The Cerebrum
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
cerebrum
largest part of the brain
sense of “self”
where decision making happens
cerebral cortex
outer layer of gray matter of the cerebrum
function of gray matter
processing
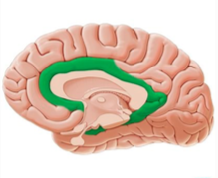
thicker band of the corpus callosum =
higher level intelligence & cognition
corpus callosum connects
2 hemispheres of the brain
significantly thinner band of corpus callosum =
struggle with cognition
where the corpus callosum is located
the floor of the longitudinal fissure
gray matter is made of
cell bodies & dendrites
white matter is made of
myelinated axons
Brodmann’s Areas are numbered according to
the order in which they were studied/discovered
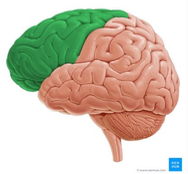
frontal lobe
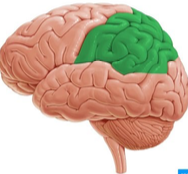
Parietal lobe
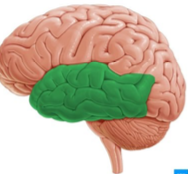
Temporal lobe
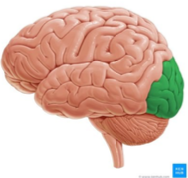
Occipital lobe
Insular lobe
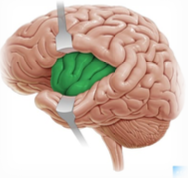
Limbic lobe
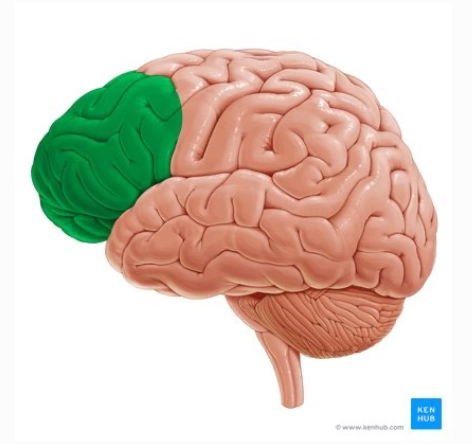
Largest lobe of the brain
frontal
frontal lobe forms
anterior portion of the cerebral hemispheres
Boundaries of the frontal lobe
posterior: central sulcus
posteroinferior: lateral sulcus
functional divisions of the frontal lobe
prefrontal cortex
motor cortex
broca’s area
functions of the prefrontal cortex
planning
organizing
motivation
discipline
problem solving
self control
emotional regulation
function of the precentral gyrus
planning
control
execution of voluntary movements
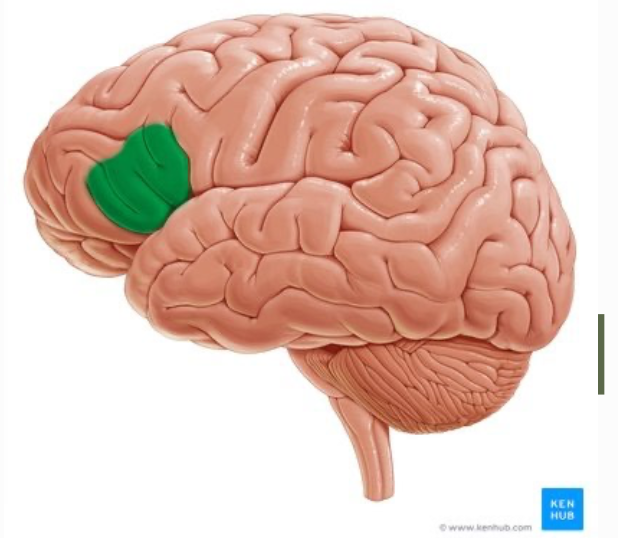
Function of Broca’s Area
motor component of speech including verbal fluency
Parietal lobe location
posterior to frontal lobe, superior to temporal/occipital lobes
