MMI Lab Final: ESKAPE, Final Exam: Biochemical Tests
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Enterococcus faecium
- 3rd most frequent cause of nosocomial bloodstream infections in the US
- 60% are Vancomycin resistant (VRE)
- gram positive cocci
Enterococcus faecium (relative)
Enterococcus raffinosus
Bacillus subtilis
Staphylococcus aureus
- MRSA ( methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus)
- gram postive cocci
Staphylococcus aureus (relative)
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Klebsiella species
- negative rod
- ESBL = Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamases
- Cross-resistance is growing
- Bloodstream infections from these organisms show increased mortality
Klebsiella species (relative)
Escherichia coli
Acinetobacter baumannii
- Multi-drug resistant (MDR) infections are increasing
- Usually a hospital-acquired infection
- negaitve coccobacillus
Acinetobacter baumannii (relative)
Acinetobacter baylyi
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Patients on ventilators or with cystic fibrosis areespecially at risk
- Negative rod
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (relative)
Pseudomonas putida
Enterobacter Species
- Health care-associated infections
- Resistance via ESBLs and carbapenemases
- negative rod
Enterobacter species (relative)
Enterobacter aerogenes
Erwinia carotovora
Selective media
-Additives suppress unwanted microbes and encourage desired microbes
- EMB, mannitol salt agar
Differential media
- Allow distinguishing of colonies of different microbes on the same plate
