RADT W7+W8 Ch 17, 12, 13, 14 Quality Assurance, Dental Images and Dental Radiographer, Patient Relation and Education
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
List the Annual quality control tests for the Dental-Xray Machines
Xray output
kV calibration
half-value layer
timer
mA
collimation
beam alignment
tubehead stability
What are the indicators of film freshness?
slight blue tint
clear
no fogginess
if the film appears fogged it is expired
How do we do quality assurance for intensifying screens?
Examined for dirt and scratches.
How do we ensure quality assurance for Cassettes?
Cassettes should be examined for worn closures, light leaks and warping.
What is the film-screen contact test?
The film–screen contact test is used in radiography (esp. extraoral cassettes) to check whether the intensifying screen and the x-ray film are in close contact inside the cassette. Poor contact makes the image look blurry or unsharp.
Steps:
Place a wire mesh test object on top of loaded cassette
Position PID using 40 inch target-receptor distance w central ray perpendicular to cassette
Expose Cassette
Process the film.
Inspect the image:
Good contact → film shows uniform density
Poor contact →varying densities; areas look fuzzy or blurred (loss of detail).→ cassette needs to be repaired or replaced

Quality Assurance: Viewbox/illuminator
Viewbox should emit uniform and subdued light. Should also be examined for dirt and discoloration of the plexiglass
How often should the dark room be checked for light-tightness and proper safe lighting?
Every 6 months
What test could you do to test Safe lighting?
To test safelighting in a darkroom, you use the coin test (a.k.a. safelight test):
Turn off all lights in darkroom including the safe light
Place a coin (or opaque object) on an unexposed film under the safelight (at least 4 inches away)
Leave it for about 3-4minutes.
Process the film normally.
Interpretation:
If film is uniformly clear → safelight is safe.
If an outline of the coin and a fogged background appears → safelight is not safe to use
Quality Assurance: Automatic processor
Automatic processor is functioning properly if:
unexposed film appears clear and dry
film exposed to light appears black and dry
If not, then corrections must be made.
How often should processing solutions be replenished/changed?
Replenished daily
Changed every 2-4 weeks (varies from office to office)
Processing solution must be evaluated each day prior to processing any patient films.
How long should it take for the film to clear if the fixer solution is at full strength? When should you decide to change the fixer solution?
2 minutes.
If the film does not clear by 3-4 minutes, fixer solution should be changed.
What is a reference radiograph?
It is a radiograph that has been processed under ideal conditions.
used to compare film densities of radiographs that are processed daily.
How do you measure whether the developer solution strength is adequate?
Compare the densities of daily radiographs to the reference radiograph.
if reference looks lighter, then developer solution is weak or cold
if reference looks darker, then developer solution is too warm or too strong
**daily check film should appear identical to the reference/control film.
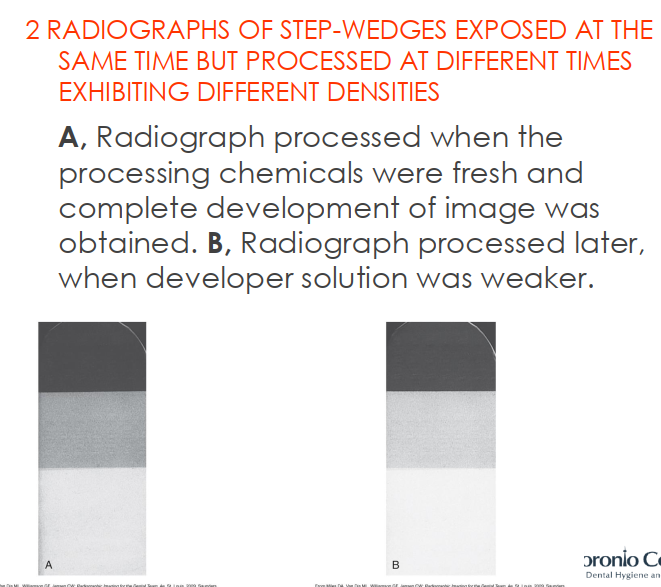
How is the step wedge used in quality assurance for dental xrays?
The step wedge is an aluminum block with steps of varying thickness.
When exposed, it creates different gray levels on the film/sensor.
Used to check consistency of x-ray exposure and processing.
If shades differ from the baseline, it signals problems with exposure, processing, or equipment.
You should use the ____ density seen on the standard step-wedge radiograph for comparison.
Middle
What is a Normalizing Device?
Normalizing devices monitor the strength of developer and film density
test films are inserted beneath a copper plate and exposure
processed test films inserted in device and compared with numbered densities.
Who is responsible for quality assurance of radiography tools and materials?
The dentist = radiation protection officer
The Quality administration programs include: (5)
description of the plan and assignment of duties
monitoring and maintenance schedule
record keeping log of all quality control tests
periodic eval and revision
in-service training
What does the Safety Code 30 outline ?
It is the recommended safety procedures for the use of dental xray equipment which includes:
Quality assurance program
procedures to reduce radiation exposure to personnel
film processing and handling
facility requirements
procedures for minimizing radiation exposures to patients.
Why is it important for the dental radiographer to have both sufficient knowledge and technical skill to perform dental radiographic procedures?
Ensures diagnostic quality radiographs (proper density, contrast, sharpness).
Minimizes radiation exposure and need for retakes.
Promotes efficiency and reduces operator errors.
Improves patient comfort and compliance.
What are the professional goals of a radiographer for Client protection?
use lowest level of xradiation
avoid retakes resulting in unnecessary client exposure
use proper equipment and tehcniques
use lead apron, thyroid collar and ultra speed films to reduce exposure time
handle and process films meticulously
Information found on dental radiographs

