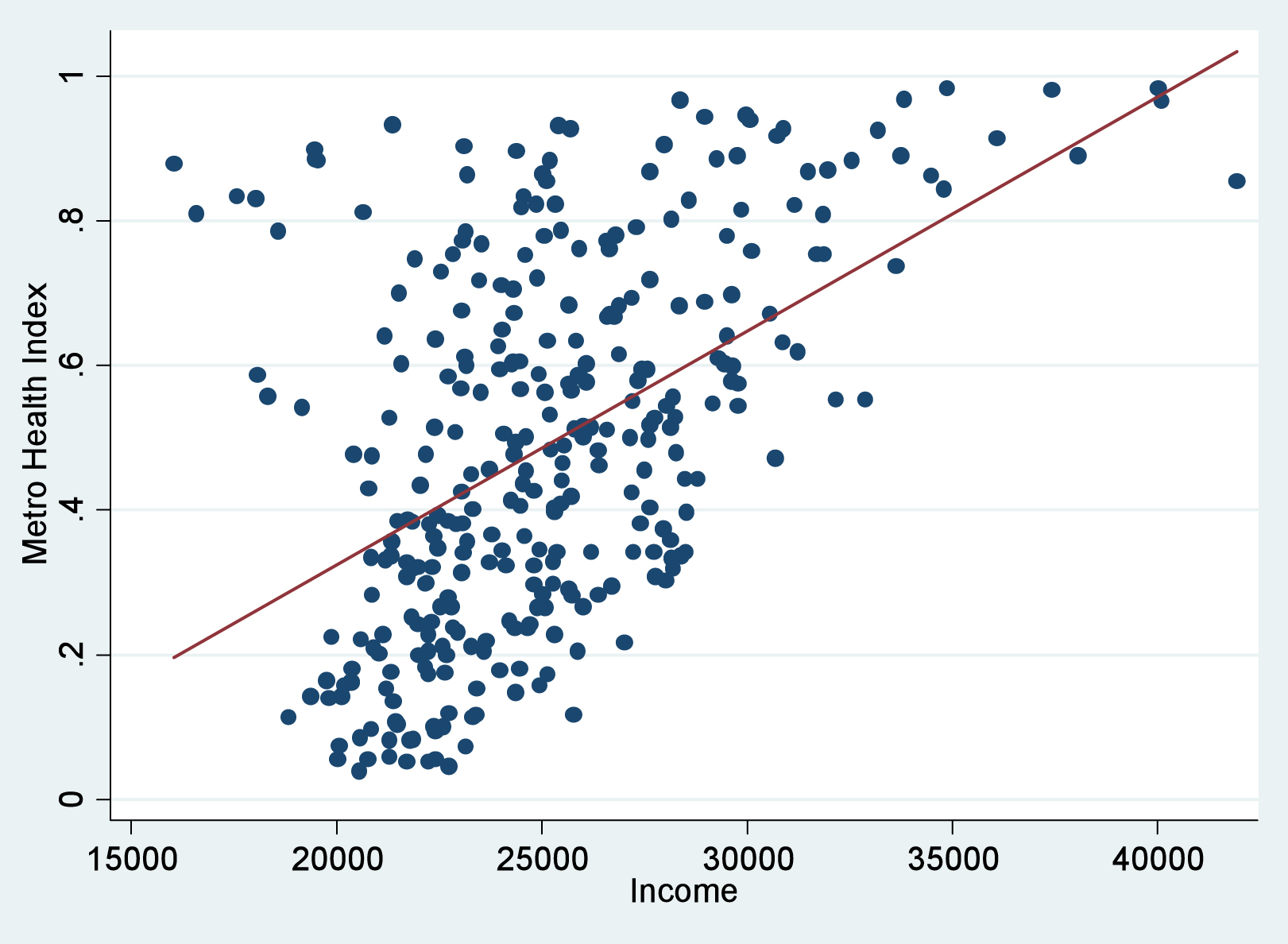
Scatterplot
A graph that displays the relationship (correlation) between two variables, showing how one variable changes in response to the other.