- alpha and beta hemolysis on blood agar; MacConkey agar, EMB, mannitol salt agar.
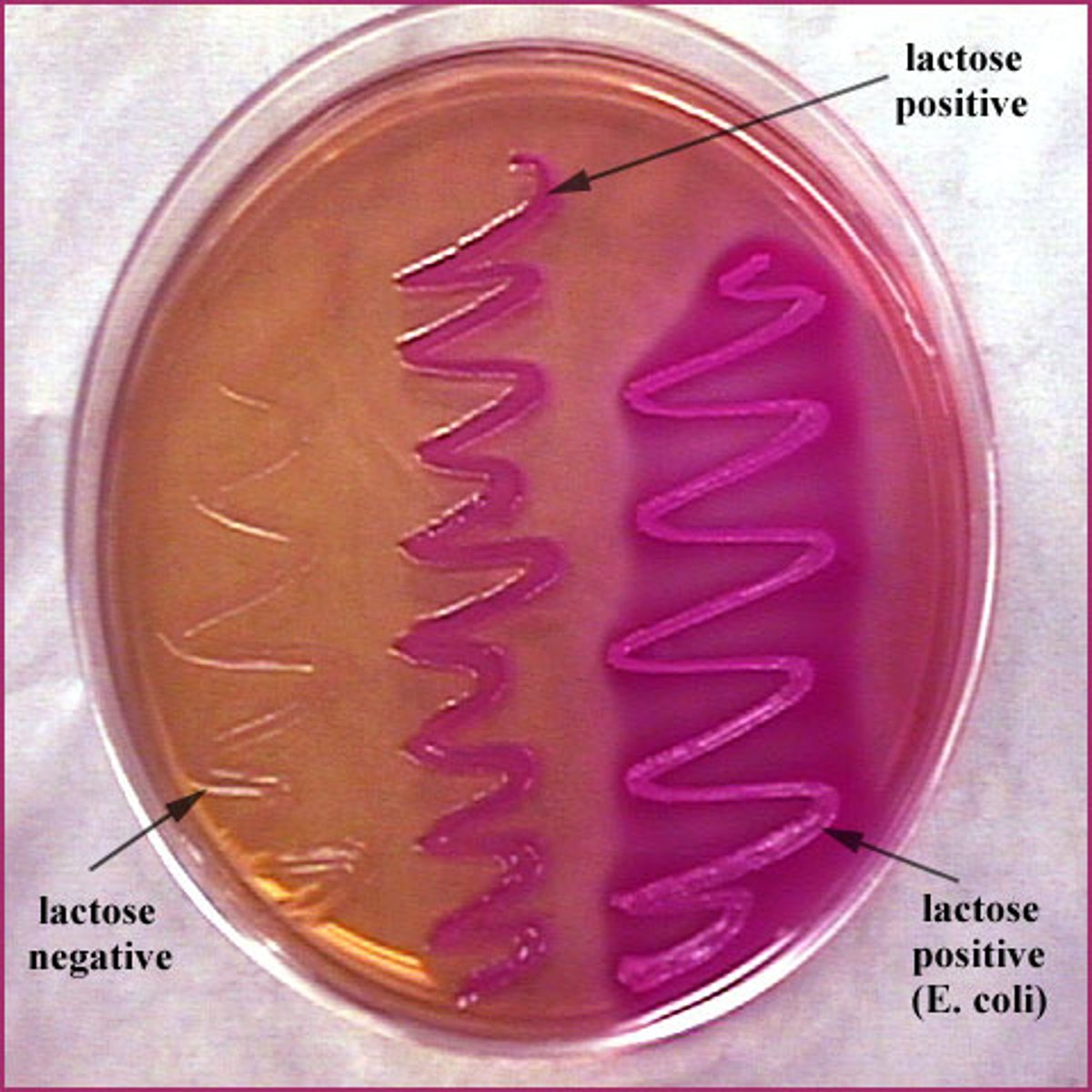
MAC (both selective & diff)
Selective: Bile salt/ CV
Diff: Checks if bacteria can ferment Lactose
MAC (Inhibitor)
Bile salts and Crystal Violet
-Inhibits G(+) growth
MAC Indicator
-neutral red dye
- pH > 6.8 colorless
- pH < 6.8 red (pink to red bile precipitate)
MAC substrate
Lactose
MAC description
Used to isolate and differentiate Enterobacteriaceae based on ability to ferment Lactose
lactose non-fermenters retain normal coloration
MAC poor growth
Inhibited by crystal violet/Bile
- Gram (+)
MAC pink to red growth + bile precipitate (R)
Not inhibited by CV/Bile + lactose fermentation
gram (-)
possible coliform
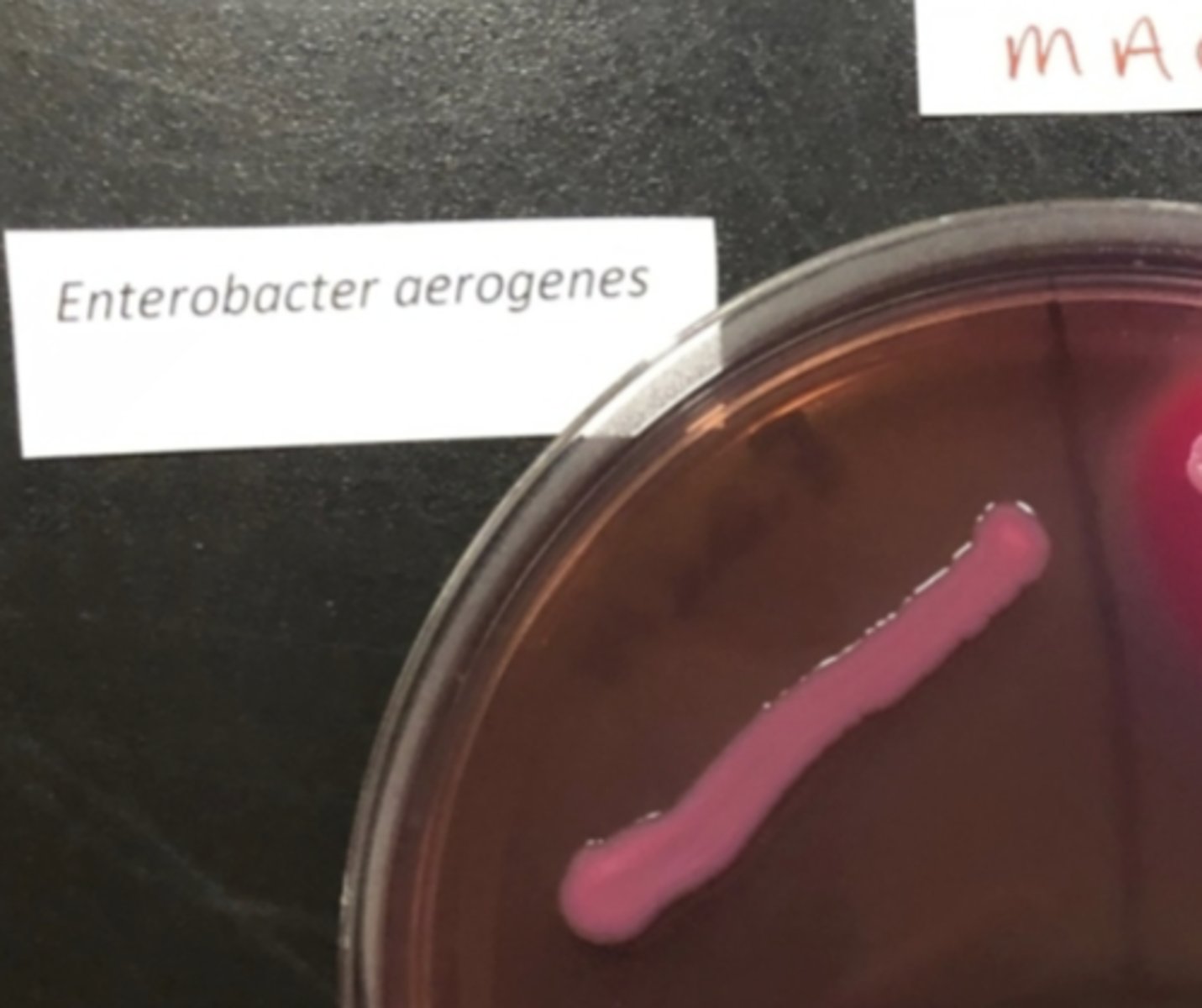
MAC Bright Pink
E.coli
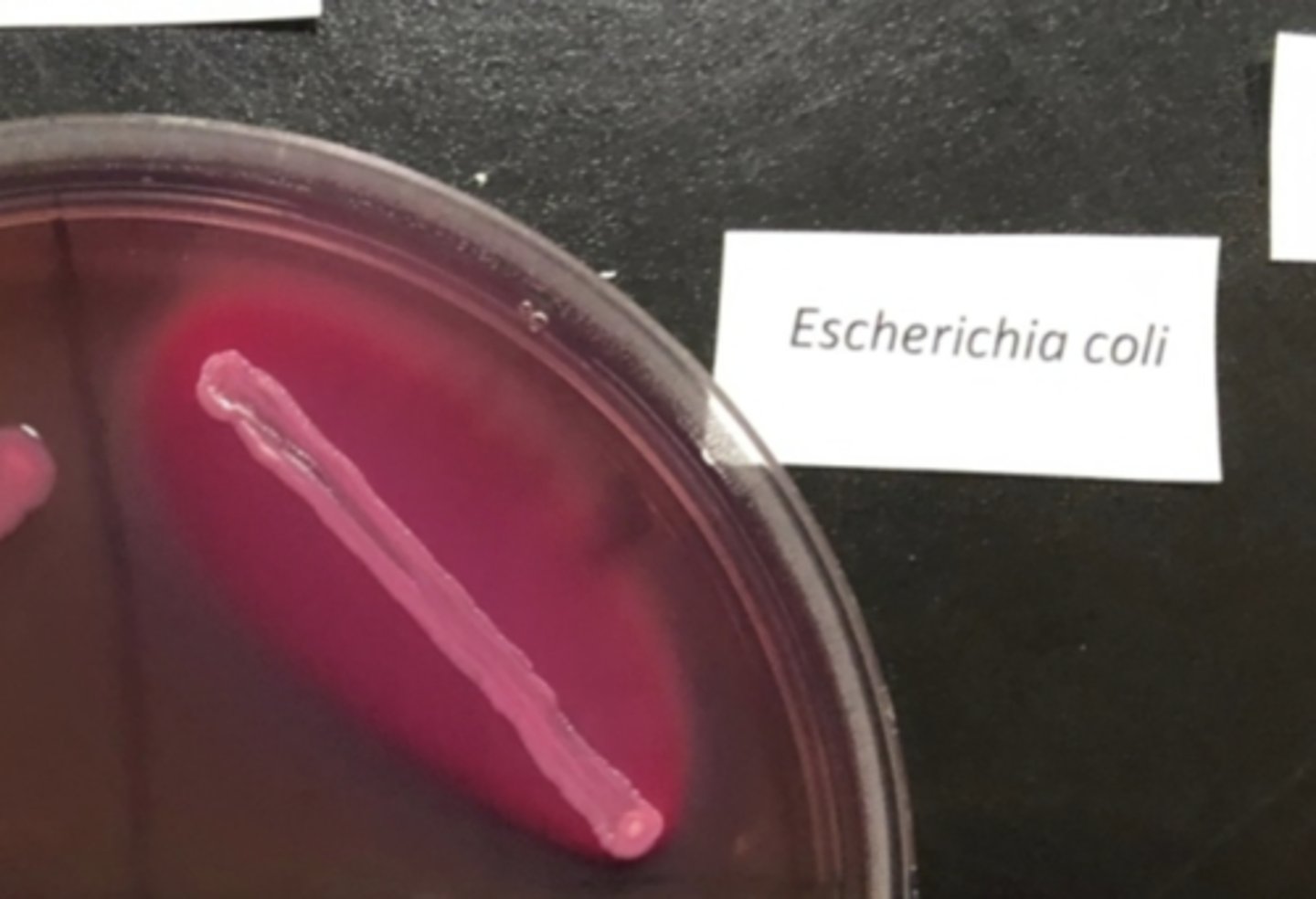
MAC good growth and colorless colonies
not inhibited by CV/bile
- gram (-)
- noncoliform
HEA (both selective & diff)
Selective: Bile salt
Differential Components:
- Lactose, sucrose, salicin
- bromothymol blue and acid fushin
- sodium thiosulfate + ferric amonium citrate
HEA Hektoen Enteric Agar Substrates
lactose, sucrose or salicin
HEA inhibition
Bile salts
- prevents or inhibits G+ organisms
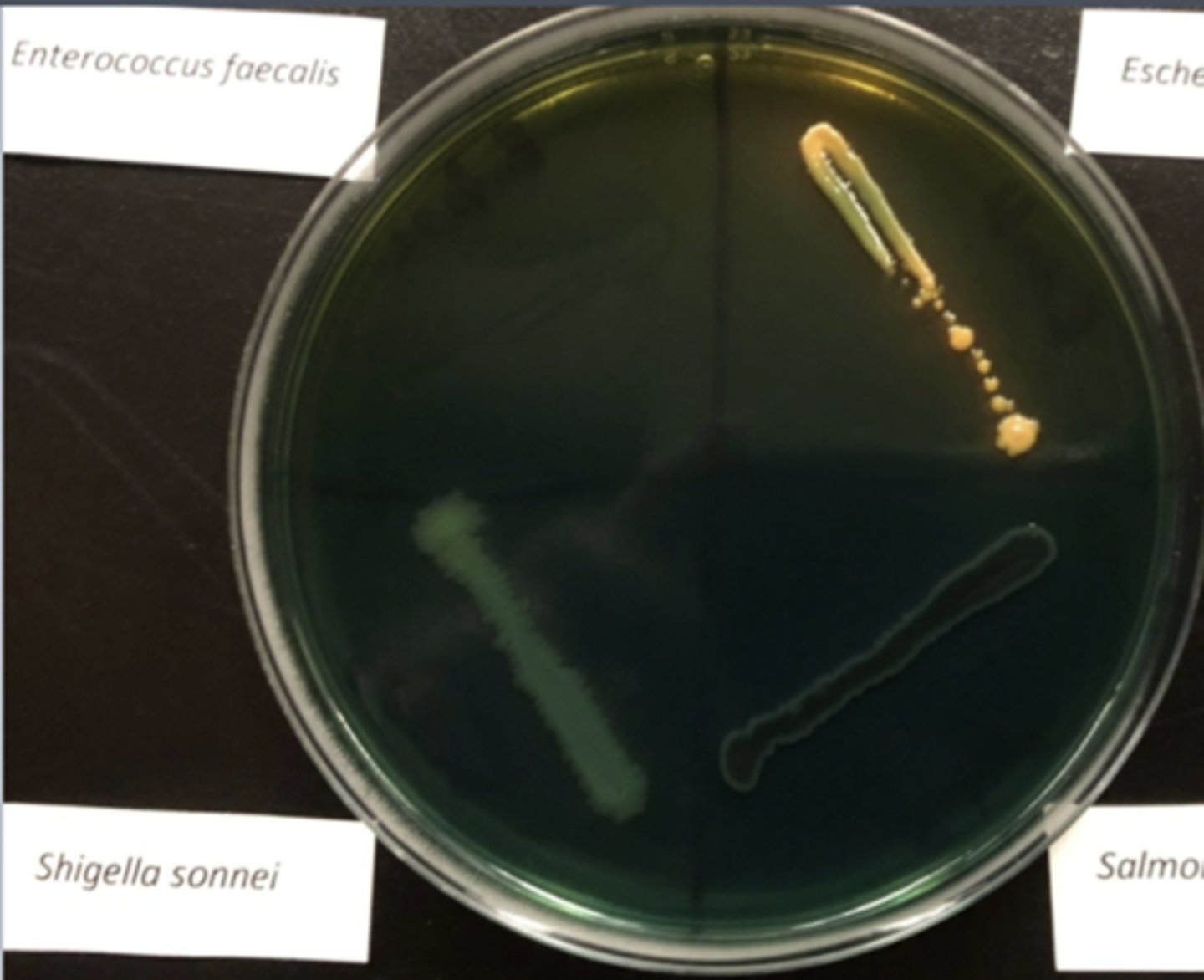
HEA used for ?
Used to isolate and differentiate Salmonella and Shigella from other enterics in patient stool samples or dairy, poultry products
HEA poor growth
Inhibited by bile or dye
- gram (+)
HEA pink/ orange growth; blue green (Bppt)
Not inhibited by bile or dye, ferments sugar
- gram (-), pi= not shigl. or samnl.