Uses of dental radiographs

Clients are more likely to present interest and retain information when…
The health professional appears interested
maintain eye contact with client to develop interpersonal relationship
practice good listening skills
inviting a client to ask questions enhances communication
Reducing worry and psychological stress is the foundation for forming …
a trusting relationship that will help facilitate the deliver of client care
What is the importance of patient education?
patient education on dental imaging will likely decrease their fears of xray exposure
a knowledged patient is more likely to accept prescribed treatment
A combination of and _ is the most effective method of educating the client about dental radiographs.
oral presentation and printed information
How often should children have dental xrays?
time interval between radiographs are based on the individual needs of a child
Can I refuse xrays and be treated without them?
No.
Treatment without necessary xrays is considered neglect
Standard of care requires that dentists refuse treatment when xrays are refused by the patient.
Instead of taking xrays can you se the xrays from previous dentists?
Yes.
previous dental radiographs can be used if they are recent and of diagnostic quality.
sometimes supplemental radiographs are still necessary
How much radiation will I receive from dental xrays?
We follow strict guidelines to limit you from the amount of radiation.
you will be protected from excess radiation with lead apron, thyroid collar, use of ultra speed films, proper radiographic settings.
Should dental xrays be taken during pregnancy?
The amount of radiation received when using a lead apron around the gonadal region is nearly zero
no detectable embryo or fetus exposure with lead apron use
ADA states the recommended guideline does not have to change due to pregnancy, but most dentists prefer to postpone radiographs
Are dental xrays safe?
The amount of radiation used in dental radiography is small
it is possible for biologic injury to occur
radiographs are prescribed only when the benefit of disease detection outweighs the risk of harm
Will dental xrays cause cancer?
Radiation exposure during dental xrays is very small and the chance of causing cancer is minimal
there has been no case of a client developing cancer from dental xrays
Can a panoramic xray be taken instead of a complete series?
No
complete series reveals changes in teeth and bone
panoramics are only useful for showing the general condition of a clients teeth and bone. It is not as detailed
Who owns my dental radiographs?
They are proper of the dentist
patients have privilege to access the records and can request a copy be sent to another dentist