boundaries of parietal lobes
anterior: central sulcus
inferior: lateral sulcus
posterior: parieto-occipital sulcus
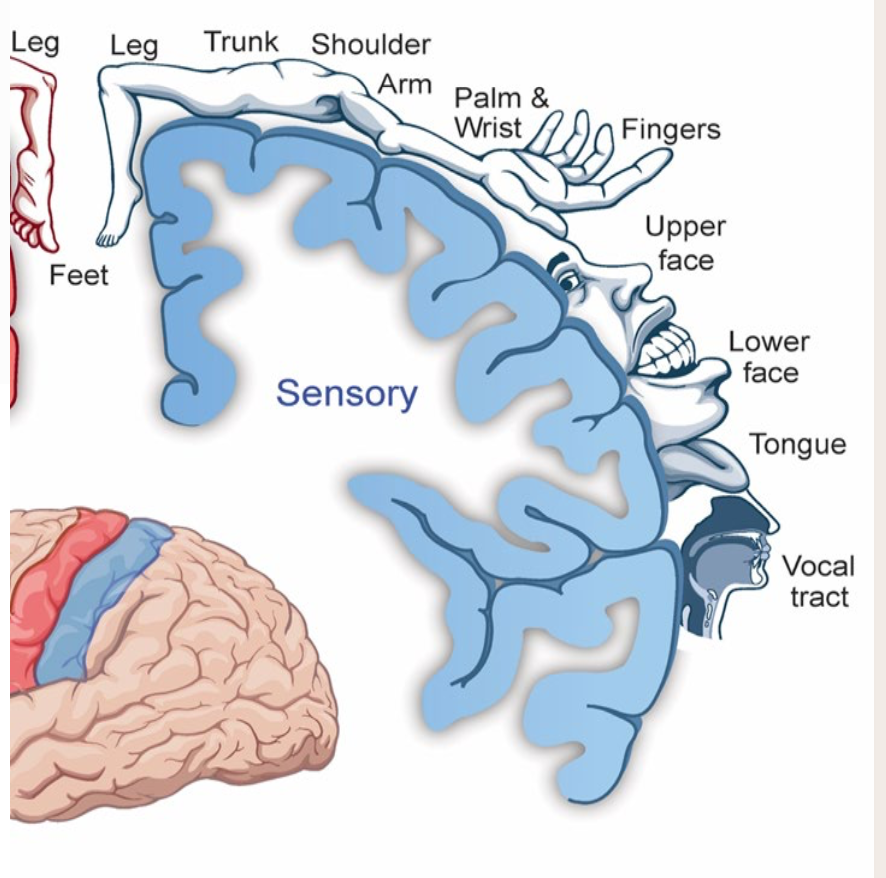
Function of postcentral gyrus
processing various types of sensory information
temp, pain, vibration, proprioception, fine touch
function of superior parietal lobule
visuospatial perception & orientation
‘where is the body in space’
combines visual & sensory info
supramarginal gyrus
processing of phonological info
angular gyrus
complex related language functions (reading, writing)
Boundaries of the temporal lobe
superior: lateral sulcus
posterior: occipital lobe
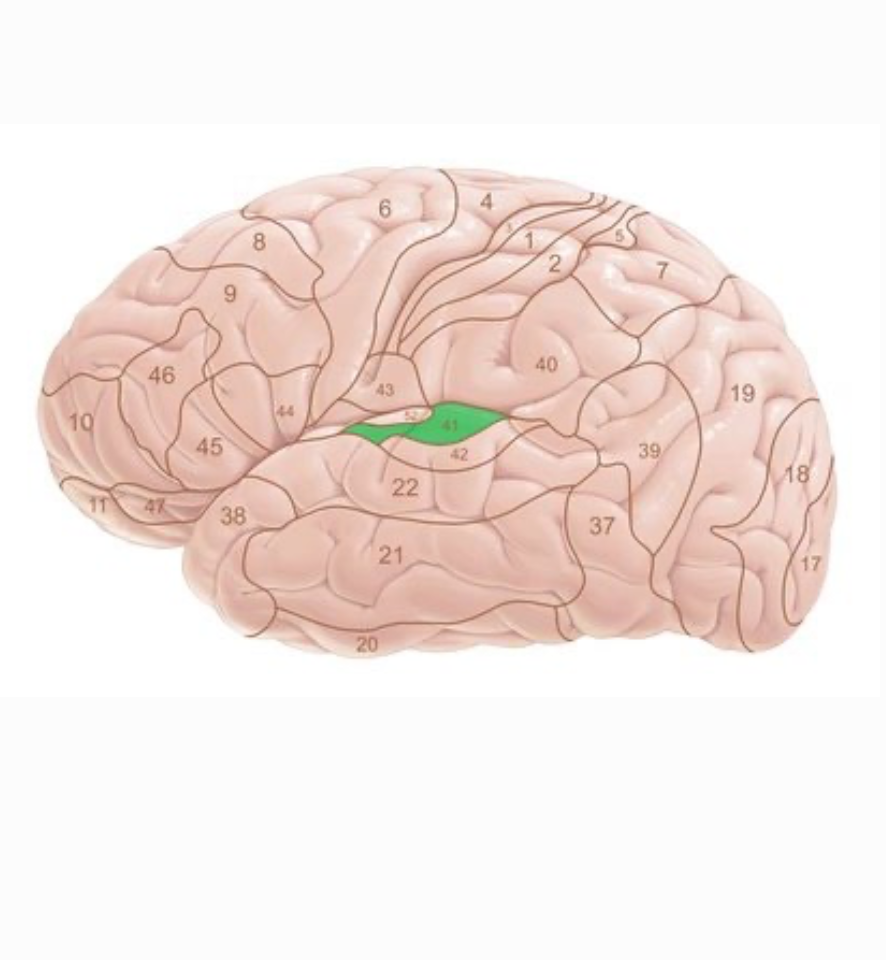
primary auditory area of the temporal lobe
Heschl’s Gyrus
function of Heschl’s Gyrus
reception of auditory info
Location of Wernicke’s Area
posterior portion of the superior temporal gyrus
