Waves
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
What are the two different types of waves?
Longitudinal and transverse
What are examples of longitudinal waves?
sound waves
ultrasound waves
seismic P-waves
What are examples of transverse waves?
light
all E.M waves
water ripples
What do longitudinal waves look like?
Vibrations are parallel to the direction of wave travel
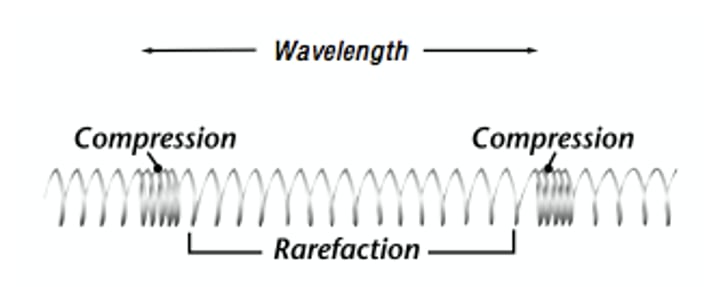
What do transverse waves look like?
Vibrations are at right angles to the direction of wave travel
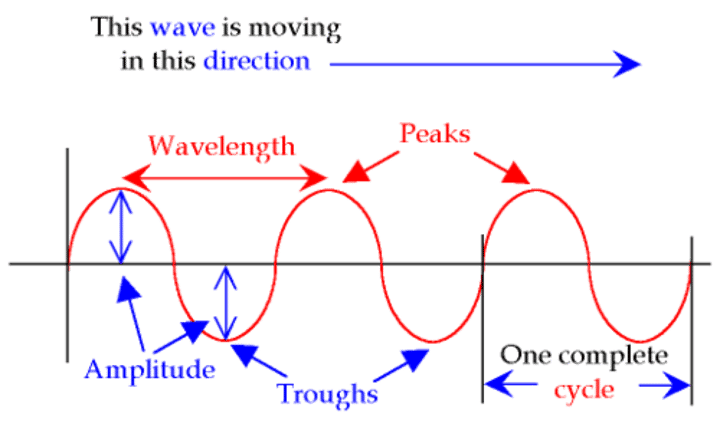
What is amplitude?
The maximum displacement of a point on a wave away from its undisturbed position
What is wavelength?
The distance from a point on one wave to the equivalent point on the adjacent wave
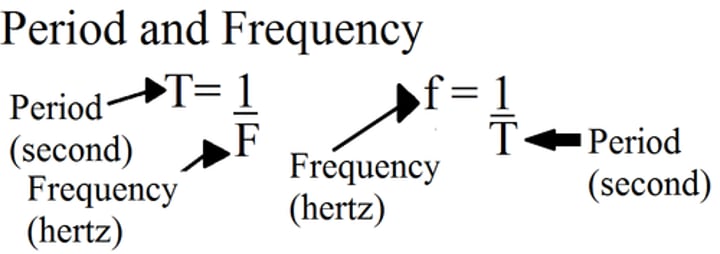
What is frequency?
The number of waves passing a point each second
How to calculate a period?
What's wave speed?
The speed at which the energy is transferred through the medium
What's the wave equation?
wave speed = frequency x wavelength
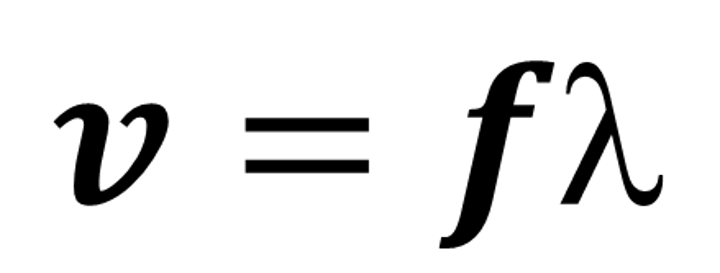
How do you measure the speed of sound waves in air?
String vibration practical
How do you measure the speed of ripples on a water surface?
Use a ripple tank
Velocity, frequency and wavelength are...
Directly proportional
What happens to a wave at a boundary between two different materials?
It's reflected, absorbed or transmitted
What are the properties of ultrasound waves?
frequency higher than upper human hearing limit
partially reflected when meeting boundary between 2 mediums
time taken for reflection to reach detector determines how far away the boundary is
What are the uses of ultrasound waves?
medical imaging
industrial imaging
jewellery cleaning
breaking kidney stones
What are seismic waves?
Waves produced by earthquakes
What are the 2 types seismic waves?
P waves and S waves
What are the properties of P-waves?
longitudinal
travel through solids and liquids
travel faster than S-waves
What are the properties of S-waves?
transverse
can only travel through solids
slower than P-waves
What can p-waves and s-waves provide evidence for?