Bppt = probable salmonella
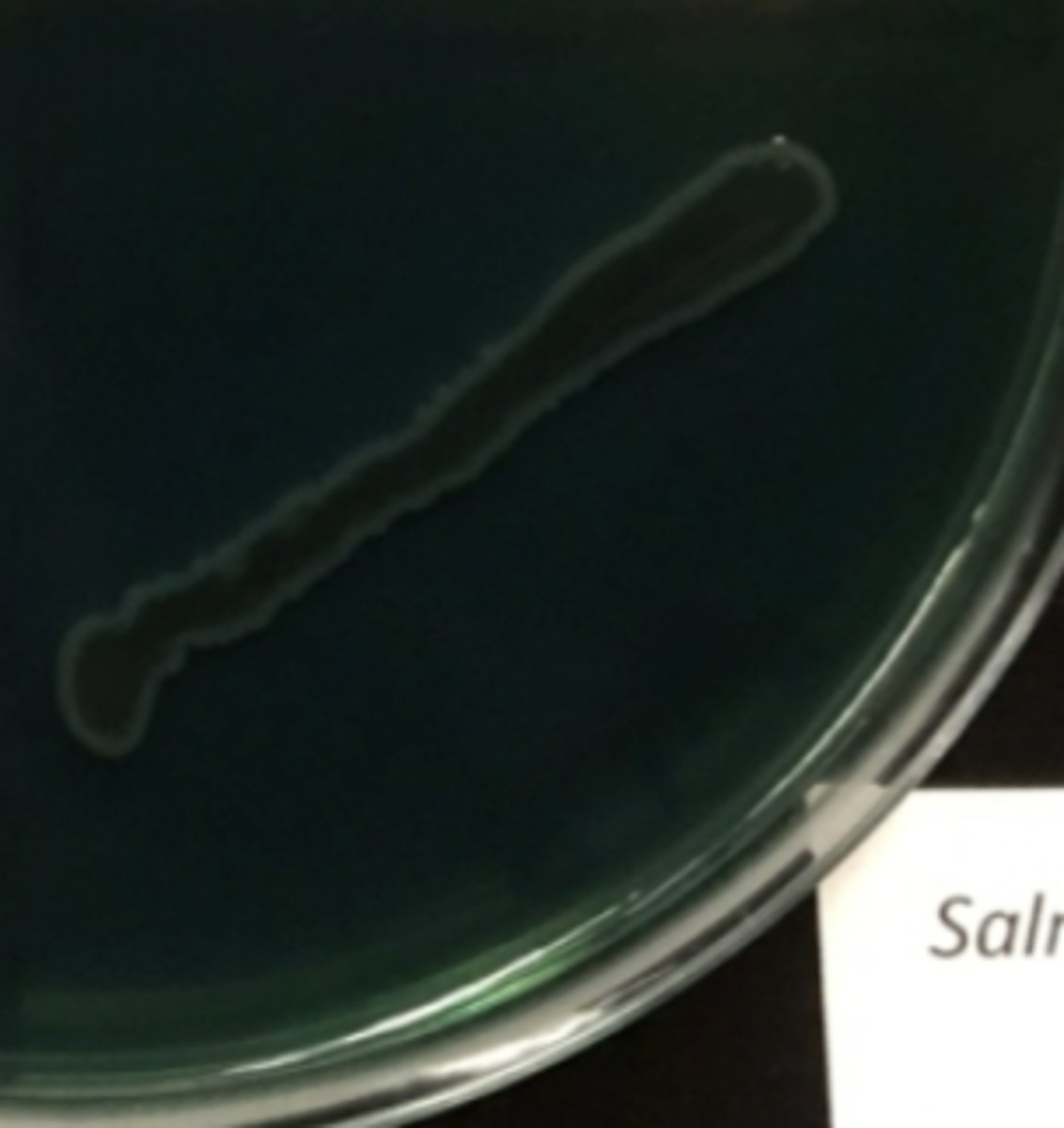
HEA blue green growth w/o black ppt
not inhibited by bile or dye
- no sugar fermentation
- gram (-)
- probable shigella
SIM Purpose
- To identify coliforms
- Useful for further ID of Enteric bacteria species
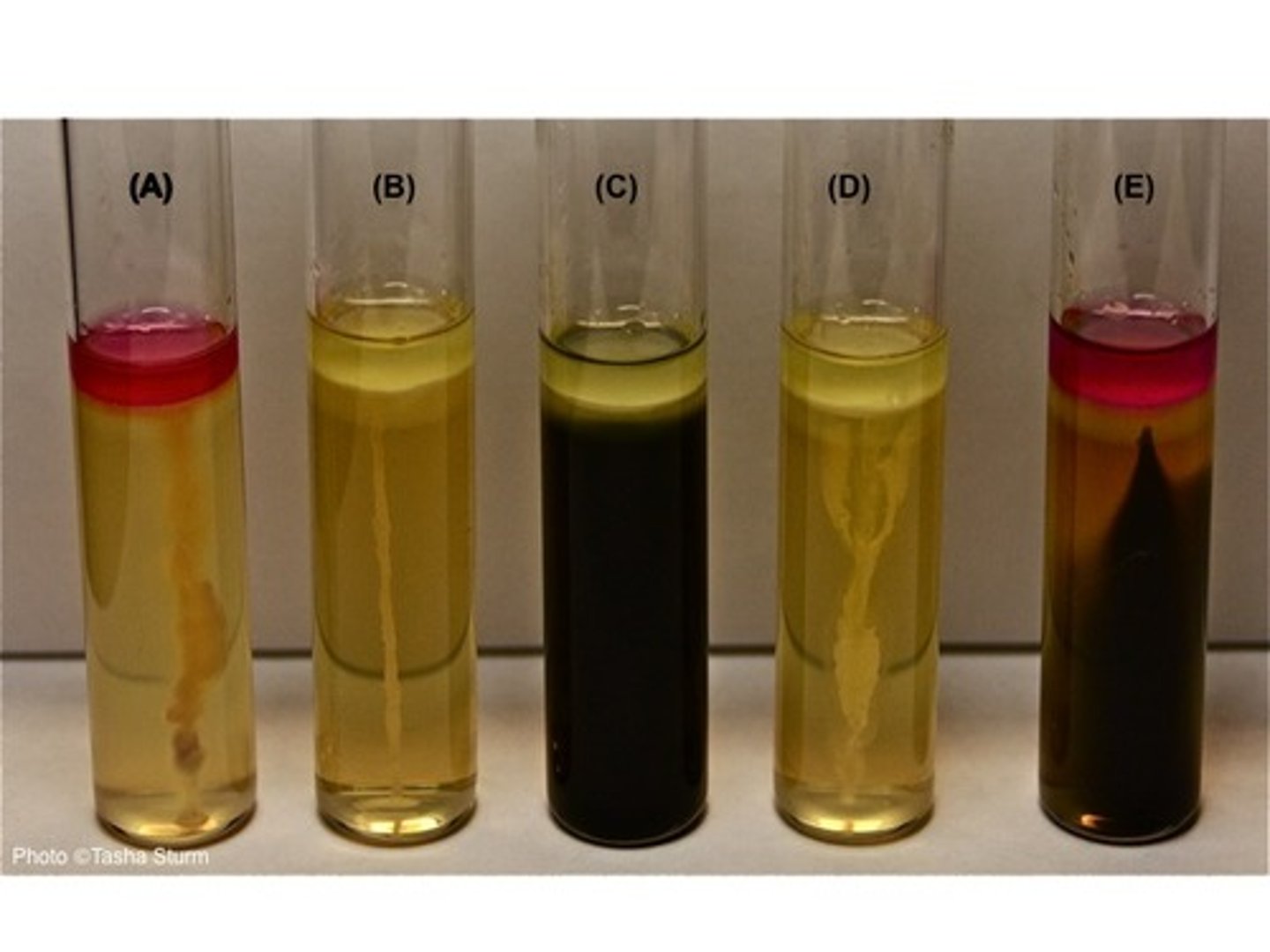
SIM
Sulfur reduction, indole production and motility
SIM (Sulfulr Reduction)
Purpose: Detects production of hydrogen sulfide (H₂S)
Key enzymes:
Cysteine desulfurase
Thiosulfate reductase
Process:
Sulfur is reduced to H₂S
H₂S reacts with ferrous ammonium sulfate in the medium
Forms black precipitate: Ferric sulfide (FeS)
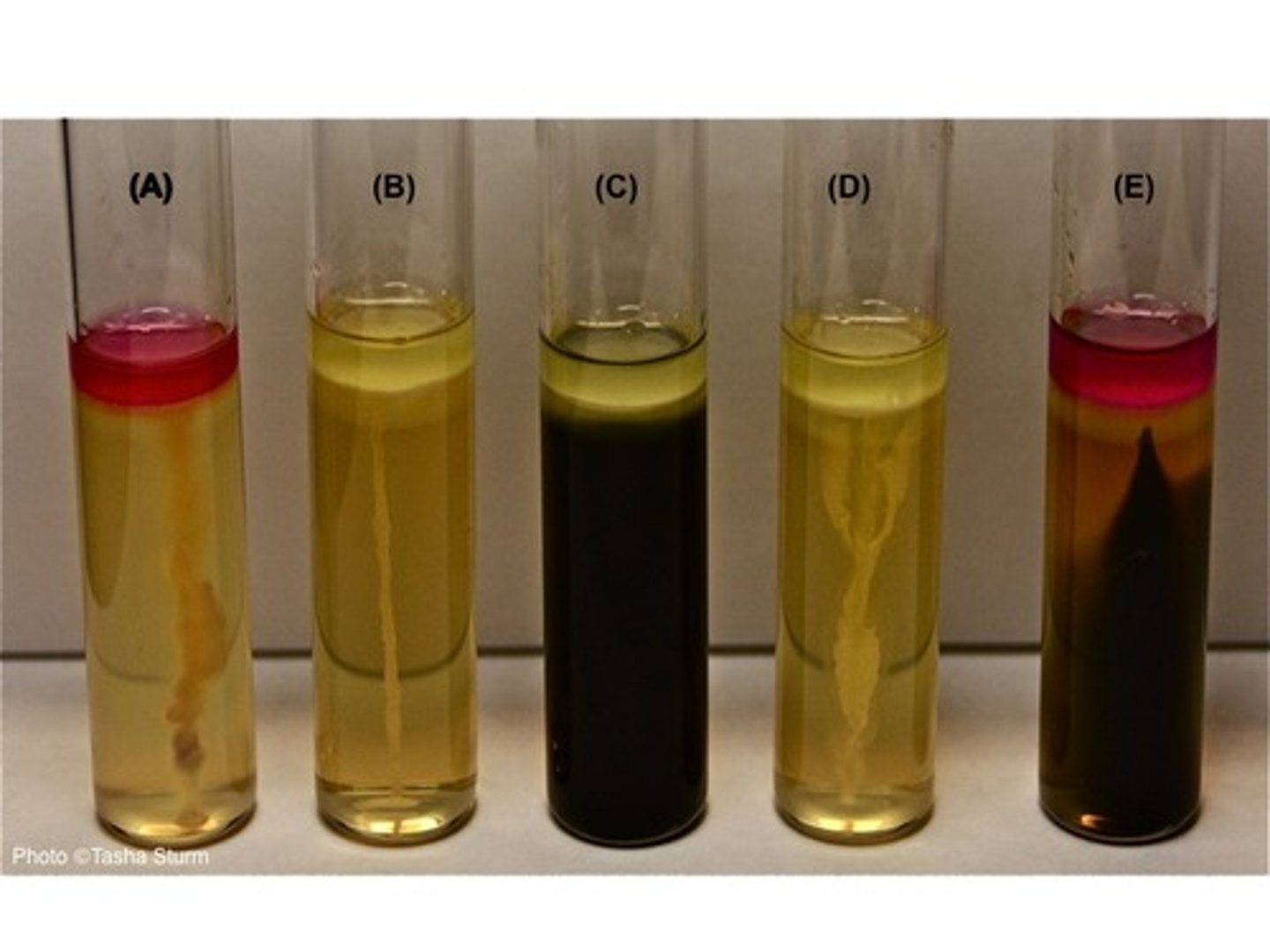
SIM (Indole Production)
Purpose: Tests for ability to break down tryptophan
Key enzyme: Tryptophanase
Reaction:
Tryptophan → Pyruvate + Ammonia = indole
Detection:
