INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS LAW
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Employment Rights Act (ERA)
1996
EMPLOYMENT LAW
Law that regulates relationship between employers and employees
Governs what employers can expect from employees
What employers can ask employees to do
Employees’ rights at work
WORKERS
Employed on part time / casual agency basis
Contract of service does not entitle them to sick pay , holiday pay and other benefits
they may not claim unfair dismissal
EMPLOYEES
Contract of service entitles them to full range of employment rights
Sick pay , holiday pay
Right to claim for unfair dismissal
INDEPENDENT CONTRACTOR
Providing services to a company but is not a employee or worker of the company
Not obligated to accept work offered
can assign someone else to do work on their behalf
EMPLOYER
Person / company / organisation that hires another person
pays employee a salary or wage
has the power to control the employee’s work duties
employs and supervises an employee
EMPLOYMENT LAW
Business may be served both by its own workers and employees under a contract of service
CONTRACT OF EMPLOYMENT
Employer offers employment
Employee accepts the offer of employment
Business agreement where both parties are presumed to intend legal relationships
EXPRESS TERMS
Specific conditions in an employment contract that both parties agree to and are usually written down.
Outline the legal rights and responsibilities of both the employer and the employee
Employees’ pay working hours etc
Agreed by both parties themselves - can be written and verbal
ERA 1996- requires employer to provide an employee with a written statement of prescribed particulars of their employment within 2 months of their commencemenrt
DUTIES OF EMPLOYER
Pay reasonable remuneration
Take reasonable care for the safety of their employees
Give reasonable notice of termination of employment
Maintain mutual co-operation , trust and confidence
provide truthful references
EMPLOYEES ENTITLEMENT
Employee is entitled to a minimum living wage , under the minimum wage act
Max hours of work required are 48 hours a week on average
Normally averaged over 17 weeks
Under 18’s cannot work more than 8 hours a day and no more than 40 hours a week
STRUCTURE OF THE COURT SYSTEM RELATION TO EMPLOYMENT
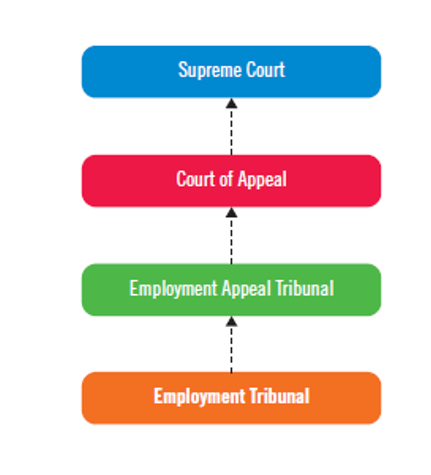
EMPLOYMENT LAW
Considered civil law
claimant can sue a defendant in a civil court
Claimant can be an employee, former employee or unsuccessful job applicant
EMPLOYMENT TRIBUNALS
Main forum for resolving disputes between employers and workers
WHAT HAPPENS IF DISPUTES NOT RESOLVED AT TRIBUNALS
They are appealed in other courts of higher jurisdiction
CONTROL TEST - EMPLOYMENT STATUS DETERMINATION
Employer has a degree of control over the work
Including how its done , when and where it’s done
INTEGRATION TEST - EMPLOYMENT STATUS DETERMINATION
Is the work done as an integral part of the business?
ECONOMIC REALITY TEST
How far is a person in business on his own account?
MUTUALITY OF OBLIGATIONS TEST?
Employer obliged to provide work and the employee obliged to accept it ?
SUMMARY DISMISSAL
Immediate termination of an employee due to their behaviour
Basis of which is gross misconduct
WRONGFUL DISMISSAL
Where an employer breaks the terms of an employee’s contract in the dismissal process
Usually concerns notice period and whether the employee was given advance notice of termination
CONSTRUCTIVE DISMISSAL
Occurs when an employee resigns as employer breached their contract of employment
Things such as : cutting wages , unlawful demotion , unfair increase in workload , unsafe work conditions
UNFAIR DISMISSAL
Dismissal that occurs when an employer terminates an employee’s employment without a fair reason
MINIMUM NOTICE PERIOD
Up to 1 month in employment - no notice is required
One month to 2 years’ employment - one week’s notice
2 years to 10 years employment - 1 week notice for every year completed
Over 10 years’ - 12 week’s notice
UNFAIR REASONS FOR DISMISSAL
Pregnancy
Joining / Not joining trade union
Family
Whistleblowing
REASONS FOR FAIR DISMISSAL
Capability
Conduct
Redundancy
Statutory bar
Other substantial reasons