The structure of the Earth and size of the Earth's core
What is echo sounding?
Use of ultrasonic waves for detecting objects in deep water and measuring the depth of water
What are electromagnetic waves?
Transverse waves that transfer energy from a source to an absorber
How do EM waves travel through a vacuum or air?
They travel at the same velocity continuously
What does the EM spectrum look like?
Could also be the other way around
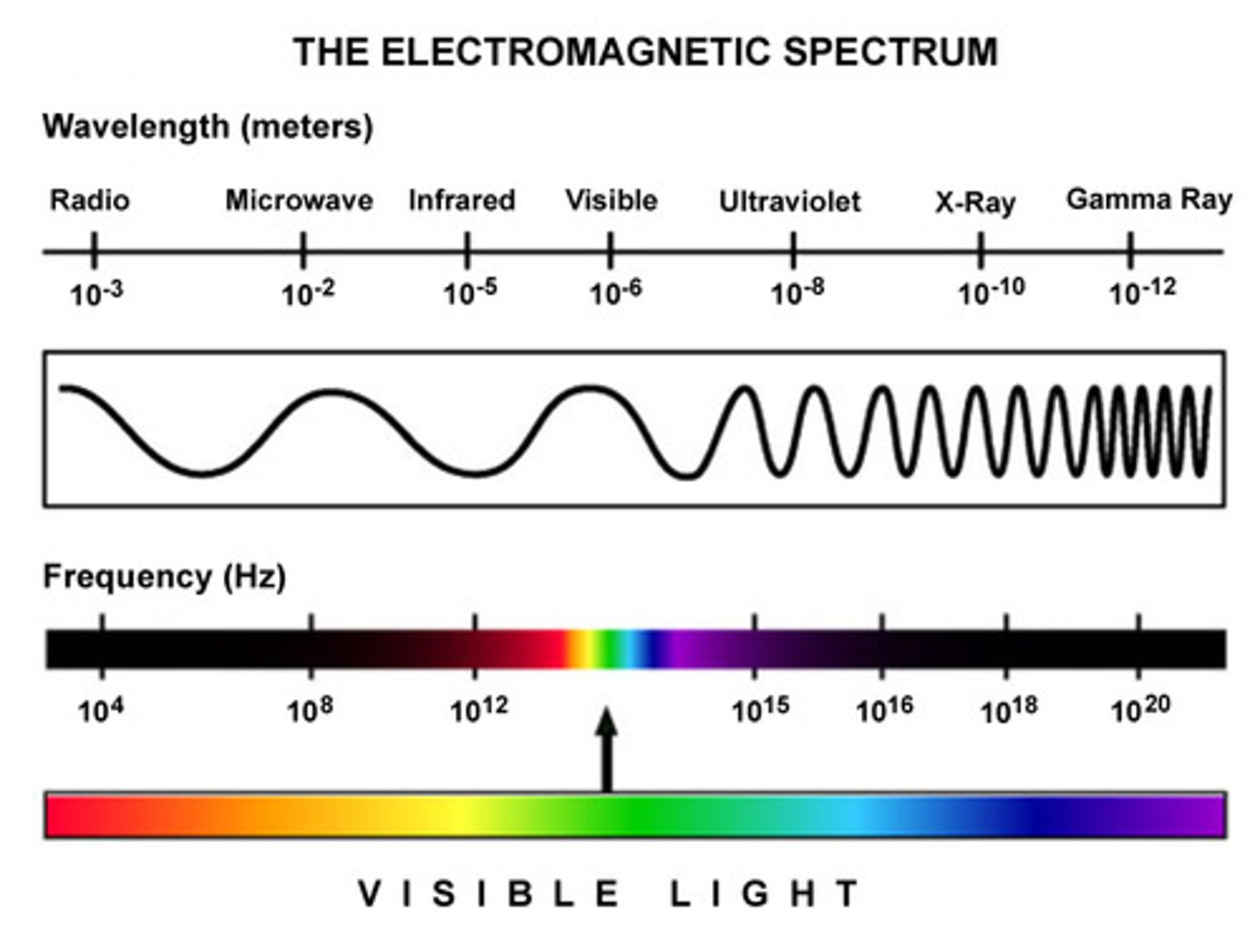
Which EM waves do human eyes detect?
Only visible light
How is energy transferred by EM waves?
By radiation
What happens when radio waves are absorbed?
Create an alternating current with the same frequency as the radio wave
How are radio waves produced?
By oscillations in electrical circuits
What are the uses of radio waves?
Television and radio
What are the uses of microwaves?