- Add Kovac's reagent (contains DMAB) then reaction is red
SIM (Motility)
Purpose: Determines if bacteria are motile
Why it works:
- Soft agar (0.5%) allows movement
Observation:
M+: diffuse, radiating turbidity from stab line
M-: growth only along stab (no spreading)
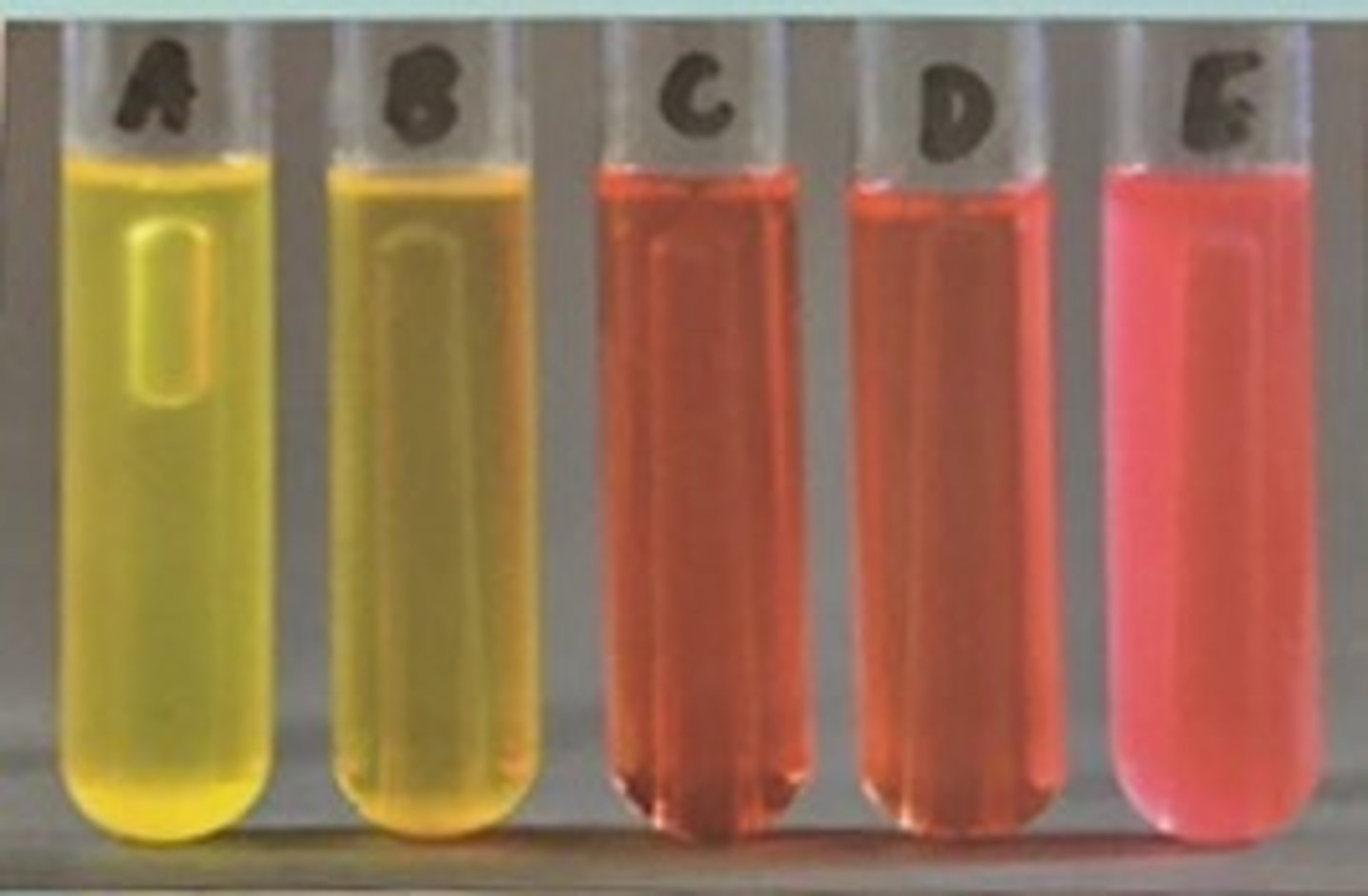
Phenol Red Fermentation Test
Tests for Sugar Fermentation
Anaerobic Microbes/some aerobes
Products: acids and sometimes gases
Differentiates Enterobacteriacae from other Gram(-) rods OR Gram(+) Fermenters
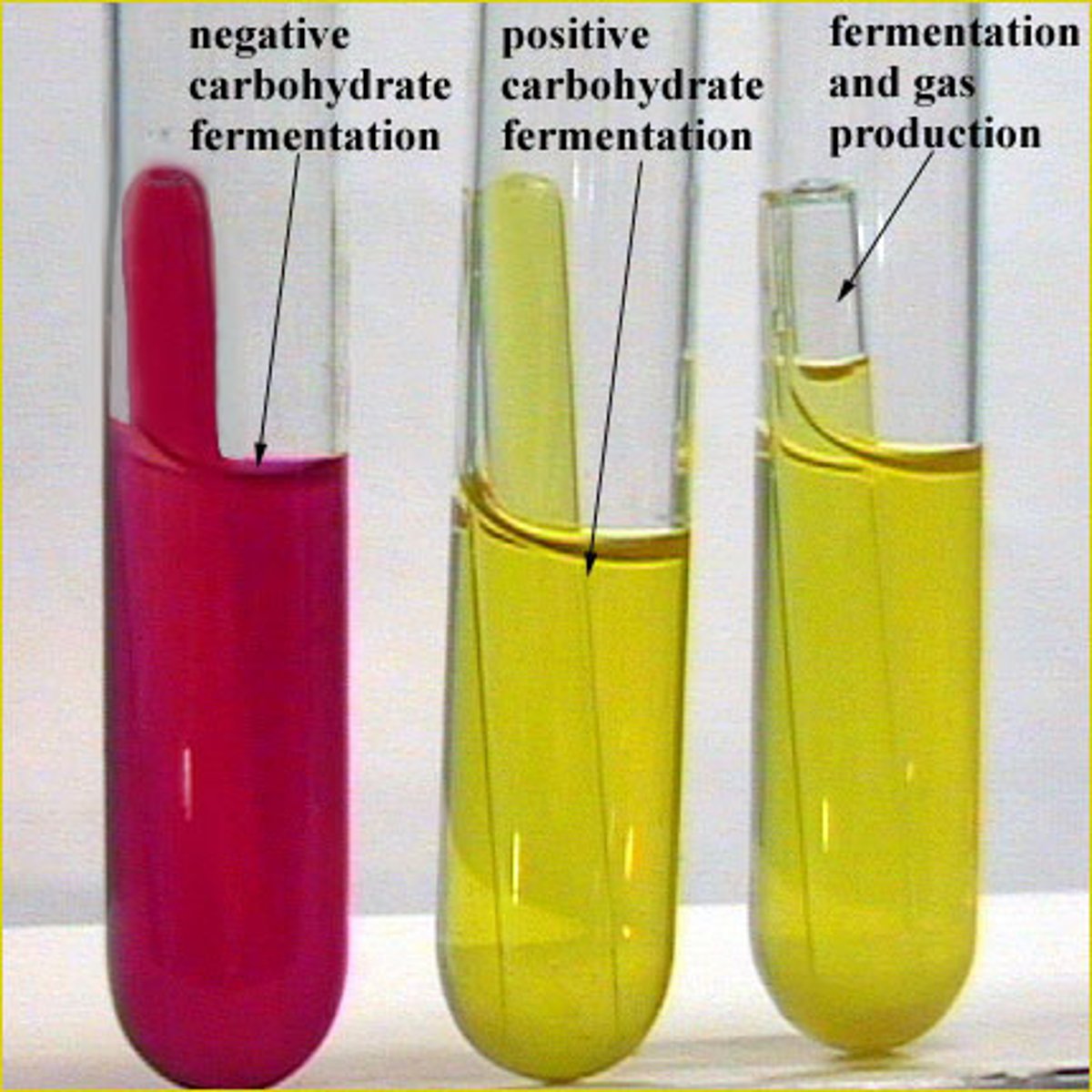
Phenol Red broth (VERSIONS)
- Glucose
- Lactose
- Sucrose
- Mannitol
Phenol Red broth indicator
Phenol Red
- pH < 6.8 = yellow (acidic)
- pH > 7.4= pink/magenta (basic)
- without inoculation = 7.3 pH
Phenol Red Yellow broth/ bubbles
Notation: A/G
Sugar fermented with acid and gas products only
