Physics - Waves (copy)
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Waves
They transfer energy and information without transferring matter. They are described as vibrations or oscillations about a fix point.
Wave motion
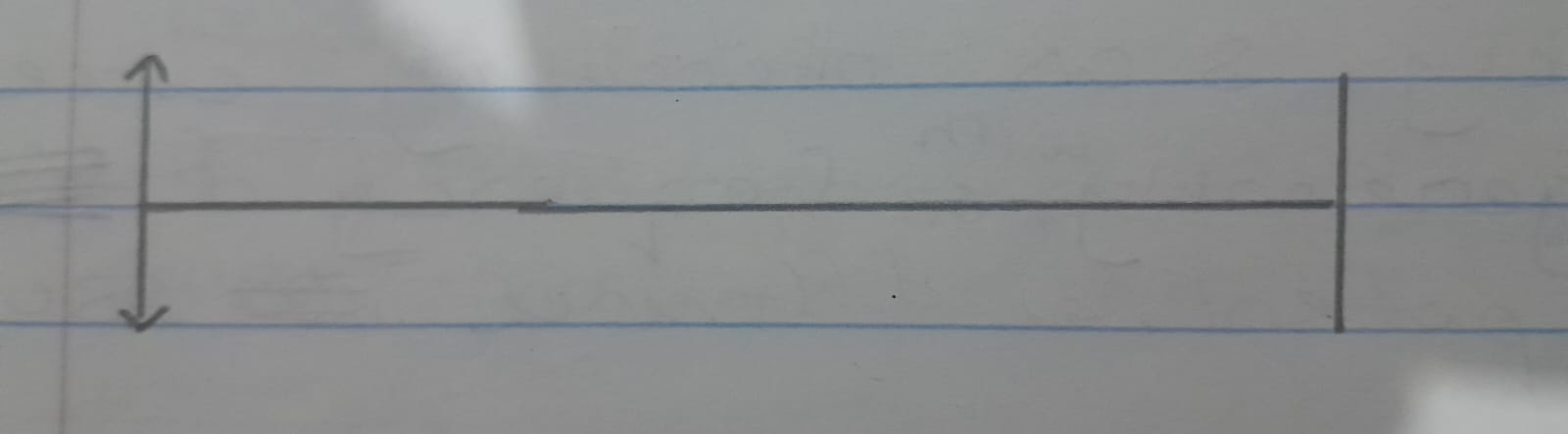
Transverse waves
A wave in which the direction of vibrations is perpendicular to the direction of movement of wave
Its wavelength can be measured from a peak to the next one.
Examples: water waves, waves on a string, electromagnetic waves (radio and light waves).
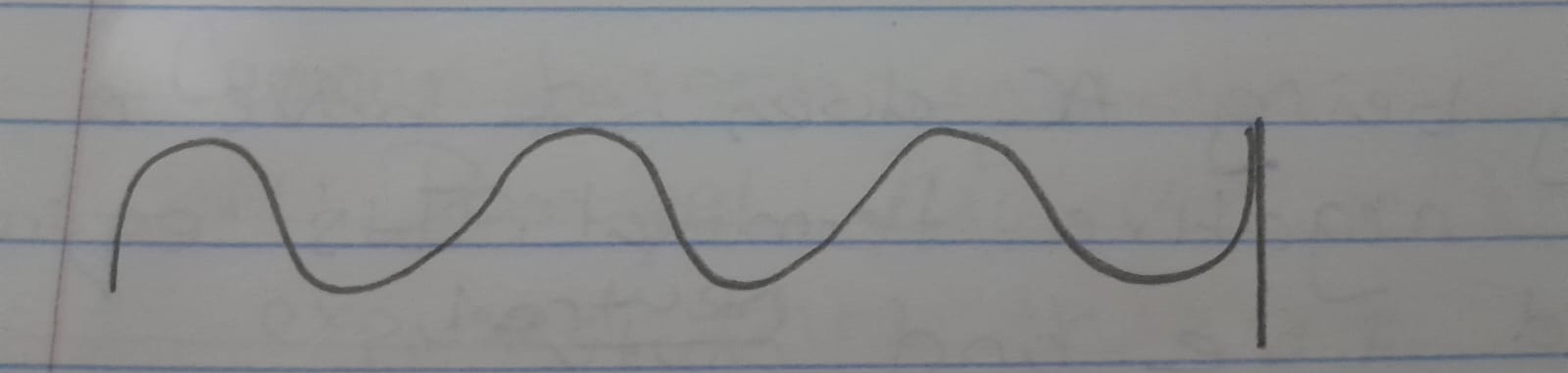
Characteristics of Transverse waves
The particles oscillated perpendicularly to the direction of travel.