Satellite communications, cooking food
What are the uses of infrared?
Electrical heaters, cooking food, infrared cameras
What are the uses of visible light?
Fibre optic communications
What are the uses of ultraviolet?
Energy efficient lamps, sun tanning
What are the uses of x-rays and gamma rays?
Medical imaging and treatments
How does a lens form an image?
By refracting light
How is an image formed in a convex lens?
Parallel rays of light are brought to a focus at the principal focus
What is the distance from the lens to the principal focus called?
Focal length
What do ray diagrams show?
The formation of images by convex and concave lenses
Which images can a convex lens be?
Either real or virtual
Which images can a concave lens be?
Always virtual
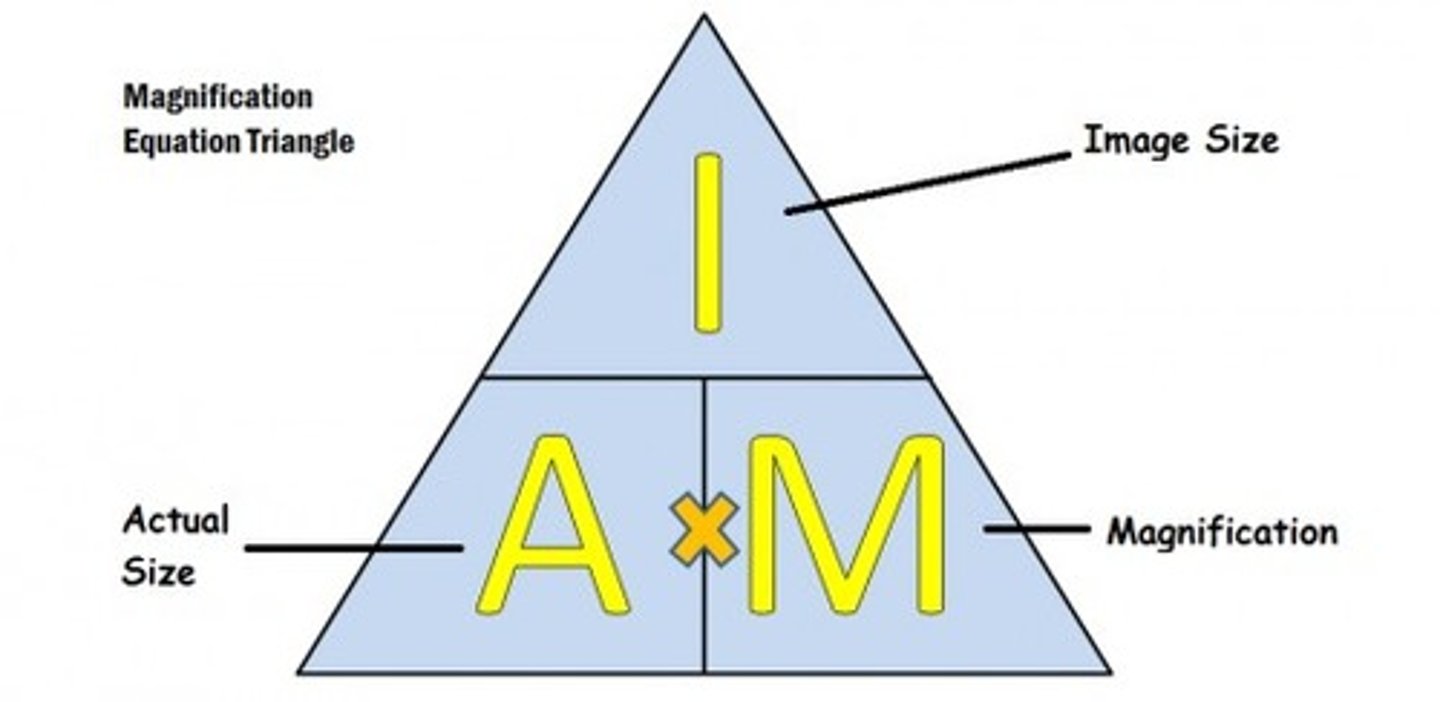
What is the equation for magnification?