Phenol Red Yellow broth/ no bubbles
A/-
Sugar fermented with acid products only
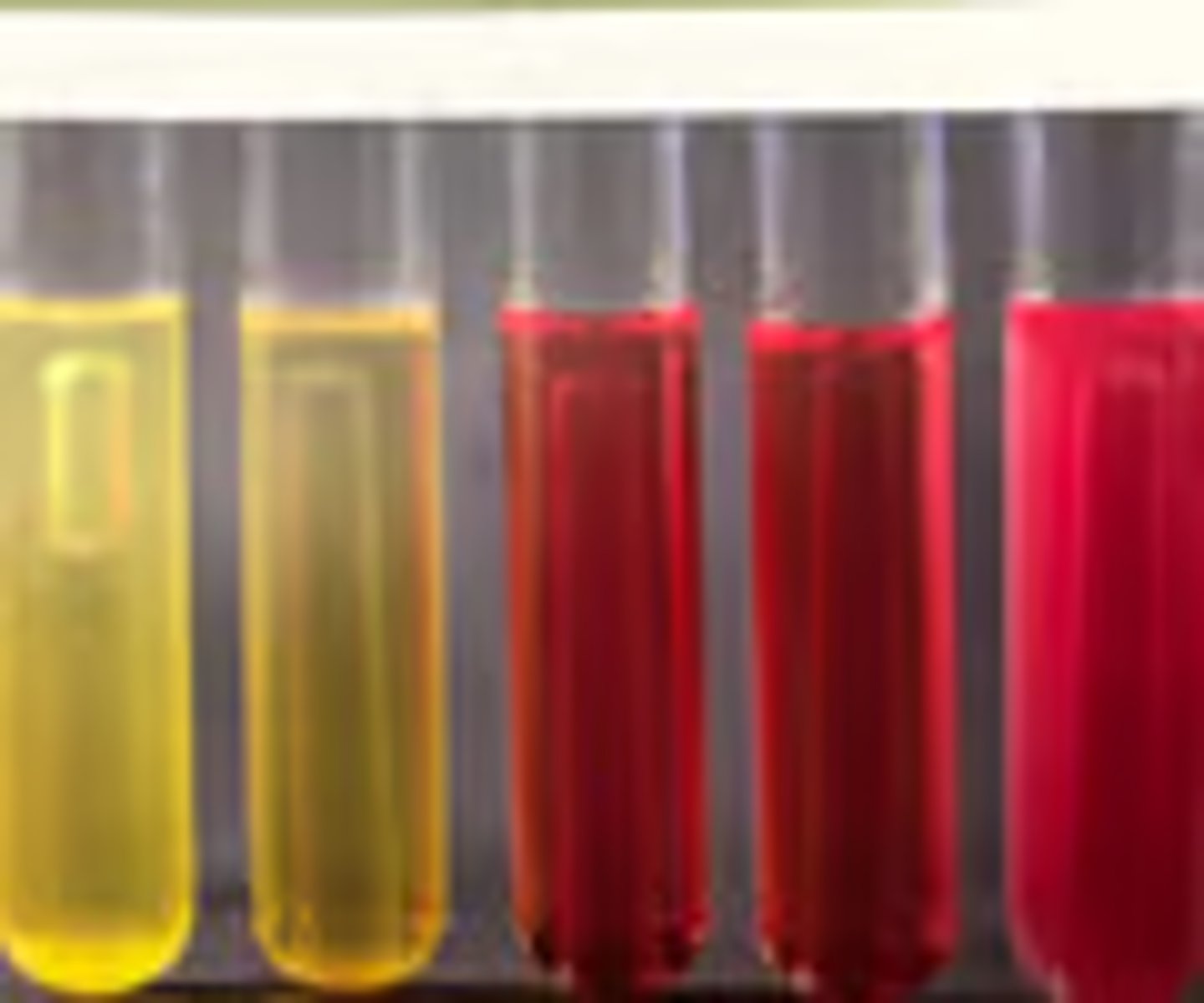

Phenol Red Red broth/ no bubbles
-/-
No sugar fermentation

Phenol Red pink broth/ no bubbles
K
No sugar fermentation, peptone degraded
Urease Purpose
Urea can be hydrolyzed to ammonia (NH3) and CO2 (basic byproducts)
- Provides nitrogen in usable form (ammonia)
- Urease is activated by bacteria when usable N is absent or urea is present
- Pathogenic Urease + bacteria:
Proteus (+)
H. Pylori (+)
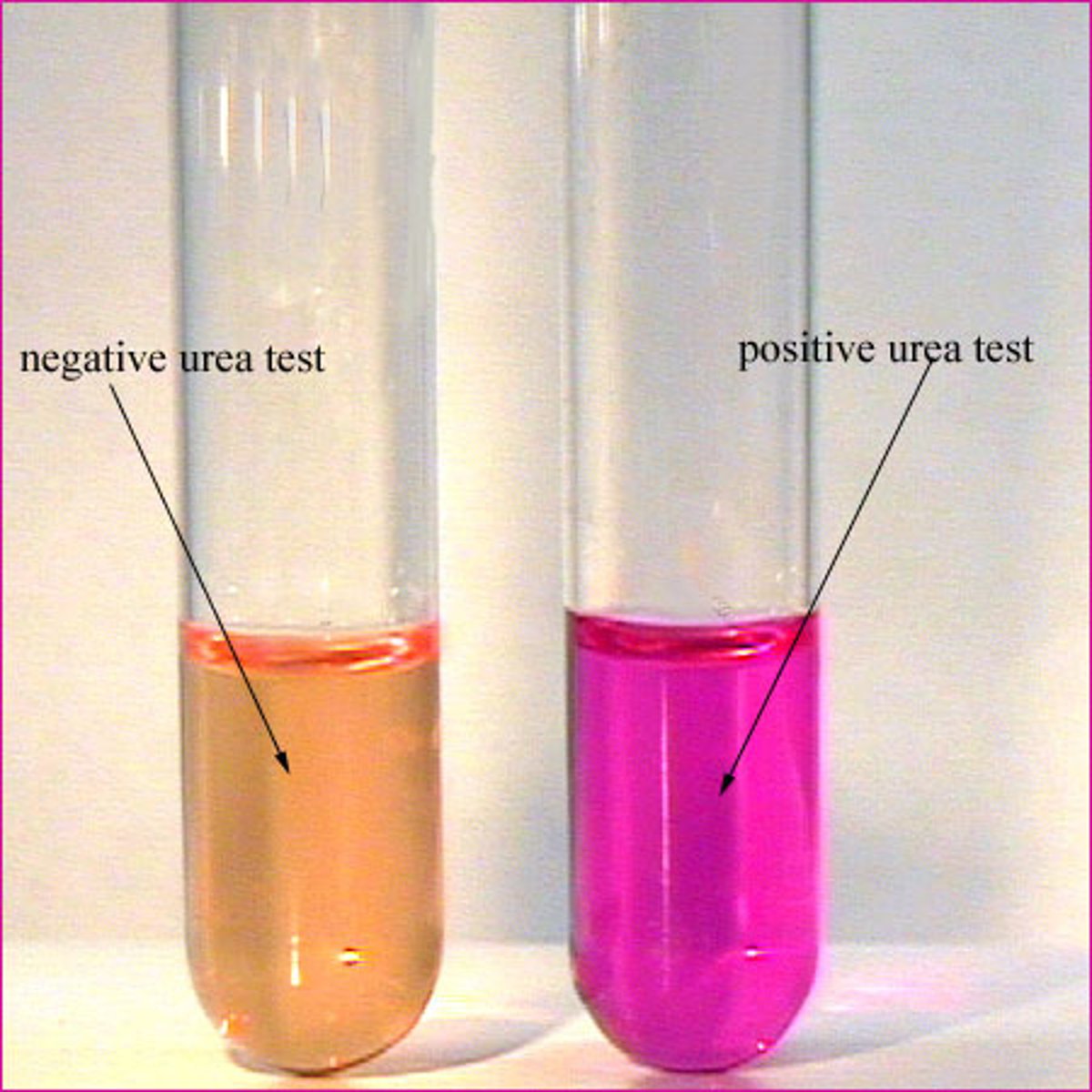
Urease Results
Indicator = Phenol red
Pink color in 24 hr = rapid urease +
Orange/ yellow = -

TSIA (Triple Sugar Iron Agar)
Differential Medium ONLY
Differentiates organisms based on the ability to reduce sulfur and ferment carbohydrates (glucose, lactose, sucrose).
