(B) Unit 2A: Renaissance Politics
1/20
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
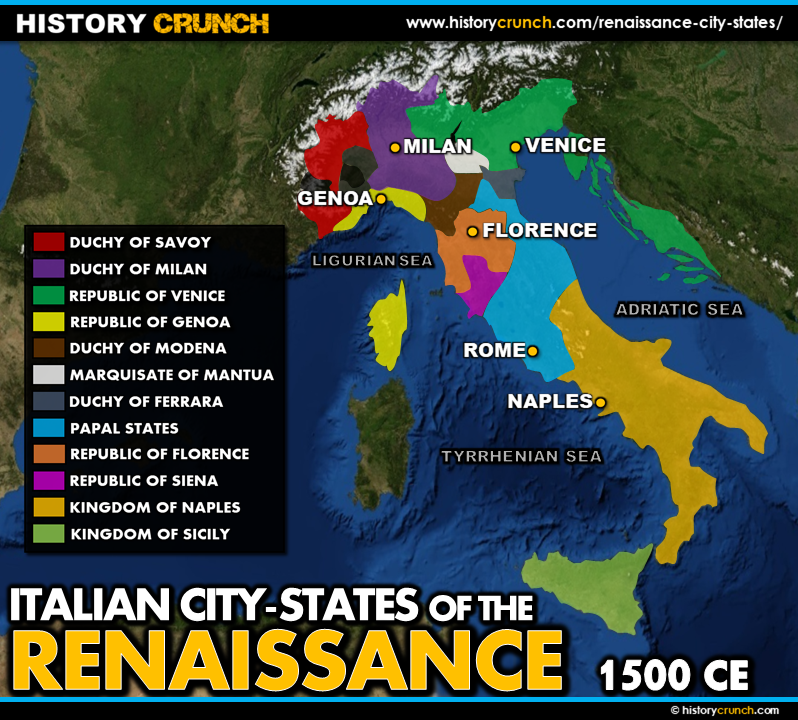
Italian City States
Independent, powerful, and prosperous states that always stood in constant clash against other states around them. No one state ever was powerful enough to conquer the others, so there always stood a constant battle.

Merchants
Traders who moved along different cities and states, selling different items such as silk, spices, etc.

Balance of Power
This refers to
A: The delicate fight between Nobles, The Church, and Monarchs over control.
B: The balance and equal power in the Italian City States.
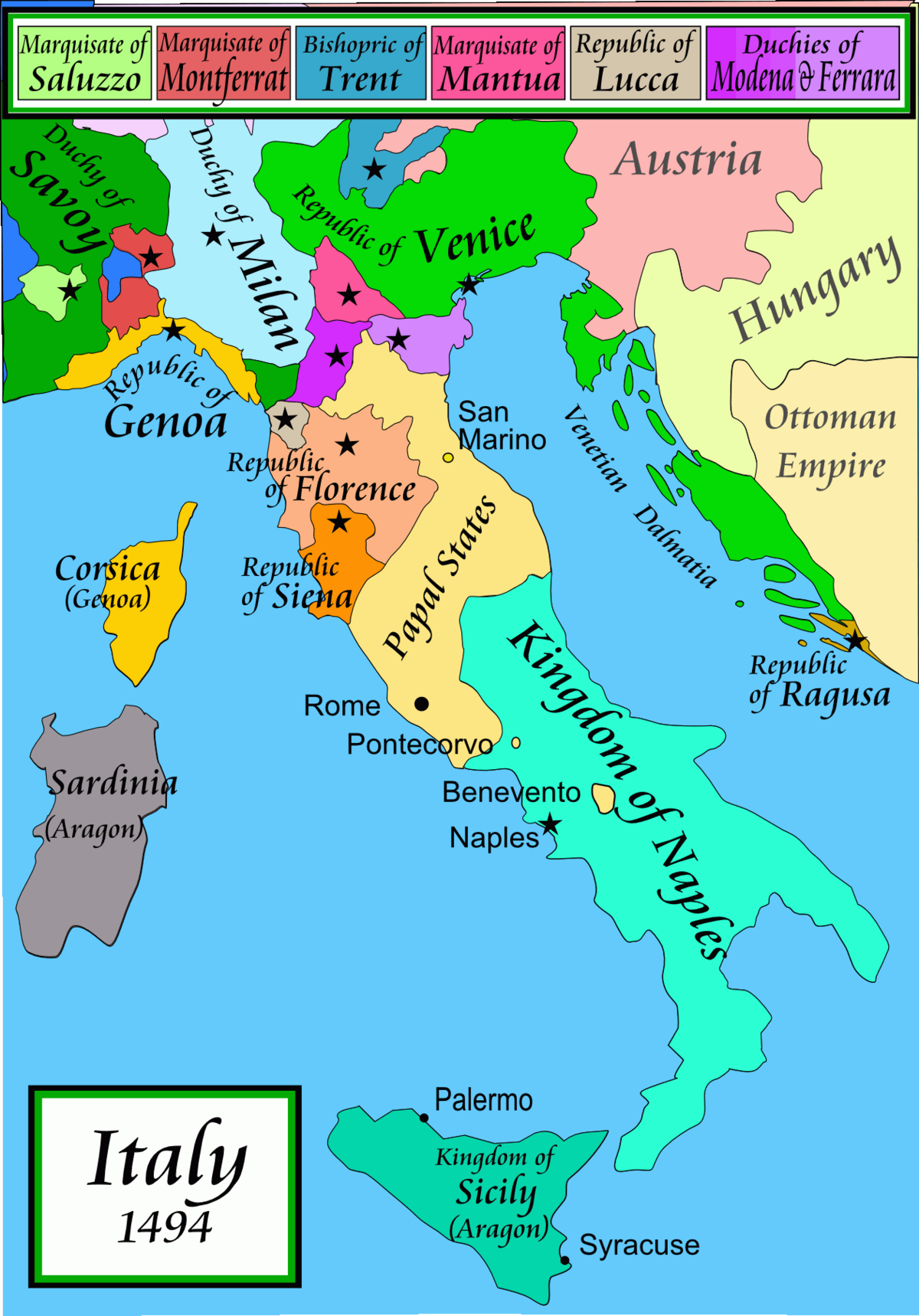
France 1494 invasion of Italy
The Invasion of Charles the Eighth through the Italian City States 1494, starting from Genoa and concluding in Naples. This caused the collapse of the Medici Family in Florence.