function of wernicke’s area
comprehension of written & spoken language
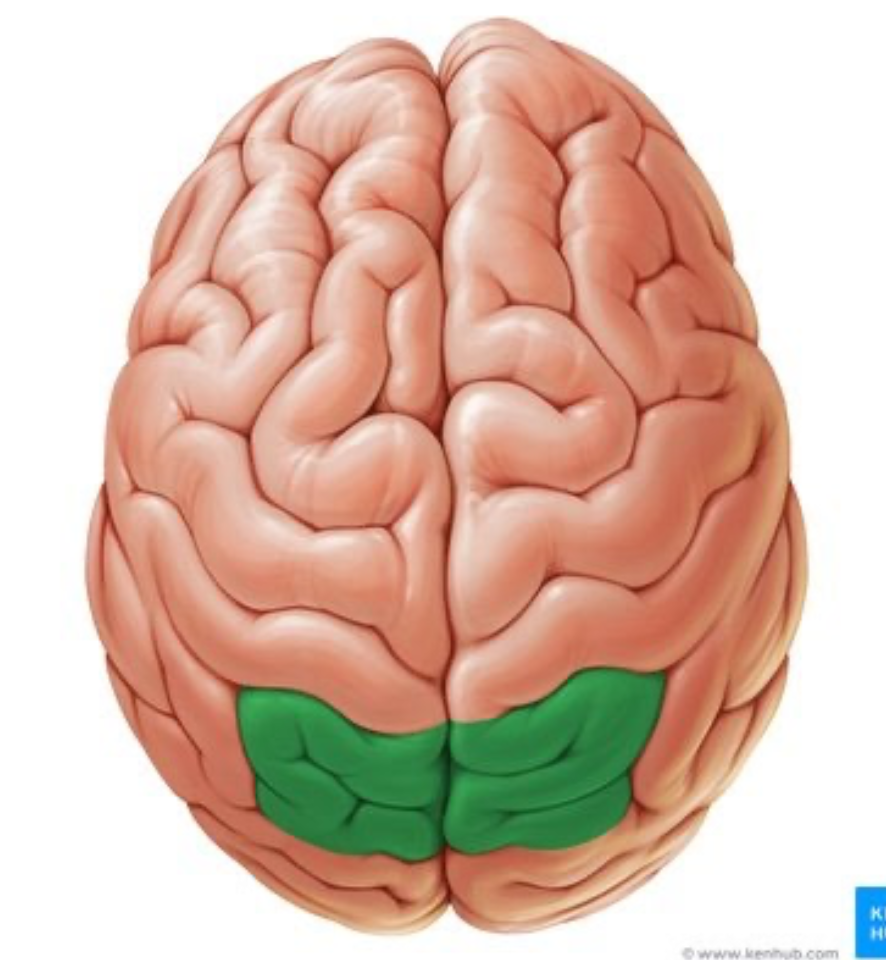
boundaries of the occipital lobe
superior: parietooccipital sulcus
lateral: temporal lobe
function of the occipital lobe
main visual processing center (perception, processing, interpretation)
color determination, facial recognition, depth perception, memory formation
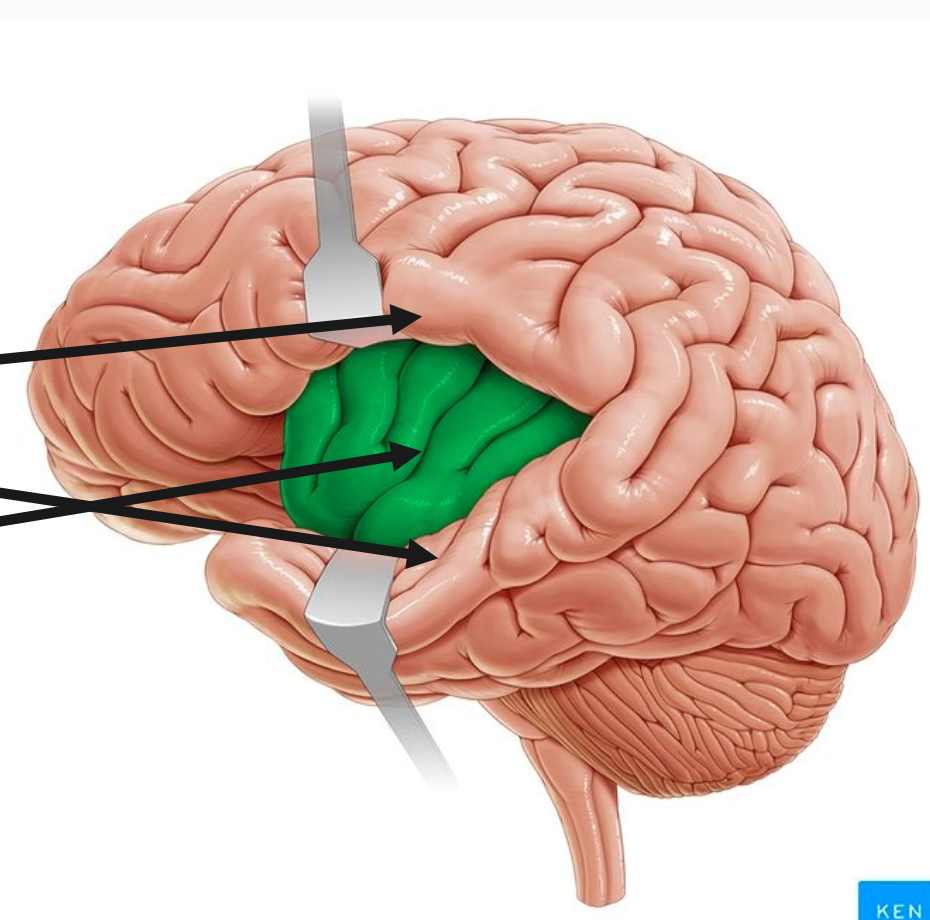
location of the insular lobe
deep within the lateral sulcus
anatomical landmarks of the insular lobe
operculum
central sulcus of the insula
location of limbic lobe
not anatomically distinct
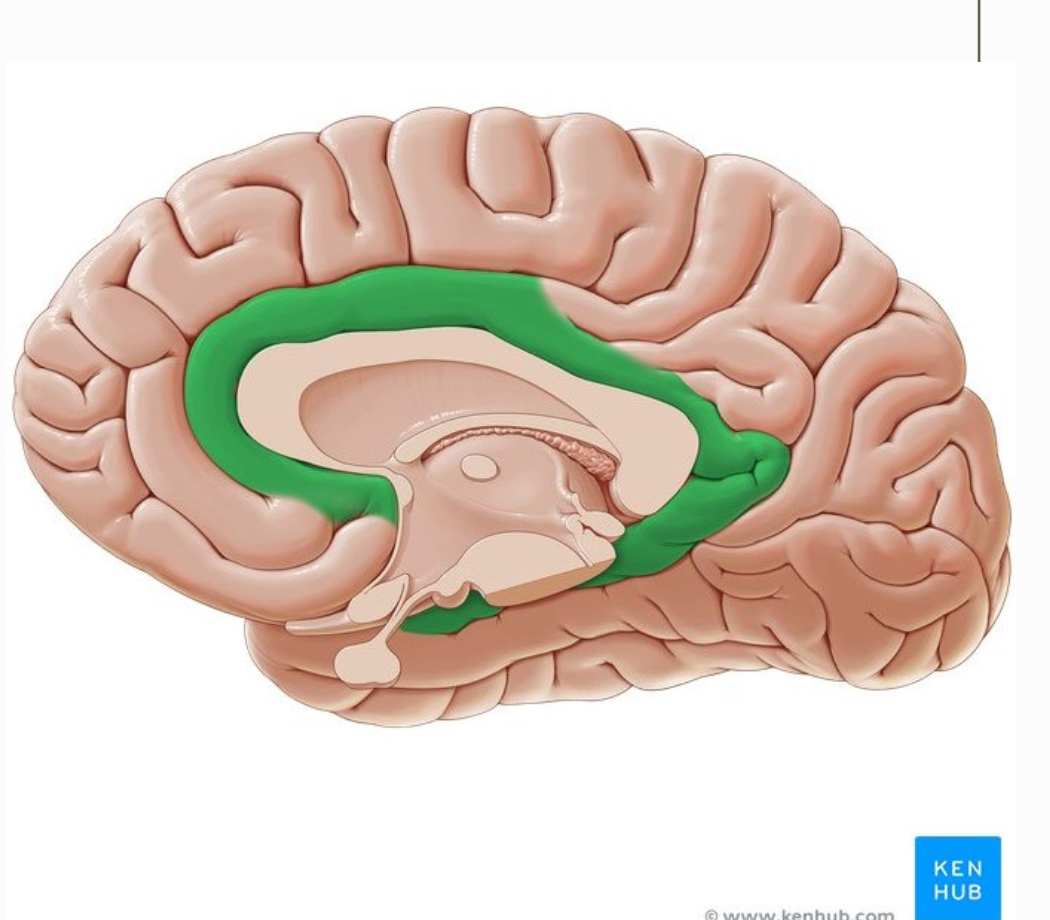
function of limbic lobe
satiety hunger
memory
emotional response
sexual reproduction / arousal
maternal instincts
3 types of communication fibers
commissural fibers
projection fibers
association fibers