Yellow = acidic
Pink = basic
Differentiates Enterobacteriaceae from other Gram (-) rods like Pseudomonas aeruginosa
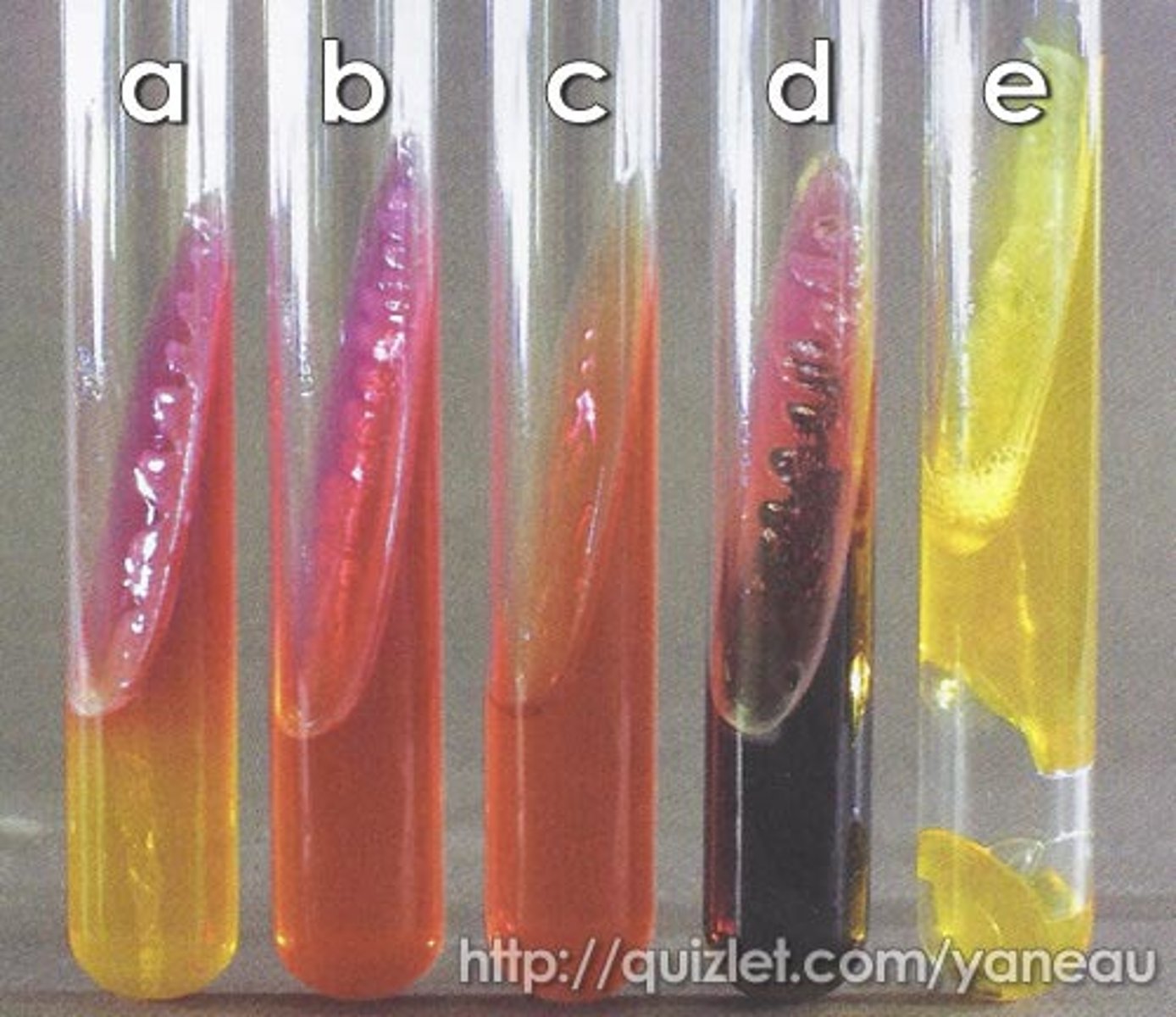

TSIA Yellow butt / yellow slant
Symbol: A/A
Glucose and lactose and/or sucrose fermentation with acid accumulation in slant and butt.
TSIA Red Slant/ yellow butt
Symbol: K/A
Glucose fermentation with acid production. Proteins catabolized aerobically (in the start) with alkaline products (reversion)
TSIA Red slant/ red butt
Symbol: K/K
No fermentation. Peptone catabolized aerobically and anaerobically with alkaline products. Not from Enterobacteriaceae
TSIA red slant/ no change in butt
Symbol: K/NC
No fermentation. Peptone catabolized aerobically with alkaline products. Not from Enterobacteriaceae
TSIA black ppt
Symbol: H2S
Sulfur reduction. (An acid condition, from fermentation of glucose or lactose, exists in the but even if the yellow colors is obscured by the black ppt)
TSIA Cracks or lifting
gas production
nitrate
