AP Psychology - Unit 0.1A Overview, History, and Psychological Perspectives
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Psychodynamic/Psychoanalytic Perspective
created by Sigmund Freud
focuses on how the unconscious mind and past experiences shape an individual’s mentality and behavior
Cognitive Perspective
Jean Piaget created theories based on cognitive development
focuses on how individuals perceive, process, interpret, and remember information
emphasizes the influence individual’s internal thoughts and perception can have on their behavior
Free Association
psychoanalysis method that explores a patient’s unconscious mind
patients must state whatever comes to their mind, no matter how insignificant or embarrassing it is
Biological Perspective
focuses on the influence our genetics and body processes have on our behaviors
Behavioral Perspective
focuses on the visible behaviors of patients rather than their inner thoughts
emphasizes the importance of positive and negative reinforcement
studied and developed by John Watson, B.F Skinner, Edward Thorndike, and Ivan Pavlov
Biopsychosocial Perspective
focuses on the interconnected relationship between biological, psychological, and social factors when understanding an individual’s behavior and thoughts
Social-Cultural Perspective
focuses on how an individual’s culture, experiences, and societal norms affect their behavior and thoughts
Evolutionary Perspective
based on Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution
focuses on the connections between how the mind works and evolution phenomena
belief that every mental process exists in order to aid human survival
Humanistic Perspective
emphasizes a person’s potential to grow as an individual
focuses on how the role of motivation plays on our thoughts and behavior
helps improve someone’s self-esteem
based on Abraham Maslow’s and Carl Roger’s theories
Natural Selection
evolutionary process discovered by Charles Darwin
genetic traits that enable organisms to survive and produce will most likely be passed on to future generations in comparison to other variations
Self-Actualization
the motivation to fulfill one’s fullest potential
proposed by Abraham Maslow along with his hierarchy of needs
once basic physical and psychological needs are met and self-esteem is achieved, self-actualization rises as the ultimate psychological need
Psychology
study of the mind and individual’s behavior
Empiricism
what is observable
most sciences are based on empiricism
Pseudopsychology
“false psychology”
the belief that common sense can replace empiricism
harmful effect: people begin to distrust actual science
The Skeptical Psychologist
important for psychologists to question scientific beliefs before supporting it
Where Does Western Thought Derive From?
Ancient Greece/Ancient Rome
Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle
popular Greek philosophers who provided a foundation for psychology
Nature vs. Nurture
basis question of psychology
early philosophers discussed about this term
The Middle Ages
The Roman Catholic Church controlled the thoughts and beliefs of citizens
Renaisaance
beginning of new thought
people challenged traditional beliefs
Descartes and Bacon
developed the scientific method
John Locke
enlightenment thinker
believed that everyone’s behavior was a reflection of the environment they lived in
Tabula Rasa
“blank slate”
aligns with John Locke’s theories
Structuralism
scientists look at the structure of the human mind in order to define human consciousness
breaks down mental processes into basic components
includes thinking, feeling, and judgement
Wilhelm Wundt
“father of psychology”
first scientist to start a psych lab which established psychology as an actual science
Edward Titchener
brought psychology to America
created the term “structuralism”
Dorthea Dix
brought reforms to hospitals and mental asylums
worked with soldiers who had PTSD
Functionalism
focuses on the purpose and function of mental processes and behaviors rather than underlying structure
William James
founder of functionalism
Mary Whiton Calkins
first female president of the APA (American Psychological Association)
student of William James
Margaret Floy Washburn
got the first PhD in psychology
second female president of the APA
student of William James
Gestalt Psychology
focused on how various stimuli/sensations create one perception → perceptual wholes
rejected structuralism; looked at the totality of the mind and behavior
Introspection
self-evaluation
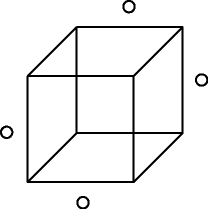
The Necker Cube
visual example of Gestalt psychology
Behaviorism
branch of psychology that focuses on observable behavior/events
focuses on an organism’s response to environmental stimuli
John B. Watson
founder of behaviorism
denied the theories of structuralism, functionalism, and gestalt psychology
believed science has to always be measurable
Sigmund Freud
founder of psychoanalysis
tried to get his patients to verbalize the unconscious by free association