Causation
Relationship where one event leads to the occurrence of another event. It implies a direct cause-and-effect connection between the two variables.
Correlation
Measures the strength and direction of a relationship between two variables. It ranges from -1 to 1, with 0 indicating no correlation.
Psychological case study of H.M.
A landmark study on memory conducted on patient H.M. who had severe amnesia due to brain surgery, shedding light on the role of the hippocampus. - Showed that the hippocampus is essential for explicit (conscious) and declarative memory (stored memory that requires conscious effort to be retrieved) but not implicit (unconscious) procedural memory (long term memory involving the performance of different actions and skills).
John B. Watson
An American psychologist known for founding behaviorism and conducting the Little Albert experiment, demonstrating classical conditioning.
Neuropsychologists
Study the relationship between the brain and behavior, focusing on how brain function impacts cognitive processes and emotions.
Experimental psychologists
Conduct research to understand behavior and mental processes using scientific methods and experiments.
Quantitative psychologists
Use statistical methods to study behavior, making predictions based on data analysis.
Margaret Floy Washburn
Was the first woman to receive a PhD in psychology and the second female president of the American Psychological Association. Studied animal behavior and motor development. Studied under Edward Titchner.
American Psychological Association (APA)
A professional organization representing psychologists in the United States. APA sets standards for research, publications, and ethical practices in psychology.
Leading questions
Questions are worded in a way that pushes the respondent toward the answer that the surveyor is hoping for. →This is a form of bias and will result in inaccurate data.
Cognitive Perspective
A psychological viewpoint that focuses on how people process, store, and retrieve information to make decisions and solve problems.
How we encode and retrieve memories
How we interpret situations
How we solve problems
How we develop language
Socio-cultural Perspective
Focuses on how society and culture influence behavior and mental processes. It emphasizes the impact of social norms, customs, and institutions on individuals.
Humanistic Perspective
Focuses on individual's capacity for personal growth, self-actualization, and free will. Emphasizes importance of self-awareness and self-improvement.
Biological Perspective
Focuses on how biological processes influence behavior and mental processes, including genetics, brain structures, and neurotransmitters.
Evolutionary Perspective
Emphasizes role of natural selection in shaping behavior, focusing on how traits that enhance survival are passed on to future generations.
Basic research
Experimental or theoretical work done to advance scientific knowledge without any immediate practical application. Used in the scientific field to understand and extend our knowledge about a specific phenomenon or field.
Experimental group
The group in an experiment that receives the treatment or intervention being studied, used to compare with the control group. - Exposed to the independent variable.
Control group
A group in an experiment that does not receive the treatment being tested. Used for comparison to determine the effectiveness of the treatment.
Random assignment
A research method where participants are placed into experimental groups by chance, minimizing bias and increasing the validity of results. - All participants have an equal chance of being in either groups.
Naturalistic observation
Involves studying subjects in their natural environment without interference, allowing researchers to observe behaviors as they naturally occur.
Case study
An in-depth analysis of a particular individual, group, or situation, often used in psychology and social sciences to gain insights and draw conclusions. - Typically includes interviews, observations, or test scores.
Survey
Collecting self reported information or data from individuals. Can be done on paper, electrically, or with an interviewer.
Population
Refers to the entire group of individuals or items that a researcher is interested in studying and drawing conclusions about.
Sample
A small portion or subset of a population selected for research to represent the whole group accurately.
Random selection
A method where each member of the population has an equal chance of being chosen for a study or experiment, increasing the likelihood of a representative sample. - You can do this by using a random name generator or drawing names from a hat.
Eclectic
A style that combines elements from various sources or styles, creating a unique and diverse approach. - Drawing from multiple psychological perspectives to understand human thought and behavior.
Stratified sampling
Involves dividing the population into subgroups based on a characteristic, then randomly selecting samples from each subgroup to ensure representation.
Sigmund Freud
Psychologist known for psychoanalysis, dream analysis, and the unconscious mind. Developed the id, ego, and superego theory. Founded psychoanalytic/psychodynamic theory.