Anaerobic respiration doesn't use O2 as final electron acceptor uses Nitrate
Enzyme Nitrate Reductase reduces Nitrate to Nitrite
Differentiates Enterobacteriaceae from other Gram(-) rods
Tests for: presence of NITROGEN REDUCTASES in bacteria and what they reduce nitrate into

Nitrate Test 1 Bubbles
Denitrification microbe is NOT a fermenter reduced nitrate to N2
Test DONE
Nitrate Test 2 (after no bubbles)
Add Reagent A and B
If tube turns red; microbe reduces nitrate to nitrite
Test Done
Nitrate Test 3 (after Reagant A, B)
Add zinc powder
If it turns red; microbe does NOT reduce nitrate
TEST done
Nitrate Test 3 (after Reagent A, B)
After adding power, still not red
microbe reduces nitrate not nitrite (NH4+, NO, N2O)
Test Done
BEA (selective and differential)
Selective: Bile salt
- inhibits most gram (+)
Diff: Esculin, ferric citrate.
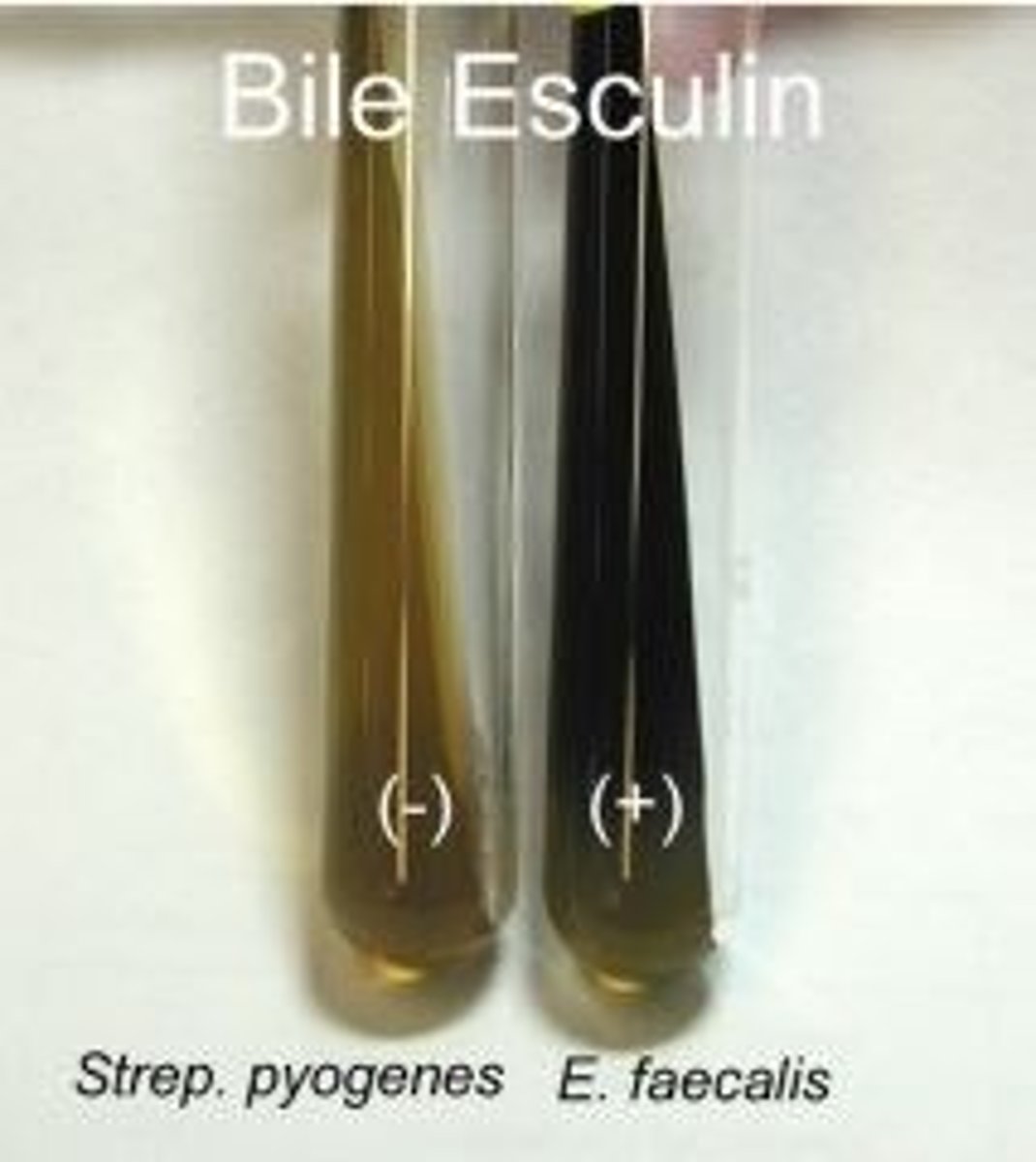
BEA
Many bacteria have esculinase, but few can hydrolyze it in the presence of bile