Charles V Habsburg, Holy Roman Emperor, sacked Rome in 1527
In 1527, a disobedient army of unpaid soldiers loyal to Holy Roman Emperor Charles V, composed of Germans and Spaniards, sacked Rome, plundering the city and causing immense destruction and loss of life. Pope Clement VII was forced to flee to Castel Sant'Angelo for refuge. The event was a brutal turning point in the Italian Wars, marking the end of the High Renaissance in Rome and leaving a lasting impact on papal authority and the political landscape of Europe.

Secularism
The idea that the state and church should be separate, and that the church should not have any political power.
Sovereign
The HIGHEST control of a state over the violence and laws of a region.
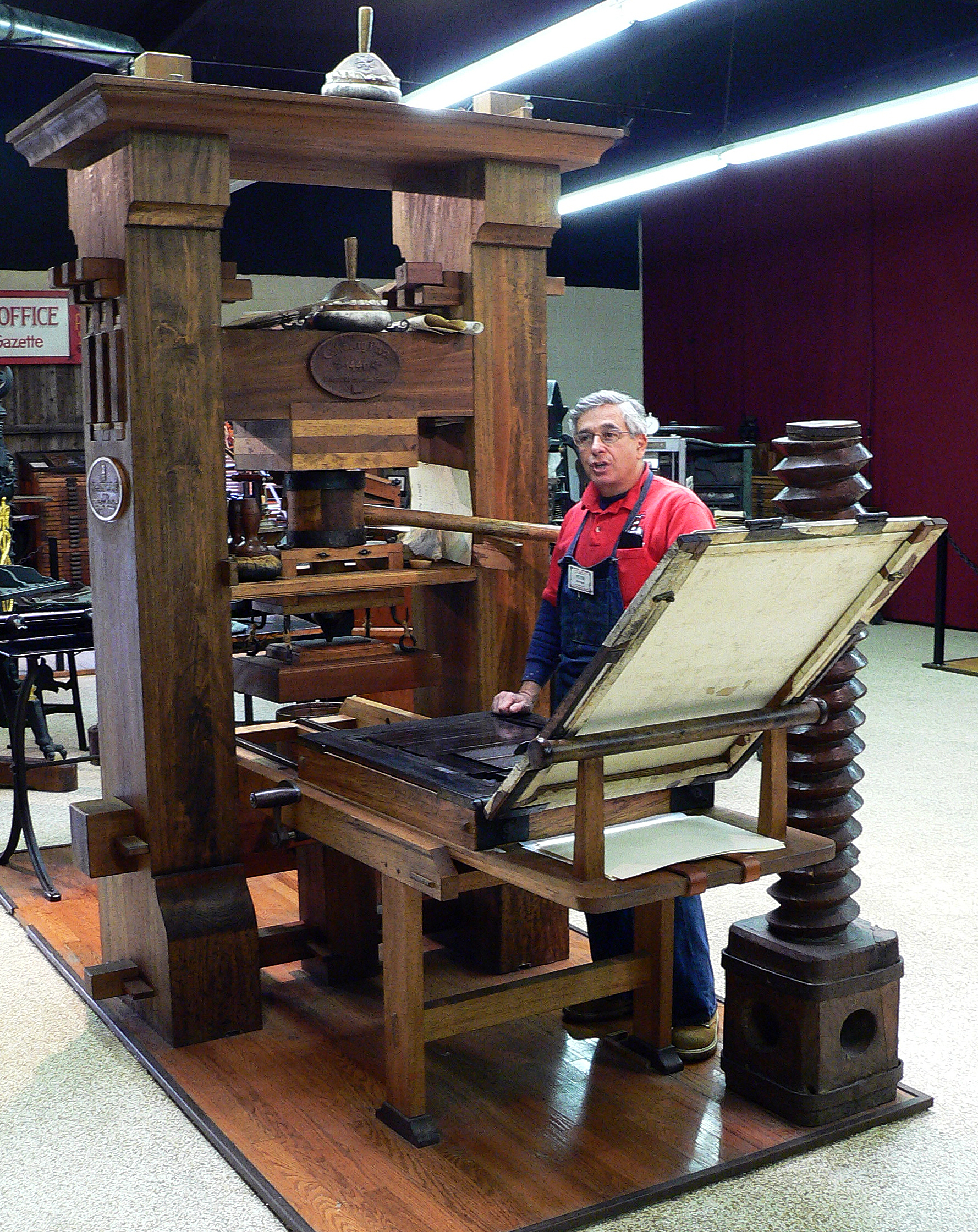

