acids, alkalis and titrations
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
what are the three indicators,
litmus
phenolphthalein
methyl orange
what does litmus change when its acidic, alkaline or neutral
acid- red
alkali- blue
neutral- purple
what does phenolphthalein show when it is acidic and alkali
acidic- colourless
alkali- bright pink
what does methyl orange show when it is acidic, neutral and alkali
acidic- red
alkali- yellow
neutral- orange
what is the ph scale 0-14 for strong acid, weak acid, neutral, weak alkali and strong alkali.
strong acid
0-3
weak acid
4-6
neutral
7
weak alkali
8-10
strong alkali
11-14
what does the univerwsal indicator do
universal indicator gives a certain colour to show the approximate ph level
what are the colours
red- strong acid
yellow- orange- weak acid
green- neutral
blue- weak alkaline
purple- strong alkaline
define acid
they are a substance that has a ph level lower than 7 and they contain hydrogen ions and are proton donors.
define bases-
substance that can neutralise and acid, they take the protons and they contain hydroxide ion.
define neutralisation
when the hydrogen ion from the acid reacts with the hydroxide ion from the base to form water
what is the word equation and the ionic equation of neutralisation
H+ + OH- —> H2O
acid + base —> salt + water
why are alkalis bases but not all bases are alkalis
since bases are a substance that neutralises and acid
and alkalis is a soluble base.
All alkalis are bases because they can dissolve in water, but not all bases are alkali because some bases cannot dissolve in the water. because
what is titration
it is an experiment that shows how much acid is needed to neutralise an alkali
what equipment must you know for titration
burette (measures variable volumes)
pipette (measures a fixed volume)
conical flask
indicator (methyl orange for example)
white tile (to see the colour change)
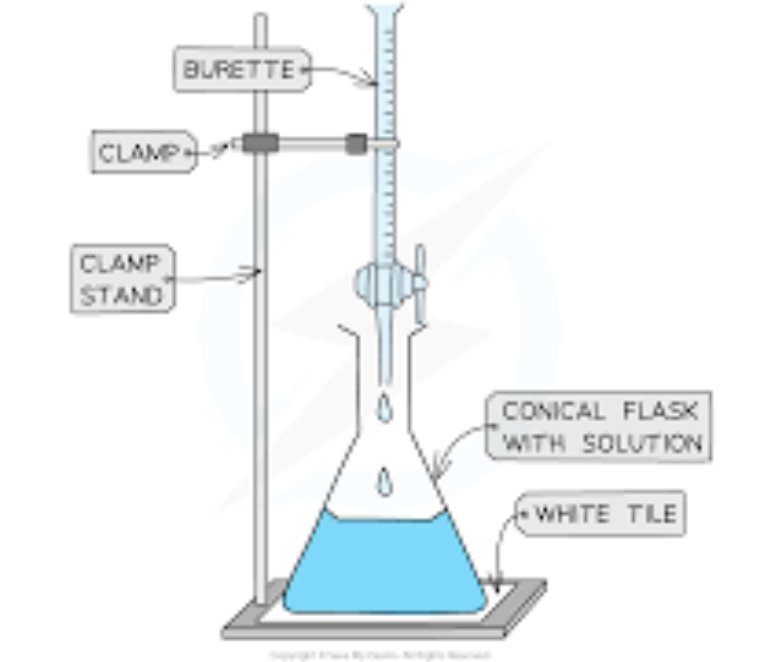
how would you do this investigation
get pipette and measure the volume of the alkali and put it into conical flask
add the indicator to the conical flask with the alkali
put the acid in the burette and record the initial volume
add acid into the conical flask slowly white swirling the flask
stop when the indicator changes colour
record the volume of the acid in the burette
calculate the volume of acid used