glycolysis + TCA
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
glycolysis occurs in both __
aerobic and anaerobic organisms
what are the 2 phases of glycolysis
investment: consumes 2 ATP and converts glucose to 2 glyceraldehyde-3-P
payoff: produces 4 ATP and 2 pyruvate
what is the net ATP gain from glycolysis
2 ATP
what are the products of glycolysis
pyruvate, ATP, NADH
how many possible fates does pyruvate have
3
what are the steps of the energy investment phase
glucose —> glucose 6-phosphate via hexokinase
glucose 6-phosphate —> fructose 6-phosphate via phosphohexose isomerase
fructose 6-phosphate —> fructose 1,6-biphosphate via phosphofructokinase-1
fructose 1,6-biphosphate —> glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + dihydroxyacetone phosphate via aldolase
what are the steps of the payoff phase
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + dihydroxyacetone phosphate —> 2 glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate via triose phosphate isomerase
2 glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate —> 2 1,3-biphosphoglycerate via glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
3-phosphoglycerate —> 2-phosphoglycerate via phosphoglycerate mutase
2-phosphoglycerate —> phosphoenolpyruvate via enolase
phosphoenolpyruvate —> pyruvate via pyruvate kinas
what is the first ATP forming reaction
(2) 1,3-biphosphoglycerate to (2) 3-phosphoglycerate
what is the second ATP forming reaction
the last step
(2) phosphoenolpyruvate to (2) pyruvate
what is the order of the enzymes in glycolysis
hexokinase
phosphohexose isomerase
phosphofructokinase-1
aldolase
triose phosphate isomerase
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
phosphoglycerate kinase
phosphoglycerate mutase
enolase
pyruvate kinase
what is the net gain of glycolysis per glucose molecule
2 ATP, 2 NADH, and 2 pyruvate
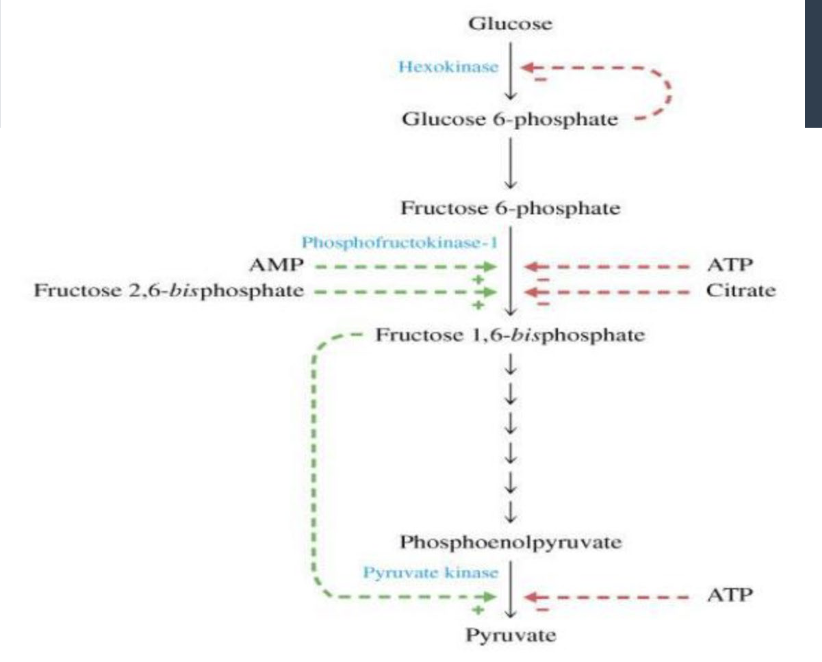
what are the key regulatory enzymes of glycolysis
hexokinase (step 1)
PFK-1 (step 3)
pyruvate kinase (step 10)
allosteric control by ATP and AMP
hormonal regulation by insulin and glucagon
what is the fate of pyruvate in aerobic conditions
pyruvate —> acetyl CoA (TCA cycle)
what are the 2 possible fates of pyruvate in anaerobic conditions
lactate or ethanol
what are the 2 possible fates of NADH
aerobic conditions: NADH is oxidiezed in the electron transport pathway, making ATP in oxidative phosphorylation
anaerobic conditions: NADH is oxidized by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) or alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) providing addition NAD+ for more glycolysis
what is the warburg effect
cancer cells divert large amounts of glucose to the pentose phosphate pathway to produce NADPH
what do rapidly proliferating cancer cells do with glucose
mainly metabolize it to lactate even when it is in aerobic conditions
what other sugars can enter glycolysis
fructose, mannose, galactose
what does TCA stand for
the tricarboxylic acid cycle (citric acid cycle)
what else can acetyl CoA be produced by
the oxidation of fats and amino acids
what enters the tca
acetyl-coa
which enzyme does
acetyl-coa + oxaloacetate —> citrate
citrate synthase
citrate ←> isocitrate
which enzyme
aconitase
isocitrate —> a-ketoglutarate
which enzyme
isocitrate dehydrogenase
produces: NADH + CO2
a-ketoglutarate —> succinyl coa
which enzyme
a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
produces: NADH + CO2
succinyl coa —> succinate
which enzyme
succinyl-coa synthetase
produces: GTP
succinate —> fumarate
which enzyme
succinate dehydrogenase
produces FADH2
fumarate —> malate
which enzyme
fumarase
malate —> oxaloacetate
which enzyme
malate dehydrogenase
produces NADH
what does 1 acetyl-coa produce in TCA
3 NADH
1 FADH2
1 GTP
1 CO2
what are the 3 major activators of the tca cycle
ADP, Ca2+ (muscle), NAD+
what are the 4 major inhibitors of the tca
ATP, NADH, Succinyl-CoA, citrate
which tca enzyme uses tpp
a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
Coke Is Ketamine Sluts Suck For Money Only
Citrate
Isocitrate
Ketoglutarate
Succinyl-CoA
Succinate
Fumarate
Malate
Oxaloacetate
where does tca take place
in the mitochondrial matrix
what is oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate catalyzed by
the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
pyruvate dehydrogenase PD is a noncovalent assembly of
three enzymes E1, E2, E3
how many coenzymes are required in the PD enzyme complex
5
what are the 3 pyruvate dehydrogenas regulatory mechanisms
phosphorylation by pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase
dephosphorylation by pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphate
hormonal control
what are the products of the tca per glucose molecule
6 NADH, 2 FADH2, 2 GTP or ATP, 4 CO2
which steps of the tca are inhibited by ATP
step 1 (citrate synthase)
step 3 (isocitrate dehydrogenase)
what are anaplerotic reactions
filling-up
replenish TCA intermediates
what are cataplerotic reations
use TCA intermediates for biosynthesis
production of amino acids
what is the most important anaplerotic reaction
pyruvate carboxylase converts pyruvate to oxaloacetate