Used for isolation and presumptive ID of BE+Enterococci (Enterococcus faecalis and E.faecium)
Or to differentiate Group D Streptococci (S. bovis, S. equinus, S. gallolyticus) from non-Group D streptococci Or to distinguish between the genera Enterobacter, Klebsiella, and Serratia (BE+) from other genera in Enterobacteriaceae
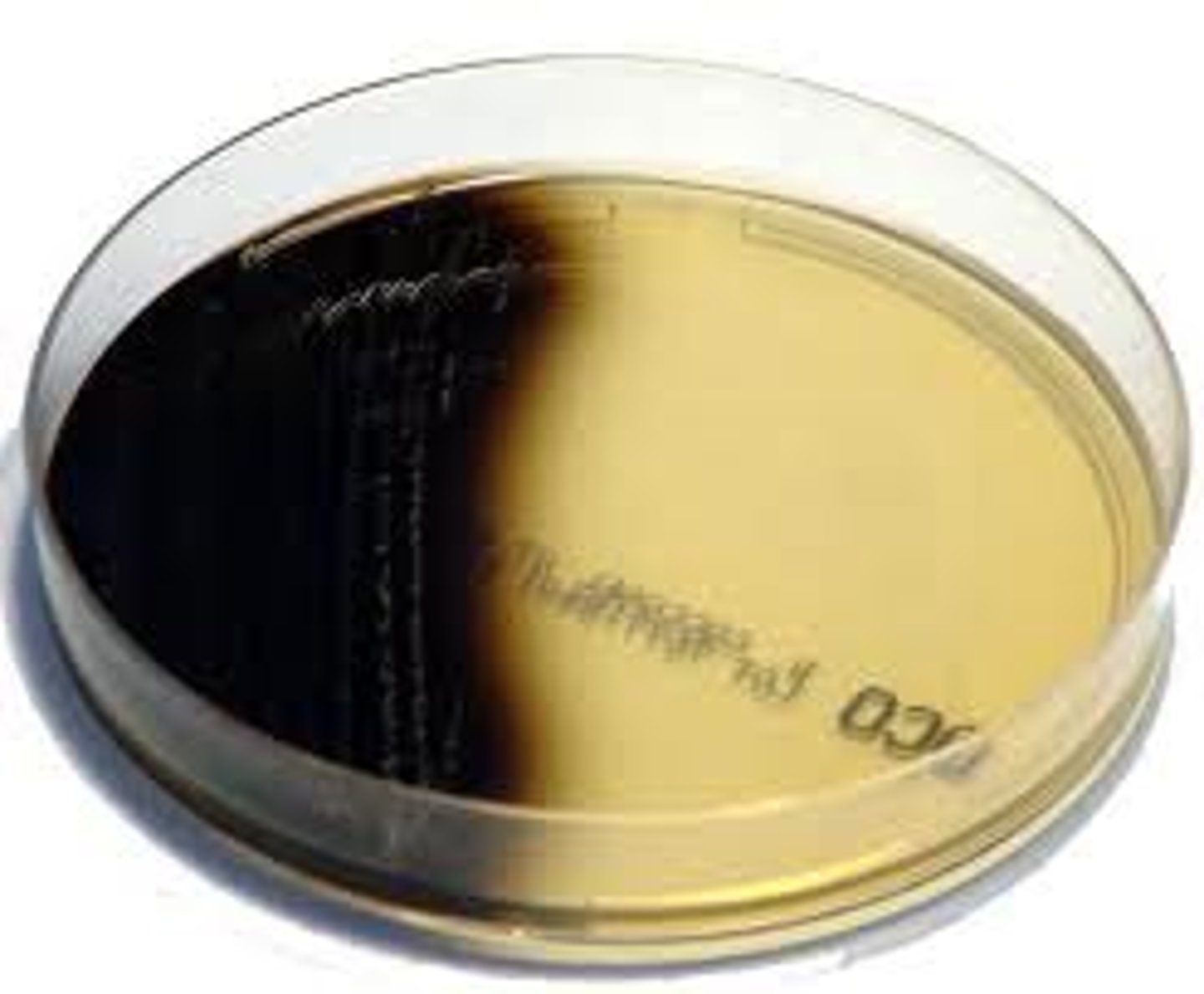
BEA Results
Positive = black ppt
No blackening = - result
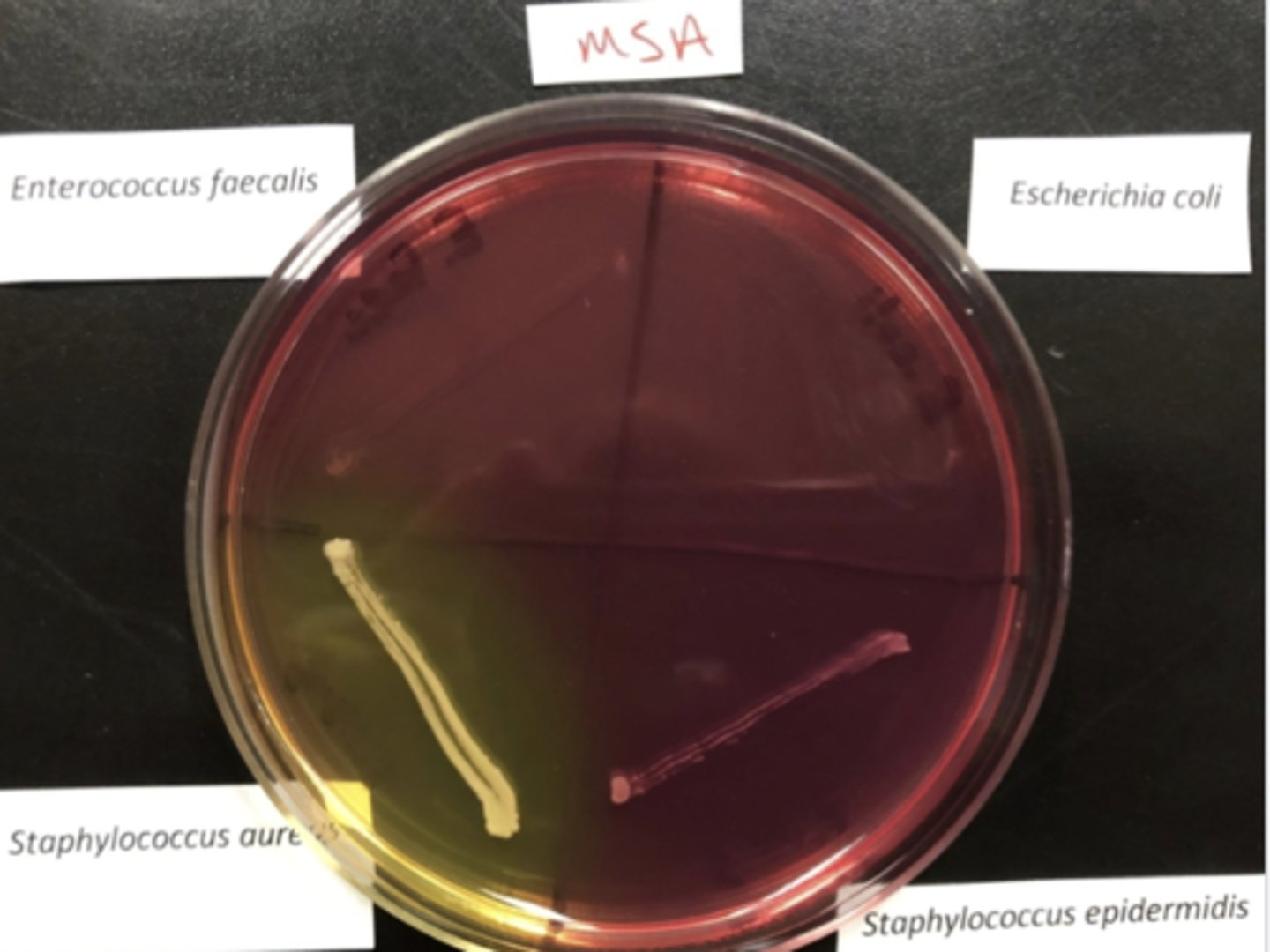
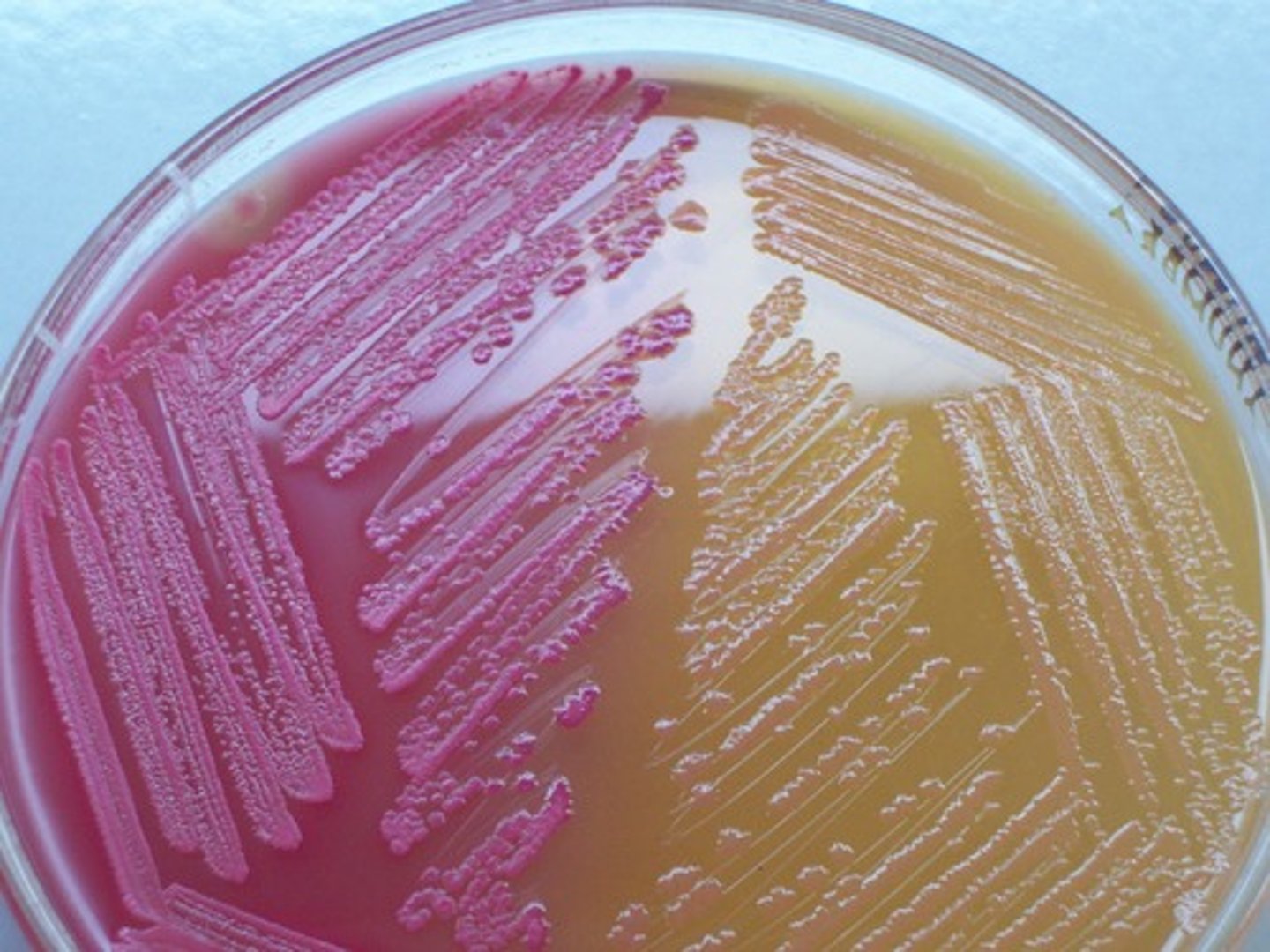
MSA (selective & differential)
Selective: 7.5% Salt
Diff: Mannitol, phenol red
MSA
Used for isolation and differentiation of Staphylococcus aureus (yellow) from other Staphylococcus species
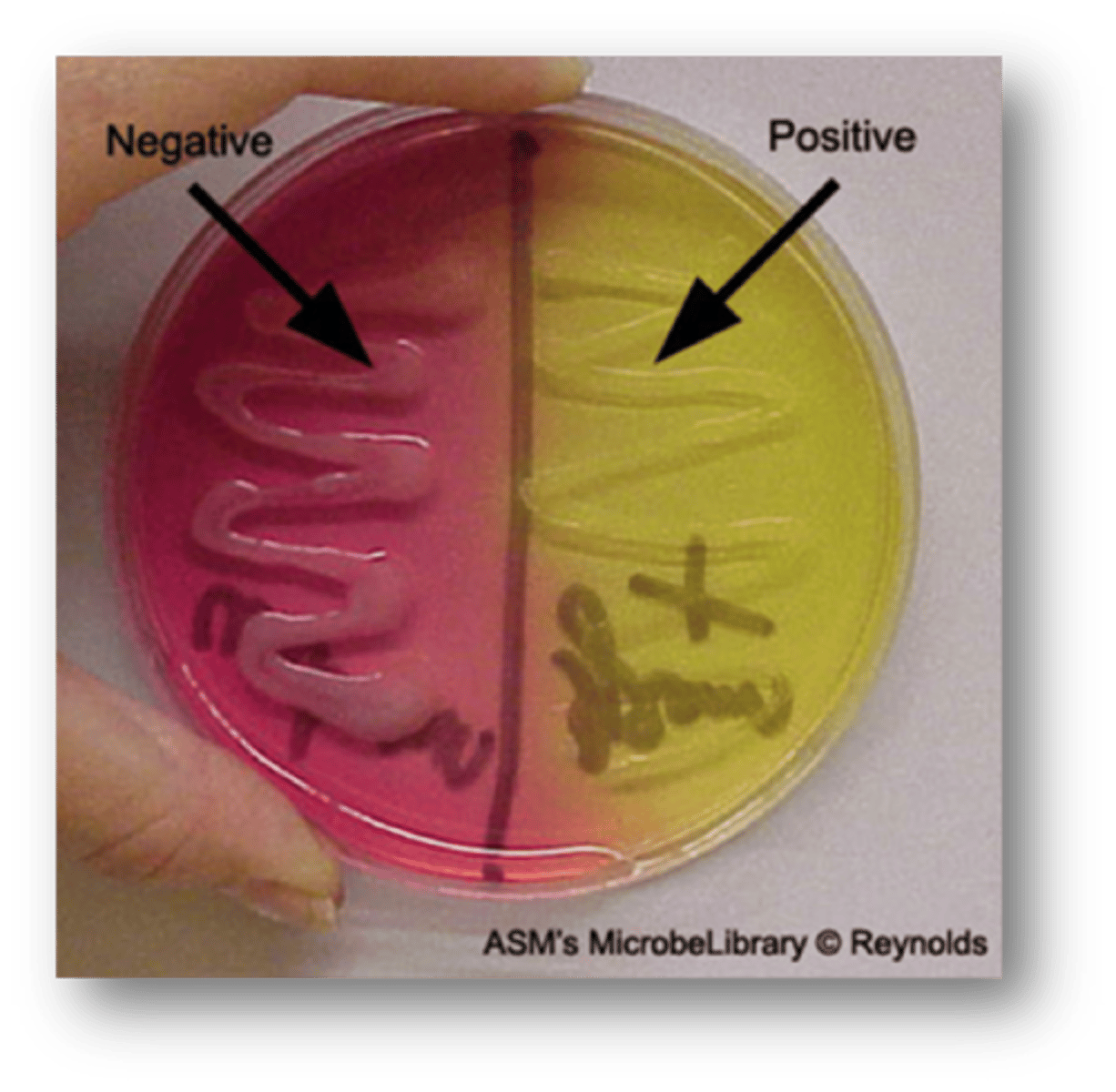
MSA Substrate (makes it differential)
Mannitol (sugar)
Indicator = phenol red
MSA poor growth
Inhibited by NaCl
- Not staph
MSA yellow/halo
Not inhibited by NaCl
- possible stap aureus
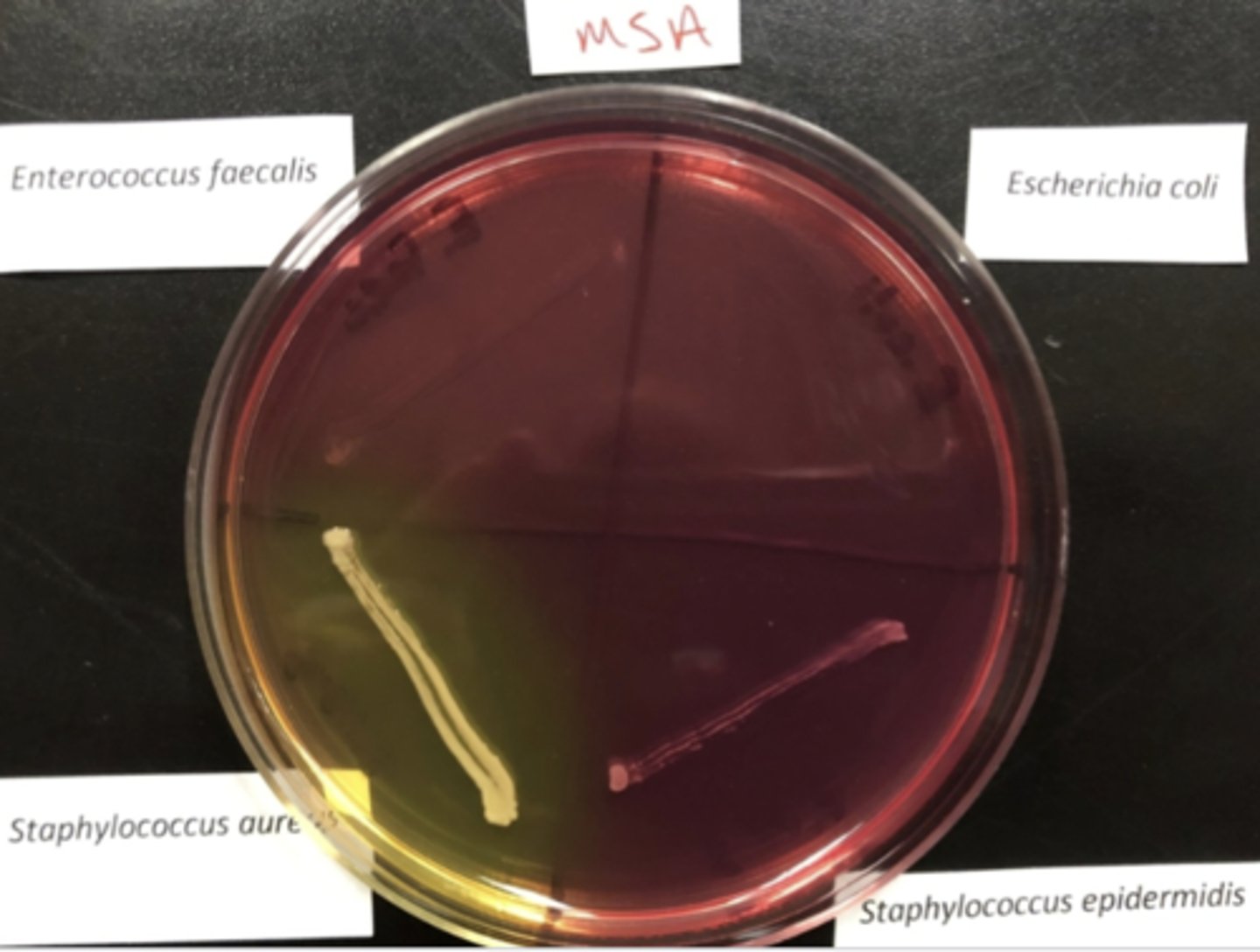
MSA red growth/ halo
Not inhibited by NaCl
- Staphylococcus other than S. aureus