Peak - highest point reached by the particle from its neutral position
Trough - lowest point reached by the particle from its neutral position.
The distance between adjacent particles remains constant, in the direction of the propagation of the wave.
The energy transfer is in the same direction as the wave motion.
They transfer energy in the same direction of the propagation of the wave.
The energy transfer is in the same direction as the wave motion.
They transfer energy, but not the particles of the medium.
They can move in solids and on the surfaces of liquids but not inside liquids or gases.
Some of them (electromagnetic waves) can move in solids, liquids and gases in vacuum.
Representing Transverse Waves
Drawn as a single continuous line, usually with a centerline showing the undisturbed position.
The curves are drawn so that they are perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer.

Longitudinal waves
A wave in which the direction of vibration is parallel to the direction of travel of the wave.
Its wavelength can be measured from the center area of one compression to the center of the next.
For examples: Sound waves and waves on slinky spring (which consists of region of rarefaction and compression).

Characteristics of Longitudinal waves
The particles oscillate along (to-and-fro) the direction of travel.
Compression: section in which the particles are closest together
Rarefaction: section in which the particles varies from a maximum value (furthest apart) to minimum value (closest together) in the direction of the propagation of the wave.
The energy transfer is in the same direction as the wave motion.
They transfer energy, but not the particles of the medium.
They can move in solids, liquids an gases.
They cannot move in a vacuum (since there are no particles).
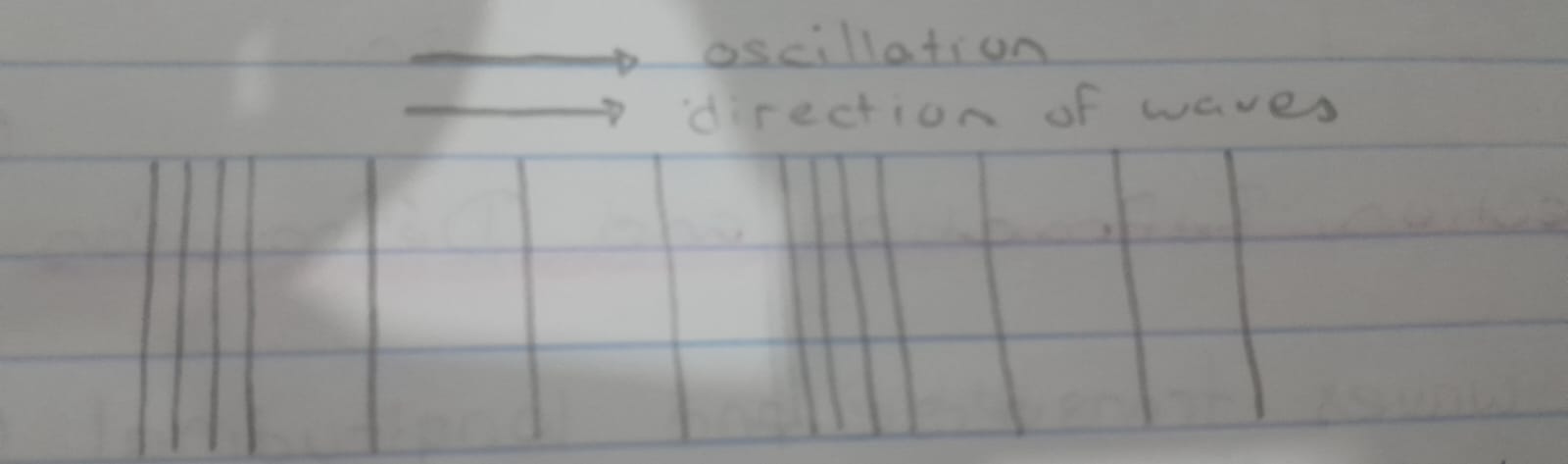
Representing Longitudinal waves
Are usually drawn as several lines to show that the wave is moving parallel to the direction of energy transfer.
Drawing the lines closer together represents the compressions.
Drawing the lines further apart represents the rarefactions.