Sampling bias
Occurs when some members of a population are more likely to be selected in a sample, leading to results that may not accurately represent the entire population.
Representative sample
A sample in which the characteristics of the participants closely matches the characteristics of the population as a whole. In other words the sample is a fairly accurate reflection of the population from which its drawn.
Modern perspective
Refers to a contemporary approach in psychology that emphasizes the importance of cultural, social, and environmental influences on behavior. - Biological, Behavioral, Cognitive, Humanistic, Psychodynamic, Socio-cultural, Evolutionary, Biopsychosocial.
Median
The middle score in a distribution. Line the scores from lowest-highest and find the middle score. Ex. 3,4,6,6,8,9,11
Mode
The most frequently according score in a distributon. Ex. 3,11,4,6,8,9,6
Mean
The average. You get it by adding all numbers up then dividing that number by the number of scores used. Ex. 3+11+4+6+8+9+6= 47 - 47/7 = 6.7.
Reliability
Consistency in measurement, producing similar results each time it is used; a reliable measure is dependable and yields stable outcomes. - Producing consistent results.
Validity
refers to how well a test or study measures what it claims to measure. It assesses if the results are accurate and meaningful. - Accuracy.
Replication
To re-create or do a study again.
Double-blind study
Research study where neither the participants nor the researchers know who is receiving the treatment or the placebo, reducing bias and increasing reliability.
The placebo effect
A phenomenon where a person experiences a real improvement in their condition after receiving a treatment that has no therapeutic effect. - In a way our own mind tricks us. It all comes down to the power of the mind.
Single-blind study
A research design where participants are unaware of the treatment they receive and the researchers are aware. reducing bias in the study results.
Operational definition
A clear and specific explanation of how a concept will be measured or observed in a particular study or experiment.
Dependent variable
The variable that is being measured and tested in an experiment. It depends on the independent variable for its value.
Independent variable
The factor manipulated or controlled by the experimenter to determine its effect on the dependent variable.
Behaviorism
A psychological theory that focuses on observable behaviors, emphasizing the role of the environment in shaping behavior through reinforcement and punishment. Behaviorists believe that as a science, psychology should only focus on what can be observed. - Founded by John B. Watson.
Freudian slip
“slip of the tongue” Its when you mean to say something but you say something else instead (you say what you’re actually thinking). Regarded as revealing subconscious feelings.
Repression
A defense mechanism where unpleasant thoughts or memories are pushed into the unconscious to reduce anxiety.
Unconscious mind
A hidden part of ourselves we form through repression. Takes place below the level of conscious awareness. Consists of deep mental processes not readily available to the conscious mind.
Gestalt psychology
Focuses on how the mind perceives and organizes patterns, emphasizing the whole being greater than the sum of its parts. - Examines a persons total experience.
Industrial/Organizational psychologists
Study workplace behavior, productivity, and employee well-being to improve organizational effectiveness and employee satisfaction.
Rehabilitation psychologists
Specialize in helping individuals with disabilities or injuries to improve their quality of life, independence, and overall well-being through therapy and support. - Help with recovery
Educational psychologists
Study how people learn and develop in educational settings to improve teaching methods and student outcomes.
Counseling psychologists
Focus on helping individuals cope with personal challenges, improve their well-being, and develop strategies for emotional and mental health.
Forensic psychologists
Apply psychological principles to legal issues, such as criminal investigations, court cases, and mental health evaluations within the legal system.
Social psychologists
Study how individuals' thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by others and by social situations. - Study how we interact with each other.
Health psychologists
Study how biological, psychological, and social factors influence health and illness. They work to promote health and prevent disease through behavior change interventions and stress management techniques.
Clinical psychologists
Mental health professionals who assess, diagnose, and treat individuals experiencing psychological distress or mental illness through therapy and interventions.
Sports psychologists
Professionals who apply psychological principles to improve athletic performance, enhance motivation, and address mental well-being in athletes.
Psychometric psychologists
Focus on measuring psychological traits, abilities, and characteristics using standardized tests and assessments.