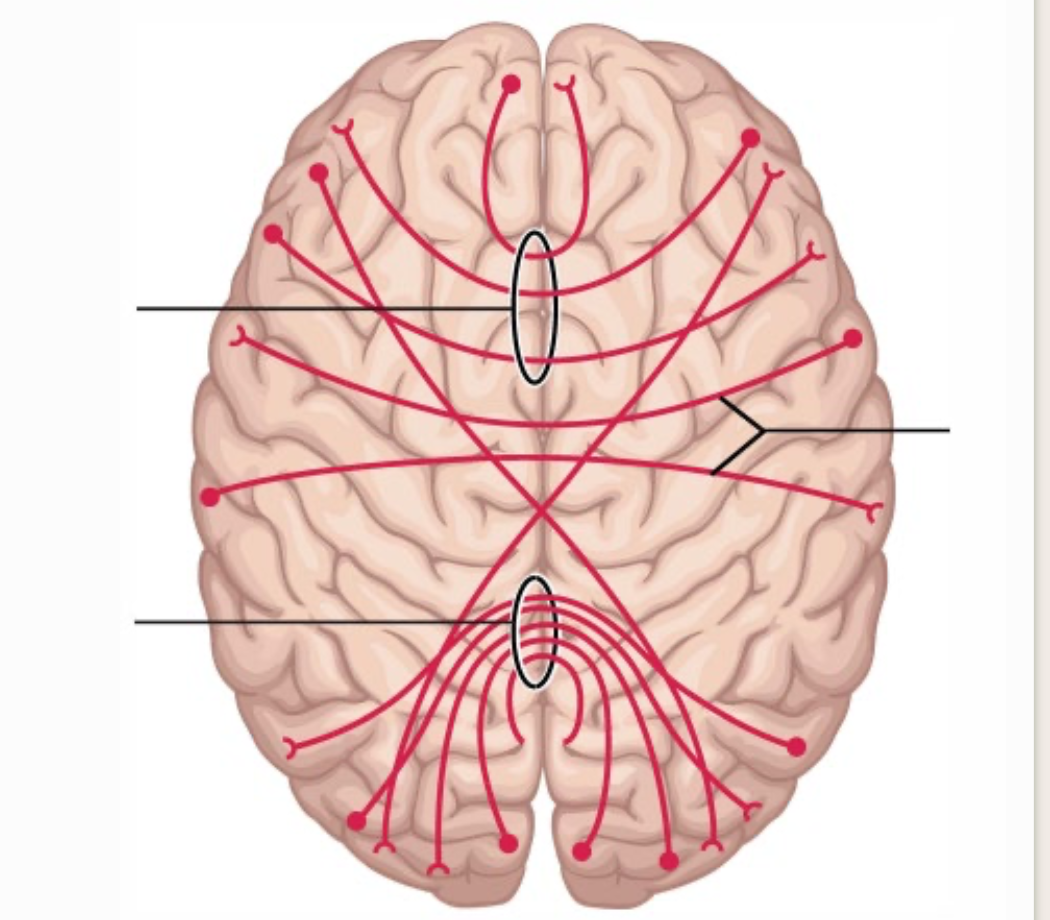
commissural fibers
connect hemispheres of the brain
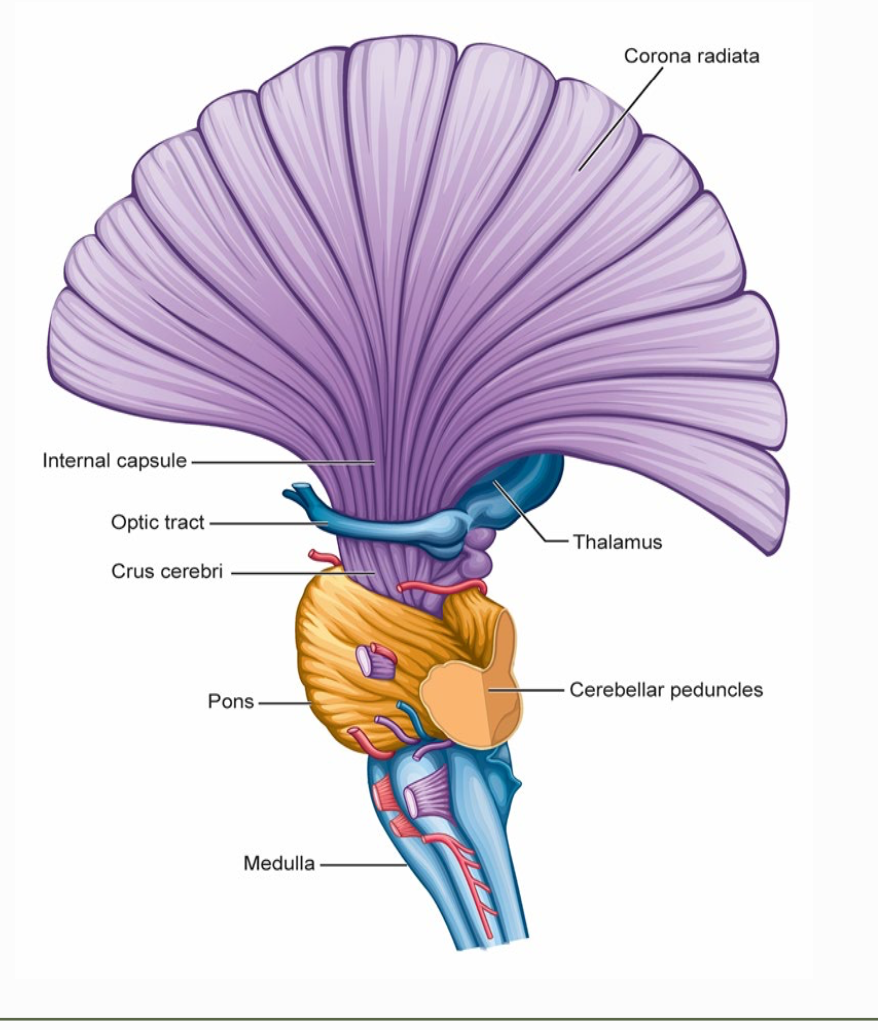
projection fibers
connect cortical structures with lower parts of the brain/spinal cord
association fibers
connect cortical regions within the same hemisphere
main function of commissural fibers
ensure integration of functions between right & left structures of the brain (memory, motor, perception)
ex: corpus callosum: connects 2 hemispheres
2 types of projection fibers
corticopetal fibers
corticofugal fibers
corticopetal fibers
transmit info from spinal cord/brainstem (afferent) to the cortex
corticofugal fibers
transmit info from cortex to brainstem & spinal targets (efferent
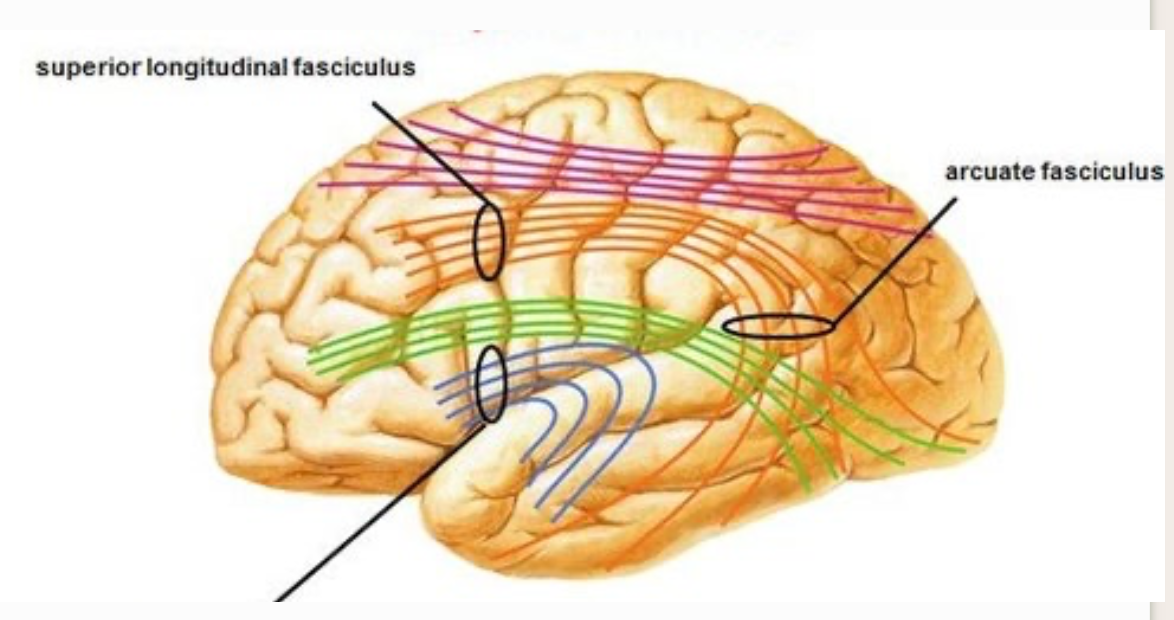
2 types of association fibers
long fibers: individually named
short fibers: arcuate fibers