Comparing Transverse and Longitudinal waves

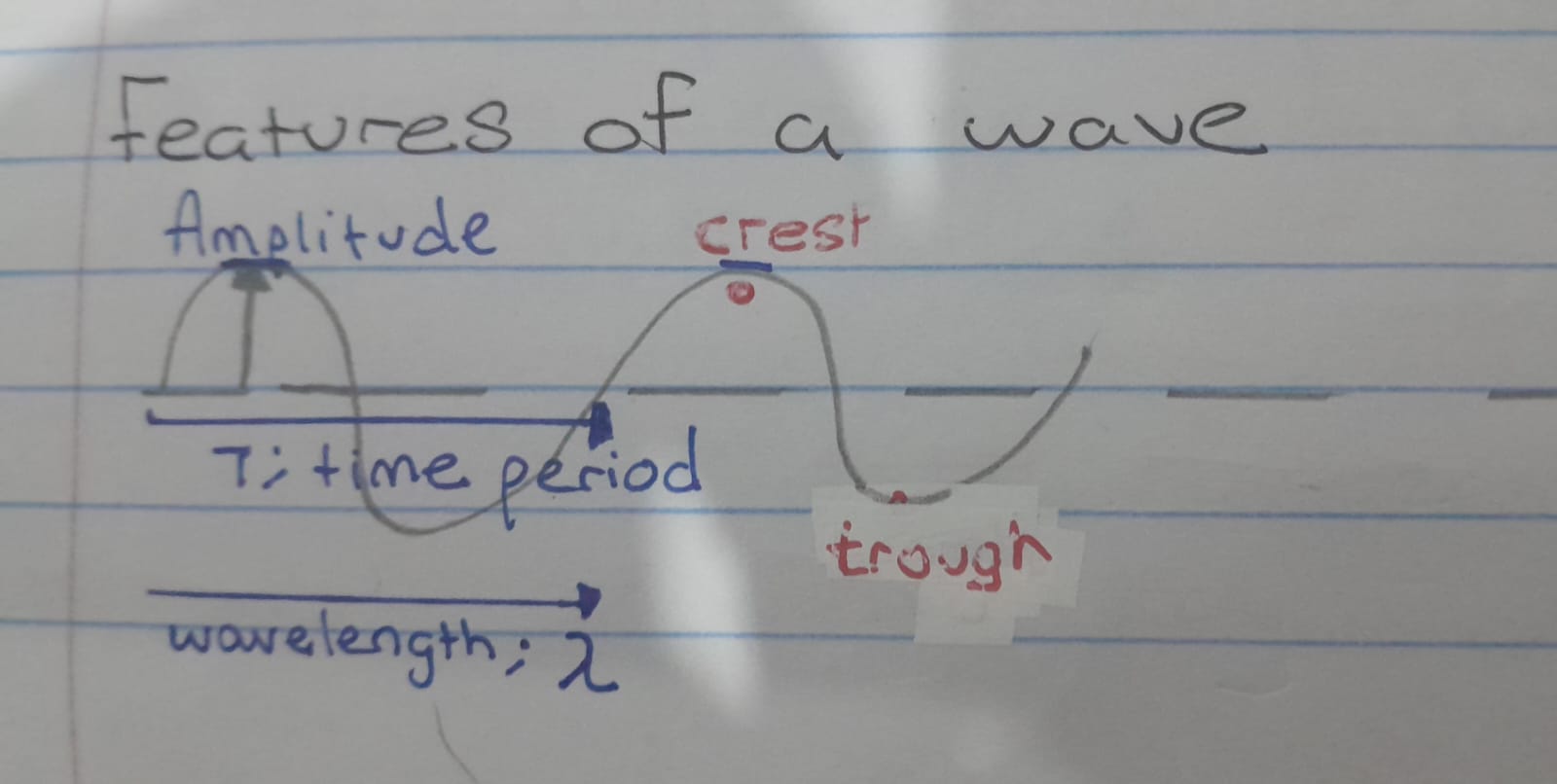
Features of a wave
Frequency
the number of waves passing a point in 1 second. It is denoted by f and its unit is Hertz; Hz.
f = 1/T , T = time period
therefore T = 1/f
Speed
Wavelength/Time period = λ/T
V=fλ, v= wave speed, f= frequency and λ = wavelength.
Crest/Peak
Defined as the highest point on a wave above the equilibrium or rest position.
Trough
Defined as lowest point on a wave below the equilibrium or rest position.
Amplitude
Defined as the distance from the equilibrium to the crest or the trough. It is denoted by the symbol, A, andis measured in meters (m) (it is the maximum displacement from the equilibrium position).
Wavelength
Defined as the distance from one point on a wave to the same point on a next wave.
Wave.
speed
The speed at which energy is transferred through a medium.
Distance travelled a wave each second.
V (m/s or ms-1) = f (Hz or s-1) λ (m)
Ray
the arrow shows the direction the wave is moving

Ray point
represents the wavelength
the closer the wavefronts, the shorter the wavelength.
the further apart the wavefronts are, the longer the wavelength.
Wavefronts