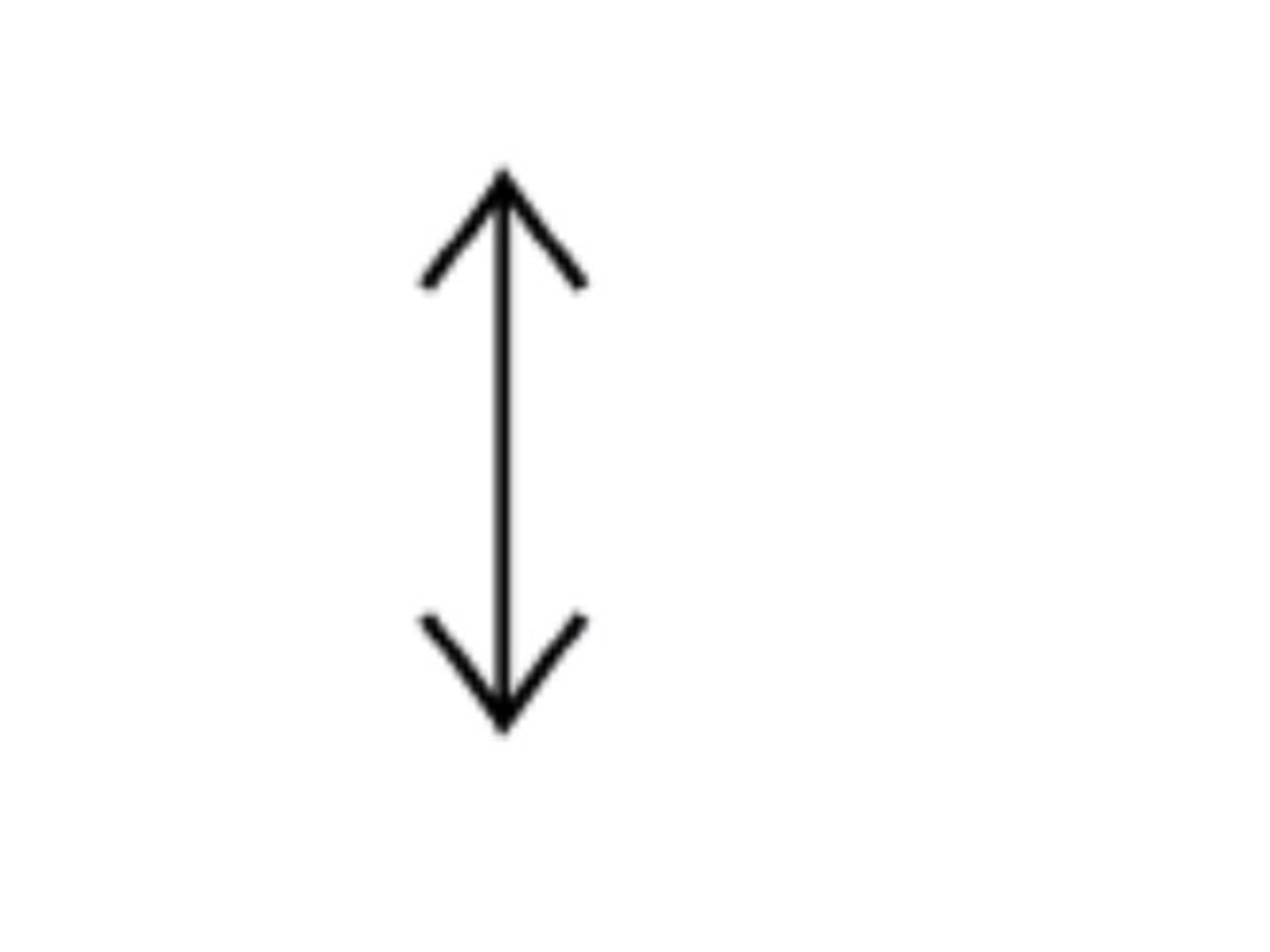
How is a convex lens represented in a ray diagram?
A line with two arrows pointing outwards
How is a concave lens represented in a ray diagram?
A line with two arrows pointing inwards
What are the two types of reflection, and from which surfaces are they formed?
Specular reflection - smooth surfaces
Diffuse reflection - rough surfaces (cause scattering)
How do colour filters work?
By absorbing certain wavelengths/colour and transmitting other wavelengths/colour
What is the colour of an opaque object determined by?
Which wavelengths of light are more strongly reflected
What happens to wavelengths that aren't reflected?
They're absorbed
Why do objects appear black or white?
Black: all wavelengths are reflected equally
White: all wavelengths are absorbed by the object
What does the colour of a surface depend on?
The pigments of the surface materials and the wavelengths of light the pigments absorb
What do all bodies (objects) do?
Emit and absorb infrared radiation
What is a perfect black body?
An object that absorbs all of the radiation incident on it. Does not reflect or transmit any radiation
As a perfect black body is a good absorber, what else is it good for?
Emitting
If a body is at a constant temperature what must its absorption and emission rate be?
Equal
If the temperature of a body increases what happens to the absorption and emission of radiation?
The body absorbs radiation faster than it emits radiation
What does the temperature of the Earth depend on?
The rates of absorption and emission of radiation, reflection of radiation into space