Printing Press
A device invented in 1440 which allowed for the mass production of text. This stands opposed to the previous method of writing text, which used scribes which rewrote an entire text by hand.

Centralization
The authority of a state coming under one monarch.
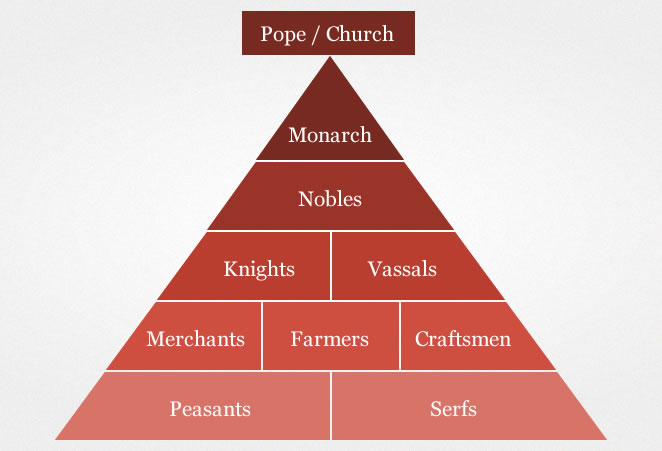
Feudalism
Land is being distributed to people by another person in exchange for their loyalty and aid in a war.
King → Duke → Vassal

Concordat of Bologna 1516
An agreement by King Francis I of Rome, and Pope Leo X that allowed the church to collect income from the Catholic Church in France, in exchange for the French being able to elect his own bishops, and limit Rome’s authority over them.

Dominican Friar Girolamo Savaronola (1452-1498)
A friar who had preached to Florence that God would punish the city for their sins. Florentines interpreted his prophecy becoming true at the invasion of the French, and expelled the Medici family. He became the leader of the new Florentine republic and promised to help them if they reformed. He established religious laws and burned many ‘humanist’ or Pagan texts and things. Eventually he was excommunicated, and was burned at the place where he burned items.
Cannon/Longbow
Technological Advancements in war, which helped during the Hundred-Year War and the collapse of Constantinople. English forces famously used longbows at battles like Crécy (1346), Poitiers (1356), and Agincourt (1415)
Patronage
The system where wealthy and powerful individuals and institutions—such as families, the Church, rulers, and merchants—commissioned artists to create art and architecture, often to display their status, piety, and political influence.
New Monarchs
The more powerful, developed, and stronger monarchs then the Medieval Monarchs.
1512
Fall of the Florentine Republic, the Medici Family is back in power.
Court Culture
A system of social and political life centered around a ruler's court, characterized by elaborate ceremonies, patronage of the arts and literature, and a strict social hierarchy.
Popolo (people)
The wealthy commoners, merchants, and artisans who, from the 13th century onwards, gained political power and formed pressure groups to challenge the dominance of the nobility in communal governments.
condottiero/signori
A condottiero was a mercenary military leader hired through a contract (condotta) to lead armies for Italian city-states and rulers, while a signore (plural: signori) was a powerful ruler or "lord" who established a hereditary, autocratic government in a city-state, often replacing republican institutions.
Sforza family
A Powerful family which ruled Milan
Star Chamber
Royal Court of England named for the stars pained on its ceiling, that existed in the late 15th to mid 17th century.