ex: superior longitudinal fasciculus, arcuate fasciculus
percentage of humans that are right handed
90%
this occurs in the left hemisphere
language & analytic functions
characteristics of left handedness
may have language & analytic functions in the right hemisphere
may have mixed laterality
mixed laterality
functions shared between the hemispheres
functional language - right hemisphere
big picture, figurative language, prosody, facial expression, pragmatics, connotative meaning, synthesis of info
functional language - left hemisphere
detail oriented, consonants, language rules, denotative meaning, analytical
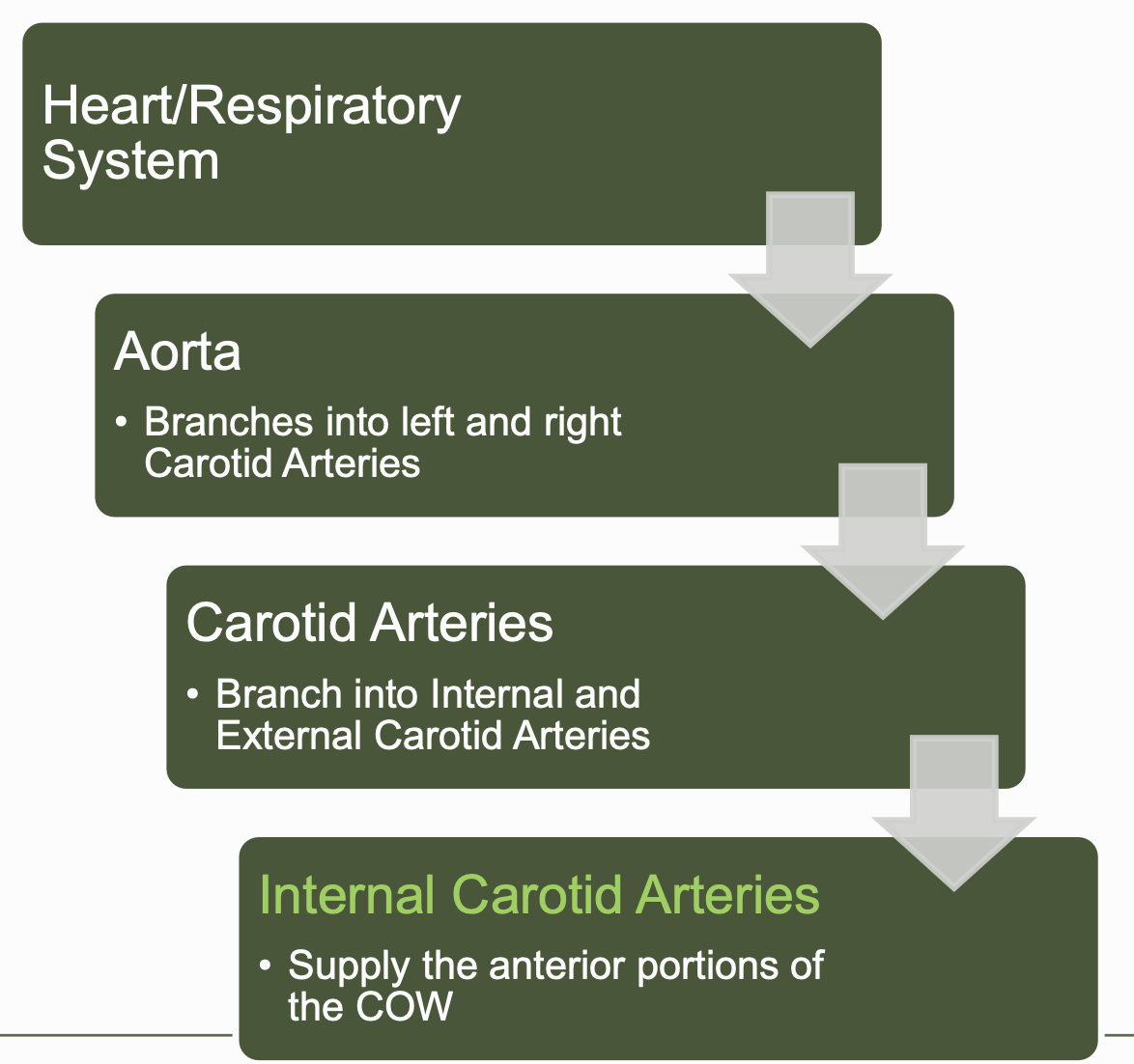
cerebrovascular system - anterior
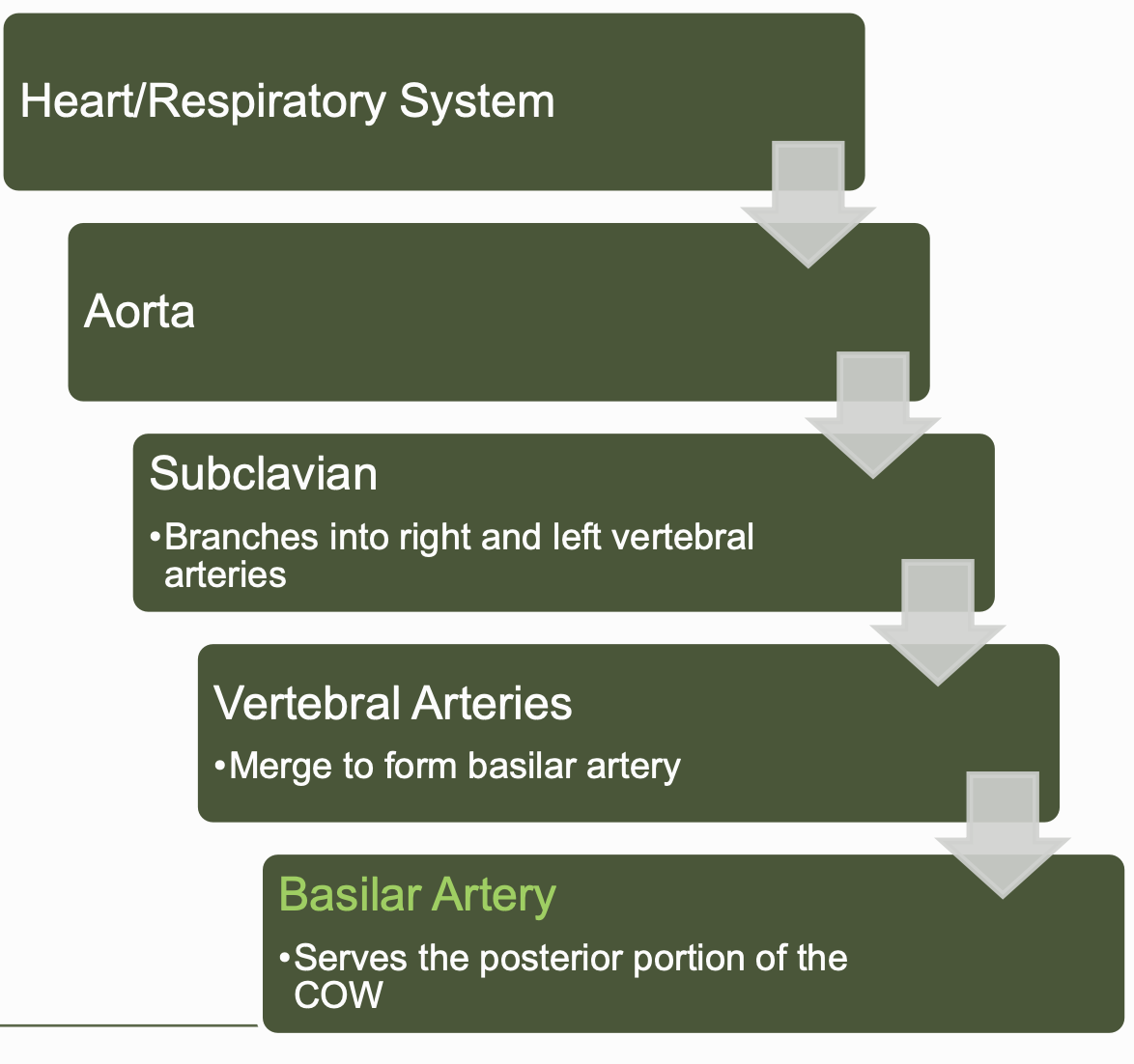
cerebrovascular system - posterior
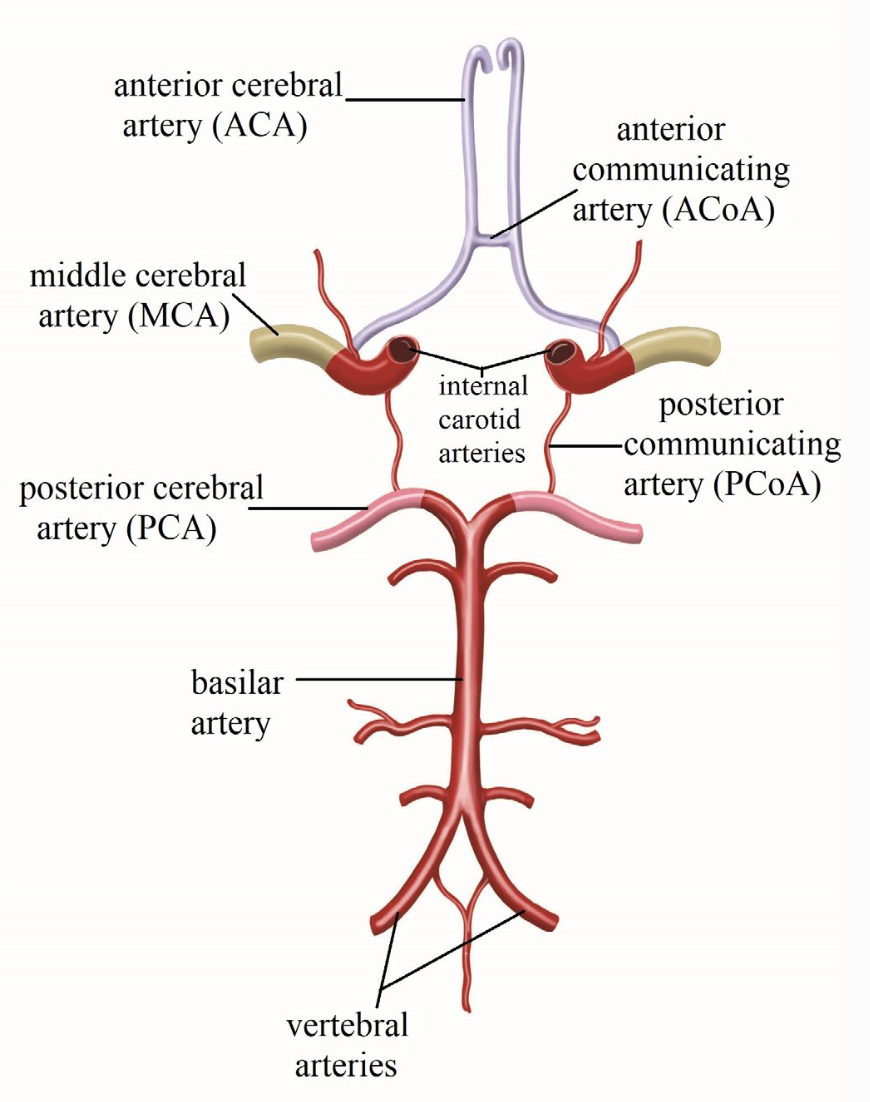
Circle of Willis
distributes blood to cerebrum via cerebral arteries
