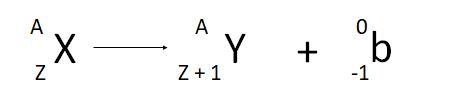4.4.2.2 Nuclear equations
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/23
Last updated 9:26 AM on 12/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
1
New cards
How small is an atom?
Atoms are extremely small, having a radius of about 1 x 10-10 m
2
New cards
what is a nuclear equation
to show alpha and beta decay
3
New cards
How small is the nucleus?
Of course much smaller than the atom, the radius of a nucleus is less than 1/10 000 of the radius of the atom. Most of the mass is in the nucleus.
4
New cards
Where are the electrons?
The electrons are arranged around the nucleus and are at different distance from the nucleus (energy levels). Absorption and emission of electromagnetic radiation causes electrons to move between different energy levels.
5
New cards
What effect does absorption of electromagnetic radiation have on the distance an electron is from the nucleus?
It causes electrons to move further away as they move to higher energy levels. They move back down when electromagnetic waves are emitted.
6
New cards
What does it mean if something is radioactive?
If an atom is radioactive it means it emits (gives out) ionising radiation or particles.
7
New cards
Why would an atom be radioactive?
Protons and neutrons are held together in the nucleus by strong nuclear forces, this ‘binding energy’ holds the nucleus together.
This force is stronger in stable nuclei to overcome the electrostatic force of repulsion between the protons and also to stop the neutrons from moving away from the nucleus.
This force is stronger in stable nuclei to overcome the electrostatic force of repulsion between the protons and also to stop the neutrons from moving away from the nucleus.
8
New cards
How does an unstable nucleus lose mass and energy to become more stable?
By emitting particles and or energy
9
New cards
alpha particle structure
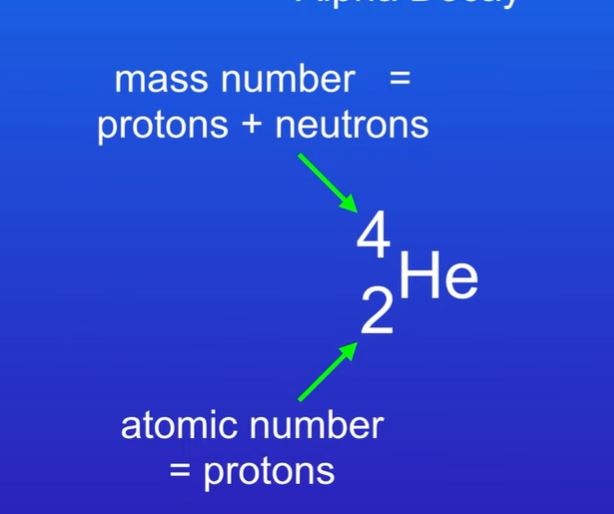
An alpha particle consists of 2 protons and 2 neutrons.
An alpha particles relative mass is 4 and relative charge is +2
same as helium
An alpha particles relative mass is 4 and relative charge is +2
same as helium
10
New cards
how to represent alpha particles symbol
11
New cards
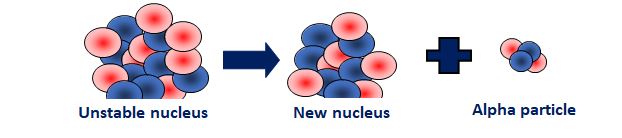
alpha decay diagram
12
New cards
Which subatomic particles, and how many of each, are emitted from the nucleus of a uranium atom during alpha decay, to form an alpha particle?
An atom decays into a new atom and emits an alpha particle (2 protons and 2 neutrons)
Alpha radiation is the same as the nucleus of a helium atom travelling at extremely high speed.
Alpha radiation is the same as the nucleus of a helium atom travelling at extremely high speed.
13
New cards
How has the mass number of the element changed during decay?
The atomic number decreases by 2 and the mass number by 4
14
New cards
How has the atomic (proton) number changed during decay?
The atomic number decreases by 2 and the mass number by 4
15
New cards
How would the charge of the element’s nucleus be affected?
The positive charge of the nucleus decreases by 2
16
New cards
what happens during beta radiation
a neutron changes to a proton and electron
the electron is ejected from the nucleus (the beta particle)
the electron is ejected from the nucleus (the beta particle)
17
New cards
alpha decay of radium 226 Ra 88

18
New cards
rules for alpha decay
the atomic number decreases by 2
the mess number decreases by 4
the mess number decreases by 4
19
New cards


20
New cards
beta decay rules
atomic number increases by 1
mass number does not change
charge increases by 1
mass number does not change
charge increases by 1
21
New cards
what is gamma decay
atomic number and mass number has no change
22
New cards
what is gamma radiation
Gamma radiation is a high energy, high frequency wave.
Gamma radiation has no mass and no charge as it is wave.
Gamma radiation has no mass and no charge as it is wave.
23
New cards
1\.What is being emitted in __**Gamma radiation**__?
An electromagnetic gamma wave
24
New cards
general equation for beta decay