forms the Circle of Willis
internal carotid arteries and basilar arteries @ the base of the cerebrum
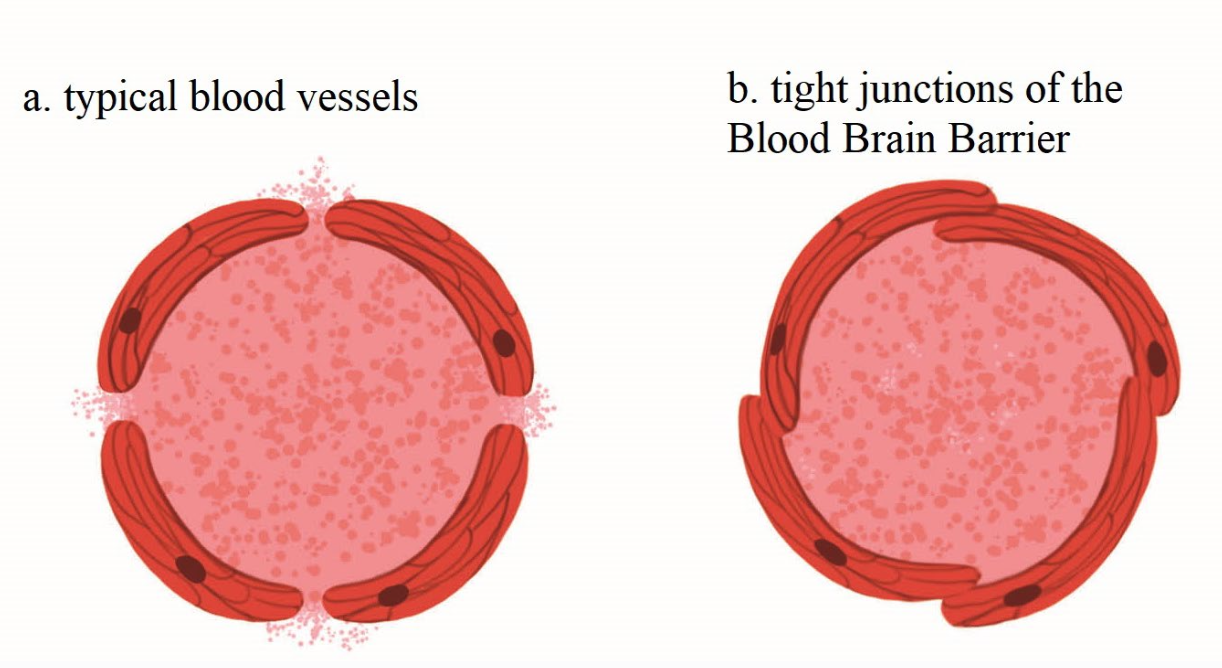
blood brain barrier
protects brain from pathogens entering the brain
difference in composition of blood vessels within brain
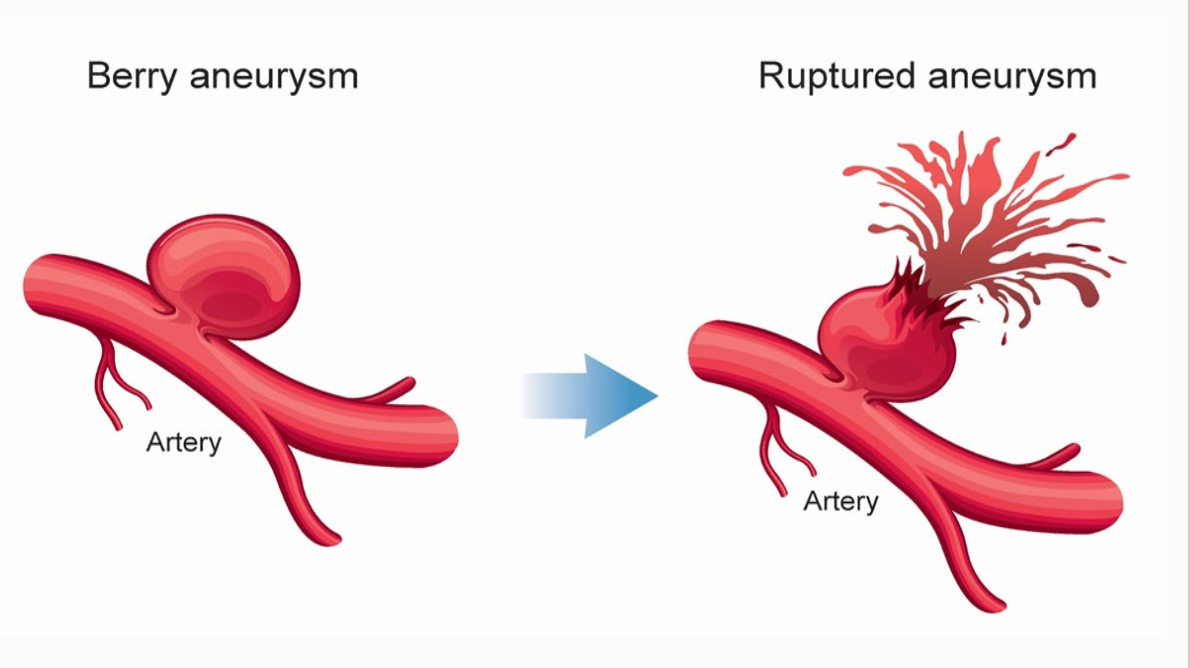
aneurysms
balloon - like distensions of the arterial wall
symptoms of aneurysms
usually no symptoms, they are discovered on accident
results of aneurysm rupture
hemorrhaging / stroke
ischemic/embolic stroke
blockage of blood flow through a vessel
transient ischemic attacks (TIA)
small emboli lodge themselves in smaller blood vessels; can resolve within mins/hrs
tissue plasminogen activator (tPA)
clot reducing pharmaceutical used to treat ischemic stroke
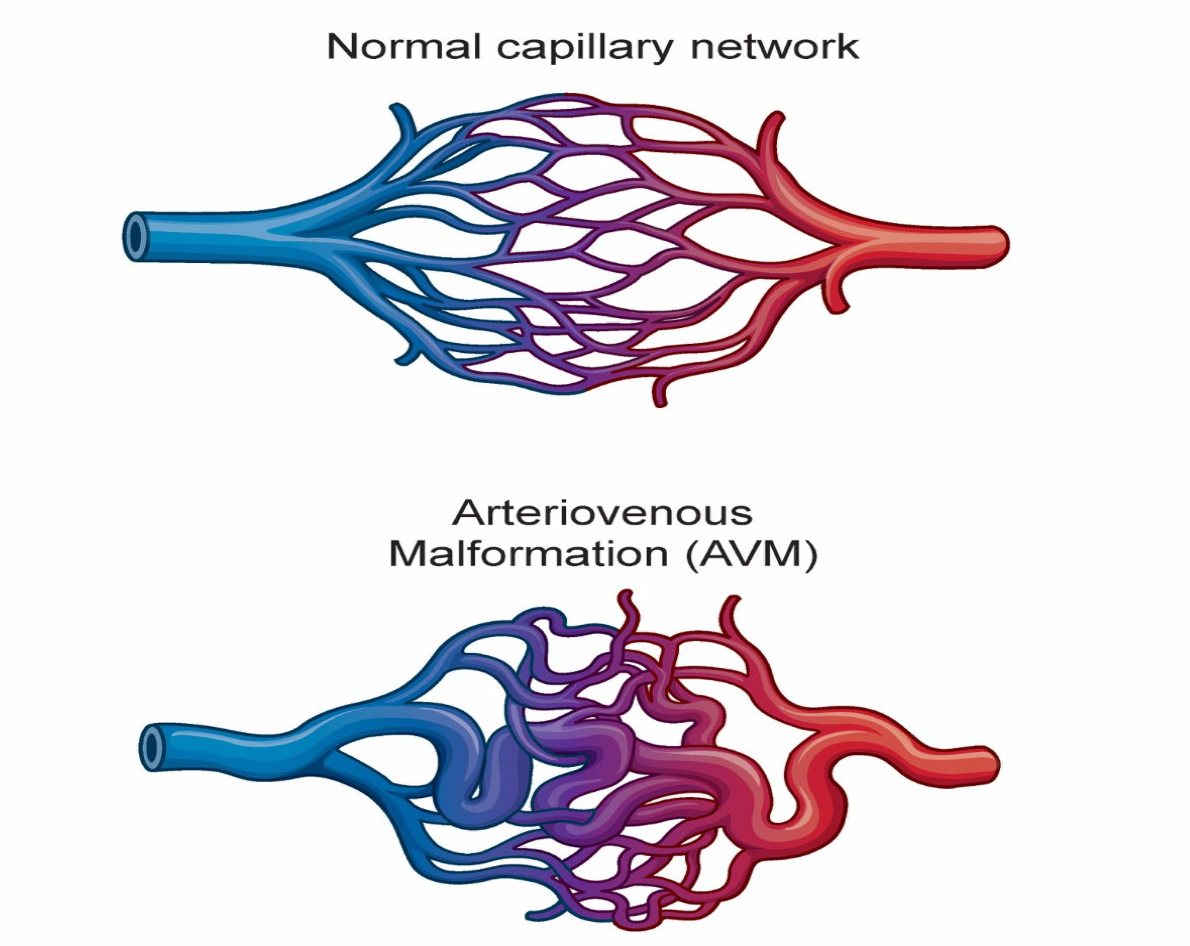
arteriovenous malformation (AVM)
congenital tangles of arteries and veins
create higher risk for seizures & migraine like headaches
signs of a stroke
numbness/weakness of face, arm, or leg
confusion/trouble talking/understanding speech
trouble seeing
trouble walking, dizziness, loss of balance/coordination
severe headache
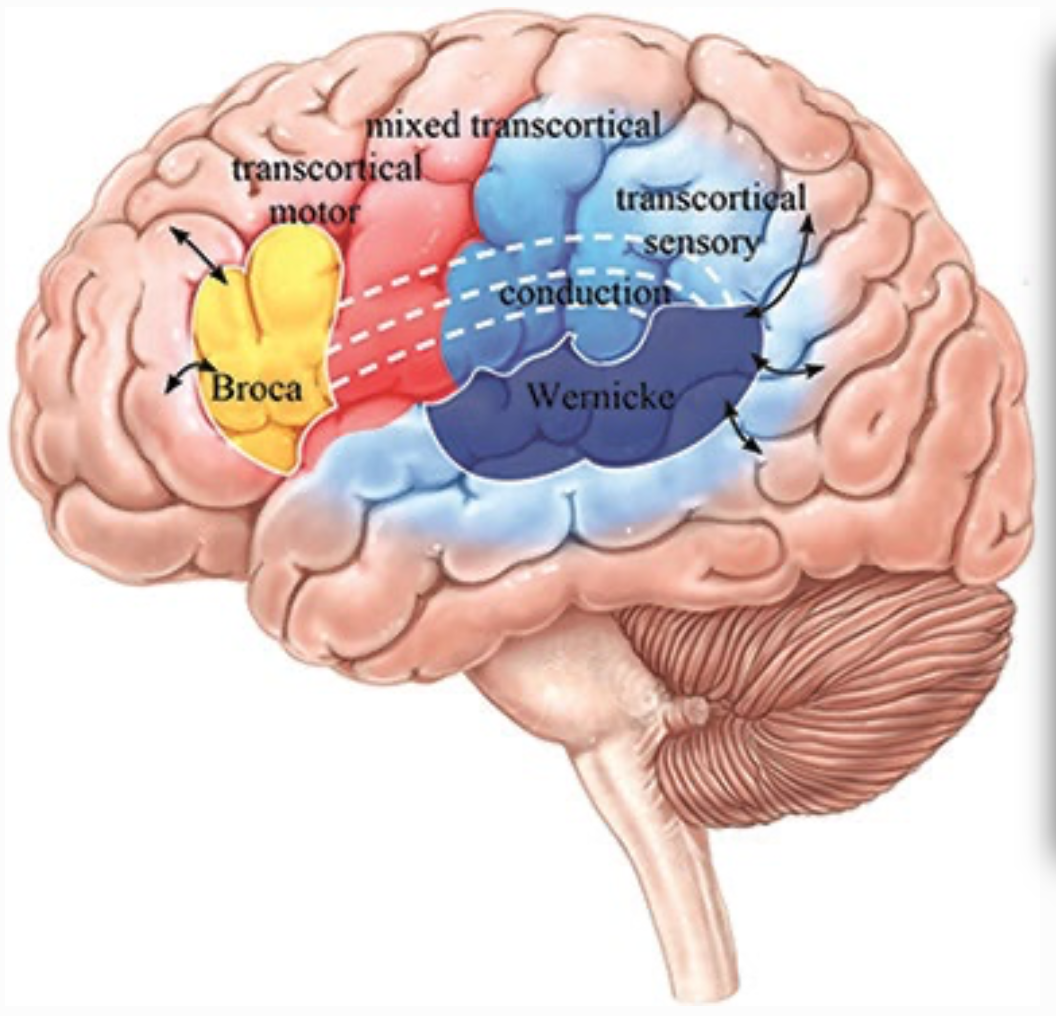
aphasia
language disorder associated with damage to the left hemisphere of the brain
impairments associated with aphasia
naming, repetition, fluency of language production, language comprehension, communication modalities
broca aphasia
fluent - no
good comprehension - yes
good repetition - no
wernicke aphasia
fluent - yes
good comprehension - no
good repetition - no
examples of recreational substances that can cross BBB
caffiene & alcohol
possible causes of aneurisms
smoking, weakened arteries, high blood pressure
hemmoragic stroke
bleeding in the brain